Home>Home Appliances>Heating & Cooling>How To Optimize Cycling In Forced Air Heating


Heating & Cooling
How To Optimize Cycling In Forced Air Heating
Modified: August 17, 2024
Learn how to optimize cycling in forced air heating systems for efficient heating and cooling. Discover expert tips for maximizing the performance of your heating and cooling system.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Forced air heating systems play a crucial role in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures, especially during the chilly months. These systems rely on cycling to efficiently distribute warm air throughout a space, ensuring consistent and pleasant warmth. However, optimizing cycling in forced air heating is essential for maximizing energy efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of the system.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of forced air heating systems and explore the various factors that influence cycling. Additionally, we will provide valuable tips for optimizing cycling in these systems, empowering homeowners to enhance their heating experience while minimizing energy consumption.
Understanding the nuances of cycling in forced air heating is pivotal for homeowners seeking to create a cozy and energy-efficient indoor environment. By gaining insights into the inner workings of these systems and implementing practical strategies, individuals can effectively manage cycling and reap the benefits of a well-maintained and optimized heating system.
Key Takeaways:
- Optimize cycling in forced air heating by maintaining clean filters, sealing air leaks, and scheduling regular maintenance. This saves energy and ensures a cozy home environment.
- Understanding thermostat settings and ductwork design helps homeowners optimize cycling, reduce energy consumption, and extend the lifespan of their heating systems.
Understanding Forced Air Heating Systems
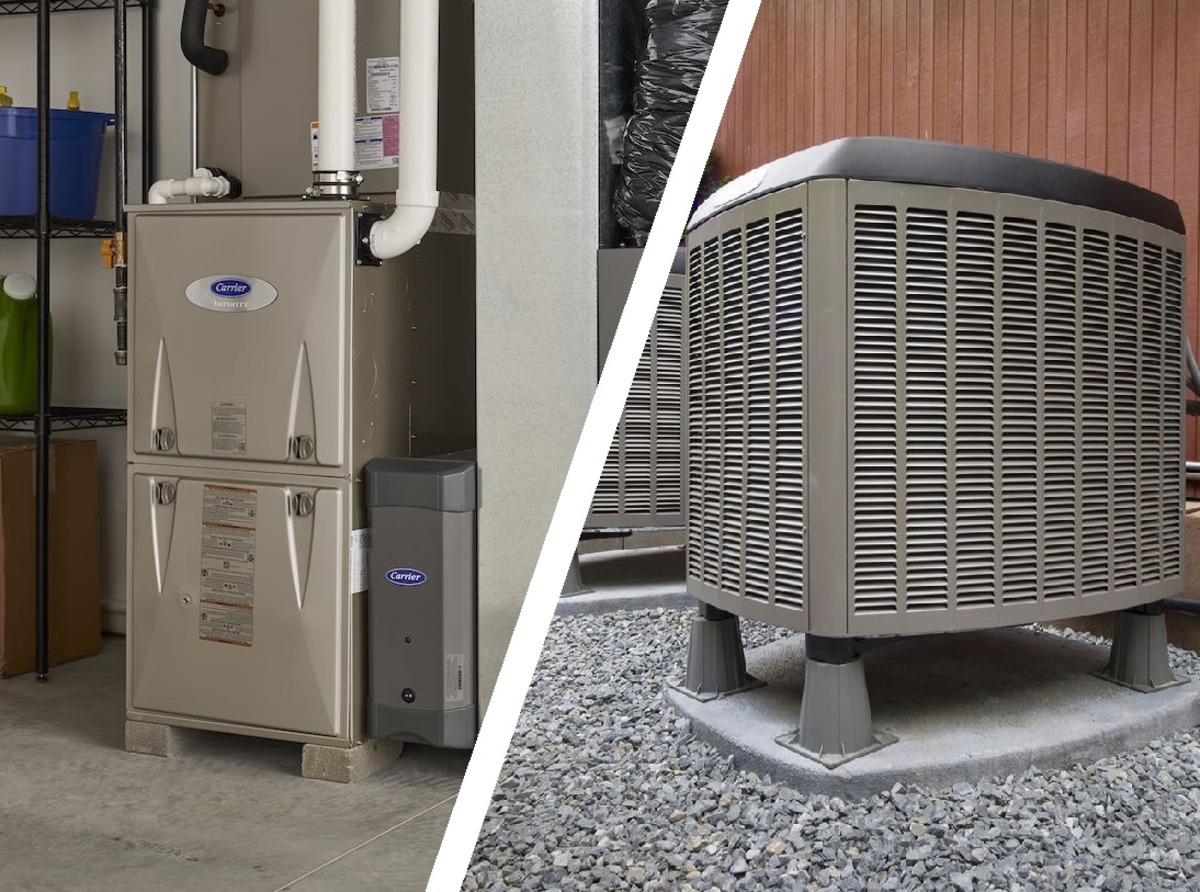
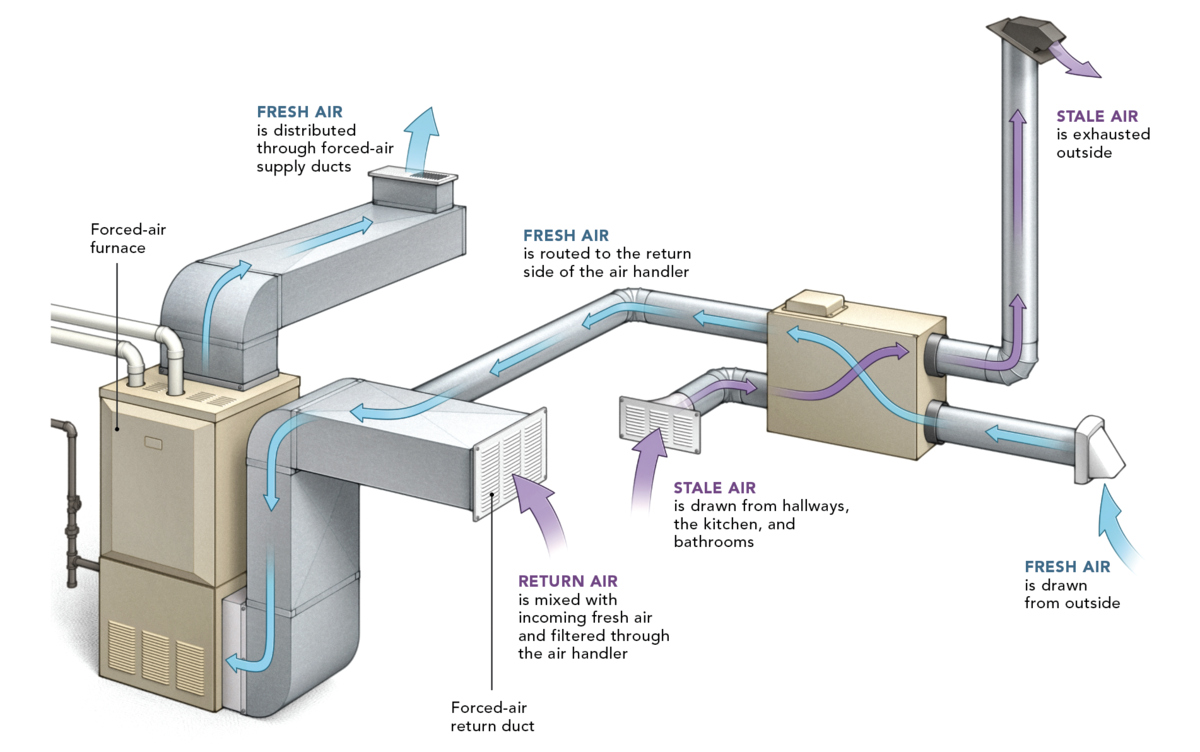
Forced air heating systems are a popular choice for many households, providing efficient and effective heating during cold weather. These systems operate by utilizing a furnace to heat air, which is then distributed throughout the home via a network of ducts and vents. The heated air is propelled into living spaces, raising the indoor temperature and creating a comfortable environment for occupants.
The key components of a forced air heating system include the furnace, ductwork, vents, and a thermostat. The furnace serves as the heart of the system, generating heat through the combustion of fuel or through electric resistance. Once the air is heated, it is propelled through the ductwork by a blower fan, which ensures even distribution to all areas of the home. Vents strategically placed in various rooms release the warm air, allowing it to circulate and maintain consistent temperatures throughout the living spaces. The thermostat acts as the control center, allowing users to set the desired temperature and regulate the heating process.
Cycling is a fundamental aspect of forced air heating systems. It refers to the process of the system turning on and off to maintain the desired temperature. When the indoor temperature drops below the set threshold, the thermostat signals the furnace to start heating the air. Once the desired temperature is reached, the furnace cycles off until the thermostat detects a need for additional heating. This continuous cycle ensures that the indoor environment remains comfortable while conserving energy.
Understanding the operation of forced air heating systems is essential for homeowners looking to optimize cycling and maximize energy efficiency. By comprehending the roles of each component and the cycling process, individuals can make informed decisions regarding system maintenance, thermostat settings, and overall system performance.
In the next section, we will explore the various factors that influence cycling in forced air heating systems, shedding light on the considerations that impact the efficiency and effectiveness of these systems. Understanding these factors is crucial for implementing strategies to optimize cycling and enhance the overall performance of the heating system.
Factors Affecting Cycling in Forced Air Heating
Several factors can significantly impact the cycling of forced air heating systems, influencing their efficiency, performance, and overall effectiveness in maintaining indoor comfort. Understanding these factors is pivotal for homeowners seeking to optimize cycling and maximize the energy efficiency of their heating systems.
-
Thermostat Settings: The thermostat serves as the control center for the heating system, dictating when the furnace cycles on and off. Inaccurate or fluctuating thermostat settings can lead to frequent cycling, resulting in energy wastage and potential wear and tear on system components. Properly calibrating the thermostat and setting it to a consistent temperature can help minimize unnecessary cycling and promote energy savings.
-
Air Leaks and Insulation: Poor insulation and air leaks within the home can lead to temperature fluctuations, causing the heating system to cycle more frequently as it strives to maintain the desired temperature. Addressing air leaks, improving insulation, and ensuring proper sealing of windows and doors can reduce the strain on the heating system, leading to more balanced and efficient cycling.
-
Air Filter Condition: A clogged or dirty air filter can obstruct airflow, forcing the heating system to work harder to distribute warm air throughout the home. This can result in increased cycling as the system attempts to compensate for restricted airflow. Regularly inspecting and replacing air filters can alleviate this issue, promoting smoother cycling and enhancing overall system performance.
-
Ductwork Design and Condition: The design and condition of the ductwork play a crucial role in the efficiency of forced air heating systems. Leaky or obstructed ducts can disrupt airflow, leading to uneven heating and potentially triggering frequent cycling as the system endeavors to balance temperatures across different zones. Ensuring well-designed, properly insulated, and well-maintained ductwork can contribute to more consistent and efficient cycling.
-
System Sizing and Capacity: An oversized or undersized heating system can result in inefficient cycling patterns. Oversized systems may short cycle, turning on and off frequently, while undersized systems may struggle to reach the desired temperature, leading to prolonged and inefficient cycling. Ensuring that the heating system is appropriately sized for the home's heating demands can promote optimal cycling and energy efficiency.
By addressing these factors and implementing appropriate measures, homeowners can effectively optimize cycling in forced air heating systems, promoting energy efficiency, prolonging system lifespan, and enhancing indoor comfort. Understanding the intricacies of these factors empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding system maintenance, upgrades, and operational practices, ultimately leading to a more efficient and reliable heating experience.
To optimize cycling in forced air heating, make sure to clean or replace the air filter regularly. A dirty filter can restrict airflow and cause the system to work harder, leading to more frequent cycling.
Tips for Optimizing Cycling in Forced Air Heating
Optimizing cycling in forced air heating systems is essential for maximizing energy efficiency and ensuring consistent indoor comfort. By implementing practical strategies and adopting proactive maintenance practices, homeowners can effectively manage cycling and enhance the overall performance of their heating systems. Here are valuable tips for optimizing cycling in forced air heating:
-
Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine maintenance for your heating system to ensure that all components are functioning optimally. This includes inspecting and cleaning the furnace, checking and replacing air filters, and examining the ductwork for any obstructions or leaks. By keeping the system well-maintained, you can promote efficient cycling and prevent potential issues that may lead to excessive energy consumption.
-
Thermostat Programming: Utilize programmable thermostats to establish temperature schedules that align with your daily routines. This allows the system to adjust temperatures based on occupancy, reducing unnecessary cycling during periods when heating is not required. Additionally, consider setting the thermostat to a consistent temperature to minimize fluctuations that can trigger frequent cycling.
-
Air Sealing and Insulation: Address air leaks and improve insulation within your home to create a more stable indoor environment. Properly sealed windows, doors, and ductwork, along with adequate insulation, can minimize temperature variations and reduce the strain on the heating system. This, in turn, promotes more balanced and efficient cycling, contributing to energy savings.
-
Air Filter Maintenance: Regularly inspect and replace air filters according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Clean filters facilitate unrestricted airflow, allowing the heating system to operate efficiently without the need for excessive cycling. By maintaining clean filters, you can promote smoother airflow and reduce the workload on the system.
-
Ductwork Optimization: Ensure that the ductwork is well-designed, properly insulated, and free from leaks or blockages. Well-maintained ductwork facilitates the even distribution of warm air, minimizing the need for the system to cycle frequently in an attempt to balance temperatures across different areas of the home.
-
Professional Assessment: Consider engaging a professional HVAC technician to assess the overall performance and efficiency of your forced air heating system. An expert evaluation can identify any underlying issues or inefficiencies that may be contributing to excessive cycling, allowing for targeted improvements to optimize system operation.
By incorporating these tips into your heating system management practices, you can effectively optimize cycling in forced air heating, promoting energy efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of your system. These proactive measures empower homeowners to create a comfortable indoor environment while minimizing energy consumption and reducing the potential for unnecessary wear and tear on system components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing cycling in forced air heating systems is a pivotal aspect of maintaining energy efficiency, prolonging system lifespan, and ensuring consistent indoor comfort. By understanding the factors that influence cycling and implementing practical strategies to enhance system performance, homeowners can effectively manage their heating systems and reap the benefits of a well-maintained and optimized environment.
The intricate interplay of thermostat settings, air leaks, air filter condition, ductwork design, and system sizing significantly impacts the cycling patterns of forced air heating systems. Addressing these factors through regular maintenance, thermostat programming, air sealing, air filter maintenance, ductwork optimization, and professional assessment empowers homeowners to take proactive measures in optimizing cycling and promoting energy efficiency.
By adhering to a comprehensive maintenance schedule and leveraging programmable thermostats, homeowners can establish a conducive environment for efficient cycling, reducing unnecessary energy consumption and minimizing wear and tear on system components. Furthermore, addressing air leaks, improving insulation, and maintaining clean air filters contribute to a more stable indoor environment, reducing the strain on the heating system and promoting balanced cycling.
The optimization of ductwork design and condition, along with the assessment of system sizing and capacity, ensures that forced air heating systems operate at their full potential, minimizing excessive cycling and maximizing energy efficiency. Engaging professional HVAC technicians for system evaluations and targeted improvements further enhances the overall performance and reliability of heating systems, providing homeowners with peace of mind and long-term cost savings.
In essence, the optimization of cycling in forced air heating systems is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a holistic approach to system management. By integrating the tips and strategies outlined in this guide, homeowners can take proactive steps to create a comfortable, energy-efficient indoor environment while extending the lifespan of their heating systems. Embracing these practices not only benefits individual households but also contributes to broader energy conservation efforts, promoting sustainability and responsible energy usage.
Ultimately, by prioritizing the optimization of cycling in forced air heating systems, homeowners can enjoy a harmonious balance between comfort, efficiency, and environmental stewardship, creating a warm and inviting home environment while minimizing their carbon footprint.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Optimize Cycling In Forced Air Heating
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.















0 thoughts on “How To Optimize Cycling In Forced Air Heating”