Home>Garden Essentials>When Do I Put My Germinated Seeds Under Light


Garden Essentials
When Do I Put My Germinated Seeds Under Light
Modified: March 16, 2024
Wondering when to move your germinated seeds under light in your garden? Get expert advice and tips on the best time to provide light for your growing plants.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to your journey as a garden enthusiast! As you embark on your gardening endeavors, one crucial aspect to understand is the germination process of seeds. Properly germinating seeds and providing them with the right conditions for growth is essential to ensure healthy and robust seedlings.
While factors such as temperature and moisture play key roles in seed germination, another critical factor that is often overlooked is light. Light is not only vital for the growth of established plants but also for the development of germinated seeds into strong, healthy seedlings.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of light for germinated seeds and explore how to provide optimal lighting conditions to support their growth. By understanding the significance of light and learning how to properly introduce it to germinated seeds, you will be on your way to nurturing thriving plants in your garden.
Key Takeaways:
- Light is crucial for germinated seeds’ growth, providing energy for photosynthesis, promoting strong stems and healthy leaves. Choose natural sunlight or artificial grow lights, and monitor light intensity for optimal development.
- Timing and duration of light exposure are vital. Introduce light after emergence, provide 12-16 hours of light per day, and monitor seedlings’ response to ensure healthy growth.
Read more: When Do Tulips Germinate
Understanding the Germination Process
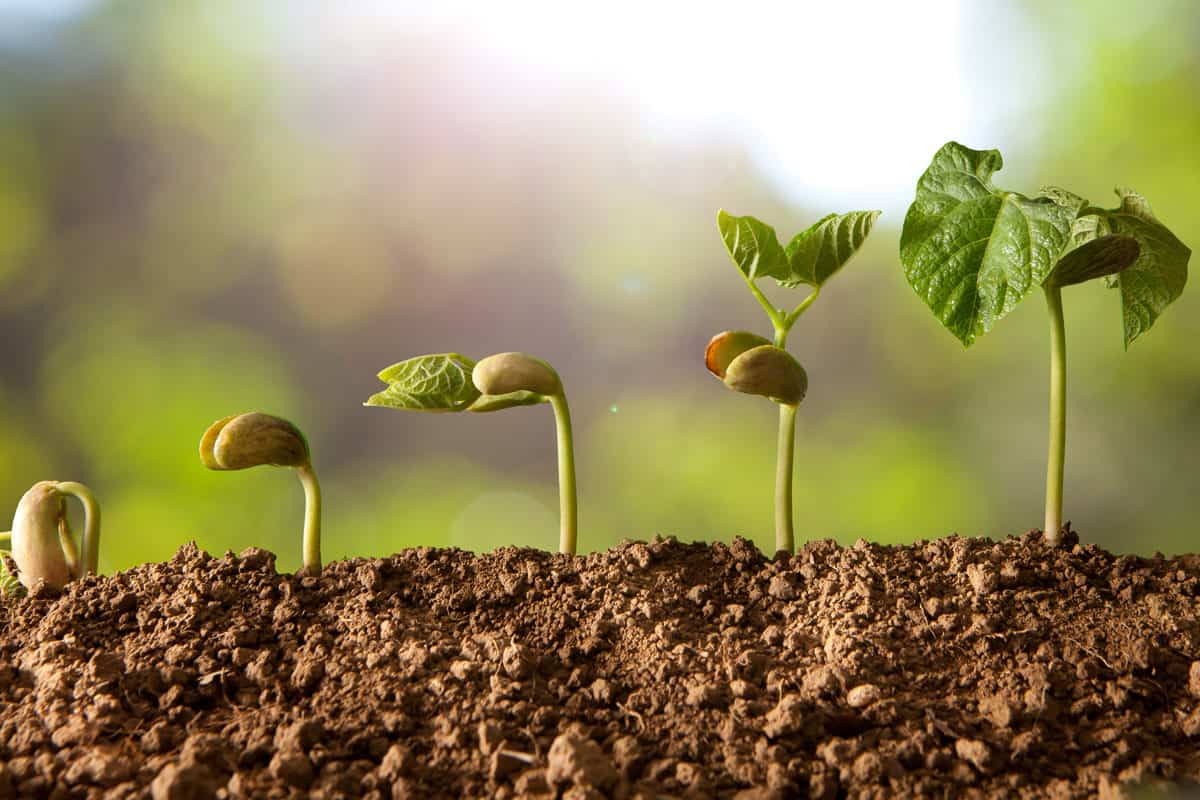
Before we dive into the role of light in the growth of germinated seeds, let’s first understand the germination process itself. Germination is the process by which a seed transforms into a young plant. It begins when a seed absorbs water, which triggers the metabolic processes within the seed, leading to the emergence of a radicle, or embryonic root.
Once the radicle emerges, it continues to grow and develops into the primary root system of the seedling. As the root system expands, the cotyledons, or seed leaves, also begin to appear, followed by the development of true leaves. The growth of these leaves enables the seedling to initiate photosynthesis and produce its own energy through the absorption of light.
During the germination process, seed embryos rely on stored energy reserves within the seed to fuel their growth until they can generate energy through photosynthesis. This is where proper light exposure becomes crucial for the successful development of germinated seeds into healthy seedlings.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the germination process, let us explore the factors that can affect the development of seedlings.
Factors Affecting Seedling Development
Several factors can influence the development of seedlings after germination. Understanding these factors and providing the appropriate conditions will facilitate optimal growth and ensure the vitality of your seedlings.
1. Temperature: The temperature plays a crucial role in seed germination and subsequent seedling development. Different types of seeds have specific temperature requirements for successful germination. Generally, seeds require a warm and stable environment to stimulate growth.
2. Moisture: Adequate moisture is essential for seed germination. It helps soften the outer seed coat, allows the embryo to swell, and activates enzymes necessary for growth. However, it is important to strike a balance and avoid overwatering, as excessively damp conditions can lead to fungal diseases and rot.
3. Air circulation: Good air circulation is important for supplying the seedlings with oxygen and preventing the buildup of excess moisture, which can encourage the growth of mold and diseases.
4. Nutrients: Seedlings require a sufficient supply of nutrients to support their growth. The soil or growing medium should be rich in essential minerals and organic matter to provide the necessary nutrients for healthy development.
5. Light: As mentioned earlier, light is a crucial factor in seedling development. It provides the energy needed for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert light into chemical energy to fuel their growth and development.
Let’s now delve into the importance of light for germinated seeds and how you can provide the best lighting conditions during their early stages of growth.
Importance of Light for Germinated Seeds
Light is one of the most critical factors influencing the development of germinated seeds. It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, ultimately fueling their growth and development. Here are a few key reasons why light is essential for the growth of germinated seeds:
1. Energy Production: Light provides the energy necessary for germinated seeds to produce the carbohydrates they need for growth. Through photosynthesis, plants convert light, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. This glucose serves as a primary source of energy for the seedlings, fueling their growth and development.
2. Chlorophyll Production: Light is crucial for the production of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for capturing light energy during photosynthesis. Chlorophyll gives plants their green color and is essential for the absorption of light. Without adequate light exposure, seedlings may exhibit weak and unhealthy growth due to insufficient chlorophyll production.
3. Stem Development: Proper light exposure helps promote strong stem development in seedlings. When seedlings receive insufficient light, they tend to grow tall and spindly in an attempt to reach for more light. This condition, known as etiolation, weakens the stems and leaves, making the seedlings more susceptible to damage.
4. Leaf Development: Light also plays a crucial role in the development of leaves in germinated seeds. The presence of light triggers the growth and expansion of leaves, enabling seedlings to increase their surface area for photosynthesis. Adequate light exposure results in healthy, green, and vibrant leaves that optimize photosynthetic efficiency.
In summary, light is of utmost importance for germinated seeds as it provides the energy needed for growth, stimulates chlorophyll production, promotes strong stem development, and enables the formation of healthy leaves. By ensuring your seedlings receive adequate light, you are setting them up for success in their early stages of growth.
Choosing the Right Light Source
When it comes to providing light for germinated seeds, choosing the right light source is crucial. Here are a few considerations to keep in mind:
1. Natural Sunlight: Natural sunlight is the most ideal light source for seedlings. It provides a full spectrum of light that contains all the necessary wavelengths for optimal plant growth. If possible, place your seedlings near a sunny window or in a greenhouse where they can receive direct sunlight for a minimum of 6-8 hours per day.
2. Artificial Grow Lights: In situations where natural sunlight is limited or unavailable, artificial grow lights can be a great alternative. LED grow lights, fluorescent tubes, and high-intensity discharge (HID) lights are popular options for indoor gardening. Look for lights with a balanced spectrum that includes both blue and red wavelengths, which are essential for photosynthesis.
3. Light Intensity: The intensity of light is an important consideration. Seedlings typically require a light intensity of around 2000-3000 lux, which is equivalent to the brightness of a cloudy day. Make sure your chosen light source can deliver the necessary intensity to support healthy seedling growth.
4. Light Duration: Germinated seeds typically require around 12-16 hours of light exposure per day. This extended duration mimics the long daylight hours of spring and summer, providing the seedlings with the optimal conditions for growth. Use a timer to ensure consistent light cycles and avoid overexposure or underexposure to light.
Remember to position your light source at an appropriate distance from the seedlings. The ideal distance will depend on the light source and its intensity. Aim to provide enough light without causing excessive heat that could damage the seedlings.
By carefully selecting the right light source and ensuring the proper intensity and duration of light exposure, you can create an environment that supports the healthy growth and development of germinated seeds.
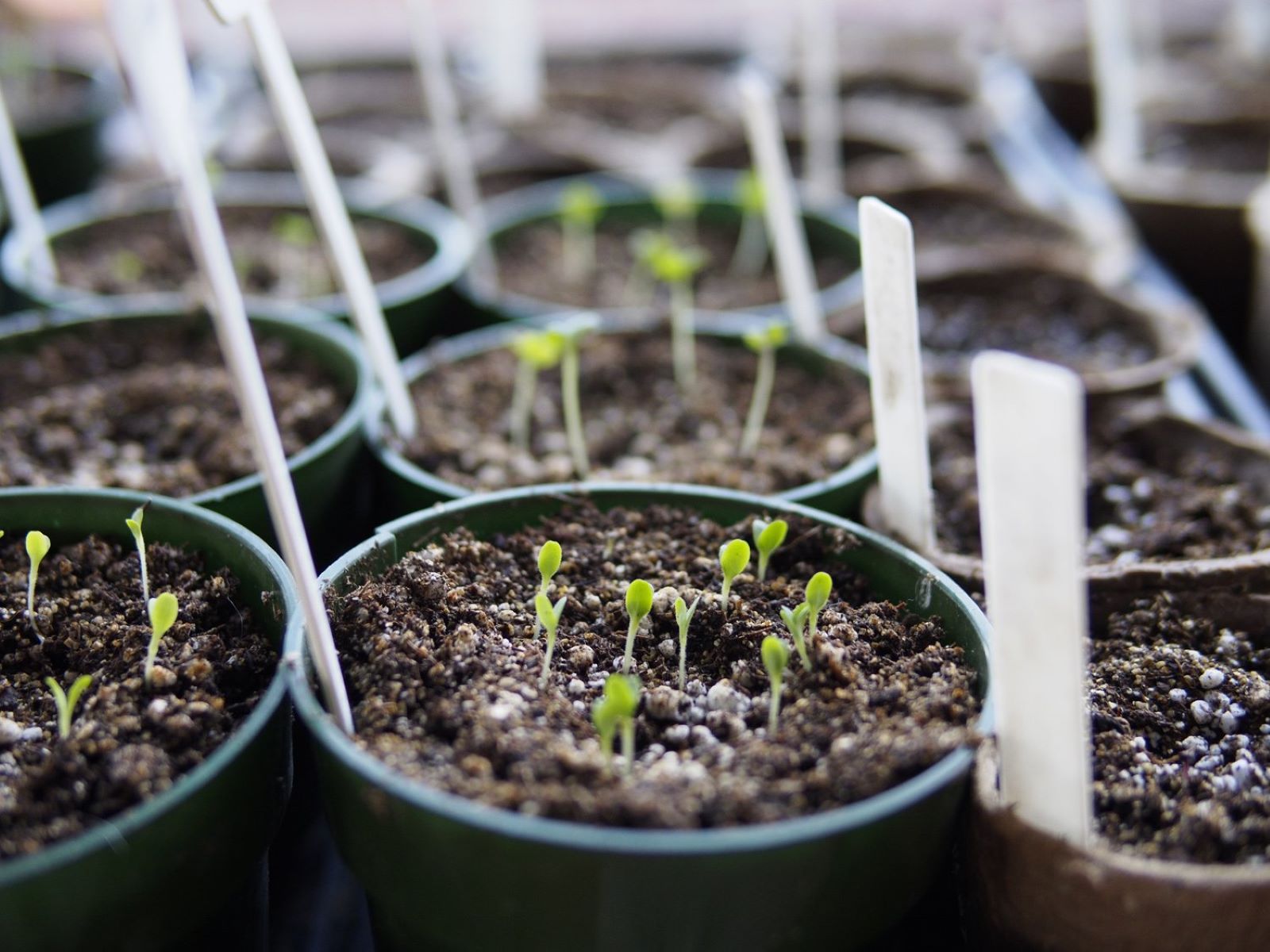
Once your seeds have germinated and the first set of true leaves appear, it’s time to put them under a grow light. This usually occurs 2-3 weeks after germination. Make sure the light is positioned 2-3 inches above the plants to prevent stretching.
Read more: When Do Weeds Germinate
Optimal Timing to Introduce Light
Timing is crucial when it comes to introducing light to germinated seeds. While seeds initially need a dark and moist environment to trigger the germination process, they will eventually require light for proper growth. Here are some guidelines for the optimal timing to introduce light to your germinated seeds:
1. Wait for Emergence: After sowing your seeds and providing the ideal germination conditions (such as proper temperature and moisture), allow the seeds to germinate and wait for the emergence of the radicle, or the embryonic root. It is important to wait until the seedlings have emerged before exposing them to light.
2. Keep Seedlings Covered: While waiting for the emergence of the radicle, keep your seedlings covered with a humidity dome or plastic wrap to maintain a moist environment. This cover helps create a greenhouse-like effect and promotes optimal germination. However, ensure that the cover still allows some airflow to prevent the buildup of excess moisture.
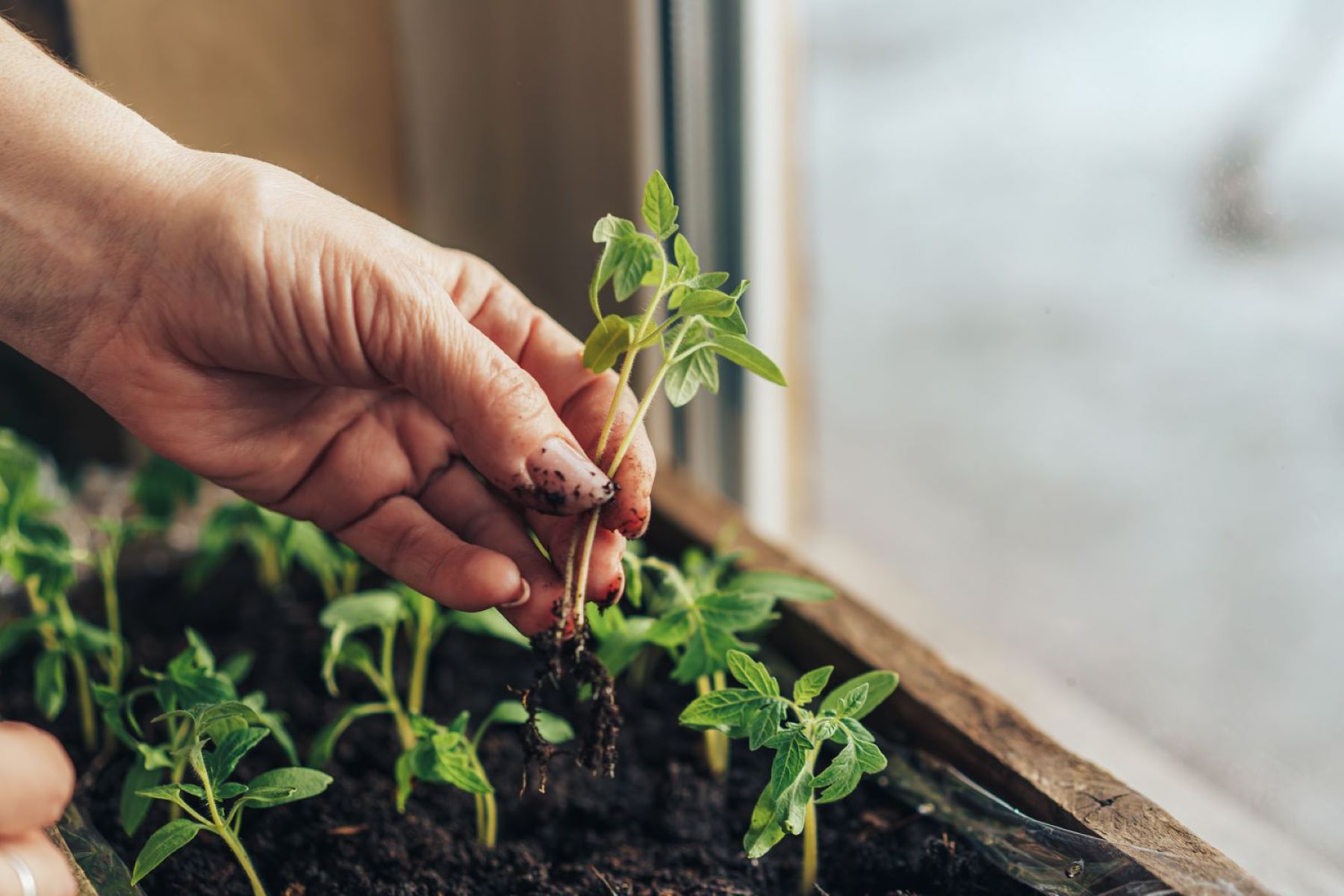
3. Uncover and Introduce Light: Once the radicle has emerged and the seedlings have started to grow, it is time to uncover them and introduce light. Remove the humidity dome or plastic wrap and place the seedlings in a well-lit area or under an artificial grow light. Ensure that the light source is positioned at an appropriate distance to provide adequate light intensity without causing heat stress to the seedlings.
4. Gradual Light Exposure: Initially, expose the seedlings to light for a few hours each day, gradually increasing the duration over the course of a week. This gradual exposure helps the seedlings acclimate to the new light conditions and prevents them from becoming stressed or shocked by the sudden change.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your germinated seeds receive the right timing and transition smoothly into the light phase of their growth. Providing light at the appropriate stage will promote healthy development and set the foundation for strong and resilient seedlings.
Duration of Light Exposure
The duration of light exposure is essential for the growth and development of germinated seeds. It is crucial to provide sufficient light to support photosynthesis and provide the energy needed for healthy seedling growth. Here are some guidelines for the duration of light exposure for your germinated seeds:
1. 12-16 Hours of Light: Germinated seeds generally require around 12-16 hours of light exposure per day. This duration mimics the long daylight hours of spring and summer, which are optimal for plant growth. Providing adequate light during this timeframe ensures that the seedlings have enough energy to carry out photosynthesis and promote robust growth.
2. Consistent Light Cycles: It is important to maintain consistent light cycles for your germinated seeds. Using a timer can help you set up a regular schedule for the duration of light exposure. This consistency helps establish a predictable routine for the seedlings, promoting healthy growth patterns and preventing any disruptions in their development.
3. Darkness for Rest: Just like humans, plants also require a period of darkness for rest. Providing a break from continuous light exposure allows the seedlings to recover and rejuvenate. It is recommended to provide a period of darkness for 8-12 hours per day, allowing the seedlings to rest and carry out essential metabolic processes.
4. Avoid Excessive Light: While providing sufficient light is crucial, it is important to avoid excessive light exposure as well. Too much light can lead to heat stress and potentially damage the seedlings. Additionally, prolonged exposure to bright light without any rest periods can disrupt the natural growth and development of the seedlings. Finding the right balance between light and darkness is key to promoting healthy and optimal growth.
By providing your germinated seeds with the appropriate duration of light exposure, you are ensuring they have the necessary energy for photosynthesis and creating the ideal conditions for their growth and development. Maintaining consistent light cycles and incorporating periods of darkness will help establish a healthy routine and set the stage for thriving seedlings.
Monitoring and Adjusting Light Intensity
Monitoring and adjusting the light intensity is crucial to ensure the optimal growth and development of your germinated seeds. Light intensity directly affects photosynthesis, which is essential for producing the energy needed for healthy seedling growth. Here are some tips on how to monitor and adjust the light intensity:
1. Use a Light Meter: A light meter (also known as a lux meter) is a tool that measures the intensity of light. By using a light meter, you can accurately determine the light intensity reaching your seedlings. This allows you to ensure that they are receiving the appropriate amount of light for their growth stage.
2. Position the Light Source Correctly: The distance between the light source and your seedlings significantly affects the light intensity. Each type of light source has a recommended distance for optimal intensity. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions or refer to gardening resources for specific recommendations. Adjust the height of the light source accordingly to achieve the desired light intensity.
3. Observe Seedling Response: Keep a close eye on your seedlings and observe how they respond to the light. Healthy seedlings will display vigorous growth, with no signs of stretching or wilting. If the seedlings appear leggy or spindly, it could indicate that they are receiving insufficient light. On the other hand, if they show signs of leaf burn or discoloration, it could be a sign of excessive light intensity.
4. Optimize Light Spectrum: Different stages of plant growth require different light spectrums. For seedlings, a balanced spectrum that includes both blue and red wavelengths is essential. Blue light promotes compact and strong growth, while red light supports leaf development and root growth. Consider incorporating full-spectrum LED grow lights or using a combination of different light sources to provide the optimal spectrum for your seedlings.
5. Adjust Light Duration: If you notice any adverse effects on your seedlings, such as scorched leaves or stunted growth, it may be necessary to adjust the duration of light exposure. Decrease the duration slightly to alleviate any stress on the seedlings. Conversely, if your seedlings appear weak or elongated, you may need to increase the duration of light exposure to give them more energy for photosynthesis.
By regularly monitoring the light intensity and making necessary adjustments, you can provide your germinated seeds with the optimal lighting conditions for healthy growth and development. Remember that finding the right balance is key, and the needs of your seedlings may change as they progress through different growth stages.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While providing light to germinated seeds is crucial for their growth, it’s important to avoid common mistakes that can hinder their development. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when it comes to light exposure for your seedlings:
1. Insufficient Light: One of the most common mistakes is not providing enough light to germinated seeds. Insufficient light can lead to weak and leggy seedlings as they stretch towards the nearest light source. Ensure that your seedlings are receiving adequate light exposure by placing them near a sunny window or providing artificial grow lights with the appropriate light intensity.
2. Excessive Light: On the other hand, exposing seedlings to excessive light can cause damage and stress. Too much light can result in burned or scorched leaves and stunted growth. Be mindful of the light intensity and duration, and adjust accordingly to prevent overexposure.
3. Inconsistent Light Cycles: Consistency is key when it comes to light cycles for germinated seeds. Avoid irregular or inconsistent light schedules, as this can disrupt the natural growth patterns of the seedlings. Use a timer to maintain a consistent light cycle of 12-16 hours of light and 8-12 hours of darkness per day.
4. Improper Distance: The distance between the light source and the seedlings is crucial in maintaining the right light intensity. Placing the light source too close can cause heat stress and damage the seedlings, while placing it too far away can result in insufficient light exposure. Follow the recommended distance guidelines for your specific light source and adjust as needed.
5. Lack of Monitoring: Monitoring the progress and response of your seedlings is essential. Regularly check for signs of healthy growth, such as strong stems, vibrant leaves, and steady development. On the other hand, keep an eye out for any signs of stress, stretching, or discoloration, which could indicate problems with light exposure. Adjust the light intensity, duration, or distance accordingly based on your seedlings’ needs.
6. Ignoring Natural Light: While artificial grow lights can be beneficial, don’t overlook the importance of natural sunlight. Whenever possible, allow your seedlings to receive direct sunlight, as natural light provides a full spectrum of wavelengths that are essential for plant growth. Supplementing with artificial lights may be necessary in environments with limited or no access to natural light.
By avoiding these common mistakes and taking a proactive approach to providing light for your germinated seeds, you can set the stage for healthy and thriving seedlings. Remember to be attentive, make necessary adjustments, and provide a balanced and consistent light environment for optimal growth.
Read more: When Do Cosmos Germinate
Conclusion
Light is a fundamental element in the growth and development of germinated seeds. By understanding the importance of light and providing the right conditions, you can ensure the successful transition of your seedlings into thriving plants. From the optimal timing to introduce light to choosing the right light source, monitoring and adjusting light intensity, and avoiding common mistakes, every step plays a crucial role in nurturing healthy seedlings.
Remember that each plant species has specific light requirements, so it’s essential to research and understand the needs of your particular seeds. Whether you are using natural sunlight or artificial grow lights, maintaining consistent light cycles and providing the appropriate light intensity and duration is key to promoting photosynthesis and generating the energy needed for growth.
Regular monitoring of your seedlings’ response to light and making necessary adjustments ensures that they receive the optimal conditions for their development. Paying attention to signs of healthy growth or stress will guide you in fine-tuning the light exposure to meet their needs.
As you embark on your journey as a gardener, remember that light is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to nurturing plants. Factors such as temperature, moisture, air circulation, and nutrient availability also play crucial roles in seedling development. By considering all of these factors and providing a balanced environment, you can set your seedlings up for success.
With a solid understanding of the importance of light and the necessary steps to provide the right lighting conditions, you can confidently support the growth and development of your germinated seeds. Stay attentive, adapt to the needs of your seedlings, and enjoy the rewarding experience of watching them thrive into robust and beautiful plants.
Frequently Asked Questions about When Do I Put My Germinated Seeds Under Light
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “When Do I Put My Germinated Seeds Under Light”