Home>Garden Essentials>What Is Germinate


Garden Essentials
What Is Germinate
Modified: May 6, 2024
Learn what germination is in gardening and how it helps seeds grow into plants. Discover the process and importance of germinating seeds in your garden.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the wonderful world of gardening! Whether you are an experienced gardener or just starting out, understanding the process of germination is essential for success. Germination is the magical journey that seeds embark on to develop into vibrant plants. It is the very beginning of a garden’s life cycle and sets the stage for a bountiful harvest or a stunning flower display.
In this article, we will explore the definition, process, factors affecting germination, and the importance of this crucial stage in gardening. Additionally, we will provide you with real-life examples that showcase the beauty of germination in action.
So, grab your gardening gloves and get ready to dive into the fascinating world of germination!
Key Takeaways:
- Germination is the magical process where seeds come to life, sprouting into plants. Factors like water, temperature, and soil quality play a big role in this natural wonder.
- Understanding germination is crucial for gardeners. It helps in growing new plants, producing food, creating beautiful landscapes, and preserving biodiversity. It’s like witnessing nature’s own magic show in your garden!
Read more: What Is The Fastest Plant To Germinate
Definition of Germination
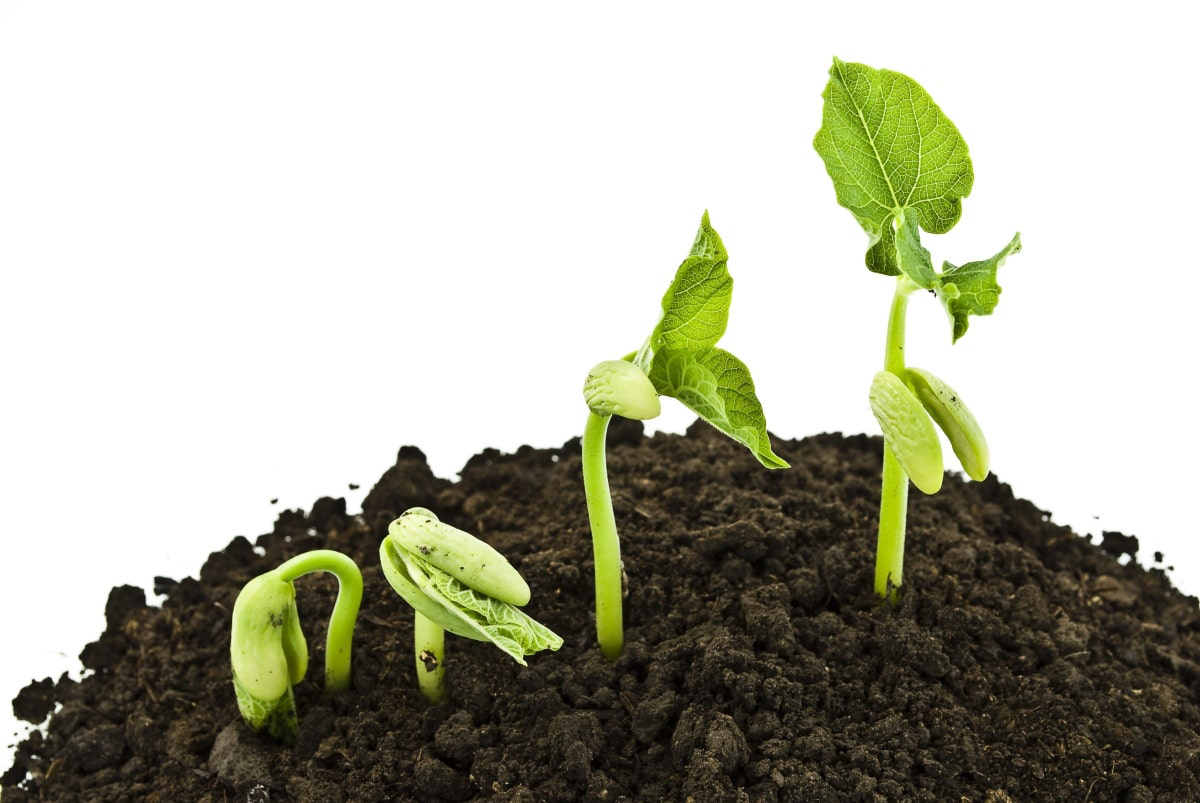
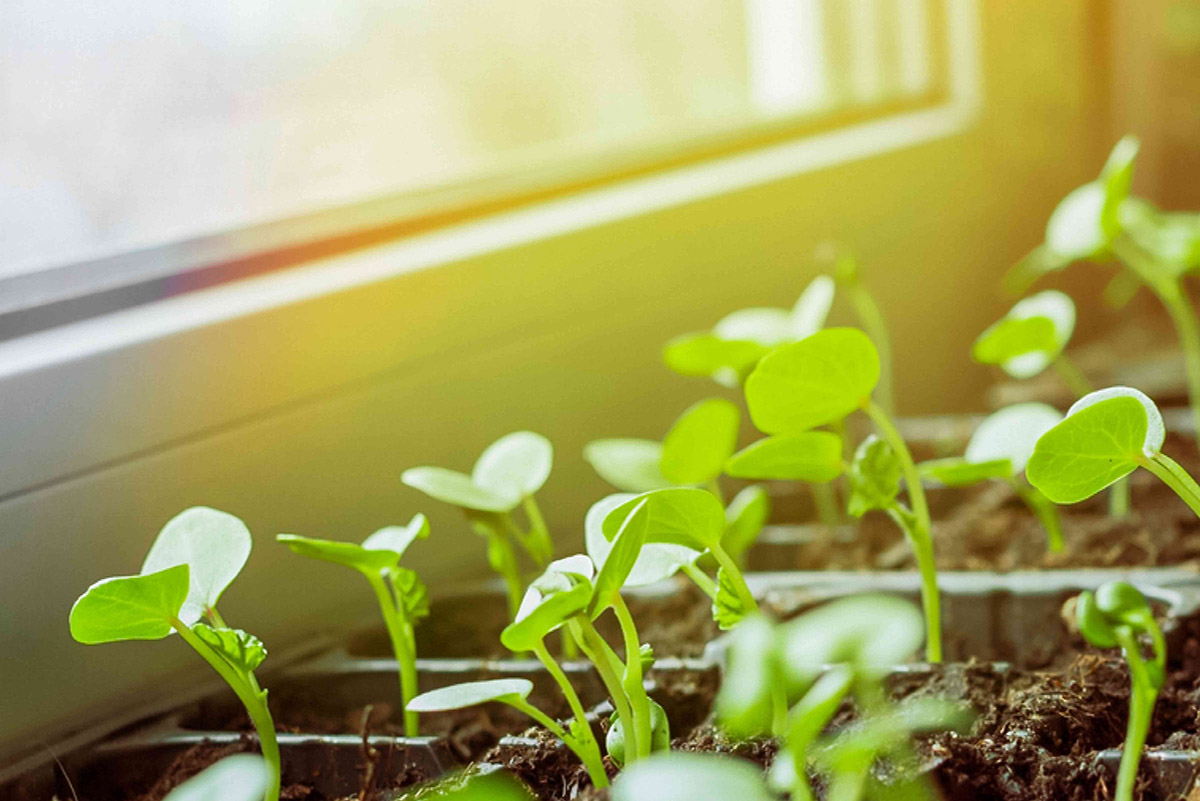
Germination refers to the process by which a seed transforms into a new plant. It is the awakening of life within a seed, as it breaks through its protective covering and sprouts roots and shoots. This marks the starting point of a plant’s growth cycle.
During germination, the seed absorbs water and begins to metabolize stored nutrients. As a result, the embryo inside the seed awakens and starts to metabolize, triggering growth and development. Over time, the seed coat cracks open, and a tiny root emerges, followed by the emergence of the shoot or stem.
Germination is a remarkable natural process that is influenced by various environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, light, and oxygen availability. Each plant species has its own unique germination requirements, making it a fascinating area of study.
Understanding the process of germination is crucial for gardeners as it allows them to provide optimal conditions for seeds to sprout and thrive. By harnessing the power of germination, gardeners can grow a variety of plants, including flowers, vegetables, and herbs, in their own backyard.
Now that we have a basic understanding of germination, let’s delve into the intricate details of how it happens.
Process of Germination
The process of germination can be divided into several key stages, each with its own significance in the plant’s development.
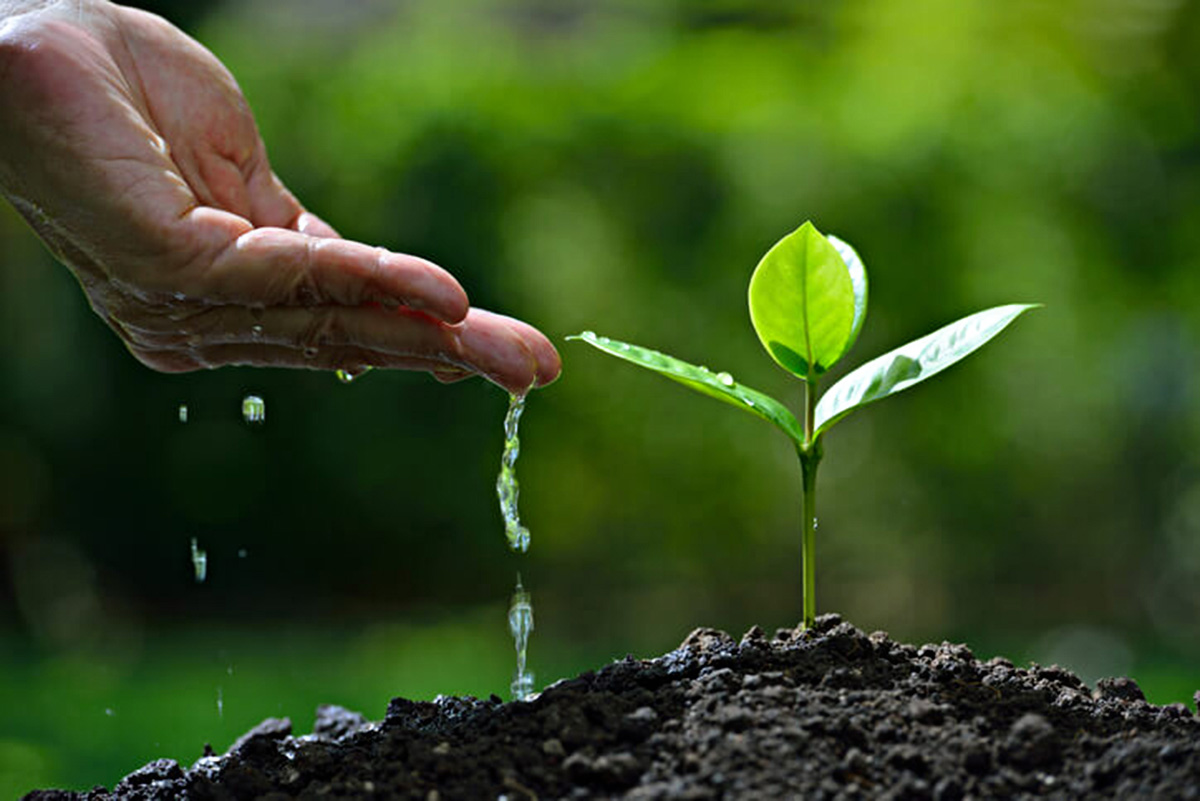
1. Imbibition: The first step in germination is imbibition, where the seed takes in water through its outer covering, the seed coat. The absorbed water softens the seed coat and activates enzymes that break down stored nutrients.
2. Activation of enzymes: As the seed imbibes water, dormant enzymes within the seed become activated. These enzymes are responsible for breaking down complex molecules, such as starches and proteins, into simpler forms that can be used for growth.
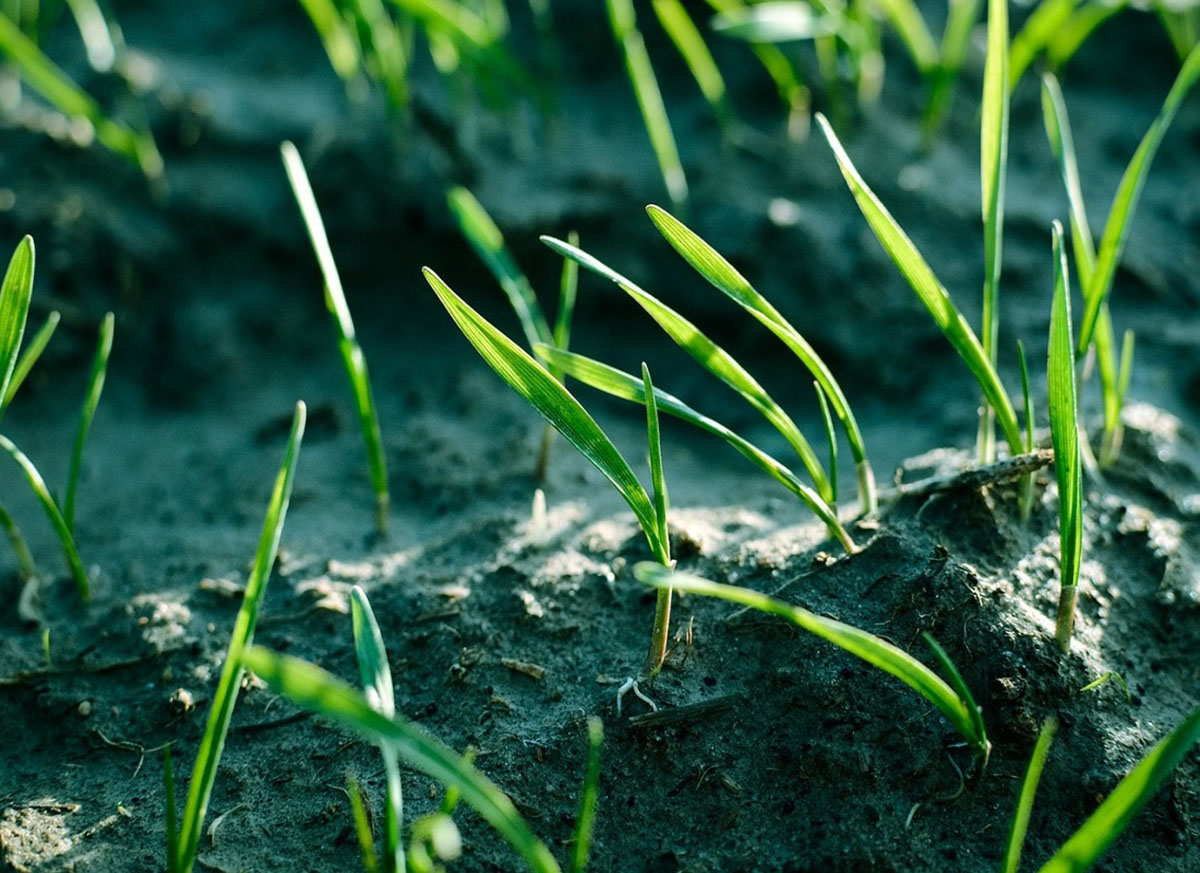
3. Embryo growth: Once the enzymes are activated, the growth of the embryo commences. The radicle, which will become the root, emerges first and anchors the plant into the soil. Next, the plumule, which will develop into the shoot, begins to elongate.
4. Development of roots and shoots: Root development is crucial for the plant to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Simultaneously, the shoot grows towards the surface, seeking sunlight for photosynthesis. The shoot eventually breaks through the soil, allowing the leaves to unfold and capture sunlight.
5. Photosynthesis: Once the shoot emerges, the plant’s ability to carry out photosynthesis is activated. Photosynthesis is the process in which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, enabling them to produce their own food.
6. Establishment of seedlings: As the plant grows, it becomes more independent of the seed’s stored nutrients. The young plant develops true leaves and begins to rely on its root system for water, minerals, and nutrients.
Throughout this process, the plant undergoes various physiological changes and transitions from being a dormant seed to a thriving seedling. It is an intricate dance of biological processes that culminate in the birth of a new plant.
Now that we have explored the process, let’s move on to understanding the factors that play a significant role in germination.
Factors Affecting Germination
Germination is influenced by several key factors that determine whether a seed successfully sprouts and grows into a healthy plant. These factors include:
1. Temperature: Seeds have specific temperature requirements for optimal germination. Some seeds require warm temperatures, while others need cool temperatures to break dormancy and trigger germination. Extreme temperatures can hinder or even inhibit germination.
2. Moisture: Adequate moisture is critical for seed germination as it helps to soften the seed coat and initiate metabolic processes. However, excessive moisture can lead to rot or fungal diseases. It is important to provide the right balance of moisture for each plant species.
3. Light: Light requirements for germination vary among different plant species. Some seeds need exposure to light to germinate, while others require darkness. Understanding these light requirements is essential for ensuring successful germination.
4. Oxygen: Like all living organisms, seeds require oxygen for respiration. Oxygen is necessary for energy production during germination. Adequate oxygen flow in the planting medium is crucial for healthy seedling development.
5. Seed Dormancy: Some seeds have built-in mechanisms that prevent them from germinating immediately after dispersal. This dormancy can be caused by factors such as hard seed coats or chemical inhibitors. Scarification or stratification techniques may be needed to break seed dormancy and promote germination.
6. Soil Quality: The quality of the soil, including its texture, nutrient content, and drainage, greatly affects germination. A well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter provides an optimal environment for seeds to sprout and grow.
7. Seed Viability: The quality and viability of the seed itself play a significant role in germination. Fresh, healthy seeds are more likely to germinate successfully compared to old or damaged seeds.
By understanding and manipulating these factors, gardeners can create the ideal conditions for successful germination of their desired plants.
Now that we have explored the factors influencing germination, let’s discover the importance of germination in gardening.
Germination is the process where a seed begins to sprout and grow into a new plant. To help seeds germinate, keep them moist and warm, and provide them with sunlight.
Importance of Germination
The process of germination is of utmost importance in gardening for several reasons:
1. Plant Propagation: Germination is the primary method of plant propagation. By understanding and facilitating germination, gardeners can grow new plants, whether they are vegetables, flowers, or trees, from seeds. This allows for the expansion and reproduction of plant species.
2. Crop Production: In agriculture, germination is the first step towards crop production. It is essential for growing a wide variety of food crops, such as grains, fruits, and vegetables. Farmers rely on successful germination to yield abundant harvests and meet food demands.
3. Biodiversity: Germination plays a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity. It allows plants to reproduce and spread their genetic diversity, which is vital for ecological balance and sustainability. By promoting germination, gardeners contribute to preserving and enhancing biodiversity in their local ecosystems.
4. Beautification of Landscapes: Germination is essential for creating beautiful and vibrant landscapes. By sowing seeds and facilitating germination, gardeners can design and develop aesthetically pleasing gardens, parks, and green spaces. The process of germination brings life and color to our surroundings.
5. Environmental Rehabilitation: Germination is often used in environmental rehabilitation projects, such as reforestation and habitat restoration. By encouraging the germination of native plant species, we can help restore ecosystems, combat soil erosion, and enhance wildlife habitats.
6. Educational Value: Germination provides a valuable educational experience for both children and adults. By observing the germination process, we gain insights into the science of plant growth and learn about the interconnectedness of living organisms and their environment.
7. Personal Satisfaction: Witnessing the successful germination of seeds and nurturing them into healthy plants can bring great joy and satisfaction to gardeners. It is a rewarding experience to see the fruits of one’s labor and to be connected to the natural cycle of life.
Understanding the importance of germination empowers gardeners to create optimal conditions for seed growth and maximize the potential of their gardens.
Now, let’s explore some real-life examples of germination in action.
Read more: What Grass Germinates The Fastest
Examples of Germination
Germination is a fascinating process that can be observed in various plant species. Here are a few notable examples of germination:
1. Sunflower (Helianthus annuus): Sunflower seeds are familiar to many, and their germination process is quite captivating. The large, oval-shaped seeds, when planted in well-drained soil and provided with adequate moisture and sunlight, germinate within 7 to 10 days. The growth begins with the emergence of a small root, followed by the growth of tall, sturdy stems and the iconic yellow flower heads.
2. Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris): Beans are versatile and popular garden plants. The germination process for beans typically involves soaking the seeds overnight to speed up water absorption. Once planted, the seeds sprout within a week, with the appearance of a root and then the development of the cotyledons and true leaves. In a few weeks, healthy bean plants are ready for transplanting or continued growth in the garden.
3. Maple Trees (Acer spp.): The germination of maple seeds, often referred to as “helicopters,” is a fascinating sight. These winged seeds are dispersed by the wind and often land in fertile soil. When conditions are favorable, the seeds germinate, and a tiny root emerges, followed by the appearance of two small leaves. Over time, the tree grows taller, forming the characteristic crown shape and providing shade and beauty.
4. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum): Tomato seeds are commonly started indoors before being transplanted into the garden. When placed in a warm, moist environment, the seeds germinate within a week. The initial growth includes the development of a root and a shoot. As the seedlings mature, true leaves emerge, and they are ready to be transplanted into larger containers or directly into the garden for further growth and fruit production.
5. Morning Glory (Ipomoea spp.): Morning glory seeds are known for their hard seed coats that require scarification or nicking to aid in the germination process. Once adequately prepared, the seeds are planted in well-drained soil with consistent moisture. The process begins with the appearance of a small root, followed by the emergence of a vine with heart-shaped leaves. Morning glory flowers are a breathtaking sight, opening in the morning and adding a vibrant touch to any garden.
These are just a few examples of the fascinating germination process that occurs in different plant species. Each plant’s germination journey is unique, and as gardeners, we have the privilege of witnessing and nurturing these beautiful transformations.
As we wrap up our exploration of germination, it is clear that this process is not only crucial for plant growth and propagation but also holds immense beauty and wonder. By understanding the factors influencing germination and providing optimal conditions, we can cultivate thriving gardens and connect deeply with the intricate cycles of life.
Remember, as you embark on your gardening journey, embrace the magic of germination and let it inspire and guide you to create flourishing and vibrant gardens.
Happy gardening!
Conclusion
Germination is the miraculous process through which seeds come to life, sprouting into plants that beautify our landscapes, provide food, and contribute to the biodiversity of our planet. Understanding the different stages of germination, the factors that influence it, and its importance in gardening is essential for successful cultivation.
From the imbibition of water to the activation of enzymes, the growth of roots and shoots, and the establishment of seedlings, germination is a complex and captivating series of events. Factors such as temperature, moisture, light, oxygen, seed dormancy, soil quality, and seed viability all play a role in determining the germination success rate.
The importance of germination cannot be overstated. It serves as the foundation for plant propagation, crop production, landscape beautification, environmental rehabilitation, and the preservation of biodiversity. Germination also offers educational value and brings personal satisfaction to gardeners.
Real-life examples of germination, such as sunflowers, beans, maple trees, tomatoes, and morning glories, demonstrate the diversity and beauty of this process in action.
As we conclude our exploration of germination, let us be inspired by the awe-inspiring journey of seeds and the power they hold. Let us embrace the role of gardeners and create optimal conditions for germination to occur, nurturing life and contributing to the natural cycle of birth and growth.
So, put on your gardening gloves, prepare your soil, and sow those seeds with intention and care. Watch in amazement as the magic of germination unfolds before your eyes, filling your garden with the wonders of life and transforming your space into a sanctuary of nature.
Happy germination and happy gardening!
Ready to see how quickly your seeds can spring to life? Check out our guide on seed germination. It's packed with helpful tips for gardeners of all skill levels. Meanwhile, for those considering a new look for their garden boundaries, our article on garden fence ideas offers plenty of inspiration. These stylish yet practical solutions are perfect for elevating any garden space.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Germinate
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is Germinate”