Home>Gardening & Outdoor>Plant Care & Gardening Tips>How Does The Wildflower Defend Itself


Plant Care & Gardening Tips
How Does The Wildflower Defend Itself
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover how wildflowers defend themselves and get expert plant care and gardening tips to help your garden thrive. Explore natural defense mechanisms and practical advice for optimal plant care.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
**
Introduction
**
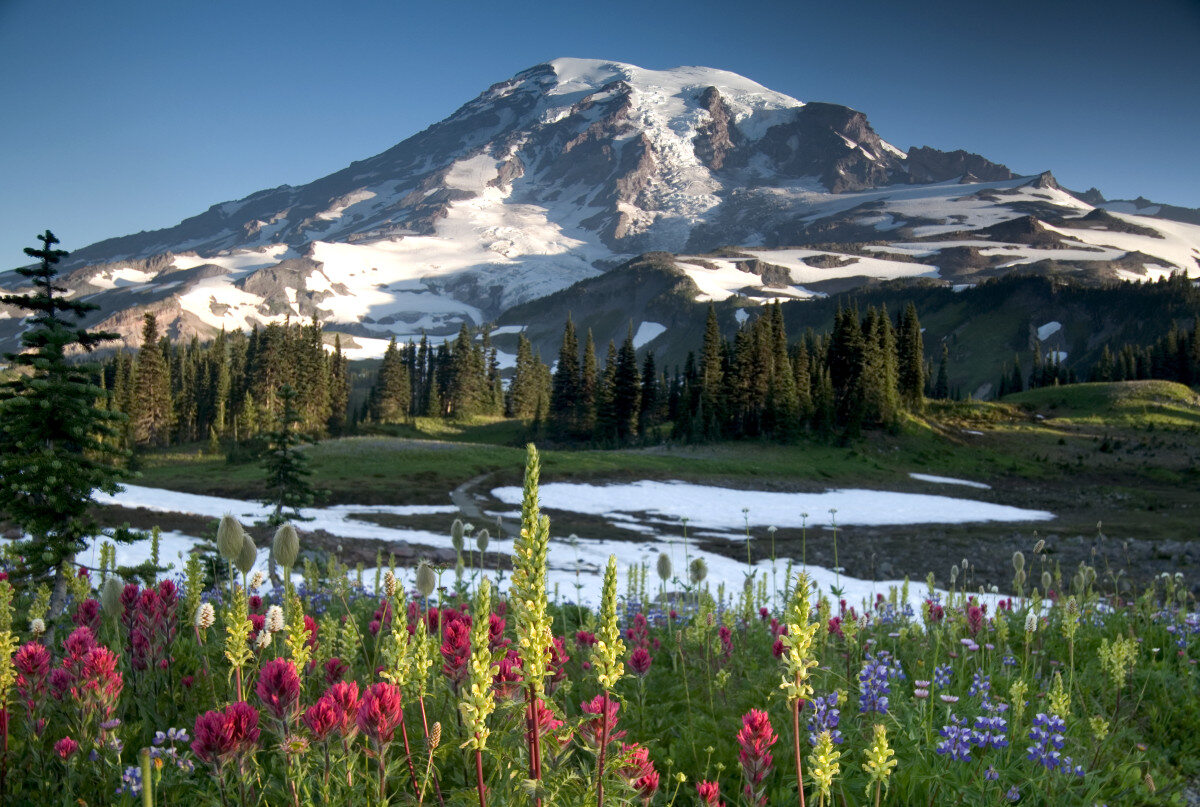
When strolling through a meadow or hiking along a forest trail, one can't help but admire the vibrant hues and delicate beauty of wildflowers. However, beneath their seemingly tranquil façade lies a world of fascinating defense mechanisms and survival strategies. Wildflowers have evolved an array of tactics to protect themselves from herbivores, attract pollinators, and thrive in diverse ecosystems. From chemical defenses to mimicry, these blossoms have honed their ability to adapt and endure in the natural world. In this article, we will delve into the captivating realm of wildflower defenses, exploring the ingenious ways in which these botanical marvels safeguard themselves and ensure their continued existence.
Wildflowers, with their enchanting blooms and captivating fragrances, are not just passive bystanders in the ecosystem. They actively engage in a complex dance of survival, deploying an impressive arsenal of strategies to thwart threats and entice allies. Join us as we uncover the secrets of wildflower defenses, shedding light on the remarkable adaptations and mechanisms that enable these floral wonders to flourish amidst the challenges of the natural world.
**
Key Takeaways:
- Wildflowers use chemical compounds and physical adaptations to defend themselves from herbivores and attract pollinators, showcasing their resilience and ingenuity in the natural world.
- Through mimicry and specialized structures, wildflowers entice and engage their pollinator partners, ensuring the successful transfer of pollen and the continuation of their species.
Chemical Defenses
**
One of the most potent and widespread defense mechanisms employed by wildflowers is the use of chemical compounds to deter herbivores and protect against pathogens. Through the synthesis and release of an assortment of organic chemicals, these plants effectively shield themselves from being consumed and thwart the growth of harmful microorganisms.
Many wildflowers produce secondary metabolites such as alkaloids, terpenoids, and phenolics, which serve as deterrents to herbivores due to their bitter taste, toxicity, or unpleasant odor. For instance, the vibrant petals of the foxglove contain cardiac glycosides, which are toxic to both humans and animals. Similarly, the bitter-tasting alkaloids found in lupines discourage herbivores from consuming these plants, effectively safeguarding them from being devoured.
Furthermore, wildflowers harness the power of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to defend themselves. These compounds, emitted by the flowers and leaves, can act as airborne signals to nearby plants, alerting them to the presence of herbivores and enabling them to prepare their own defenses. Additionally, some VOCs serve as attractants for beneficial insects, which in turn act as bodyguards for the plants by preying on herbivorous pests.
While chemical defenses are a formidable deterrent against herbivory, they also play a crucial role in the intricate web of ecological interactions. By producing a diverse array of chemical compounds, wildflowers not only protect themselves but also contribute to the overall balance of their ecosystems. These compounds can influence the behavior and survival of herbivores, shape the composition of plant communities, and even impact the health of surrounding organisms.
Intriguingly, the intricate dance of chemical warfare waged by wildflowers underscores the remarkable sophistication of their defense strategies. Through the subtle alchemy of organic compounds, these floral denizens have mastered the art of self-preservation, weaving a tapestry of protection and ecological influence that enriches the natural world.
**
Physical Defenses
**
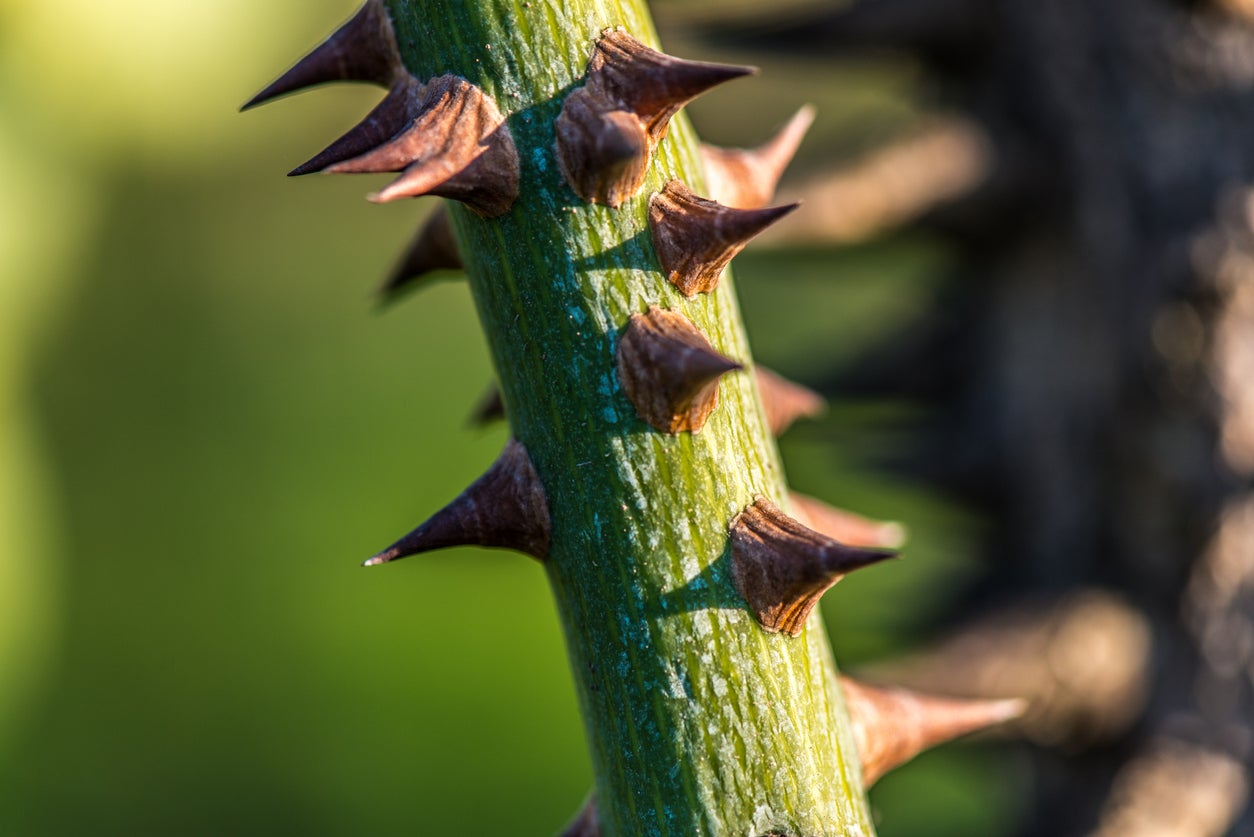
While chemical defenses are a formidable tool in the wildflower's arsenal, many of these floral wonders also boast an impressive array of physical adaptations to deter herbivores and safeguard their delicate structures. From thorns and spines to tough leaves and hairy surfaces, wildflowers have evolved an assortment of physical defenses that serve as barriers against would-be predators.
One of the most recognizable physical defenses employed by wildflowers is the presence of thorns and spines. These sharp protrusions not only dissuade herbivores from grazing on the plants but also provide a formidable barrier against larger animals seeking to trample or consume them. The rose, with its iconic thorns, exemplifies this strategy, using its prickly armor to ward off potential threats and protect its blooms from harm.
Additionally, many wildflowers exhibit adaptations such as tough, leathery leaves or hairy surfaces, which act as deterrents to herbivory. The fuzzy leaves of lamb's ear, for example, not only lend the plant a charming appearance but also serve as a physical barrier against pests, making it less palatable to would-be grazers. Similarly, the tough, fibrous leaves of certain wildflowers provide a robust defense against herbivores, deterring them from consuming these resilient plants.
Another intriguing physical defense mechanism employed by wildflowers is the production of tough seed coats or structures that protect the seeds from predation. Some wildflowers produce seeds with hard, resistant coatings, ensuring that they are not easily consumed by foraging animals. This adaptation allows the seeds to remain viable and ready for germination, contributing to the continued survival and propagation of the plant species.
By combining chemical and physical defenses, wildflowers demonstrate a remarkable capacity for self-preservation and resilience. These botanical marvels have honed their ability to withstand the pressures of the natural world, deploying a diverse array of strategies that underscore their tenacity and adaptability. From thorny barriers to resilient foliage, wildflowers stand as testaments to the ingenuity of nature's defenses, weaving a tapestry of protection that ensures their enduring presence in the tapestry of the natural world.
**
Wildflowers defend themselves by producing chemical compounds that deter herbivores and competing plants. These compounds can be toxic or unpalatable, helping the wildflower to survive and thrive in its environment.
Mimicry
**
Within the realm of wildflowers, the phenomenon of mimicry unfolds as a captivating strategy employed to deceive and deter potential threats. Mimicry, in its various forms, allows wildflowers to adopt the appearances, behaviors, or attributes of other organisms, thereby gaining a survival advantage in their natural habitats.
One of the most intriguing manifestations of mimicry in wildflowers is floral mimicry, where certain blossoms evolve to resemble the appearance of other organisms or objects, often with the aim of attracting pollinators or deterring herbivores. For instance, some wildflowers exhibit remarkable floral mimicry by resembling the forms of insects or other animals, thereby luring pollinators to their nectar-rich blooms. This clever ruse not only ensures the transfer of pollen for reproduction but also serves as a means of defense, as the deceptive appearance may deter herbivores that mistake the flower for a potential threat.
Furthermore, wildflowers may engage in mimicry to exploit the defensive characteristics of other organisms. For example, certain plants mimic the appearance or scent of toxic or unpalatable species, effectively deterring herbivores from consuming them. By adopting the traits of these unappealing counterparts, the mimicking wildflowers gain a protective advantage, reducing the likelihood of being targeted by herbivores and increasing their chances of survival.
Another intriguing form of mimicry observed in wildflowers is the adoption of structural or behavioral attributes that mimic the surrounding environment, a phenomenon known as cryptic mimicry. By blending seamlessly into their habitats, these plants evade detection by herbivores and other potential threats, effectively camouflaging themselves amidst their surroundings.
The captivating world of mimicry in wildflowers serves as a testament to the remarkable ingenuity and adaptability of these botanical marvels. Through the artful deception of floral mimicry, these plants not only ensure their own survival but also contribute to the intricate web of ecological interactions, shaping the dynamics of their ecosystems and enriching the natural world with their captivating strategies of defense and adaptation.
**
Adaptations for Attracting Pollinators
**
Within the enchanting realm of wildflowers, the process of pollination unfolds as a vital and intricate dance, with plants evolving a myriad of adaptations to entice and engage their pollinator partners. From vibrant colors and enticing fragrances to specialized structures and nectar rewards, wildflowers have honed an impressive array of strategies to ensure the successful transfer of pollen and the continuation of their species.
One of the most striking adaptations employed by wildflowers to attract pollinators is the display of vibrant and conspicuous blooms. These colorful floral displays, often adorned with intricate patterns and striking hues, serve as visual beacons that attract the attention of pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. By showcasing these captivating blooms, wildflowers effectively draw in their pollinator partners, initiating the crucial process of pollen transfer that is essential for reproduction.
Furthermore, wildflowers harness the power of enticing fragrances to captivate pollinators. The production of aromatic compounds, often found in the nectar of flowers, serves as a potent lure for bees, butterflies, and other pollinating insects. These alluring scents guide the pollinators to the flower's nectar reserves, ensuring that they come into contact with the plant's pollen and facilitate the vital process of pollination.
In addition to visual and olfactory cues, wildflowers have evolved specialized structures and adaptations to facilitate the transfer of pollen by their pollinator partners. Some flowers exhibit unique morphological features, such as long tubular shapes or intricate landing platforms, which are tailored to the specific characteristics of their primary pollinators. By providing convenient access to nectar and pollen, these floral adaptations ensure efficient pollination and enhance the likelihood of successful reproduction.
Moreover, the provision of nectar serves as a powerful incentive for pollinators, rewarding them for their vital role in the plant's reproductive cycle. The sweet, energy-rich nectar found within wildflower blooms acts as a potent attractant, enticing pollinators to visit the flowers and facilitating the transfer of pollen as they forage for this valuable resource.
Through the captivating adaptations for attracting pollinators, wildflowers not only ensure their own reproductive success but also contribute to the intricate web of ecological interactions, fostering the vital relationships between plants and their pollinator partners. These botanical marvels stand as testaments to the remarkable ingenuity and diversity of nature's strategies, weaving a tapestry of allure and reward that enriches the natural world with their captivating beauty and vital ecological contributions.
**
Read more: When Does Grass Seed Itself
Conclusion
**
As we journey through the enchanting realm of wildflowers, we uncover a tapestry of captivating defenses and ingenious adaptations that underscore the resilience and ingenuity of these botanical marvels. From the potent arsenal of chemical compounds to the formidable array of physical defenses, wildflowers have honed a diverse set of strategies to safeguard themselves from herbivores and thrive in their natural habitats.
Furthermore, the captivating phenomenon of mimicry unveils the artful deception and adaptive prowess of wildflowers, as they employ a myriad of strategies to deceive, deter, and thrive amidst the challenges of the natural world. Through floral mimicry, these plants not only ensure their own survival but also contribute to the delicate balance of their ecosystems, shaping the dynamics of their habitats with their captivating strategies of defense and adaptation.
Moreover, the enchanting adaptations for attracting pollinators highlight the vital role of wildflowers in fostering the crucial relationships between plants and their pollinator partners. With vibrant blooms, enticing fragrances, and specialized structures, these floral wonders entice and engage their pollinators, ensuring the successful transfer of pollen and the continuation of their species.
As we marvel at the intricate web of defenses and adaptations displayed by wildflowers, we come to appreciate the remarkable resilience and adaptability of these botanical treasures. Their captivating strategies not only ensure their own survival but also enrich the natural world with their beauty, vitality, and vital ecological contributions.
In the delicate dance of survival and adaptation, wildflowers stand as testaments to the enduring power of nature's creativity and ingenuity, weaving a tapestry of enchantment and resilience that enriches the tapestry of the natural world. As we continue to explore and cherish the wonders of wildflowers, may we find inspiration in their captivating defenses and adaptive strategies, recognizing the profound beauty and significance of these floral marvels within the intricate tapestry of the natural world.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does The Wildflower Defend Itself
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Does The Wildflower Defend Itself”