Home>Gardening & Outdoor>Landscaping Ideas>Why Is Grass Used For Erosion Control


Landscaping Ideas
Why Is Grass Used For Erosion Control
Modified: August 16, 2024
Learn why grass is a popular choice for erosion control in landscaping ideas. Discover the benefits of using grass to prevent soil erosion.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Erosion is a natural process, but when left unchecked, it can have detrimental effects on the environment, leading to loss of topsoil, decreased water quality, and compromised stability of landscapes. In the realm of landscaping, combating erosion is a crucial endeavor, and one of the most effective and sustainable methods for erosion control involves the strategic use of grass. In this article, we will delve into the reasons why grass is a preferred choice for erosion control, the mechanisms through which it prevents erosion, the types of grass commonly utilized for this purpose, and best practices for implementing grass in erosion control efforts. Whether you're a homeowner looking to protect your property from erosion or a landscaping professional seeking sustainable solutions, understanding the role of grass in erosion control is essential for effective land management. Let's explore the benefits, mechanisms, and best practices associated with using grass for erosion control.
Key Takeaways:
- Grass is a powerful ally against erosion, stabilizing soil, enhancing water absorption, and promoting biodiversity. Its use in erosion control offers sustainable and cost-effective benefits for preserving landscapes.
- Selecting the right grass species and implementing best practices, such as proper planting techniques and regular maintenance, can maximize the effectiveness of grass in preventing erosion and preserving the environment.
The Benefits of Grass for Erosion Control
Grass serves as a powerful ally in the battle against erosion, offering a multitude of benefits that make it a preferred choice for sustainable land management. Its widespread use in erosion control efforts is attributed to several key advantages:
- Natural Soil Stabilization: Grass has an extensive root system that intertwines with the soil, effectively anchoring it in place and preventing erosion caused by wind and water. This natural stabilization helps maintain the integrity of the topsoil, reducing the risk of sediment runoff and preserving the landscape’s structure.
- Water Absorption and Filtration: The dense network of grass roots enhances water absorption, reducing surface runoff and minimizing the impact of heavy rainfall on soil erosion. Additionally, the roots act as a natural filtration system, trapping sediments and impurities as water percolates through the soil, thus contributing to improved water quality.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: By fostering a supportive habitat for diverse microorganisms and small creatures, grass contributes to the overall biodiversity of an ecosystem. This biodiversity not only enriches the natural environment but also plays a role in promoting ecological balance and resilience against environmental stressors.
- Visual Appeal and Aesthetic Value: Beyond its functional benefits, the lush greenery of grass enhances the visual appeal of landscapes, making it an attractive choice for erosion control in both residential and commercial settings. Its aesthetic value complements the surrounding environment, creating a harmonious and inviting atmosphere.
- Sustainable and Cost-Effective: Grass is a sustainable erosion control solution that offers long-term benefits without the need for extensive maintenance. Compared to engineered structures or chemical treatments, the use of grass is a cost-effective approach that aligns with eco-friendly practices, making it an environmentally conscious choice for erosion management.
These inherent benefits underscore the significance of grass in erosion control, positioning it as a natural and versatile tool for preserving the integrity of landscapes and mitigating the adverse effects of erosion. Understanding these advantages is essential for harnessing the full potential of grass in sustainable land stewardship.
How Grass Prevents Erosion
Grass exerts a remarkable influence in preventing erosion through a combination of biological, physical, and ecological mechanisms that collectively safeguard the integrity of the soil and the surrounding environment. Understanding the ways in which grass mitigates erosion is pivotal for appreciating its role as a natural erosion control agent.
Root Reinforcement: One of the primary mechanisms through which grass prevents erosion is its extensive root system. The intricate network of roots binds the soil together, creating a cohesive matrix that resists displacement by wind and water. This root reinforcement effectively stabilizes the topsoil, reducing the likelihood of erosion and minimizing the impact of natural forces on the landscape.
Soil Structure Enhancement: Grass roots play a pivotal role in enhancing soil structure by promoting aggregation and reducing compaction. As the roots penetrate the soil, they create passageways for water and air, facilitating improved soil porosity and permeability. This enhanced soil structure not only fosters optimal root growth but also bolsters the soil’s resistance to erosion, as well-structured soil is less prone to being washed away or displaced.
Water Absorption and Redistribution: The dense network of grass roots enhances the soil’s capacity to absorb and retain water, mitigating the impact of heavy rainfall and reducing surface runoff. By effectively capturing and redistributing water throughout the soil profile, grass helps regulate moisture levels, preventing excessive saturation and minimizing the erosive potential of water flow. This water absorption and redistribution mechanism significantly contributes to erosion control, particularly in areas susceptible to runoff-induced erosion.
Vegetative Cover and Surface Protection: The dense foliage of grass provides a protective vegetative cover that shields the soil from the erosive forces of wind and water. By intercepting rainfall and reducing the kinetic energy of raindrops before they reach the ground, the grass canopy helps prevent soil detachment and surface erosion. Additionally, the aboveground biomass of grass serves as a natural barrier, attenuating the impact of wind and reducing the likelihood of soil displacement.
Ecological Resilience and Biodiversity: Grass contributes to ecological resilience by fostering a diverse and dynamic ecosystem within the soil matrix. The interactions between grass roots, soil microorganisms, and invertebrates create a robust ecological network that enhances soil stability and resilience. This biodiversity not only fortifies the soil against erosion but also promotes overall ecosystem health, reinforcing the natural defense mechanisms against environmental degradation.
By harnessing these multifaceted mechanisms, grass emerges as a formidable guardian against erosion, leveraging its biological, physical, and ecological attributes to sustainably protect landscapes from the perils of soil displacement and degradation.
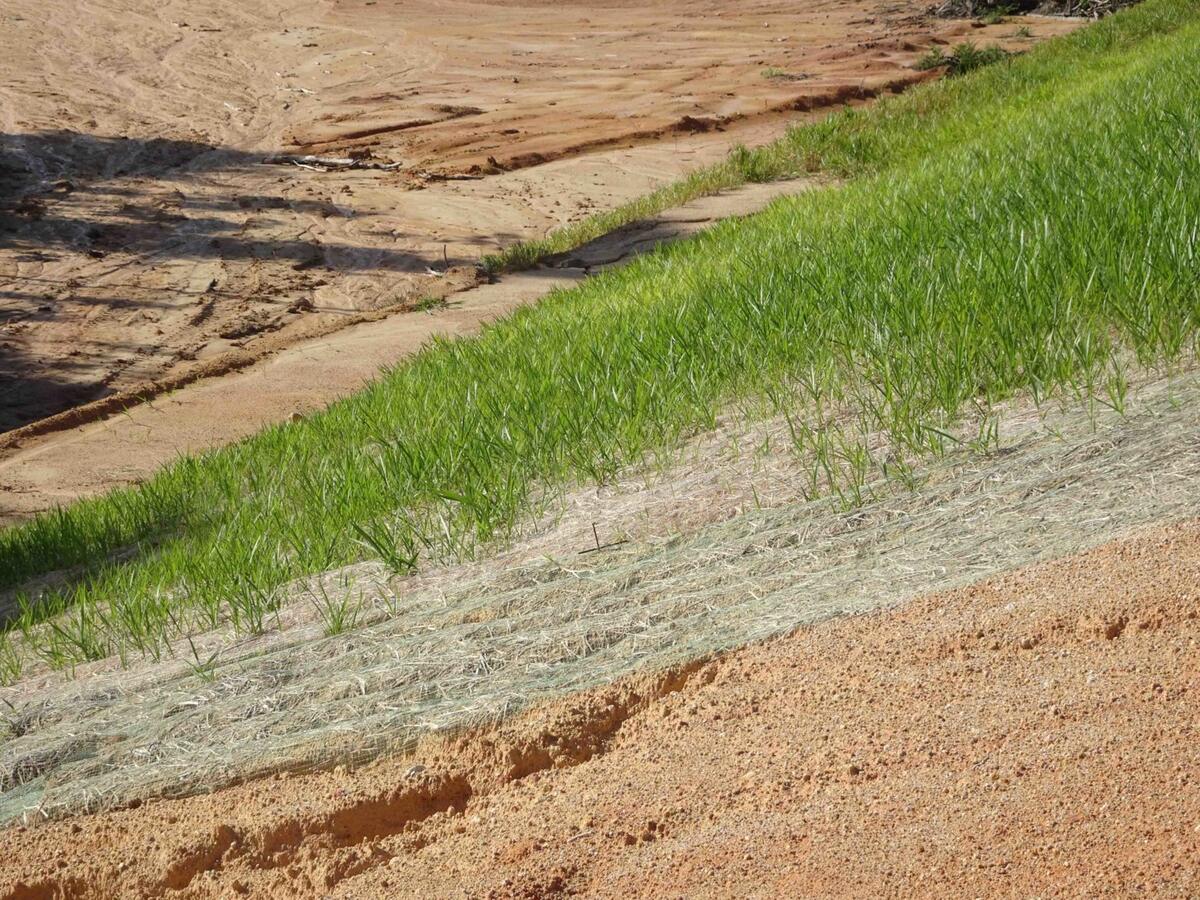
Grass is used for erosion control because its roots help hold soil in place, preventing it from washing away during heavy rain or wind. Planting grass on slopes or bare soil can help prevent erosion and protect the land.
Types of Grass Used for Erosion Control
When it comes to erosion control, various types of grass are employed based on their adaptability, resilience, and effectiveness in stabilizing soil and preventing erosion. The selection of grass species is influenced by factors such as climate, soil conditions, and the specific erosion challenges faced in a given area. Here are some of the most commonly used grasses for erosion control:
- Bermuda Grass (Cynodon dactylon): Known for its rapid growth and robust root system, Bermuda grass is a warm-season perennial grass that thrives in sunny, well-drained areas. Its extensive rhizomes and stolons enable it to form dense, interlocking mats that effectively bind the soil, making it a popular choice for erosion-prone areas with high foot traffic or frequent disturbances.
- Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea): Tall fescue is a cool-season grass valued for its adaptability to a wide range of soil types and its resilience in challenging environmental conditions. With deep roots and a coarse texture, tall fescue excels in stabilizing slopes and controlling erosion, making it a favored option for reclamation projects and erosion-prone landscapes.
- Zoysia Grass (Zoysia spp.): Zoysia grass, a warm-season grass renowned for its drought tolerance and dense growth habit, is prized for its ability to form intricate root systems that effectively hold soil in place. Its creeping growth pattern and tolerance to foot traffic make it an ideal choice for erosion control in areas requiring both functional stability and aesthetic appeal.
- Buffalograss (Buchloe dactyloides): Native to the Great Plains region of North America, buffalograss is a warm-season grass celebrated for its low water requirements and exceptional drought tolerance. Its deep root system and fine-textured foliage contribute to its erosion control capabilities, making it a valuable asset in conservation and restoration efforts in arid and semi-arid regions.
- Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum): A versatile warm-season grass indigenous to North America, switchgrass is esteemed for its adaptability and resilience in diverse soil and climate conditions. With its deep, fibrous roots and upright growth habit, switchgrass excels in stabilizing soil, making it a favored choice for erosion control in conservation projects, riparian areas, and wildlife habitats.
These grass species, among others, play a pivotal role in erosion control, offering diverse attributes that cater to specific environmental demands and land management objectives. By leveraging the unique characteristics of these grasses, land stewards and landscaping professionals can effectively combat erosion and preserve the ecological integrity of landscapes.
Best Practices for Using Grass for Erosion Control
Implementing grass for erosion control entails a strategic approach that integrates best practices to maximize its effectiveness in preserving soil integrity and mitigating erosion. By adhering to these best practices, land managers and property owners can harness the full potential of grass as a sustainable erosion control solution:
- Site Assessment and Soil Preparation: Conduct a thorough assessment of the site to evaluate soil conditions, topography, and environmental factors. Select grass species based on the site’s specific requirements, ensuring compatibility with soil type, moisture levels, and sunlight exposure. Prepare the soil by addressing compaction, improving drainage, and incorporating organic amendments to create an optimal environment for grass establishment.
- Appropriate Grass Selection: Choose grass species that align with the site’s climatic conditions, water availability, and erosion risk. Consider factors such as root depth, growth habit, and adaptability to ensure the selected grass is well-suited for erosion control in the target area. Opt for native or regionally adapted grass species to promote ecological harmony and enhance long-term sustainability.
- Proper Planting Techniques: Employ suitable planting methods such as seeding, sodding, or hydroseeding, adhering to recommended seeding rates and depths. Ensure adequate seed-to-soil contact and implement erosion control blankets or mulches to facilitate germination and establishment. Utilize erosion control matting or netting in steep or vulnerable areas to stabilize the soil and protect newly planted grass from erosion forces.
- Regular Maintenance and Monitoring: Establish a maintenance regimen that includes irrigation, weed control, and mowing practices to promote healthy grass growth and root development. Monitor the site for signs of erosion, compaction, or nutrient deficiencies, and take proactive measures to address any emerging issues. Implement erosion control measures such as terracing, contouring, or vegetative barriers in collaboration with grass establishment to enhance erosion resistance.
- Integration with Landscaping Design: Integrate grass for erosion control into the overall landscaping design, considering factors such as slope stabilization, water management, and aesthetic harmony. Incorporate grassed waterways, bio-swales, or riparian buffers to effectively manage water flow and minimize erosion potential, blending functional erosion control with visually appealing landscape features.
- Educational Outreach and Community Engagement: Foster awareness and community engagement regarding the importance of grass in erosion control and sustainable land management. Empower stakeholders with knowledge about the benefits of grass-based erosion control and encourage responsible land stewardship practices to collectively safeguard the environment and promote ecological resilience.
By embracing these best practices, stakeholders can optimize the efficacy of grass for erosion control, fostering resilient landscapes and contributing to the preservation of natural resources. Through informed decision-making and proactive implementation, the integration of grass as an erosion control tool can yield enduring benefits for both the environment and the communities it serves.
Read more: How Does Grass Prevent Soil Erosion
Conclusion
Grass stands as a stalwart guardian in the realm of erosion control, offering a myriad of benefits, diverse species, and effective mechanisms that collectively fortify landscapes against the perils of soil displacement and degradation. From its natural soil stabilization and water absorption capabilities to its ecological resilience and aesthetic appeal, grass emerges as a versatile and sustainable solution for combatting erosion and preserving the ecological integrity of diverse landscapes.
By understanding the pivotal role of grass in erosion control, land managers, homeowners, and landscaping professionals can harness its inherent strengths to create resilient, visually captivating, and environmentally conscious environments. The strategic selection and implementation of grass species, coupled with best practices in site assessment, soil preparation, and maintenance, empower stakeholders to leverage the full potential of grass as a natural erosion control tool.
As communities strive to embrace sustainable land management practices and foster ecological harmony, the integration of grass for erosion control stands as a testament to the enduring partnership between nature and human stewardship. Through educational outreach, community engagement, and responsible landscaping design, the utilization of grass as an erosion control agent becomes an integral component of holistic environmental conservation efforts.
Ultimately, the enduring legacy of grass in erosion control transcends its functional utility, embodying a harmonious synergy between nature’s resilience and human ingenuity. By honoring the intrinsic value of grass and its pivotal role in preserving the integrity of landscapes, we embark on a collective journey towards sustainable land stewardship and the enduring protection of our natural heritage.
Embracing the verdant embrace of grass, we pave the way for a greener, more resilient future, where the undulating meadows and steadfast prairies stand as testaments to the enduring partnership between nature and human endeavor.
Frequently Asked Questions about Why Is Grass Used For Erosion Control
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Why Is Grass Used For Erosion Control”