Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>How Can You Tell If Glass Is Tempered

Interior Design Trends
How Can You Tell If Glass Is Tempered
Modified: February 18, 2024
Learn how to identify tempered glass for your interior design projects. Discover the latest interior design trends for incorporating tempered glass.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Tempered glass is a crucial component in various architectural and interior design applications. Its exceptional strength and safety features make it a popular choice for windows, doors, shower enclosures, and furniture. Identifying tempered glass is essential for ensuring its appropriate use and maintenance. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of tempered glass and the methods to identify it, providing valuable insights for homeowners, interior designers, and anyone involved in the selection and maintenance of glass products. Understanding how to distinguish tempered glass from its non-tempered counterparts is vital for making informed decisions regarding its installation and upkeep. Let's delve into the world of tempered glass and uncover the techniques to recognize this durable and versatile material.
Key Takeaways:
- Tempered glass is stronger and safer than regular glass, making it ideal for windows, doors, and furniture. Look for markings, surface distortions, and use tests to identify tempered glass accurately.
- Visual inspection, polarized light test, and thermal stress test are practical methods to identify tempered glass. These techniques help ensure the right use and maintenance of tempered glass in architectural and interior design projects.
Read more: How To Tell If Glass Is Tempered
What is tempered glass?
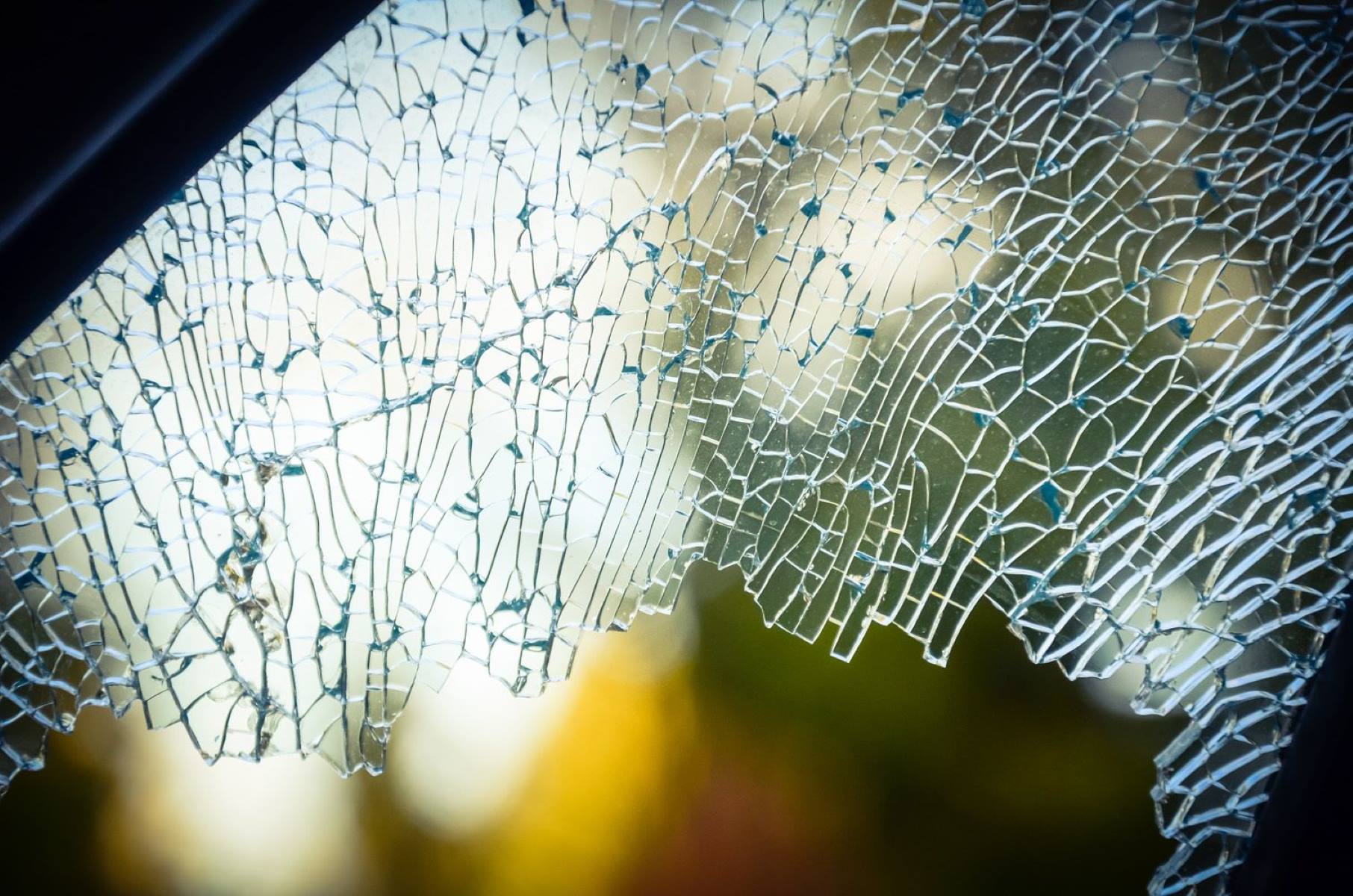
Tempered glass, also known as toughened glass, is a type of safety glass that is processed through controlled thermal or chemical treatments. This specialized manufacturing process enhances the strength and durability of the glass, making it significantly stronger than standard annealed glass. The key characteristic of tempered glass is its ability to shatter into small, granular pieces when broken, as opposed to sharp, jagged shards typical of regular glass. This unique feature minimizes the risk of serious injury, making tempered glass a preferred choice for various applications where safety is paramount.
During the tempering process, the glass is heated to high temperatures and then rapidly cooled using air jets or chemical treatments. This rapid cooling induces high surface compression and thermal stress within the glass, resulting in its increased strength and resilience. As a result, tempered glass exhibits exceptional resistance to impact, thermal stress, and mechanical loads, making it suitable for demanding environments and applications.
The strength and safety properties of tempered glass make it an ideal choice for architectural and interior design purposes. It is commonly used in windows, doors, shower enclosures, glass railings, tabletops, and other structural elements where safety and durability are essential. The ability of tempered glass to withstand higher wind loads, thermal stress differentials, and accidental impacts makes it a reliable and secure option for both residential and commercial settings.
In addition to its safety benefits, tempered glass also offers optical clarity and light transmission properties, allowing it to enhance the aesthetic appeal of interior spaces. Its versatility and resilience make it a valuable material for modern design concepts, enabling the creation of sleek, minimalist, and secure architectural elements.
Overall, tempered glass represents a significant advancement in glass technology, providing a compelling combination of strength, safety, and aesthetic appeal. Its widespread use in contemporary architecture and interior design underscores its importance as a versatile and reliable material for creating secure and visually appealing spaces.
Characteristics of tempered glass
Tempered glass exhibits a distinctive set of characteristics that distinguish it from standard annealed glass and other types of glass materials. These unique properties make tempered glass a preferred choice for a wide range of architectural and interior design applications. Understanding the key characteristics of tempered glass is essential for identifying and utilizing it effectively in various design and construction projects.
Exceptional Strength: One of the primary characteristics of tempered glass is its exceptional strength. Through the tempering process, the glass undergoes controlled thermal or chemical treatments that induce high surface compression and internal stress. This results in a glass product that is significantly stronger and more durable than standard annealed glass. The enhanced strength of tempered glass enables it to withstand higher mechanical loads, making it suitable for applications where impact resistance and structural integrity are crucial.
Safety Features: Tempered glass is designed with safety in mind. When broken, tempered glass shatters into small, granular pieces with rounded edges, reducing the risk of serious injury from sharp, jagged shards. This unique breakage pattern is a key safety feature that distinguishes tempered glass from non-tempered glass types. The ability of tempered glass to minimize the risk of injury in the event of breakage makes it an ideal choice for applications where safety is a priority, such as windows, doors, and shower enclosures.
Thermal Resistance: Another notable characteristic of tempered glass is its enhanced thermal resistance. The tempering process creates a glass product that can withstand higher thermal differentials compared to standard glass. This thermal resilience makes tempered glass suitable for applications exposed to varying temperature conditions, such as glass facades, skylights, and outdoor enclosures. The ability of tempered glass to resist thermal stress differentials contributes to its longevity and reliability in diverse environmental settings.
Impact Resistance: Tempered glass exhibits remarkable impact resistance, making it suitable for applications where accidental impacts or high wind loads may occur. Its ability to withstand sudden forces without shattering into hazardous shards enhances the safety and durability of architectural elements and interior fixtures. This impact resistance is a critical characteristic that positions tempered glass as a reliable and secure material for both residential and commercial use.
Optical Clarity: Despite its exceptional strength and safety features, tempered glass maintains optical clarity and light transmission properties. This characteristic allows it to enhance the aesthetic appeal of interior spaces by providing unobstructed views, natural light penetration, and a sense of openness. The optical clarity of tempered glass makes it a versatile material for creating visually appealing architectural elements and interior design features.
In summary, the characteristics of tempered glass, including its exceptional strength, safety features, thermal resistance, impact resistance, and optical clarity, position it as a versatile and reliable material for modern architectural and interior design applications. Its unique properties make it an ideal choice for creating secure, visually appealing, and durable spaces that prioritize safety and aesthetic excellence.
Methods to identify tempered glass
Identifying tempered glass is essential for ensuring its appropriate use and maintenance. There are several methods to distinguish tempered glass from its non-tempered counterparts, providing valuable insights for homeowners, interior designers, and professionals involved in glass installation and maintenance. By understanding these identification techniques, individuals can make informed decisions regarding the selection, handling, and care of glass products.
Visual Inspection
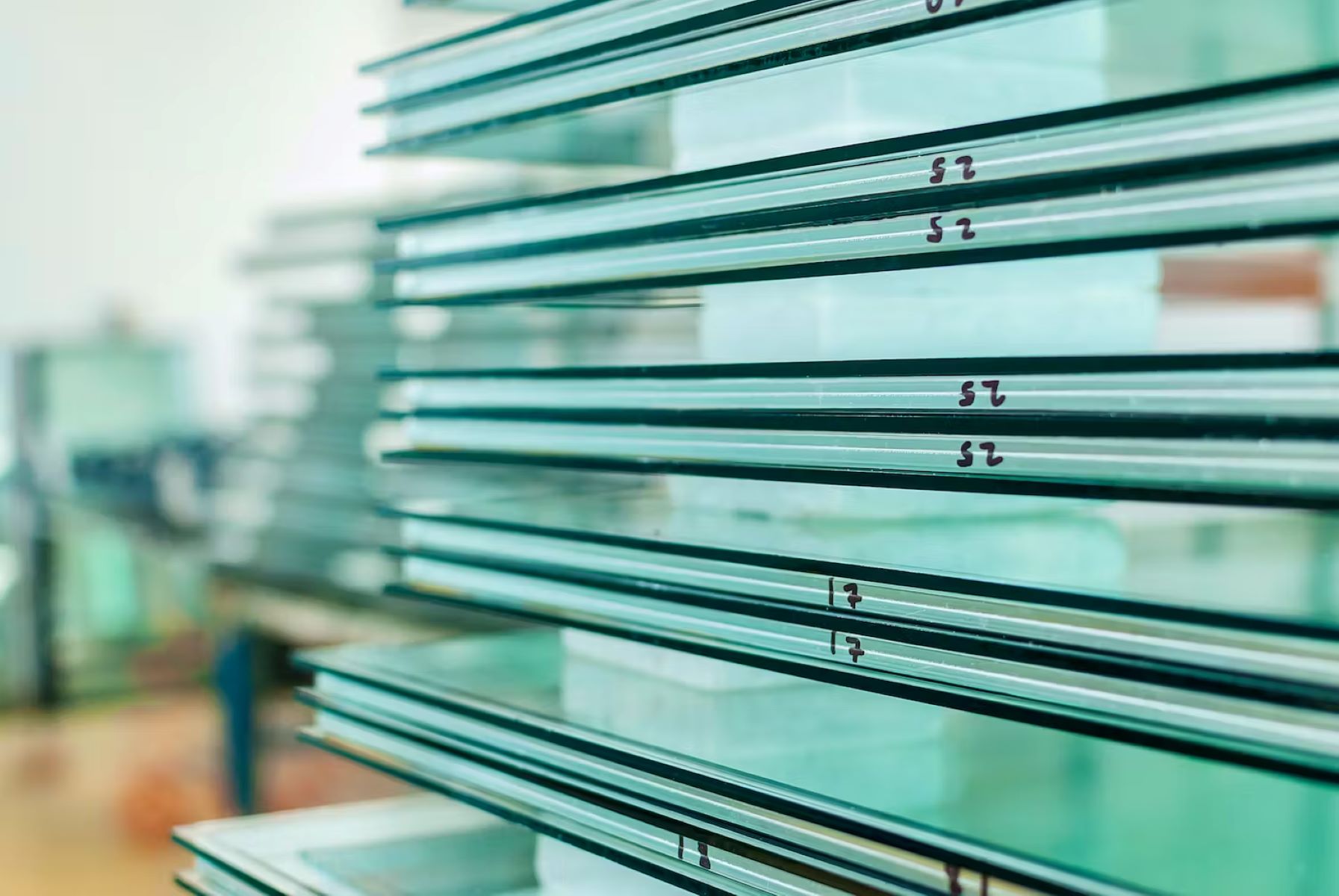
Visual inspection is a fundamental method for identifying tempered glass. When examining a piece of glass, look for any markings or labels that indicate it has been tempered. These markings may include a "tempered" or "safety" label etched into the glass surface. Additionally, tempered glass often exhibits slight surface distortions, known as roller wave, resulting from the tempering process. These distortions are visible when observing the glass from various angles and can help differentiate tempered glass from standard annealed glass.
Polarized Light Test
Another method to identify tempered glass is the polarized light test. When viewed through a polarizing filter, tempered glass displays distinct patterns of stress and strain that are a result of the tempering process. By examining the glass under polarized light, these patterns become visible, allowing for the identification of tempered glass based on its unique stress characteristics.
Thermal Stress Test
Conducting a thermal stress test is an effective way to identify tempered glass. This test involves applying a small, localized heat source to the surface of the glass, such as a handheld torch, and then observing the glass's reaction. Tempered glass will withstand the thermal shock and remain intact, while non-tempered glass is likely to break or crack when subjected to localized heat. This method provides a practical way to differentiate tempered glass from other glass types based on its thermal resilience.
Ultraviolet Light Test
The ultraviolet (UV) light test is another technique for identifying tempered glass. When exposed to UV light, tempered glass may exhibit a subtle, uniform pattern known as the "quench mark." This pattern is a result of the rapid cooling process during tempering and can be observed under UV light, aiding in the identification of tempered glass based on its unique visual response to ultraviolet illumination.
Sound Test
An auditory method for identifying tempered glass involves tapping the glass surface and listening to the resulting sound. Tempered glass produces a distinct, higher-pitched tone compared to non-tempered glass. This difference in sound can help differentiate tempered glass based on its acoustic properties, providing a simple yet effective method for identification.
By utilizing these methods, individuals can confidently identify tempered glass and make informed decisions regarding its use and maintenance. Whether inspecting glass installations in residential settings, commercial spaces, or interior design projects, understanding these identification techniques is essential for ensuring the appropriate application and care of tempered glass products.
Read more: How Can You Tell Crystal From Glass
Visual inspection
Visual inspection is a fundamental method for identifying tempered glass. When examining a piece of glass, look for any markings or labels that indicate it has been tempered. These markings may include a "tempered" or "safety" label etched into the glass surface. Additionally, tempered glass often exhibits slight surface distortions, known as roller wave, resulting from the tempering process. These distortions are visible when observing the glass from various angles and can help differentiate tempered glass from standard annealed glass.
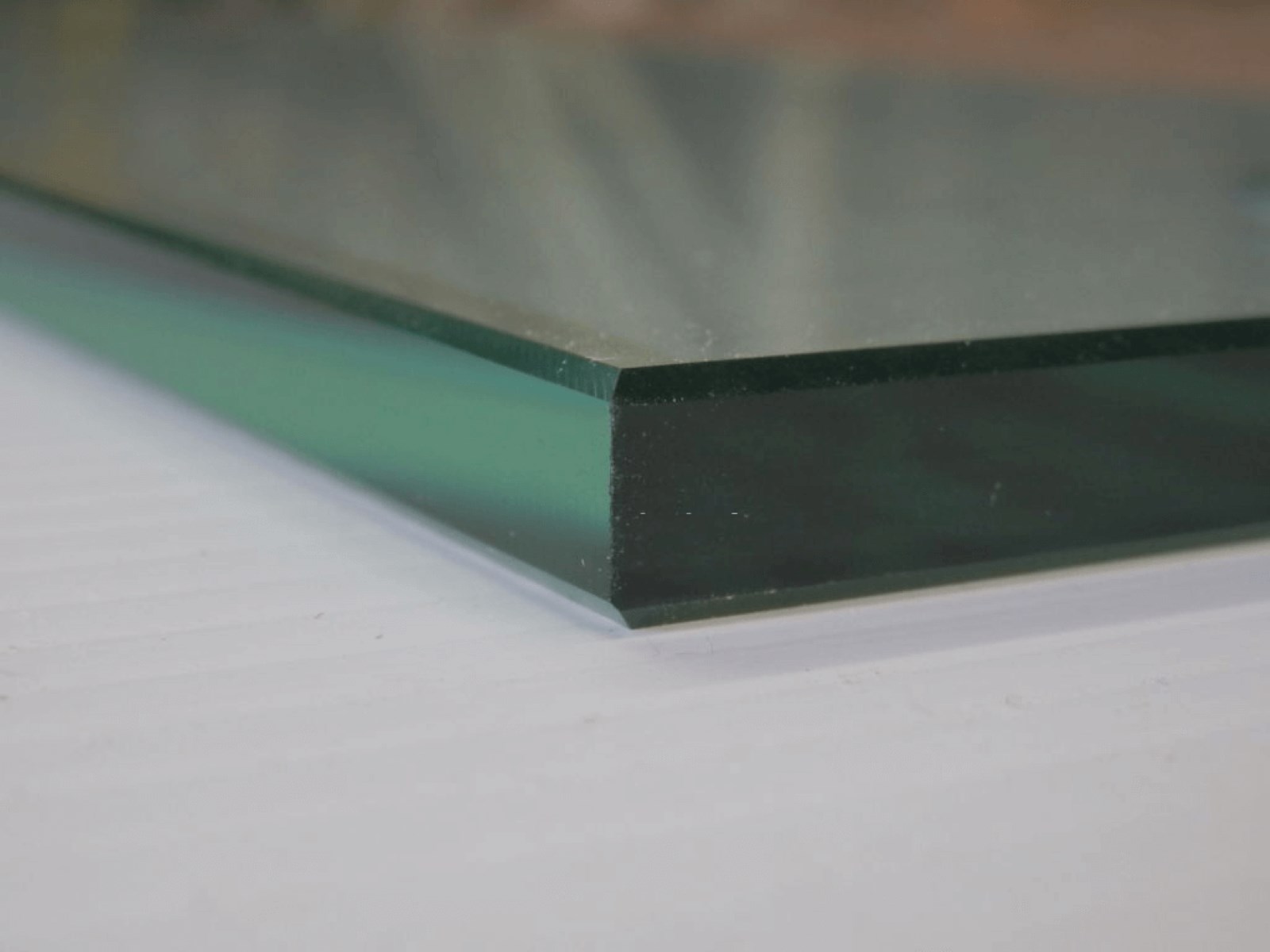
During visual inspection, it is essential to carefully examine the edges of the glass. Tempered glass typically has smoother, rounded edges due to the tempering process, which involves heating and rapid cooling. These rounded edges serve as a visual indicator of the glass's tempered nature. In contrast, non-tempered glass may have sharper, more irregular edges, reflecting its annealed state.
Furthermore, observing the glass under specific lighting conditions can reveal visual cues that aid in identifying tempered glass. When viewed under polarized light, tempered glass may display distinct stress patterns, providing additional confirmation of its tempered nature. These stress patterns are a result of the tempering process and can be observed as unique visual characteristics when the glass is subjected to polarized light.
In some cases, tempered glass may bear a manufacturer's stamp or logo, providing valuable information about its tempering and safety specifications. These markings are typically located in the corners or along the edges of the glass and can serve as definitive indicators of the glass's tempered status.
Overall, visual inspection serves as a primary method for identifying tempered glass, allowing individuals to assess the glass's markings, surface distortions, edge characteristics, and response to specific lighting conditions. By carefully examining these visual cues, it becomes possible to confidently differentiate tempered glass from its non-tempered counterparts, enabling informed decision-making regarding its installation and maintenance.
Polarized light test
The polarized light test is a valuable method for identifying tempered glass based on its unique stress patterns and optical characteristics. When subjected to polarized light, tempered glass exhibits distinct visual patterns that result from the tempering process. This method provides a non-invasive and practical way to differentiate tempered glass from its non-tempered counterparts, offering valuable insights for homeowners, interior designers, and professionals involved in glass installation and maintenance.
To conduct the polarized light test, a polarizing filter is utilized to observe the glass's response to polarized light. When tempered glass is placed between two polarizing filters and viewed under polarized light, it reveals intricate stress patterns that are indicative of its tempered nature. These stress patterns are a result of the controlled thermal or chemical treatments applied during the tempering process, which induce internal stress and surface compression within the glass.
The stress patterns observed during the polarized light test appear as a series of colorful, shimmering bands or patterns that are visible when the glass is rotated or viewed from different angles. These patterns are unique to tempered glass and are not typically present in non-tempered glass. By carefully examining the stress patterns under polarized light, individuals can confidently identify tempered glass based on its distinctive optical response.
In addition to stress patterns, the polarized light test can also reveal any residual birefringence present in the glass, further confirming its tempered status. Birefringence refers to the optical property of a material that splits light into two polarized components, resulting in distinct visual effects when observed under polarized light. In tempered glass, residual birefringence may be visible as colorful or iridescent patterns that provide additional confirmation of the glass's tempered nature.
Overall, the polarized light test offers a practical and visually engaging method for identifying tempered glass based on its unique stress patterns and optical response to polarized light. By leveraging this method, individuals can gain valuable insights into the tempered nature of glass products, enabling informed decisions regarding their selection, installation, and maintenance in various architectural and interior design applications.
Thermal stress test
The thermal stress test is a practical and effective method for identifying tempered glass based on its ability to withstand localized heat without breaking or shattering. This method provides valuable insights for homeowners, interior designers, and professionals involved in glass installation and maintenance, offering a straightforward way to differentiate tempered glass from its non-tempered counterparts.
To conduct the thermal stress test, a small, localized heat source, such as a handheld torch or heat gun, is applied to the surface of the glass. The heat is focused on a specific area of the glass, and the glass's reaction to the thermal shock is observed. In the case of tempered glass, it will withstand the thermal stress and remain intact, demonstrating its resilience to sudden temperature differentials. This ability to resist localized heat without breaking is a key characteristic of tempered glass and serves as a definitive indicator of its tempered nature.
In contrast, non-tempered glass is likely to break or crack when subjected to localized heat, as it lacks the enhanced thermal resilience and surface compression characteristic of tempered glass. By observing the glass's response to the thermal stress test, individuals can confidently differentiate tempered glass from its non-tempered counterparts based on its ability to withstand thermal shock.
The thermal stress test provides a practical and non-destructive method for identifying tempered glass, allowing individuals to assess the glass's thermal resilience and response to localized heat. This method can be particularly useful when inspecting glass installations in various settings, including residential homes, commercial spaces, and interior design projects. By leveraging the thermal stress test, individuals can make informed decisions regarding the selection, handling, and maintenance of glass products, ensuring the appropriate use of tempered glass in diverse architectural and design applications.
Overall, the thermal stress test offers a straightforward and reliable method for identifying tempered glass based on its ability to withstand localized heat, providing valuable insights for ensuring the appropriate application and care of tempered glass products in architectural and interior design contexts.
Look for a small “bug” or logo in one of the corners of the glass. Tempered glass is usually marked to indicate its strength.
Conclusion
In conclusion, identifying tempered glass is essential for ensuring its appropriate use and maintenance in various architectural and interior design applications. The methods discussed, including visual inspection, the polarized light test, the thermal stress test, the ultraviolet light test, and the sound test, provide valuable techniques for differentiating tempered glass from its non-tempered counterparts. By leveraging these identification methods, individuals can make informed decisions regarding the selection, installation, and maintenance of glass products, ensuring the safety, durability, and aesthetic integrity of architectural and interior design elements.
The visual inspection method allows for the examination of glass markings, surface distortions, edge characteristics, and response to specific lighting conditions, providing visual cues that aid in identifying tempered glass. This fundamental method serves as a primary means of differentiating tempered glass from standard annealed glass, enabling individuals to assess the glass's markings, surface distortions, and edge characteristics with confidence.
The polarized light test offers a non-invasive and practical way to identify tempered glass based on its unique stress patterns and optical characteristics. By subjecting the glass to polarized light and observing the resulting stress patterns and birefringence, individuals can gain valuable insights into the tempered nature of glass products, enhancing their ability to make informed decisions regarding their selection and use.
The thermal stress test provides a straightforward and effective method for identifying tempered glass based on its ability to withstand localized heat without breaking or shattering. This practical method allows individuals to assess the glass's thermal resilience and response to thermal shock, providing valuable insights into its tempered nature and suitability for various architectural and interior design applications.
The ultraviolet light test and the sound test offer additional techniques for identifying tempered glass, providing alternative means of differentiating tempered glass from non-tempered glass based on its unique visual response to ultraviolet illumination and acoustic properties.
By understanding and utilizing these identification methods, individuals can confidently identify tempered glass and make informed decisions regarding its use and maintenance. Whether inspecting glass installations in residential settings, commercial spaces, or interior design projects, the ability to differentiate tempered glass from its non-tempered counterparts is essential for ensuring the appropriate application and care of glass products.
In summary, the methods to identify tempered glass discussed in this article offer valuable insights for homeowners, interior designers, and professionals involved in glass installation and maintenance. By leveraging these techniques, individuals can enhance their ability to recognize tempered glass and make informed decisions regarding its selection, installation, and maintenance, contributing to the safety, durability, and aesthetic excellence of architectural and interior design elements.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Can You Tell If Glass Is Tempered
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Can You Tell If Glass Is Tempered”