Home>Garden Essentials>What Is Infill Drilling In Mining


Garden Essentials
What Is Infill Drilling In Mining
Modified: March 7, 2024
Discover what infill drilling is in the field of mining and how it relates to your garden. Learn about its purpose, process, and benefits.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
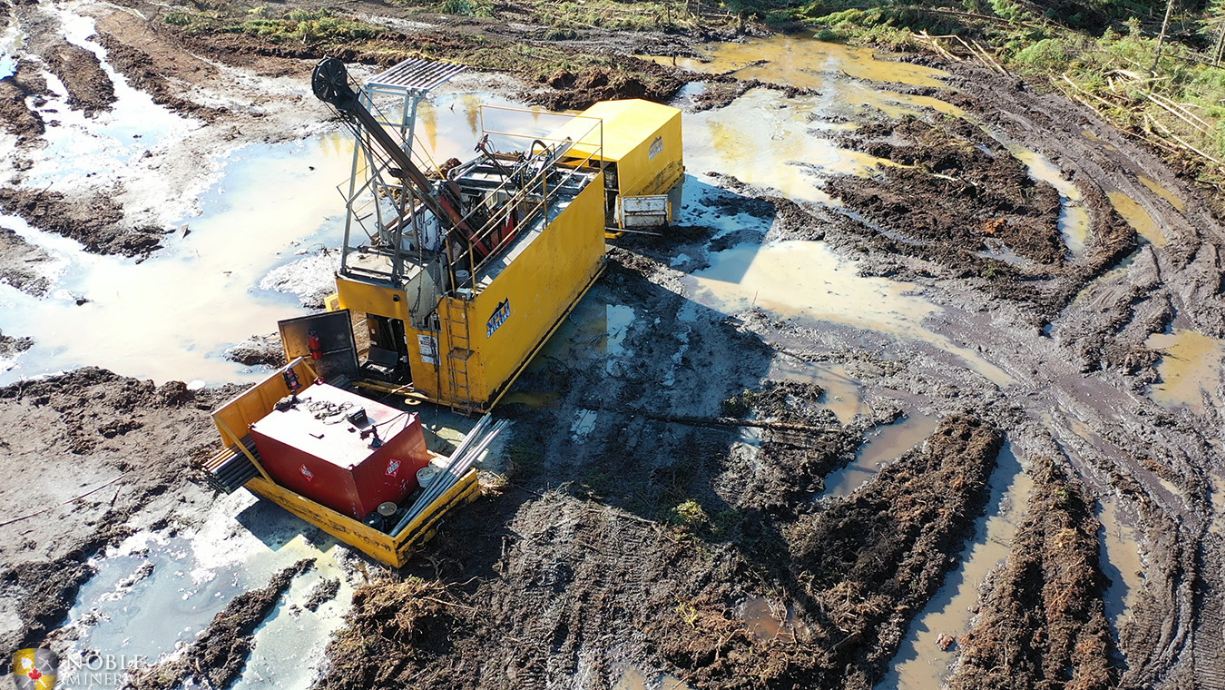
Welcome to the exciting world of infill drilling in the mining industry! Infill drilling plays a crucial role in the exploration and extraction of minerals from the earth. This technique has revolutionized the way mining operations are conducted, enabling more efficient and strategic resource extraction.
Infill drilling is a process that involves drilling additional boreholes within an existing mining area. These boreholes are strategically placed to provide a more detailed and accurate understanding of the underground mineral deposits. Infill drilling helps mining companies make informed decisions about their operations, optimize resource extraction, and maximize profitability.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the definition, purpose, benefits, methods, factors influencing infill drilling, and the challenges associated with its implementation. So, let’s dive deeper into the fascinating world of infill drilling.
Key Takeaways:
- Infill drilling helps miners gather detailed info about minerals underground, making mining more efficient and profitable. It’s like using a magnifying glass to find hidden treasures in the earth!
- Different drilling methods, like diamond and percussion drilling, are used to uncover valuable minerals. It’s like solving a puzzle to figure out where the best minerals are hiding!
Definition of Infill Drilling
Infill drilling, also known as infill sampling or infilling, is a technique used in the mining industry to gather detailed information about the distribution and quality of mineral deposits within a mining area. It involves drilling additional boreholes or drill holes in areas that have already been partially explored or mined.
The primary objective of infill drilling is to increase the geological and geotechnical knowledge of a mining site, particularly in areas where data may be limited or inconsistent. By obtaining more precise information through infill drilling, mining companies can make accurate resource estimates, plan efficient mine layouts, and optimize production.
Infill drilling is typically carried out using various drilling methods, including diamond drilling, reverse circulation drilling, or percussion drilling. The choice of drilling method depends on factors such as the depth, target mineral, geological conditions, and the size of the mining operation.
During infill drilling, core samples or cuttings are collected from the drill holes at regular intervals. These samples are then analyzed to determine the mineral content, grade, and quality of the deposit. This data is crucial for geological modeling, resource estimation, mine planning, and decision-making.
It is important to note that infill drilling is performed after an initial exploration program has been conducted. This program typically includes methods such as mapping, sampling, geophysical surveys, and initial drilling to identify potential ore deposits. Infill drilling builds upon this preliminary data to provide a more detailed understanding of the subsurface geology and the distribution of valuable minerals.
Overall, infill drilling serves as a vital tool in the mining industry, contributing to better resource management, increased operational efficiency, and improved financial outcomes.
Purpose of Infill Drilling
The purpose of infill drilling in mining is to obtain a more accurate and detailed understanding of the subsurface geology and mineral deposits within a mining area. It serves as a crucial step in the resource evaluation and planning process, offering several key benefits to mining companies. Let’s explore the main purposes of infill drilling:
- Improved Resource Estimation: Infill drilling helps mining companies refine their resource estimates by providing additional data points within a mining block. This enables a more precise calculation of the mineral content, grade, and tonnage of the deposit. With accurate resource estimation, mining companies can make informed decisions regarding the feasibility and economic viability of their operations.
- Enhanced Geological Understanding: By drilling additional boreholes in strategic locations, infill drilling helps geologists and mining engineers gain a comprehensive understanding of the geological features and structures present in the mining area. This information is essential for geological modeling, identifying potential ore zones, and designing efficient mine layouts.
- Optimized Mine Planning and Design: Infill drilling assists in developing detailed mine plans and layouts. By gathering data on the distribution and quality of mineral deposits, mining companies can better plan the extraction sequence, determine the optimal mining methods, and design appropriate infrastructure for efficient mining operations. This leads to improved productivity and cost-effectiveness.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Infill drilling plays a vital role in optimizing resource extraction by identifying areas of higher-grade mineralization. This enables mining companies to prioritize mining activities in these regions, leading to higher ore recovery rates and reduced waste. By maximizing the utilization of available resources, infill drilling helps improve operational efficiency and profitability.
- Minimized Investment Risks: Infill drilling helps mitigate the geological and economic risks associated with mining operations. By providing detailed information on the quality, quantity, and distribution of mineral deposits, mining companies can make more accurate feasibility assessments and investment decisions. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected challenges or cost overruns during the mining process.
Overall, infill drilling serves the purpose of enhancing resource estimation, geological understanding, mine planning, operational efficiency, and risk management in the mining industry. It is a critical step in the determination of a mining project’s viability and its long-term success.
Benefits of Infill Drilling
Infill drilling in the mining industry offers several key benefits that contribute to the success and profitability of mining operations. Let’s explore some of the main advantages of infill drilling:
- Improved Accuracy of Resource Estimates: Infill drilling provides additional data points within a mining block, allowing for more accurate estimation of mineral content, grade, and tonnage. This enhanced accuracy leads to improved resource management and economic decision-making, ultimately maximizing the value extracted from the deposit.
- Enhanced Understanding of Geological Features: By drilling additional boreholes at strategic locations, infill drilling provides a more comprehensive understanding of the geological features and structures present in the mining area. This knowledge is crucial for effective geological modeling, identifying potential ore zones, and optimizing mine planning and design.
- Targeted Extraction: Infill drilling helps identify areas of high-grade mineralization within a deposit. This allows mining companies to target these specific regions for extraction, optimizing the use of resources and maximizing the ore recovery rates. By focusing on higher-grade areas, operational efficiency and profitability can be significantly improved.
- Optimized Mine Planning and Design: Infill drilling data enables mining engineers to develop detailed mine plans and layouts. With a better understanding of the subsurface geology and mineral distribution, mining companies can design more efficient and cost-effective mining methods, infrastructure, and equipment utilization. This leads to improved productivity and operational efficiency.
- Reduced Risk: Infill drilling helps mitigate geological and economic risks associated with mining operations. By obtaining detailed information on the deposit’s quality, quantity, and distribution, mining companies can make more informed investment decisions and better assess the feasibility and economic viability of the project. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected challenges and costly surprises during mining operations.
- Increased Return on Investment (ROI): The combination of accurate resource estimation, targeted extraction, and optimized mine planning achieved through infill drilling leads to a higher return on investment for mining companies. By maximizing the value extracted from the deposit and minimizing costs, infill drilling contributes to improved financial outcomes and increased profitability.
Infill drilling plays a crucial role in enhancing resource management, operational efficiency, and risk mitigation in the mining industry. It enables mining companies to make data-driven decisions, optimize extraction strategies, and maximize the value of their mineral deposits, ultimately leading to long-term success.
Infill drilling in mining is used to fill in the gaps between existing drill holes to provide a more accurate understanding of the mineral deposit’s size and quality. This helps in better planning and decision-making for mining operations.
Methods Used in Infill Drilling
Infill drilling in the mining industry employs various drilling methods to gather valuable data about mineral deposits within a mining area. The choice of drilling method depends on several factors, including the depth of the deposit, target mineral, geological conditions, and the scale of the mining operation. Let’s explore some of the commonly used methods for infill drilling:
- Diamond Drilling: Diamond drilling, also known as core drilling, is one of the most widely used methods in infill drilling. It involves using a diamond-encrusted drill bit to extract cylindrical rock samples or cores from the subsurface. These cores are then analyzed to determine the mineral content, grade, and quality of the deposit.
- Reverse Circulation Drilling: Reverse circulation (RC) drilling is a popular method for infill drilling, especially in exploration and larger-scale mining operations. It utilizes a dual-walled drill pipe with an inner tube that collects rock samples while air or water is circulated downward through the outer annulus. RC drilling is known for its fast drilling speed and efficient collection of samples, making it suitable for quickly obtaining information about the subsurface geology and mineralization.
- Percussion Drilling: Percussion drilling, also known as hammer drilling, is a method that utilizes a downward force and repeated impacts to break the rock and create boreholes. This technique is often employed when drilling through hard rock formations. The drill bit is attached to a hammer-like mechanism that strikes the rock surface, causing it to break and allowing for the insertion of the drill string.
- Auger Drilling: Auger drilling is a method commonly used for shallow infill drilling. It involves using a rotating helical screw, known as an auger, to remove the soil or soft rock material. This method is suitable for obtaining samples from unconsolidated or loosely consolidated mineral deposits.
- Sonic Drilling: Sonic drilling is a relatively newer technology used in infill drilling. It utilizes high-frequency vibrations generated by a sonic drill head to break the rock and extract samples. Sonic drilling is known for its efficiency in challenging geological conditions, such as unconsolidated materials or difficult-to-drill formations.
Each of these drilling methods has its advantages and suitability depending on the specific geological and logistical considerations of the mining project. The choice of method is often determined by factors such as the depth of the deposit, desired sample quality, drilling cost, and time constraints.
Mining companies may also employ a combination of drilling methods during the infill drilling process to gain a comprehensive understanding of the subsurface geology and mineral distribution. The collected samples are then analyzed in laboratories to provide valuable data for resource estimation, mine planning, and decision-making.
By utilizing these different drilling methods, mining companies can gather precise geological information, maximize sample recovery, and optimize their infill drilling efforts, leading to improved resource management and operational outcomes.
Read more: What Is An Infill Speed
Factors Influencing Infill Drilling
Several factors influence the planning and implementation of infill drilling in the mining industry. These factors play a crucial role in determining the design, spacing, and extent of the drill holes. Let’s explore some of the key factors that influence infill drilling:
- Geological Knowledge: The existing geological knowledge of the mining area is a critical factor in determining the need for infill drilling. If the geological data is limited or inconsistent, additional drilling may be necessary to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the subsurface geology and mineral distribution.
- Deposit Size and Shape: The size and shape of the mineral deposit influence the spacing and extent of infill drilling. Larger deposits may require a denser grid of drill holes to accurately assess the mineral content and grade. Similarly, irregularly shaped deposits may require drilling in specific areas to capture the variability in mineralization.
- Target Mineral: Different minerals have different characteristics and distribution patterns within a deposit. The target mineral’s behavior and concentration influence the design and strategy of infill drilling. For example, high-grade deposits may warrant closer spacing of drill holes to capture smaller-scale variations in mineralization.
- Mining Scale and Planning: The scale of the mining operation and the mine planning process impact the spacing and extent of infill drilling. For larger-scale mining projects, a more extensive infill drilling program may be required to ensure accurate resource estimation, optimized mine planning, and efficient extraction.
- Sampling Objectives: The specific objectives of sampling, such as determining the grade, continuity, variability, or rock characteristics, influence the design of the infill drilling program. Different sampling objectives may require specific types of drill holes, spacing, or sample collection techniques.
- Logistical Considerations: Logistical constraints, including accessibility, terrain conditions, drilling equipment availability, and environmental considerations, impact the feasibility and execution of infill drilling. These factors need to be taken into account during the planning and implementation phases.
- Technology and Costs: The availability and affordability of drilling technologies and associated costs influence the scope and scale of infill drilling. Technological advancements and cost-effective drilling methods can enable more extensive infill programs, leading to better resource estimation and operational optimization.
It is important for mining companies to carefully consider these factors and conduct thorough evaluations before initiating an infill drilling program. This ensures that the drilling effort is designed to obtain the most accurate and valuable information to support decision-making and maximize the potential of the mining project.
Challenges in Implementing Infill Drilling
While infill drilling offers numerous benefits in the mining industry, there are also several challenges associated with its implementation. These challenges can vary depending on the specific geological, logistical, and operational factors of each mining project. Let’s explore some of the common challenges in implementing infill drilling:
- Geological Complexity: Mining projects often encounter complex geological conditions, such as fault zones, varying rock types, and structural complexities. These geological complexities can pose challenges in the selection of drilling locations and the interpretation of drilling data. It requires experienced geologists and mining engineers to analyze and overcome these challenges.
- Uncertain Sampling Representativeness: Infill drilling aims to provide a representative sample of the subsurface geology and mineralization. However, variations in geological heterogeneity, mineral distribution, and drilling accuracy can lead to uncertainties in the representativeness of the samples collected. Careful sampling techniques and diligent data analysis are necessary to mitigate this challenge.
- High Costs: Infill drilling can be a significant cost factor in mining operations. The expenses associated with drilling equipment, manpower, drilling consumables, and sample analysis can accumulate quickly. Balancing the need for detailed geological information with cost considerations is a challenge that mining companies need to address to optimize their infill drilling programs.
- Time Constraints: Infill drilling programs can be time-consuming, particularly in larger-scale mining operations with extensive drilling campaigns. The time needed for drilling, sample collection, analysis, and interpretation can delay project timelines and impact production schedules. Efficient planning and scheduling are crucial to minimize the impact on overall project timelines.
- Logistical Limitations: Infrastructural limitations, difficult terrains, and remote locations can pose logistical challenges during infill drilling. Limited access, transportation constraints, and the availability of drilling equipment and support services can hinder the smooth implementation of the drilling program. Overcoming these challenges requires careful logistics planning and coordination.
- Environmental Considerations: Mining operations are increasingly under scrutiny regarding environmental impacts. Infill drilling activities may need to comply with environmental regulations and permit requirements. Assessing and mitigating potential environmental risks, such as soil erosion, water pollution, or disturbance to flora and fauna, is an essential aspect of implementing infill drilling responsibly.
- Data Interpretation: Obtaining data through infill drilling is one thing, but effectively interpreting and incorporating it into the decision-making process is another challenge. The analysis and interpretation of drilling data require a skilled team of geologists and mining engineers to ensure accurate resource estimation, mine planning, and operational optimization.
Despite these challenges, mining companies recognize the value of infill drilling in enhancing resource management, operational efficiency, and risk mitigation. By proactively addressing these challenges and employing best practices, mining companies can overcome the obstacles and reap the benefits that infill drilling brings to their operations.
Conclusion
Infill drilling plays a vital role in the mining industry, offering valuable insights into the subsurface geology and mineral deposits within a mining area. Through the collection and analysis of additional boreholes or drill holes, infill drilling provides mining companies with more accurate resource estimation, improved geological understanding, optimized mine planning, and increased operational efficiency.
The definition of infill drilling encompasses the process of drilling additional holes within existing mining areas to gather detailed information about the distribution and quality of mineral deposits. This technique is used after an initial exploration program has been conducted, building upon the existing geological knowledge to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the subsurface.
The primary purpose of infill drilling is to improve resource estimation, enhance geological understanding, optimize mine planning, increase operational efficiency, and reduce investment risks. By targeting areas of high-grade mineralization and refining the understanding of deposit size, shape, and characteristics, mining companies can make informed decisions that lead to better financial outcomes and long-term success.
Infill drilling utilizes various methods such as diamond drilling, reverse circulation drilling, percussion drilling, auger drilling, and sonic drilling. The choice of method depends on factors such as deposit depth, target mineral, geological conditions, and logistical considerations. The integration of these methods helps gather precise geological information and optimize the effectiveness of the infill drilling program.
Several factors, including geological knowledge, deposit size and shape, target mineral, mining scale and planning, sampling objectives, logistical considerations, technology, and costs, influence infill drilling operations. Understanding these factors is crucial in designing a successful infill drilling campaign that provides accurate geological data and addresses project-specific needs.
While infill drilling offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges such as geological complexity, uncertainties in sampling representativeness, high costs, time constraints, logistical limitations, environmental considerations, and data interpretation. Mining companies must proactively address these challenges and implement best practices to maximize the effectiveness and efficiency of their infill drilling programs.
In conclusion, infill drilling is a powerful tool in the mining industry, providing valuable information to support decision-making, optimize resource extraction, and improve operational efficiency. By leveraging the benefits of infill drilling while overcoming the associated challenges, mining companies can unlock the full potential of their mineral deposits and pave the way for sustainable growth and success in an ever-evolving industry.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Infill Drilling In Mining
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is Infill Drilling In Mining”