Home>Furniture>Bedroom Furniture>How Fast Do Bed Bugs Reproduce


Bedroom Furniture
How Fast Do Bed Bugs Reproduce
Modified: October 28, 2024
Discover how quickly bed bugs reproduce in your bedroom furniture. Learn about their breeding habits and find effective solutions to prevent infestations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the exciting world of bedroom furniture! Whether you’re redecorating a room or looking for a cozy new bed, it’s important to have a good understanding of the different types of furniture available and how to choose the right pieces. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of bedroom furniture, from beds and mattresses to dressers and nightstands.
Bedroom furniture not only serves a functional purpose but is also a reflection of your personal style and taste. A well-designed and carefully curated bedroom can promote relaxation, improve sleep quality, and enhance overall well-being. It’s important to invest in high-quality, durable pieces that will stand the test of time and create a tranquil and inviting space.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about bedroom furniture, including the different types of beds and mattresses, the various styles and materials available, and tips for selecting the right pieces for your specific needs. We’ll also delve into the importance of proper storage solutions and highlight some of the key considerations when choosing dressers, nightstands, and other storage furniture.
Additionally, we’ll touch upon the importance of proper maintenance and care for your bedroom furniture to ensure its longevity. From cleaning and dusting to addressing common issues like squeaky beds and worn-out mattresses, we’ll provide expert advice to help you keep your furniture in excellent condition.
Lastly, we can’t forget about the importance of aesthetics. Your bedroom furniture should be a reflection of your personal style and create an ambiance that promotes relaxation and tranquility. We’ll explore different design styles, color schemes, and decorative elements that can elevate the overall look and feel of your bedroom.
So, grab a cup of tea or coffee, get comfortable, and let’s delve into the world of bedroom furniture. By the end of this guide, you’ll have all the knowledge and inspiration you need to create your dream bedroom.
Key Takeaways:
- Bed bugs reproduce rapidly, with a single female capable of laying up to 7 eggs per day and 200-500 in her lifetime. Early detection and thorough cleaning are crucial for effective control.
- Factors such as temperature, blood meal availability, and hiding sites influence bed bug reproduction speed. Implementing strategies like mattress encasements and professional pest control can disrupt their reproductive cycle.
Read more: Where Do Bed Bugs Live
Understanding Bed Bug Reproduction
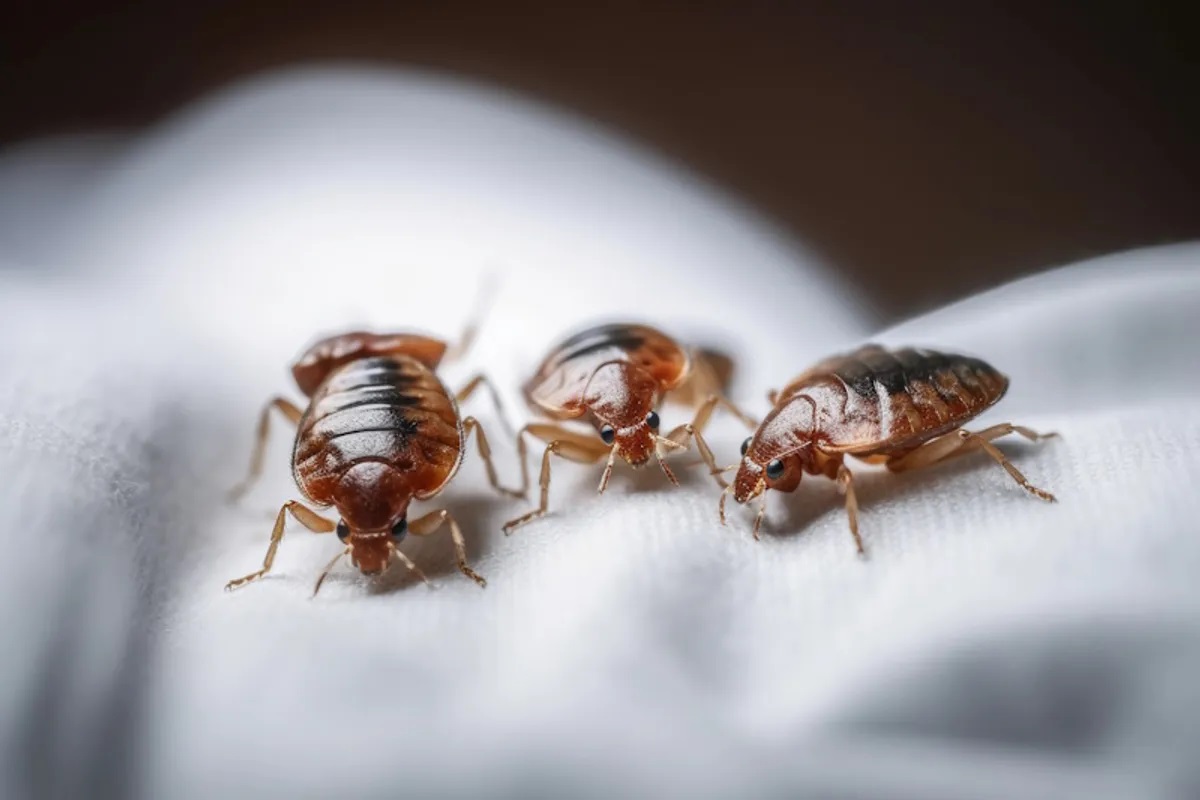
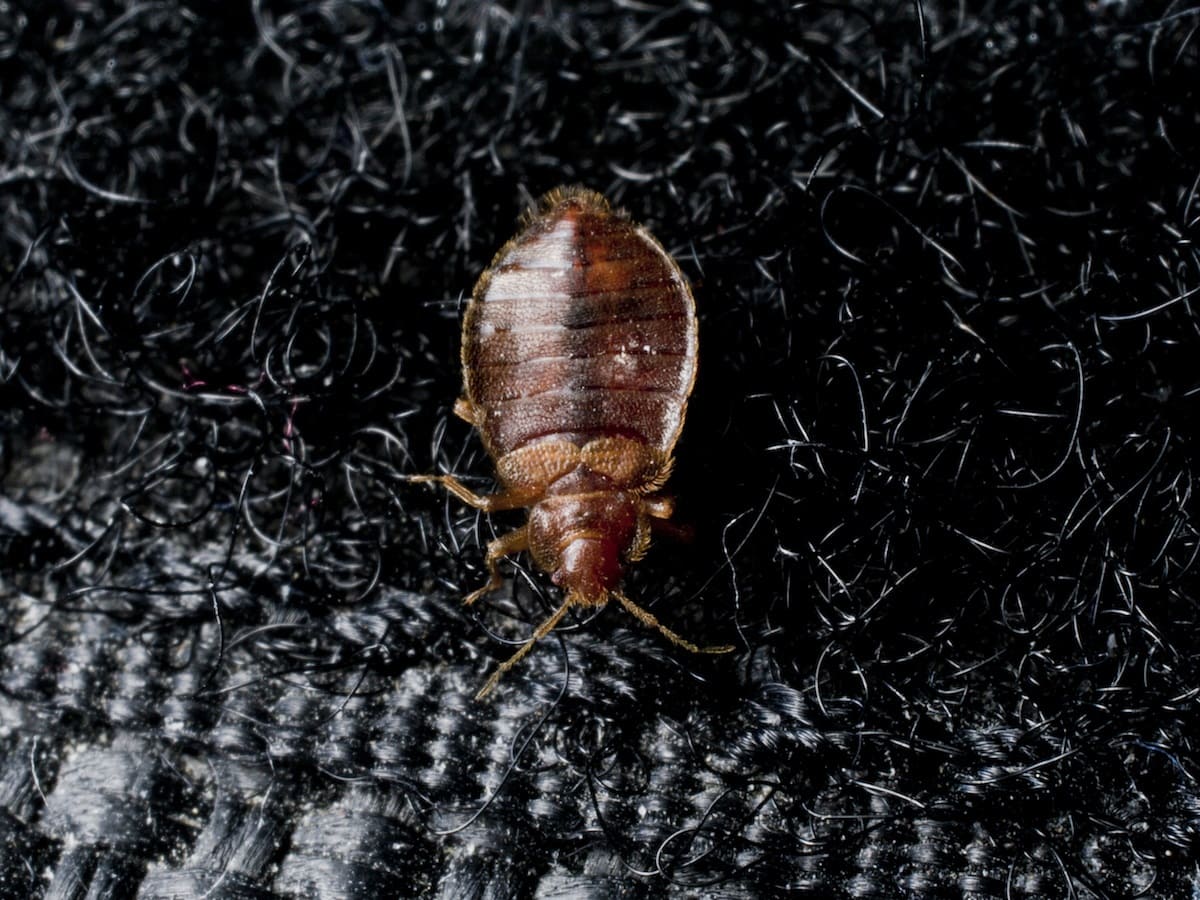
Bed bugs are not only creepy pests that invade our homes but also prolific reproducers. Understanding their reproductive behavior is crucial for effective control and prevention. So, let’s take a closer look at how bed bugs reproduce.
Bed bugs have a unique and fascinating reproductive cycle. They undergo what is known as “simple or incomplete metamorphosis.” Unlike insects that undergo a complete metamorphosis like butterflies, bed bugs hatch from eggs as nymphs, which resemble smaller versions of adults.
The reproductive process begins when a male bed bug pierces the female’s abdomen with his reproductive organ, known as a “copulatory organ.” This process is known as “traumatic insemination” and can be rather aggressive. The sperm is then released into the female’s body cavity, where it migrates to the ovaries and fertilizes the eggs.
Interestingly, female bed bugs have a unique reproductive feature called “sperm storage.” Once fertilized, the female bed bug can store sperm in a specialized structure called the “spermatheca.” This allows her to continuously lay fertilized eggs over an extended period, even without the presence of males.
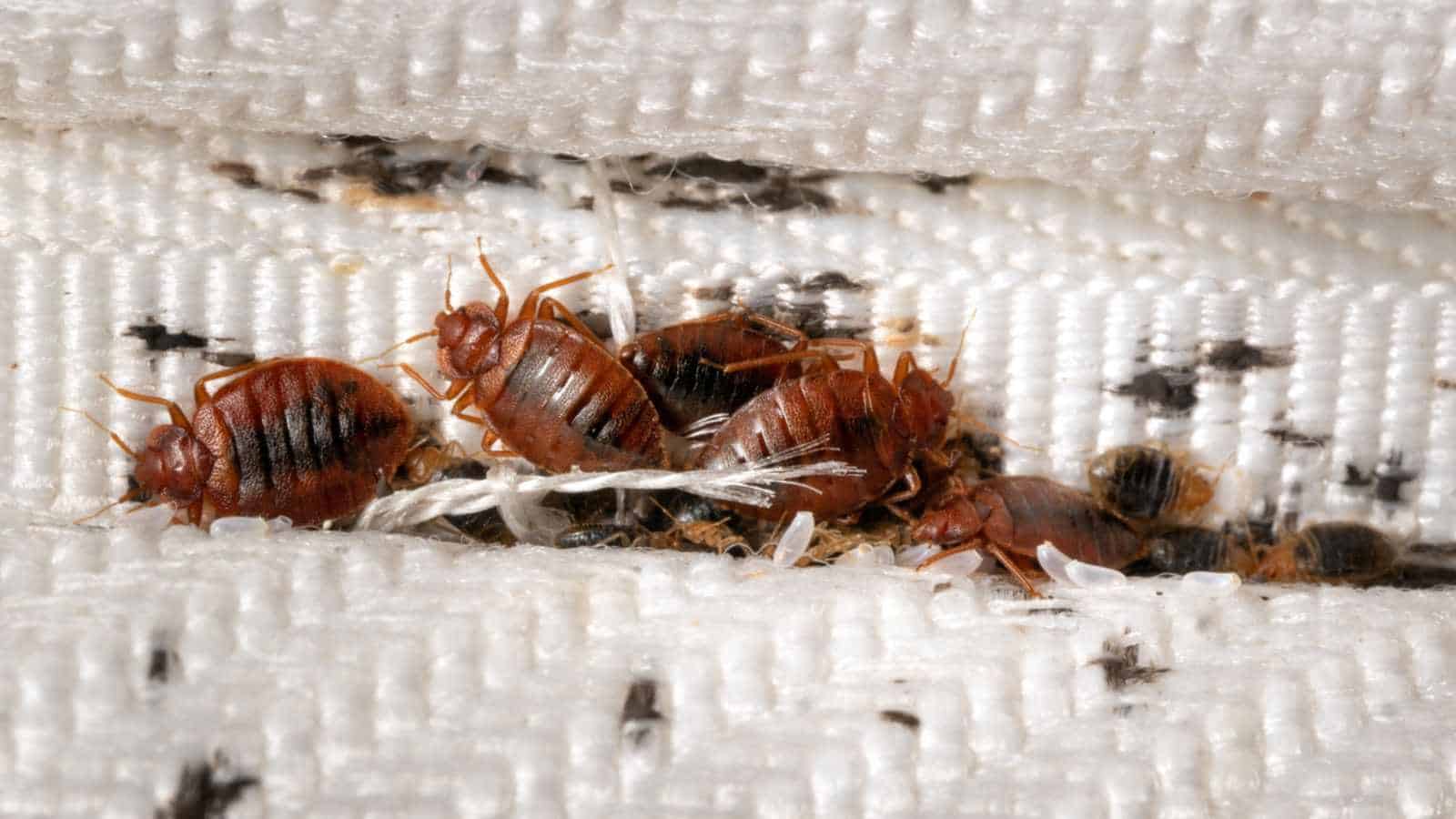
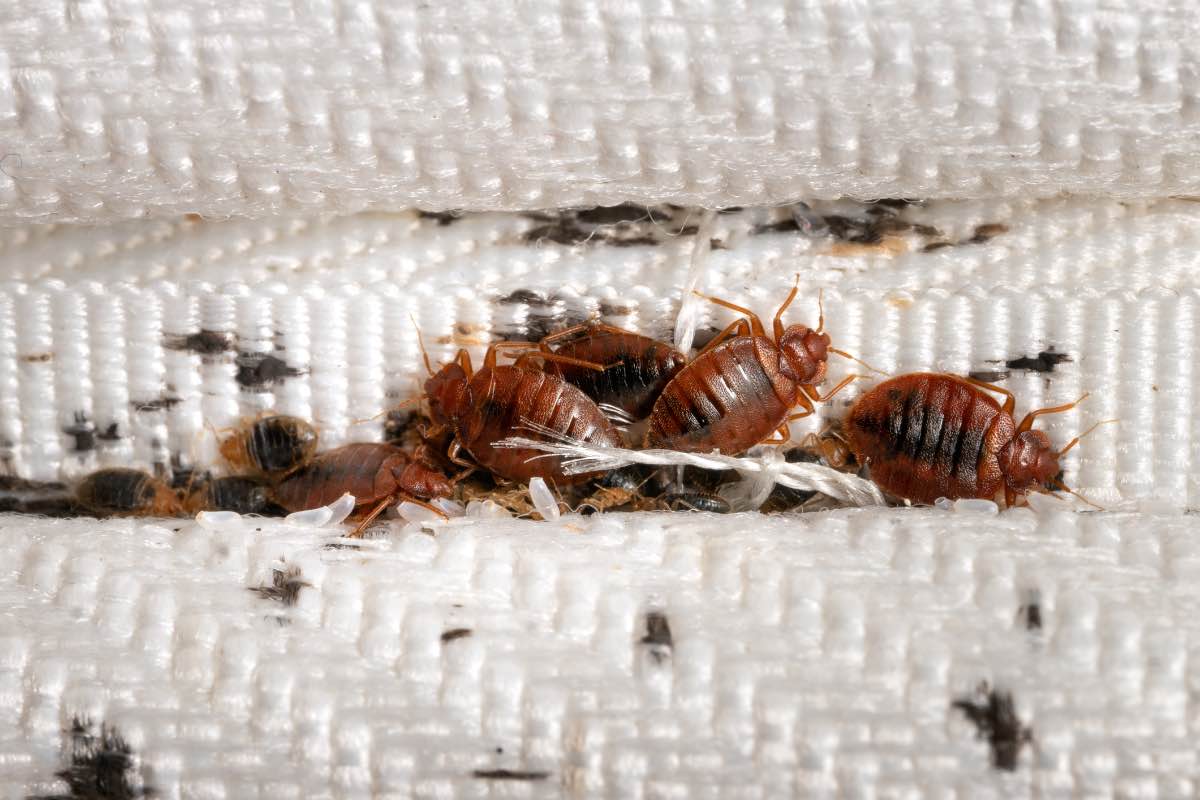
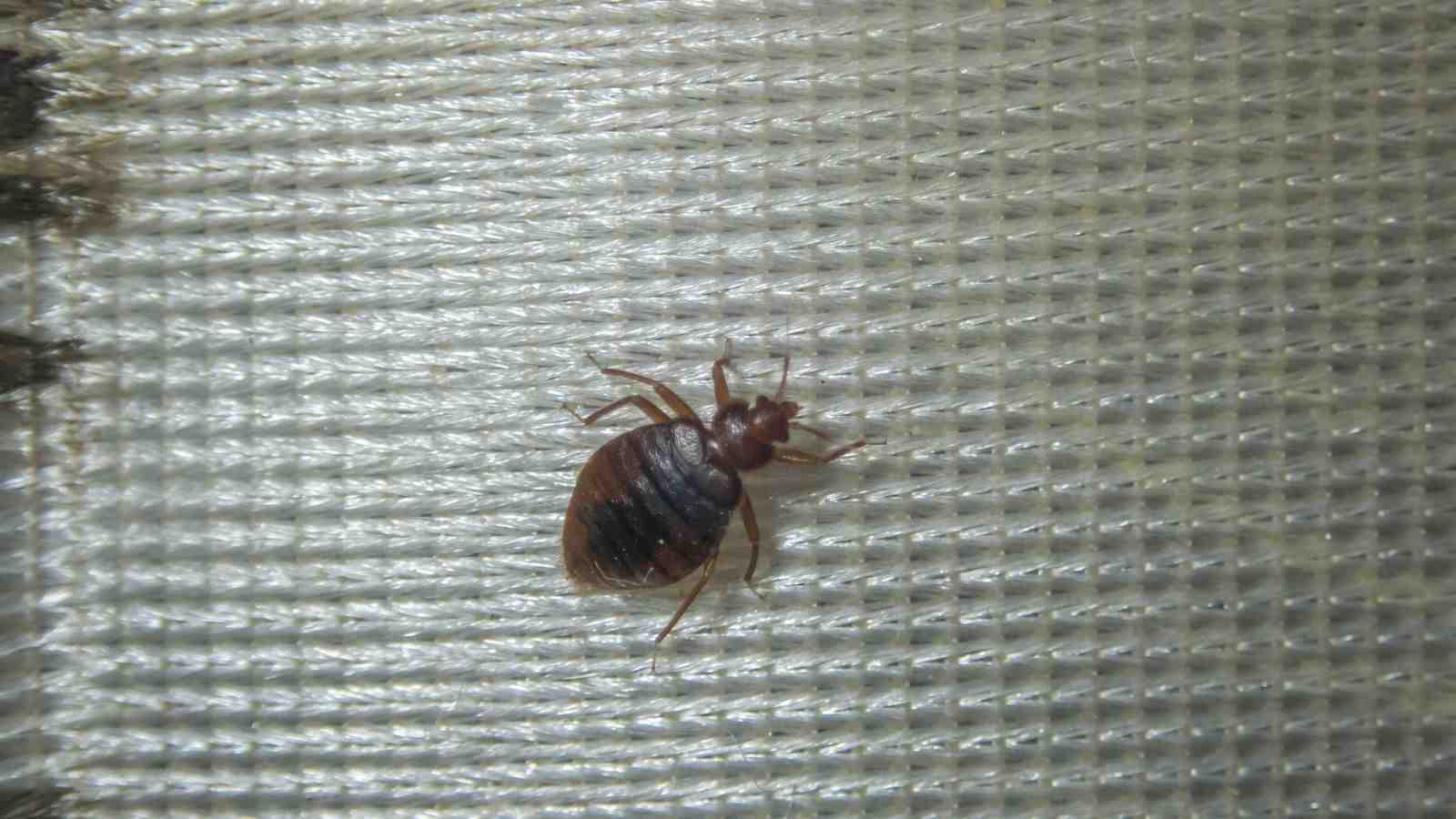
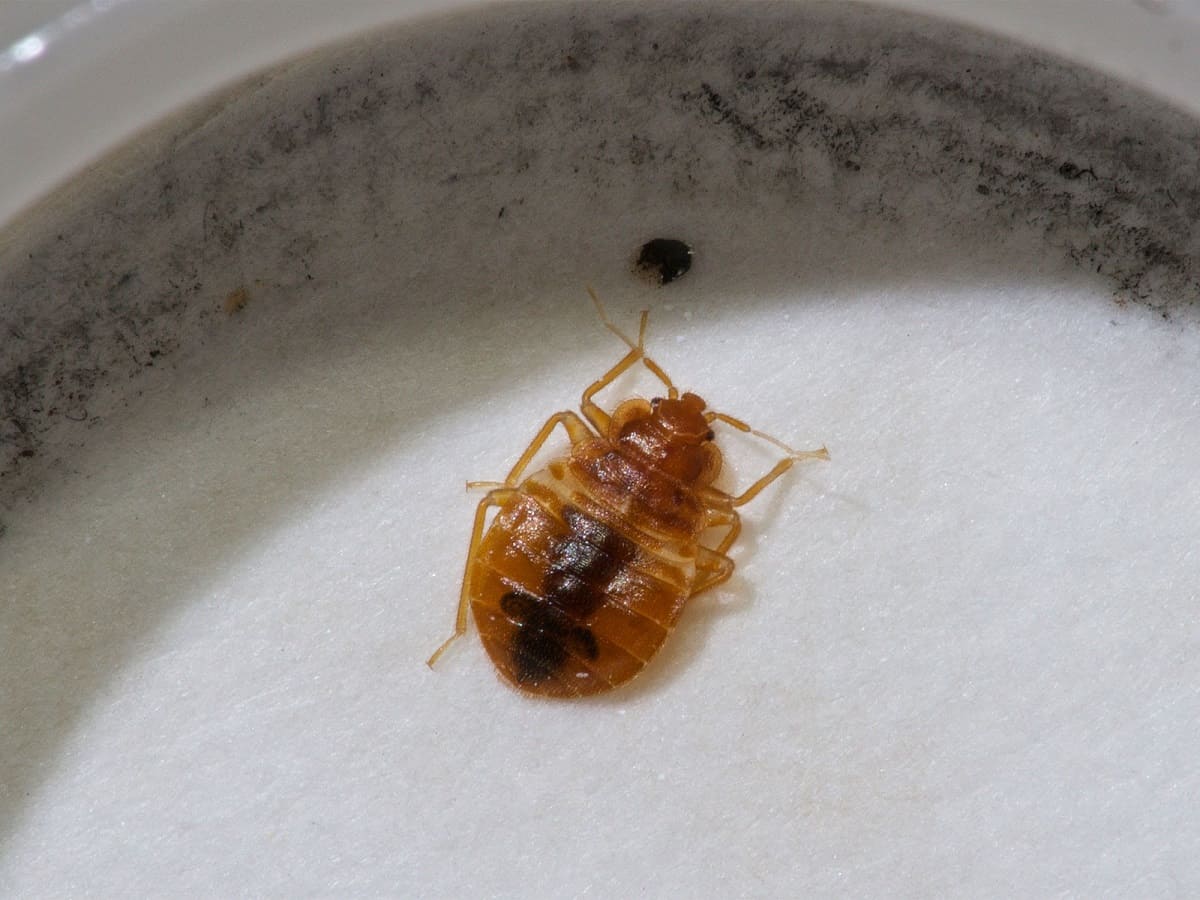
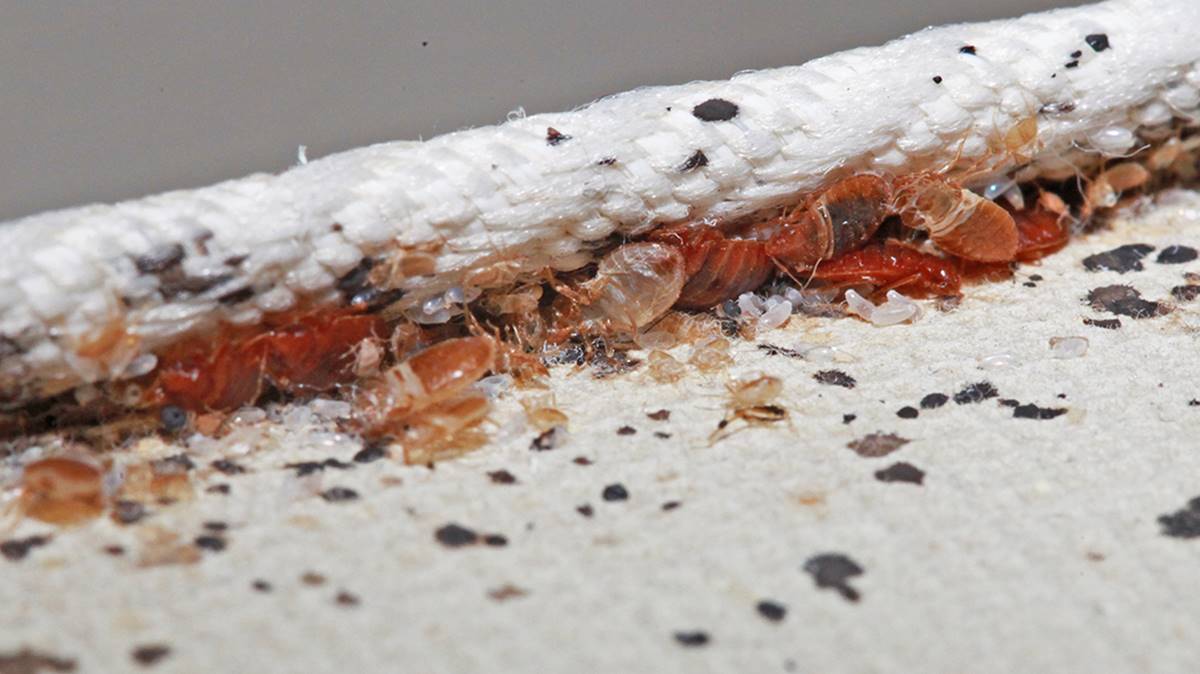
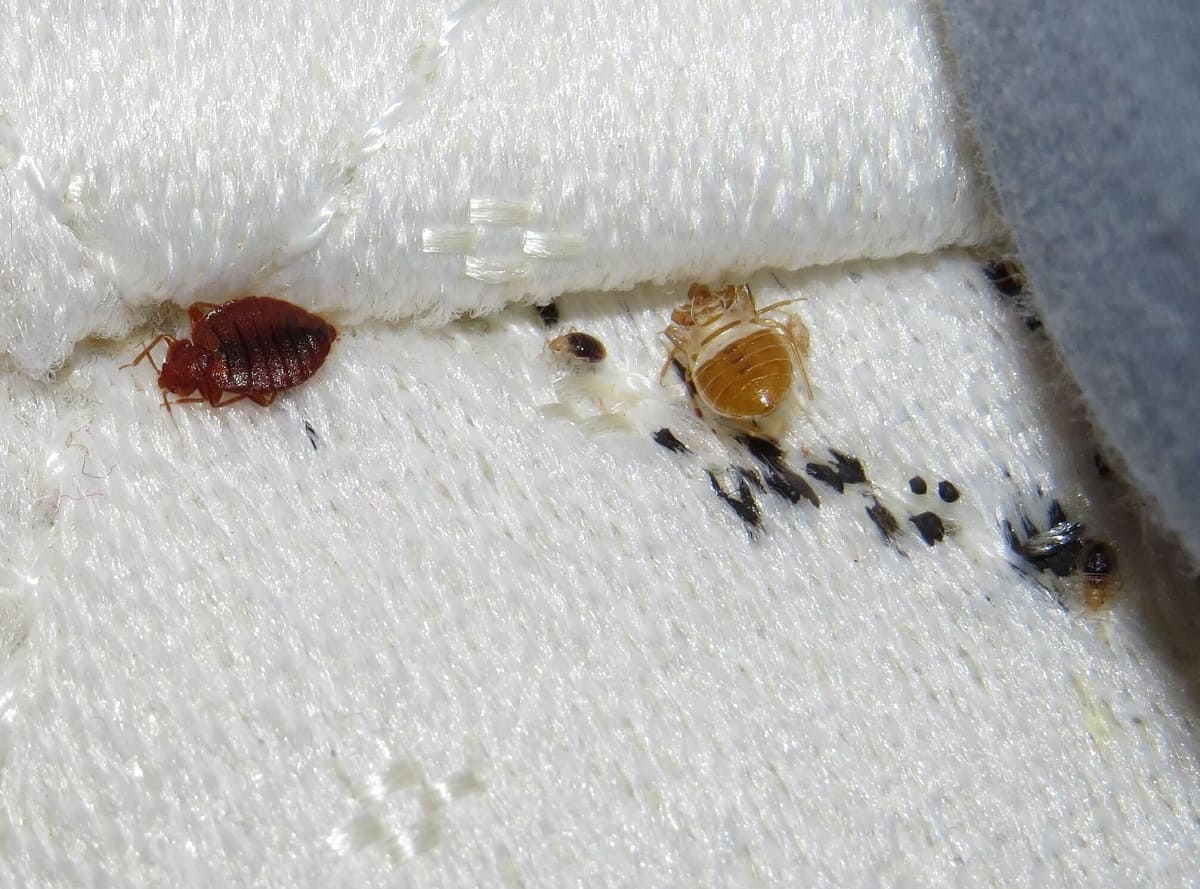
Female bed bugs can lay an astonishing number of eggs during their lifetime. On average, a female bed bug can lay between one to seven eggs per day, with a total of around 200 to 500 eggs in her lifetime. The eggs are tiny, approximately 1mm in size, and are usually laid in secluded spaces such as cracks, crevices, or even inside the seams of mattresses and other furniture.
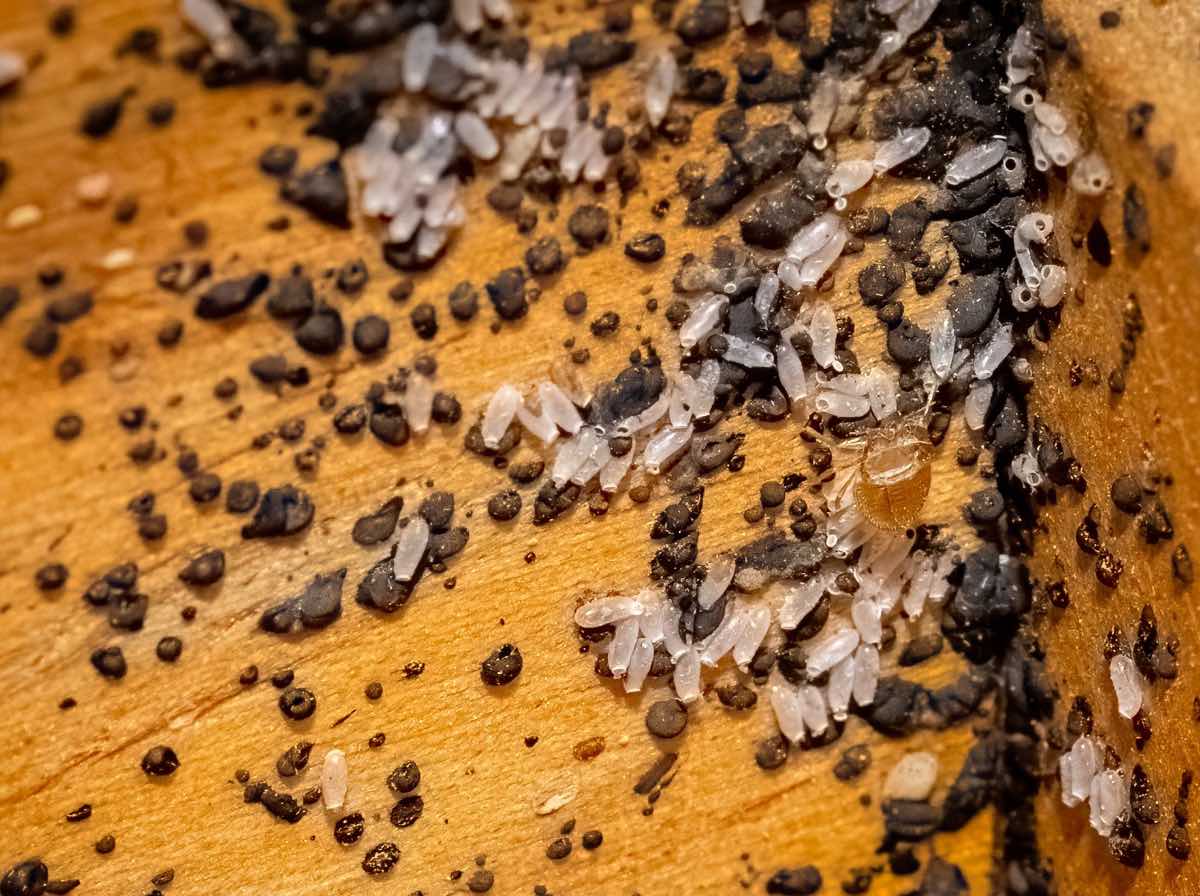
Bed bug eggs are typically white or translucent, making them difficult to detect with the naked eye. They hatch after about 6 to 10 days, depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. Once hatched, the nymphs begin seeking a blood meal, as they require blood to molt and develop into the next stage.
The nymphs go through a series of molts, shedding their exoskeletons as they grow. Each molt is known as an “instar.” Bed bugs go through five nymphal instars before reaching adulthood. Within a month, under optimal conditions, they can develop from an egg to an adult bed bug.
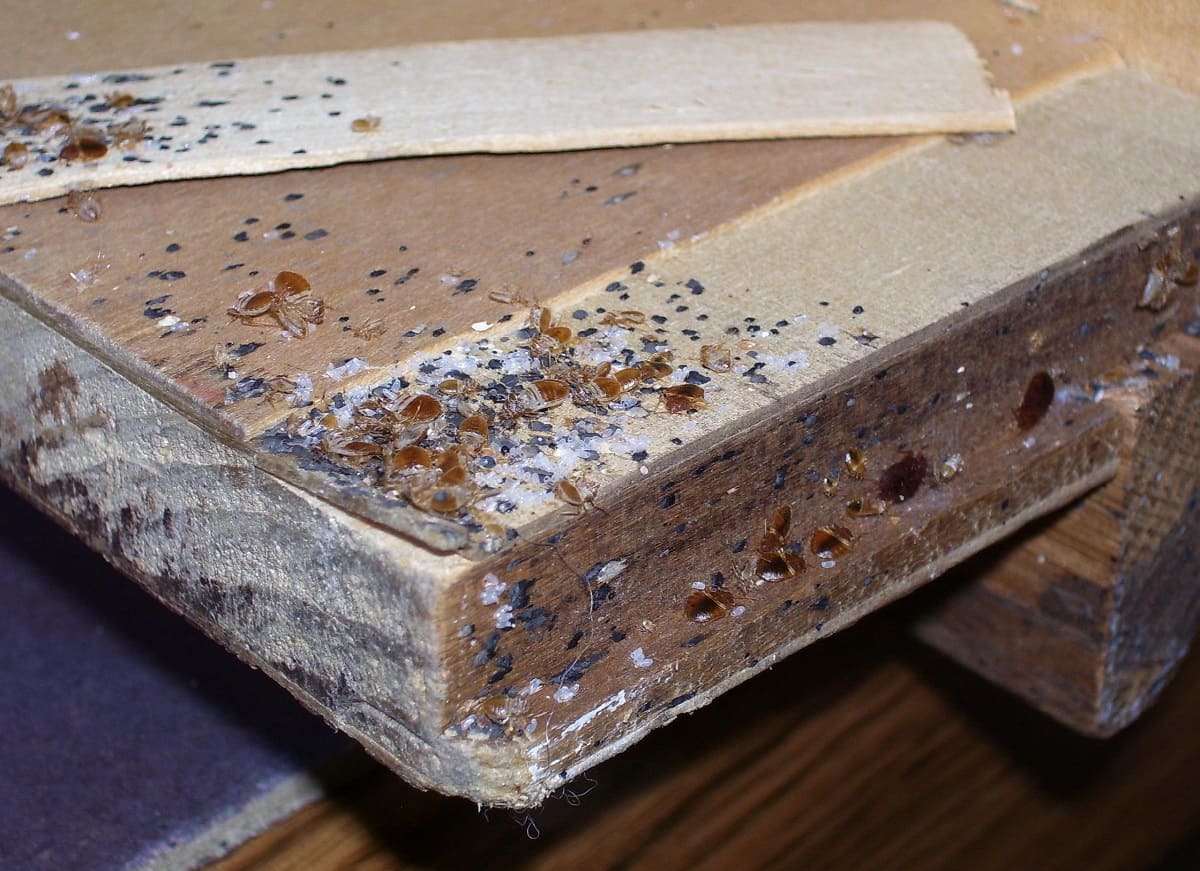
It’s important to note that bed bugs reproduce rapidly and can establish large infestations in a short period. A single female bed bug, under favorable conditions, can lead to an infestation of hundreds or thousands of bed bugs within several months.
Now that we understand how bed bugs reproduce, we can delve into the factors that influence their reproductive behavior and the speed at which they multiply. Join us in the next section as we explore these crucial aspects of bed bug reproduction.
The Reproductive Cycle of Bed Bugs
The reproductive cycle of bed bugs consists of several stages, each playing a vital role in their population growth. Understanding these stages is key to implementing effective control measures. Let’s explore the reproductive cycle of bed bugs in more detail.
Stage 1: Mating
The reproductive process begins with mating. Male bed bugs find females by following their scent trails. Once a suitable female is located, the male bed bug uses his copulatory organ to penetrate the female’s abdomen and transfer sperm. This process, known as traumatic insemination, is unique to bed bugs.
Stage 2: Egg Laying
After mating, the female bed bug begins her egg-laying phase. Each female is capable of laying numerous eggs throughout her lifetime. The eggs are typically laid in hidden and protected locations, such as cracks, crevices, and the seams of bedding. The female bed bug is careful in selecting these spots to protect the eggs from threats, ensuring their survival.
Stage 3: Egg Development
Bed bug eggs are oval-shaped and are about the size of a pinhead. They are white or translucent and can be challenging to spot without magnification. Under favorable conditions, the eggs hatch within 6 to 10 days. However, the hatching time can vary depending on factors like temperature and humidity. Proper identification and timely detection of these eggs are crucial for effective control measures.
Stage 4: Nymph Stage
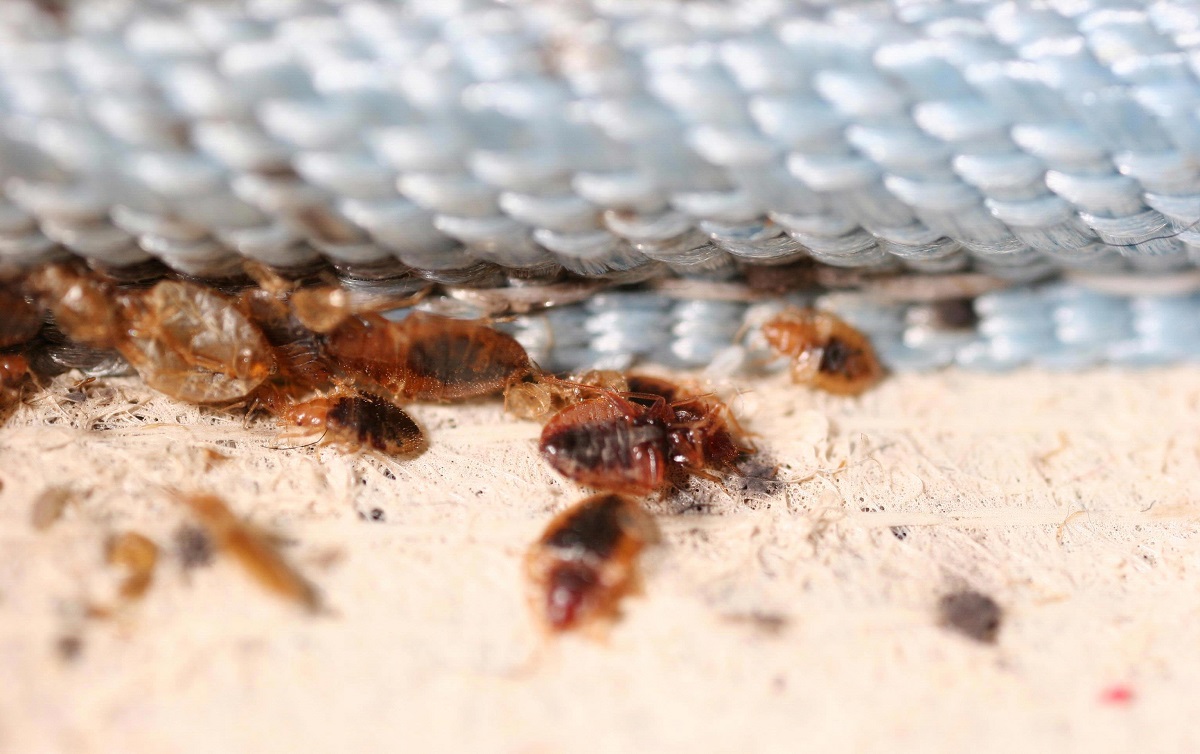
When the eggs hatch, they release nymphs. Nymphs are small, wingless bed bugs that resemble adult bed bugs but are smaller in size. Nymphs require a blood meal to progress through their five instar stages and grow into adult bed bugs. The time it takes for nymphs to molt and progress to the next instar depends on environmental conditions and their access to blood meals.
Stage 5: Adult Stage
Once the nymphs have completed their five instar stages, they molt into adult bed bugs. Adult bed bugs are approximately the size of an apple seed and have a reddish-brown color. They possess six legs, antennae, and are capable of reproducing. Adult bed bugs require regular blood meals to survive and reproduce.
Stage 6: Reproduction
Adult bed bugs are sexually mature and capable of reproduction. Female bed bugs can mate multiple times in their lifetime and can store sperm in a specialized organ called the spermatheca. This allows them to lay fertilized eggs continually, even without further mating. The reproductive cycle repeats as the newly hatched bed bugs mature into adults and start reproducing.
Understanding the different stages of the bed bug reproductive cycle is essential for effective pest control strategies. By targeting vulnerable stages and disrupting their mating and egg-laying process, it is possible to control and prevent infestations.
Now that we have explored the reproductive cycle of bed bugs, let’s delve into the factors that influence their reproduction, and ultimately, the speed at which they multiply.
Factors Influencing Bed Bug Reproduction
Several factors influence the reproduction of bed bugs, determining the speed at which they multiply and infest our living spaces. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective control and prevention methods. Let’s take a closer look at the key factors that influence bed bug reproduction.
1. Temperature:
Temperature plays a significant role in the reproductive ability of bed bugs. They thrive in environments with temperatures between 70 to 80°F (21 to 27°C). These conditions allow for optimal egg development, nymph growth, and adult bed bug activity. Higher temperatures accelerate their life cycle, resulting in faster reproduction and population growth.
2. Availability of Blood Meals:
Bed bugs require a blood meal to grow, develop, and reproduce. The availability of blood meals is a crucial factor in their reproduction rate. A steady source of blood, such as human hosts, pets, or other warm-blooded animals, enables bed bugs to feed regularly and reach sexual maturity faster. Adequate blood meals contribute to more frequent egg-laying and higher survival rates of nymphs.
3. Mating Opportunities:
The availability of mating opportunities impacts the rate of bed bug reproduction. Since bed bugs practice traumatic insemination, where males directly inseminate females through their abdominal wall, the presence of male bed bugs is essential for successful reproduction. A larger population of male bed bugs increases the chances of females finding mates and laying fertilized eggs. Conversely, a low number of males can result in reduced reproduction rates.
4. Hiding and Breeding Sites:
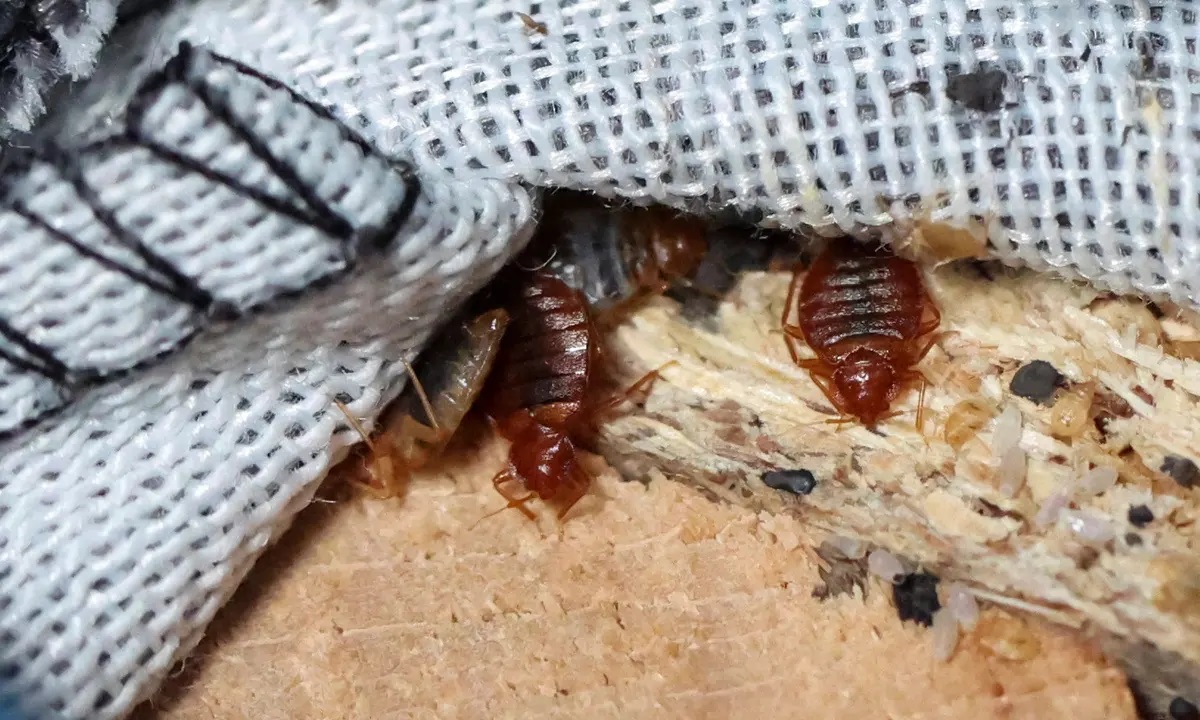
Bed bugs require suitable hiding and breeding sites to lay their eggs and ensure their survival. They prefer areas close to their hosts, which can include cracks, crevices, mattress seams, and furniture joints. The availability of suitable hiding and breeding sites within their range greatly influences their reproduction rate. Cluttered environments provide more hiding places, making it easier for bed bugs to breed and reproduce undisturbed.
5. Access to Hosts:
The ability of bed bugs to access their hosts plays a significant role in their reproductive success. Bed bugs rely on their hosts’ presence to obtain blood meals, essential for their growth and reproduction. If there are physical barriers preventing bed bugs from reaching their hosts, such as bed covers or encasements, their reproductive rate may be hindered. However, if bed bugs can easily reach their hosts, they can more readily obtain blood meals and reproduce at a faster rate.
Understanding these factors can help guide effective strategies for controlling and preventing bed bug infestations. By manipulating or eliminating these factors, it is possible to slow down their reproduction rate and limit their population growth.
Next, we will discuss the speed at which bed bugs reproduce and the implications it has for homeowners and pest control professionals.
Bed bugs can reproduce quickly, with a female laying 1-5 eggs per day. To prevent infestations, regularly inspect and clean bedding, furniture, and other potential hiding spots.
The Speed of Bed Bug Reproduction
Bed bugs are notorious for their rapid reproductive abilities, making them difficult to control once an infestation takes hold. Understanding the speed at which bed bugs reproduce is crucial for effective pest management. So, let’s explore just how fast these pests can multiply.
Under optimal conditions, bed bugs can reproduce at an alarming rate. A single female bed bug, given access to regular blood meals, can lay anywhere from one to seven eggs per day. On average, a female bed bug is capable of producing around 200 to 500 eggs in her lifetime.
The incubation period for the eggs is approximately 6 to 10 days, depending on environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. Once the eggs hatch, the nymphs emerge and begin searching for a blood meal to progress through their five nymphal instars.
Each nymphal stage lasts about a week, during which the nymphs molt and shed their exoskeleton to grow larger. After the fifth instar, the nymphs molt into adult bed bugs. From egg to adult, the entire life cycle can be completed in as little as one month.
This rapid reproductive speed is one reason why bed bug infestations can quickly escalate. A small infestation can grow into a large one within a few months if left untreated. The ability of a single female bed bug to lay numerous eggs throughout her lifetime, combined with the speedy development of nymphs, allows infestations to spread rapidly throughout a home or other living spaces.
Furthermore, the ability of female bed bugs to store sperm for extended periods contributes to the rapid reproduction cycle. Even without access to males, a female can continue to lay fertilized eggs, sustaining the population and making it challenging to eliminate the infestation completely.
It’s important to note that the speed of bed bug reproduction can vary based on environmental conditions and available resources. Factors such as temperature, access to blood meals, and the presence of suitable harborage sites all impact the reproductive rate. In warmer conditions with ample food sources, bed bugs can reproduce more rapidly and infestations can escalate at a quicker pace.
This accelerated rate of reproduction highlights the importance of addressing bed bug infestations as soon as they are detected. Early intervention can prevent the infestation from spreading, making it easier to eliminate the population and minimize the potential for extensive damage and discomfort.
In the next section, we will explore effective strategies for controlling and preventing bed bug reproduction to help you regain control of your living space.
Read more: How Do I Get Bed Bugs
How to Control Bed Bug Reproduction
Controlling bed bug reproduction is crucial to managing and eliminating infestations. By implementing effective strategies, you can disrupt their reproductive cycle and prevent their numbers from rapidly multiplying. Let’s explore some key methods to control bed bug reproduction.
1. Identification and Early Detection:
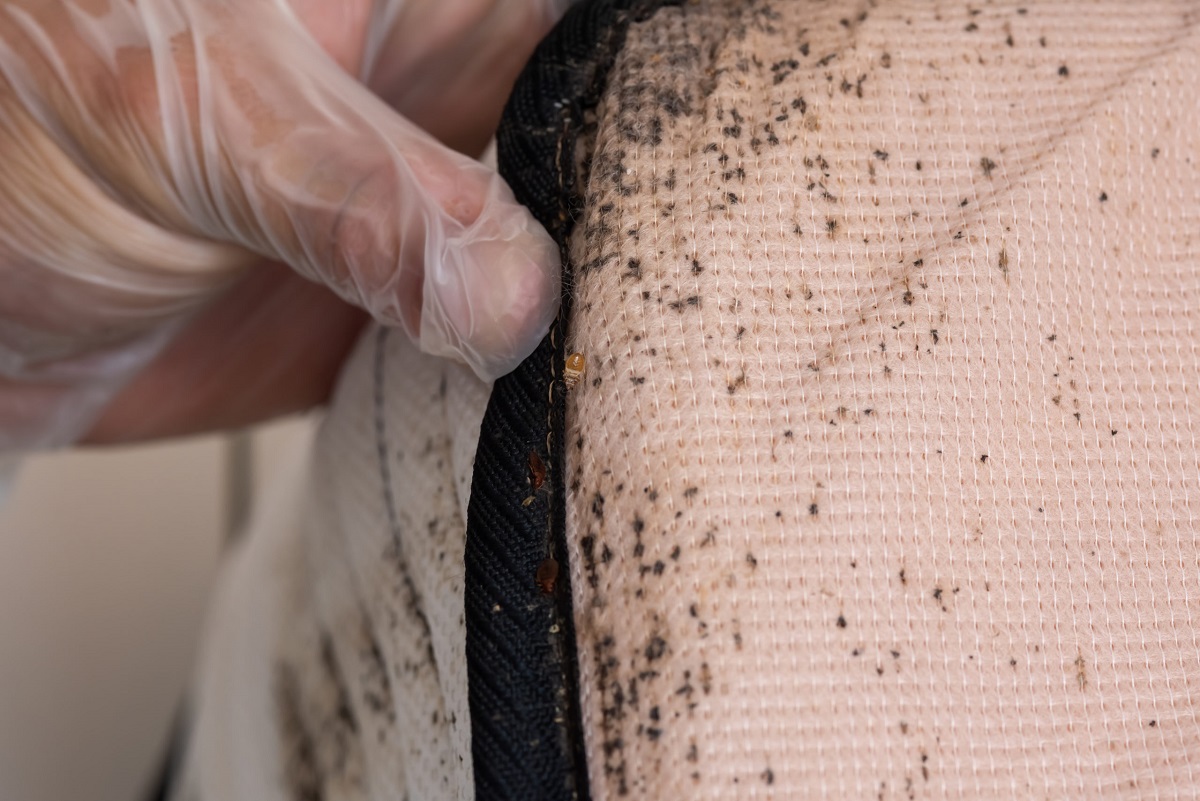
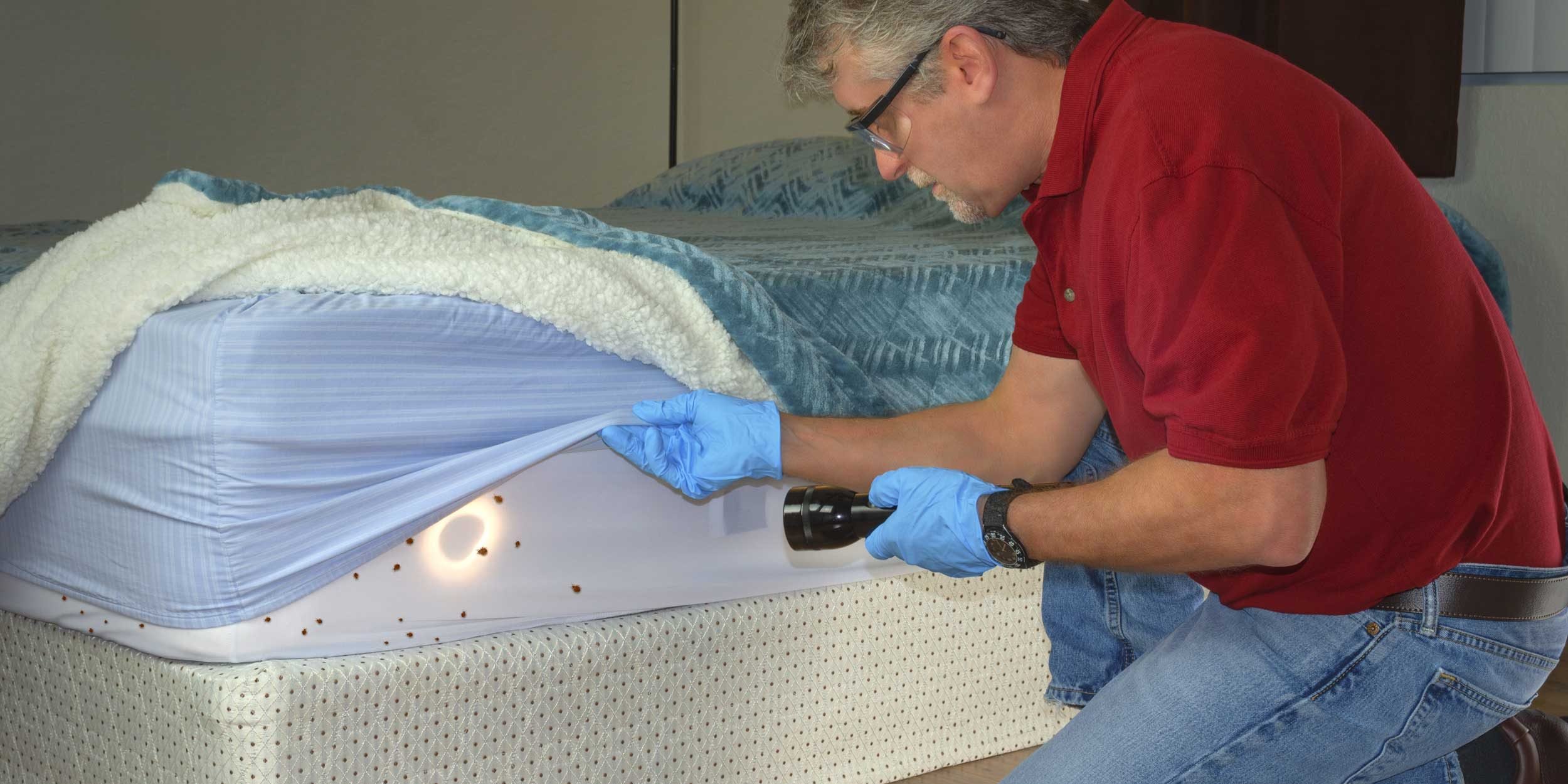
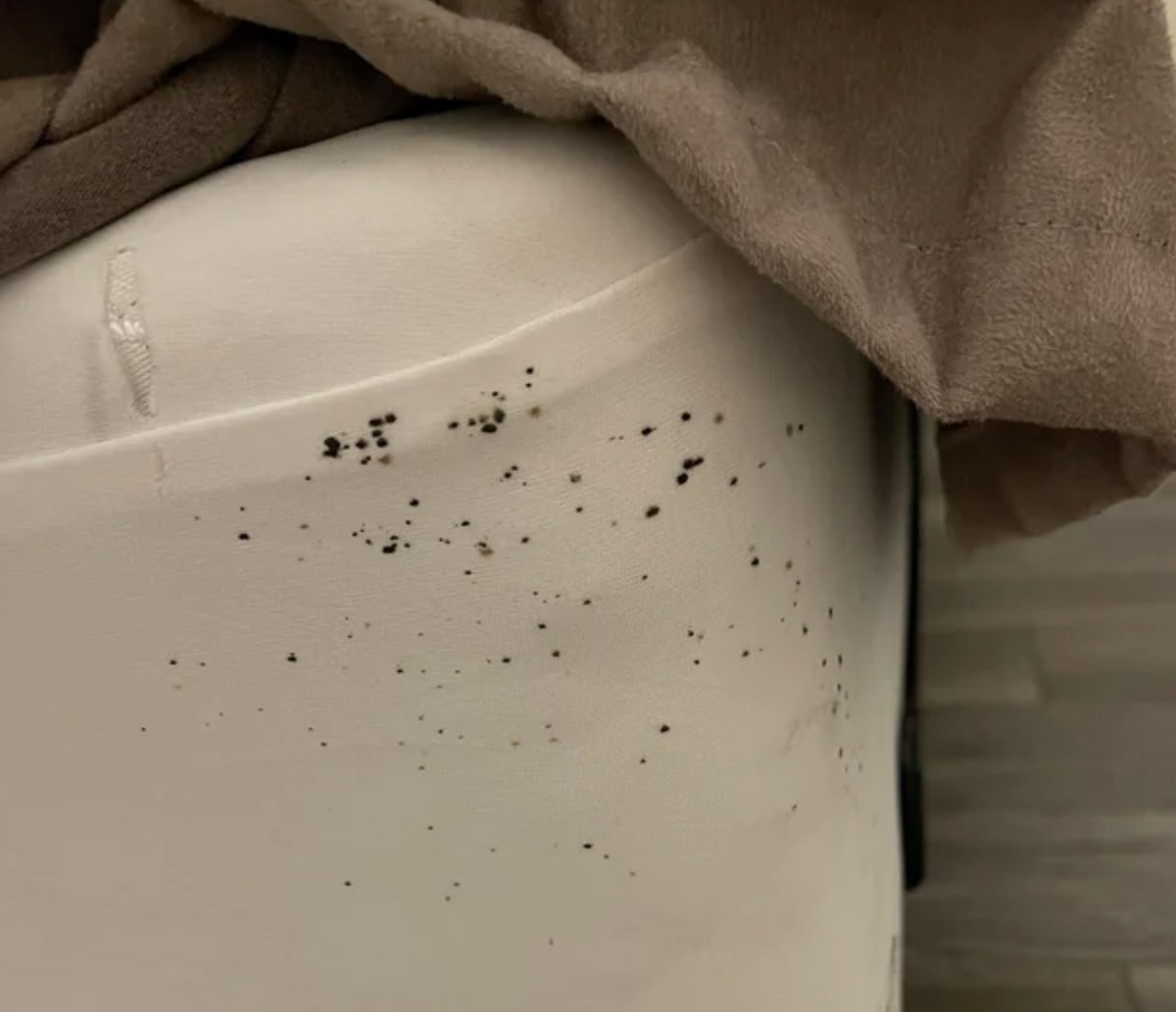
Early detection is essential for effective bed bug control. Regularly inspect your living spaces, including beds, furniture, and cracks or crevices, for signs of bed bugs. Look for live bugs, shed skins, dark spots of excrement, or small bloodstains on bedding. Prompt identification and early intervention can prevent the infestation from spreading and limit their ability to reproduce.
2. Thorough Cleaning and Vacuuming:
Vacuuming plays a vital role in reducing the number of bed bugs, especially nymphs and eggs. Vacuum all areas suspected of infestation, paying particular attention to crevices, mattress seams, and furniture joints. Dispose of the vacuum bag or empty the canister immediately after use to prevent reinfestation. Regular cleaning, including washing bedding and infested clothing in hot water, can help control bed bug populations and disrupt their ability to reproduce.
3. Encasing Mattresses and Furniture:
Encasing mattresses, box springs, and furniture can be an effective measure to prevent bed bugs from infesting these items and reproducing. Use bed bug-proof encasements that completely cover mattress and box spring surfaces, reducing their access to hiding spots. This can help limit infestation areas and provide easier detection of any remaining bugs.
4. Seal Cracks and Crevices:
Sealing cracks and crevices in walls, furniture, and other hiding spots can reduce access points and restrict bed bug movement. Use caulk or sealant to seal gaps and cracks, preventing bed bugs from harboring in these areas and laying eggs. Eliminating their preferred hiding spots and breeding sites can inhibit their ability to reproduce effectively.
5. Professional Pest Control Treatment:
If the infestation persists or continues to spread, it is advisable to seek professional help for effective pest control treatment. Professional exterminators have the expertise, experience, and access to specialized tools and products to eliminate bed bugs effectively. They can administer targeted treatments, including chemical treatments and heat treatments, to control infestations and disrupt the reproductive cycle of bed bugs.
6. Regular Monitoring and Follow-up:
Even after treatment, it’s important to monitor for any signs of reinfestation. Regularly inspect your living spaces and bedding for any indications of bed bugs. If necessary, continue implementing preventive measures, such as regular cleaning, vacuuming, and mattress encasements, to prevent a resurgence of the infestation.
By applying these methods consistently and proactively, you can control bed bug reproduction and significantly reduce their population. It’s important to be patient and persistent in your efforts, as complete eradication may take time, especially for larger infestations.
Now that we’ve explored strategies for controlling bed bug reproduction, let’s conclude with some final thoughts.
Conclusion
Bed bugs are relentless pests that can quickly take over our living spaces if left unchecked. Understanding their reproductive behavior and implementing effective control measures is essential for managing and preventing infestations. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can control bed bug reproduction and regain control of your home.
We began by exploring the fascinating world of bedroom furniture and the importance of selecting the right pieces for your space. A well-designed and comfortable bedroom can contribute to a good night’s sleep and overall well-being.
Next, we delved into the reproductive cycle of bed bugs, highlighting their unique mating habits and the various stages from egg to adult. Understanding these lifecycle stages helps in identifying infestations and implementing appropriate control measures.
We then explored the factors influencing bed bug reproduction, such as temperature, availability of blood meals, mating opportunities, hiding and breeding sites, and access to hosts. These factors play a significant role in the speed at which bed bugs multiply and infest our living spaces.
To control bed bug reproduction, we discussed the importance of early detection, thorough cleaning and vacuuming, encasing mattresses and furniture, sealing cracks and crevices, professional pest control treatment, and regular monitoring and follow-up. These strategies disrupt their reproductive cycle, limit infestation areas, and minimize their population.
It’s important to remember that controlling bed bug reproduction may take persistence and patience. Successful elimination requires consistent efforts, monitoring for any signs of reinfestation, and continuing preventive measures even after treatment.
By effectively controlling bed bug reproduction, you can create a safe, comfortable, and bed bug-free environment in your home. As you strive for a peaceful and pest-free space, remember the importance of regular maintenance, cleanliness, and vigilance to prevent future infestations.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into bed bug reproduction and control. Armed with this knowledge, you can take proactive steps to protect your home and ensure a peaceful and restful sleep for you and your family.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Fast Do Bed Bugs Reproduce
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.