Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>When Was Glass Discovered


Interior Design Trends
When Was Glass Discovered
Modified: February 25, 2024
Discover the history of glass and its impact on interior design trends. Learn about the origins and evolution of glass in interior decor.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Glass is a material that has been an integral part of human history for centuries. Its unique properties have made it a versatile and indispensable substance in various aspects of human life, from architecture and interior design to scientific instruments and everyday household items. The discovery and evolution of glass have significantly impacted the way we perceive and interact with the world around us.
The story of glass begins with its discovery in ancient times, a pivotal moment that revolutionized human craftsmanship and creativity. The journey of glassmaking spans across civilizations and cultures, each contributing to its development and refinement. From the ancient techniques of glassblowing to the modern innovations in glass manufacturing, the evolution of this remarkable material reflects the ingenuity and resourcefulness of human civilization.
As we delve into the early history of glass and explore the ancient techniques that shaped its production, we gain a deeper appreciation for the artistry and skill involved in creating this transparent wonder. The spread of glassmaking technology across different regions further illustrates its significance in shaping trade, culture, and technological advancements throughout history.
In the modern era, the art and science of glassmaking have reached new heights, with cutting-edge techniques and technologies pushing the boundaries of what is possible with this remarkable material. The fusion of tradition and innovation has led to the creation of breathtaking architectural marvels, exquisite artworks, and functional everyday objects that enrich our lives in countless ways.
Join us on a journey through time as we unravel the captivating tale of glass, from its ancient origins to its contemporary manifestations. Discover the secrets of ancient glassmaking techniques, witness the global impact of glass trade and technology, and marvel at the transformative power of modern glassmaking innovations. Let us embark on this enlightening exploration of one of the most fascinating materials known to humanity.
Key Takeaways:
- Glass was discovered in ancient times, sparking innovation and creativity. Ancient civilizations like the Phoenicians and Romans contributed to its development, shaping its cultural and economic significance.
- Modern glassmaking techniques blend tradition and innovation, using advanced furnaces, automation, coatings, and digital design. This evolution has expanded the possibilities for creating stunning glass creations that enhance the built environment.
Read more: How Was Glass Discovered
Early History of Glass
The early history of glass dates back to ancient civilizations, where the accidental discovery of this remarkable material revolutionized human craftsmanship. The exact origins of glass remain shrouded in mystery, with various accounts and legends attributing its discovery to different cultures. One of the most enduring tales is that of Phoenician sailors who, upon landing on the sandy shores of the Belus River, used blocks of natron (a naturally occurring mixture of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate) to support their cooking pots. The intense heat from their campfire fused the natron with the beach sand, resulting in a translucent liquid that solidified into glass.
Another account traces the discovery of glass to the ancient Mesopotamians, who are believed to have stumbled upon the material while firing glazes for pottery. Regardless of its exact origins, the emergence of glass marked a pivotal moment in human history, sparking a wave of innovation and creativity that would shape the course of civilization.
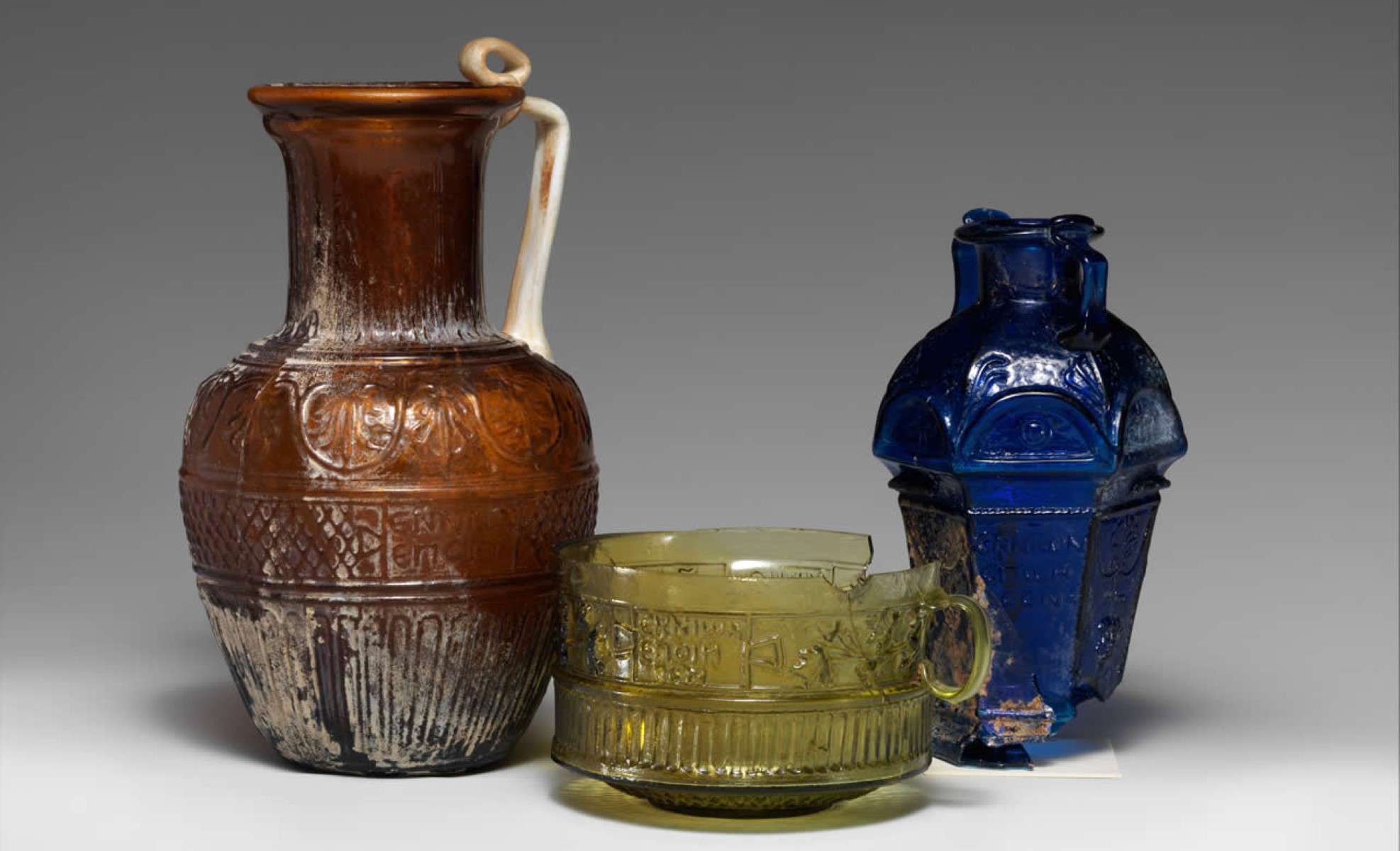
The earliest known glass objects date back to around 3500 BCE in Mesopotamia and Egypt, where artisans crafted small beads and amulets from a rudimentary form of glass. These early glass artifacts were produced using a technique known as core-forming, in which a shaped core of clay or dung was coated with molten glass to create intricate designs.
Over time, the art of glassmaking spread to other ancient cultures, including the Phoenicians, Greeks, and Romans, each contributing to the refinement and expansion of glass production techniques. The demand for glass grew as it became an essential material for creating jewelry, vessels, and decorative items, reflecting its increasing cultural and economic significance.
The ancient Egyptians, renowned for their advanced craftsmanship, developed the technique of glassblowing around the 1st century BCE, revolutionizing the production of glass vessels and enabling the creation of more intricate and delicate designs. This innovation marked a turning point in the history of glass, paving the way for the mass production of glassware and the widespread use of glass in everyday life.
As the knowledge of glassmaking techniques spread across civilizations, it laid the foundation for the global trade and exchange of glass objects, fostering cultural connections and technological advancements. The early history of glass serves as a testament to human ingenuity and the enduring allure of this transparent marvel, setting the stage for its continued evolution and impact on the world.
The journey of glassmaking is a testament to human ingenuity and the enduring allure of this transparent marvel, setting the stage for its continued evolution and impact on the world.
Ancient Glassmaking Techniques
Ancient glassmaking techniques represent a remarkable fusion of artistry, skill, and innovation, laying the groundwork for the evolution of this extraordinary material. The early artisans who mastered the craft of glassmaking employed ingenious methods to transform raw materials into exquisite glass objects, showcasing a level of craftsmanship that continues to inspire awe to this day.
One of the most significant advancements in ancient glassmaking was the development of core-forming, a technique that originated in Mesopotamia and Egypt around 1500 BCE. This method involved shaping a core of clay or dung and then carefully applying layers of molten glass to create intricate patterns and designs. The delicate artistry of core-formed glass resulted in the production of stunning beads, amulets, and small vessels, showcasing the ancient artisans' mastery of this versatile material.
The ancient Egyptians, renowned for their advanced craftsmanship, made a groundbreaking contribution to glassmaking with the invention of glassblowing around the 1st century BCE. This revolutionary technique allowed artisans to create glass vessels with unprecedented speed and precision, ushering in a new era of mass production and artistic innovation. The art of glassblowing transformed the way glass objects were crafted, enabling the creation of intricate shapes, ornate decorations, and functional vessels that served both practical and aesthetic purposes.
Furthermore, the Romans played a pivotal role in refining ancient glassmaking techniques, introducing advancements such as mold-blown glass and the use of glass for architectural purposes. Mold-blown glass allowed for the production of symmetrical and intricately patterned vessels, expanding the range of designs and styles available to ancient societies. Additionally, the Romans utilized glass in architectural applications, demonstrating its versatility and durability as a building material.
The ancient glassmaking techniques not only showcased the technical prowess of early artisans but also reflected the cultural and economic significance of glass in ancient societies. The intricate designs, vibrant colors, and functional utility of ancient glass objects attest to the enduring appeal and versatility of this remarkable material.
The legacy of ancient glassmaking techniques continues to inspire contemporary artisans and designers, serving as a testament to the enduring allure and timeless beauty of glass as a medium for artistic expression and functional innovation.
Glass was first discovered around 3500 BCE in Mesopotamia. It was likely created accidentally by ancient people who were heating and melting silica from sand and other materials.
Spread of Glassmaking Technology
The spread of glassmaking technology across ancient civilizations marked a significant milestone in the global exchange of knowledge and craftsmanship. As the art of glassmaking evolved and diversified, it transcended geographical boundaries, facilitating cultural connections and technological diffusion on an unprecedented scale.
The Phoenicians, renowned for their seafaring prowess and extensive trade networks, played a pivotal role in disseminating glassmaking techniques throughout the Mediterranean region and beyond. Their maritime expeditions facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and craftsmanship, leading to the widespread adoption of glassmaking practices in distant lands. The Phoenician influence on glassmaking technology contributed to the enrichment of cultural traditions and the advancement of artistic expression in various societies.
The expansion of the Roman Empire further accelerated the global spread of glassmaking technology, as Roman artisans and craftsmen carried their expertise to the far reaches of the empire. The establishment of glass workshops in regions such as Gaul, Hispania, and North Africa facilitated the transfer of knowledge and skills, fostering the development of local glassmaking industries and stimulating cross-cultural interactions.
The Silk Road, a network of ancient trade routes connecting the East and West, served as a conduit for the exchange of goods, including glassware and raw materials essential for glass production. The transmission of glassmaking techniques along the Silk Road facilitated cultural exchange and technological diffusion between the civilizations of Asia, the Middle East, and Europe, contributing to the diversification and refinement of glassmaking practices across different regions.
The Islamic Golden Age, characterized by remarkable advancements in science, art, and technology, played a pivotal role in the transmission of knowledge and innovation in glassmaking. Islamic scholars and artisans made significant contributions to the development of glassmaking techniques, introducing new methods and designs that enriched the global repertoire of glass craftsmanship.
The spread of glassmaking technology not only facilitated the production of utilitarian objects but also elevated glass to a revered status as a symbol of wealth, luxury, and artistic excellence. The diffusion of glassmaking knowledge across diverse cultures and civilizations fostered a rich tapestry of artistic styles and technical expertise, shaping the global heritage of glass as a medium of unparalleled beauty and functionality.
The enduring legacy of the spread of glassmaking technology serves as a testament to the interconnectedness of human societies and the enduring impact of cultural exchange on the evolution of craftsmanship and artistic expression.
Modern Glassmaking Techniques
Modern glassmaking techniques have undergone a remarkable evolution, driven by technological advancements, innovative processes, and a deep understanding of the material's properties. The fusion of tradition and cutting-edge methods has propelled glassmaking into a new era of creativity, precision, and sustainability.
One of the most significant developments in modern glassmaking is the utilization of advanced furnaces and melting technologies. These state-of-the-art furnaces, often powered by clean energy sources, enable the precise control of temperature and composition, resulting in the production of high-quality glass with exceptional clarity and uniformity. The use of sustainable energy sources aligns with the growing emphasis on environmental responsibility within the glassmaking industry, reflecting a commitment to reducing carbon emissions and minimizing ecological impact.
Furthermore, the advent of automated glass forming and shaping processes has revolutionized the efficiency and precision of glass production. Advanced machinery and robotics are employed to create intricate glass designs, from architectural panels to delicate art installations, with unparalleled accuracy and consistency. This integration of automation has not only enhanced the speed of production but also expanded the possibilities for complex and customized glass creations, catering to the diverse needs of architects, designers, and artists.
In addition, the development of innovative glass coatings and treatments has expanded the functional and aesthetic potential of glass in architectural and design applications. These specialized coatings offer enhanced thermal insulation, solar control, and self-cleaning properties, contributing to the sustainable design of energy-efficient buildings and structures. Moreover, advancements in decorative glass techniques, such as acid etching, sandblasting, and digital printing, have unlocked a myriad of artistic possibilities, allowing for the creation of bespoke glass surfaces that combine beauty with practicality.
The integration of digital design tools and computer-aided manufacturing has further revolutionized the creative process in modern glassmaking. Architects and designers can now explore complex geometries and intricate patterns with unprecedented precision, translating their visionary concepts into stunning glass installations and facades. This seamless synergy between digital innovation and traditional craftsmanship has redefined the boundaries of what is achievable in glass design, pushing the envelope of creativity and expression.
The evolution of modern glassmaking techniques embodies a harmonious blend of artistry, technology, and sustainability, paving the way for a new era of glass innovation. As the industry continues to embrace advancements in materials science, engineering, and design, the possibilities for creating awe-inspiring glass creations that captivate the imagination and elevate the built environment are boundless.
Read more: When Was Glass Invented
Conclusion
The journey of glass, from its ancient discovery to its modern manifestations, is a testament to the enduring allure and transformative power of this remarkable material. The early history of glass, marked by ingenious discoveries and pioneering techniques, laid the foundation for its evolution into a versatile medium that transcends cultural, artistic, and functional boundaries.
Ancient glassmaking techniques, such as core-forming and glassblowing, exemplify the ingenuity and artistry of early artisans, who transformed raw materials into exquisite objects that continue to inspire awe. The spread of glassmaking technology across ancient civilizations facilitated cultural exchange, technological diffusion, and the global appreciation of glass as a symbol of wealth, luxury, and artistic excellence.
In the modern era, glassmaking has embraced cutting-edge technologies, sustainable practices, and innovative design approaches, ushering in a new era of creativity and precision. Advanced furnaces, automated forming processes, specialized coatings, and digital design tools have expanded the possibilities for creating breathtaking glass installations, architectural marvels, and functional surfaces that enhance the built environment.
The enduring legacy of glass as a medium for artistic expression, architectural innovation, and everyday utility underscores its timeless relevance and significance in human civilization. From the shimmering stained glass windows of medieval cathedrals to the sleek, transparent skyscrapers of the modern metropolis, glass continues to captivate and inspire, transcending its materiality to become a symbol of transparency, clarity, and boundless potential.
As we reflect on the captivating tale of glass, we are reminded of its enduring legacy as a medium that bridges the realms of art, science, and human ingenuity. The evolution of glassmaking techniques, from ancient traditions to modern innovations, serves as a testament to the enduring spirit of creativity and the unyielding pursuit of excellence. With each shimmering surface and intricate design, glass invites us to behold the world through a lens of transparency, inviting us to envision a future illuminated by the boundless possibilities of this extraordinary material.
Frequently Asked Questions about When Was Glass Discovered
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “When Was Glass Discovered”