Home>Home Maintenance>What Is An Air Conditioner Condenser


Home Maintenance
What Is An Air Conditioner Condenser
Modified: August 28, 2024
Learn what an air conditioner condenser is and how it plays a crucial role in home maintenance. Discover the importance of maintaining your condenser for optimal cooling efficiency.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to keeping our homes cool and comfortable, air conditioners play a crucial role. They work tirelessly to maintain the desired temperature, allowing us to escape the sweltering heat of summer and create a comfortable living environment. While many of us are familiar with the main components of an air conditioning system, such as the compressor and evaporator, there is another integral part that deserves our attention – the air conditioner condenser.
The air conditioner condenser is responsible for releasing heat from the indoor unit to the outside environment. It plays a vital role in the overall cooling process, enabling the air conditioner to effectively manage the temperature in our homes. Understanding what an air conditioner condenser is, how it works, and how to properly maintain it can help ensure that our cooling systems continue to function optimally and efficiently.
In this article, we will delve into the world of air conditioner condensers, exploring their components, functions, types, and maintenance tips. Whether you are a homeowner looking to improve your knowledge about your air conditioning system or an HVAC technician seeking to enhance your expertise, this comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights.
Key Takeaways:
- The air conditioner condenser is like the cooling superhero of your home, expelling heat outside to keep you comfortable. Regular cleaning and maintenance keep it running smoothly and your home cool.
- Choosing an energy-efficient air conditioner condenser and keeping it well-maintained can save energy and money while ensuring your home stays cool and comfortable.
Definition of an Air Conditioner Condenser
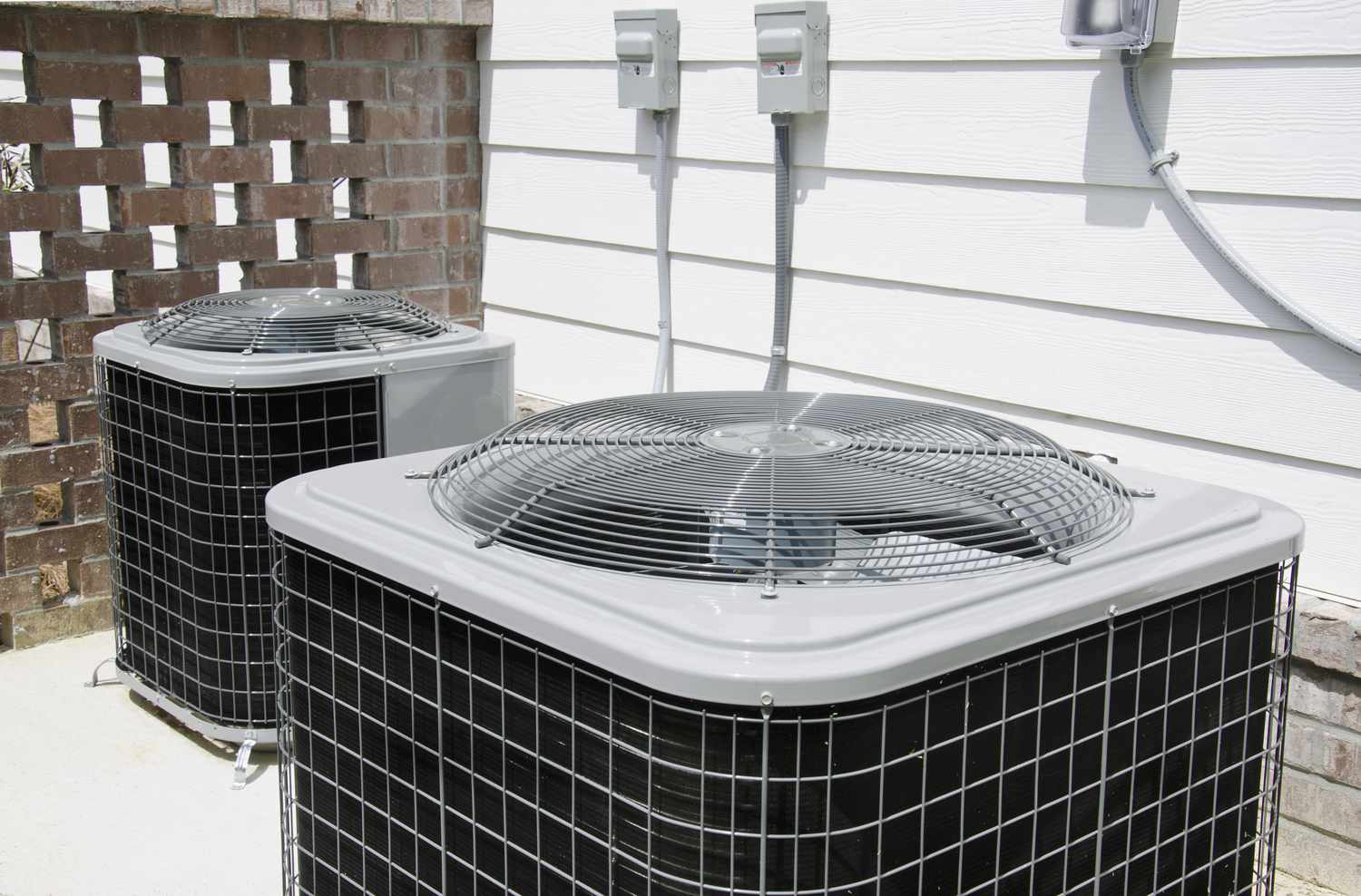
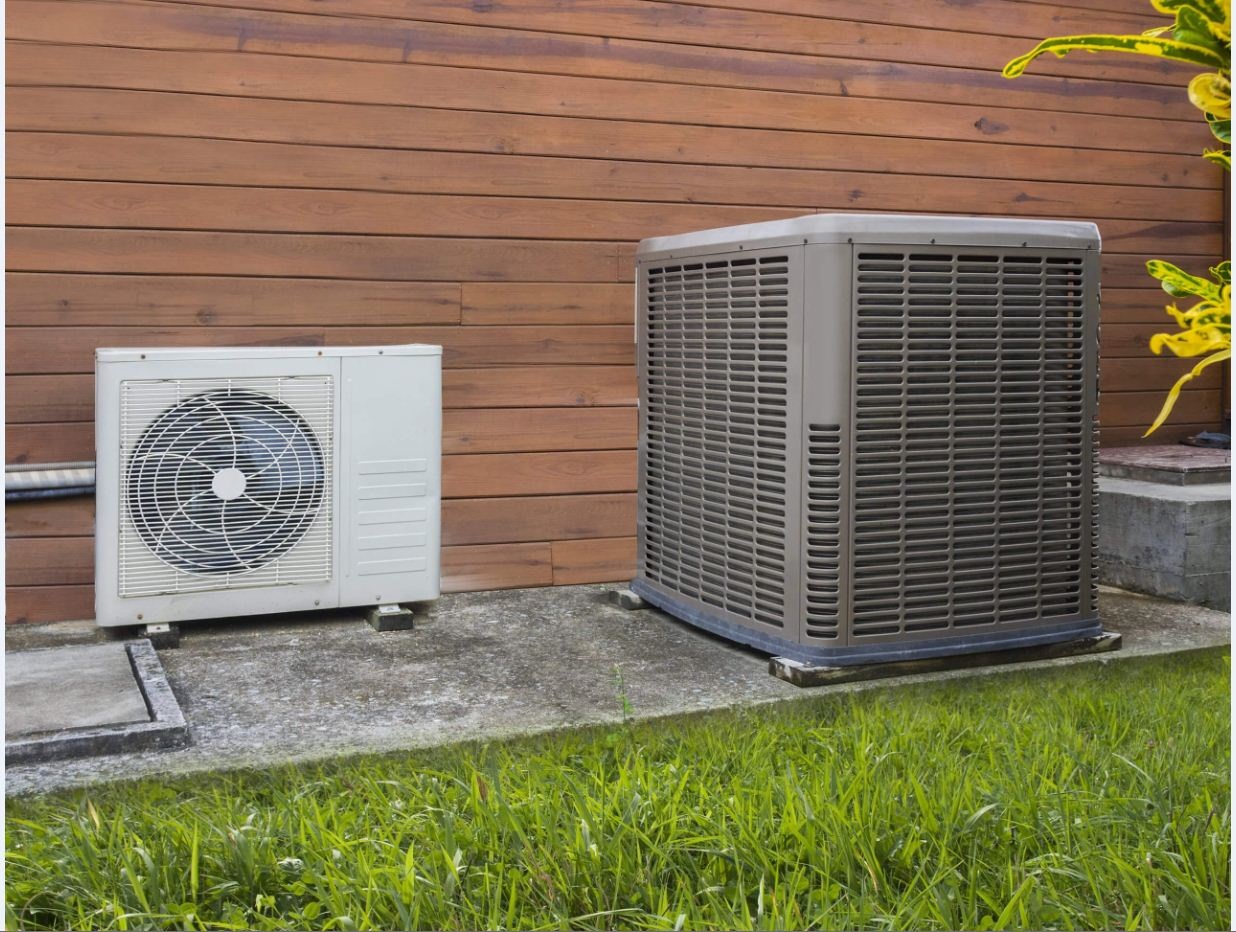
An air conditioner condenser is a vital component of an air conditioning system that is responsible for releasing heat energy from the indoor unit to the outside environment. It is typically located outside of the house and works in conjunction with the compressor and evaporator to maintain a comfortable temperature inside the home. The condenser is designed to facilitate the transfer of heat by utilizing a condensing coil and a fan.
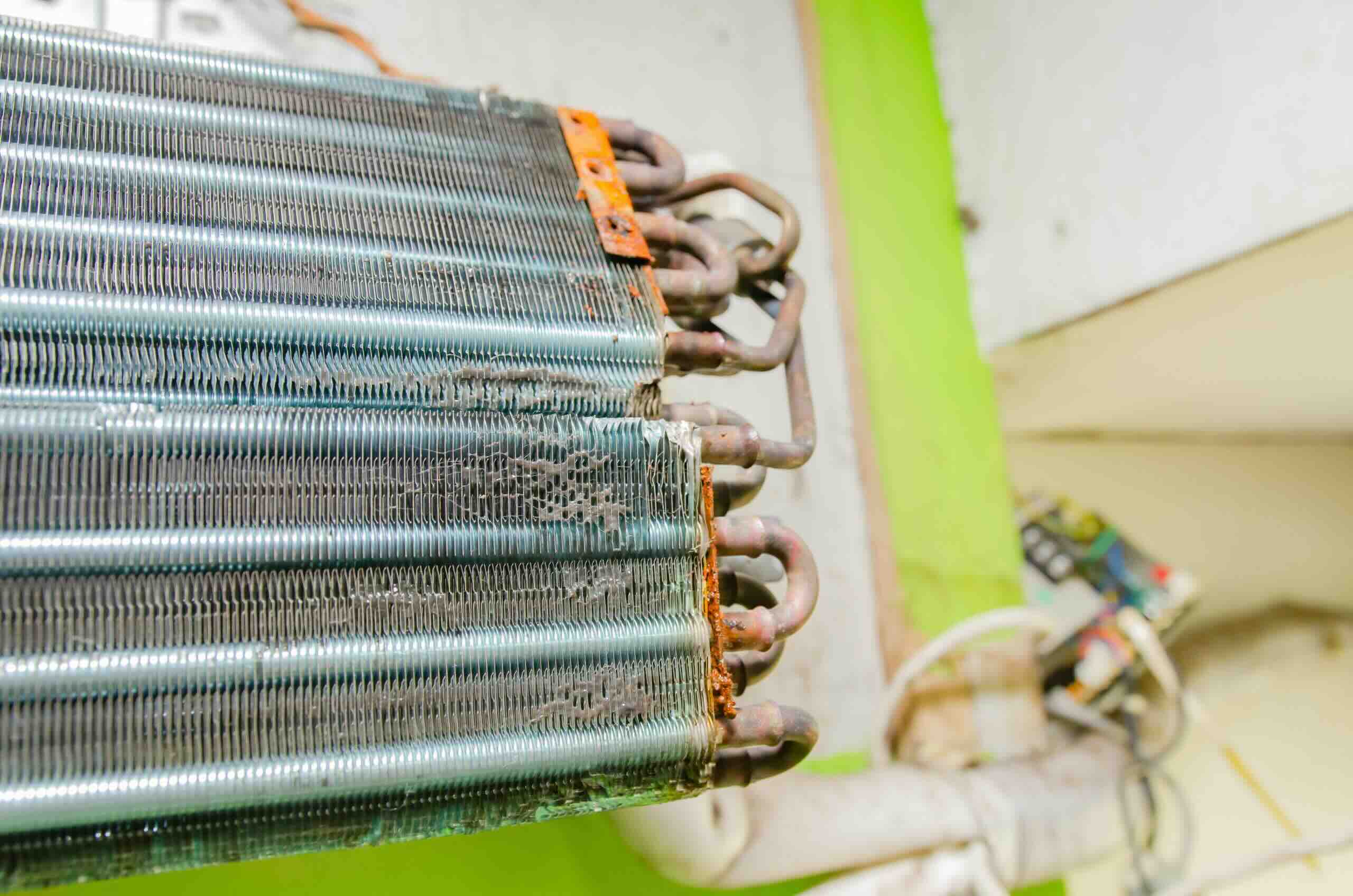
The condensing coil, which is made of copper or aluminum, is a series of pipes or tubes that are bent into a coil shape. Refrigerant flows through these coils, absorbing heat from the indoor air and carrying it to the condenser. The fan blows air over the condensing coil, which causes the refrigerant to release the absorbed heat. This process converts the high-pressure gas refrigerant back into a liquid state, allowing it to be cooled and prepared for circulation back to the evaporator.
One of the key features of an air conditioner condenser is the presence of a compressor. The compressor compresses the refrigerant, increasing its temperature and pressure before sending it to the condenser. This compression process allows for efficient heat transfer and helps maintain the cooling cycle of the air conditioning system.
Overall, the air conditioner condenser acts as a heat exchanger, expelling heat from the indoor unit to the outdoor environment. By removing heat from the indoor air and releasing it outside, the condenser plays a pivotal role in creating a comfortable and cool living space.
Components of an Air Conditioner Condenser
An air conditioner condenser consists of several key components that work together to facilitate the transfer of heat energy and ensure the efficient operation of the cooling system. Understanding the various parts of the condenser can provide insight into how the system functions and how to properly maintain it. Let’s take a closer look at the main components of an air conditioner condenser:
- Condensing Coil: The condensing coil is a crucial component of the condenser. It is made up of copper or aluminum tubes that are bent into a coil shape. The refrigerant flows through these coils, allowing heat energy to be transferred to the outside air.
- Compressor: The compressor plays a vital role in the condensing process. It is responsible for compressing the low-pressure refrigerant vapor, raising its temperature and pressure. This prepares the refrigerant for efficient heat transfer in the condensing coil.
- Fan: The condenser fan is located near the condensing coil and is responsible for drawing air over the coil. This airflow helps cool down the refrigerant, allowing it to release the absorbed heat into the outdoor environment.
- Condenser Motor: The condenser motor is responsible for driving the condenser fan. It provides the necessary power to ensure proper airflow over the condensing coil.
- Condenser Fan Blade: The fan blade is attached to the motor and is designed to efficiently move air across the condensing coil. It helps maximize heat transfer and ensures proper cooling of the refrigerant.
- Electrical Components: The condenser also contains various electrical components, such as capacitors, contactors, and relays. These components ensure the proper operation of the condenser motor and fan, allowing for effective heat dissipation.
- Refrigerant Lines: The condenser is connected to the indoor unit through refrigerant lines. These lines transport the refrigerant to and from the condenser, facilitating the heat transfer process between the indoor and outdoor units.
Each of these components plays a critical role in the functioning of an air conditioner condenser. Proper maintenance and regular inspections are essential to ensure that all components are in good working condition, maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of the condenser.
Functions of an Air Conditioner Condenser
The air conditioner condenser performs several important functions that are crucial for the proper operation of the cooling system. While its primary role is to release heat energy from the indoor unit to the outdoor environment, let’s explore in more detail the functions of an air conditioner condenser:
- Heat Dissipation: The main function of the condenser is to dissipate heat. As the refrigerant flows through the condensing coil, it releases heat energy to the surrounding air. The condenser fan helps facilitate this heat transfer process by blowing air over the coils, allowing the heat to be carried away from the system.
- Pressurization of Refrigerant: The condenser works in conjunction with the compressor to pressurize the refrigerant. Once the compressor compresses the low-pressure vapor, it sends it to the condenser. The condenser further increases the pressure of the refrigerant, preparing it for efficient heat transfer.
- Conversion of Refrigerant State: The condenser plays a key role in converting the refrigerant from a high-pressure gas to a high-pressure liquid. This state change occurs as the heat from the refrigerant is released to the outdoor environment. The condenser ensures that the refrigerant is in the proper state to continue the cooling cycle.
- Releasing Heat Energy: The condenser is responsible for releasing the heat energy that has been absorbed from the indoor air. This heat energy is expelled into the surrounding outdoor air, allowing the system to maintain the desired temperature inside the home.
- Transfer of Refrigerant: The condenser facilitates the transfer of refrigerant between the indoor and outdoor units of the air conditioning system. Through refrigerant lines, the condenser receives the low-pressure vapor from the indoor unit and sends back the high-pressure liquid refrigerant to continue the cooling process.
Overall, the functions of an air conditioner condenser are critical for maintaining a comfortable and cool indoor environment. Its ability to dissipate heat and properly pressurize the refrigerant ensures the efficient operation of the entire cooling system.
Types of Air Conditioner Condensers
There are different types of air conditioner condensers available, each designed to meet specific needs and fit different installations. The type of condenser used in an air conditioning system depends on factors such as available space, budget, and climate considerations. Let’s explore the most common types of air conditioner condensers:
- Air-Cooled Condenser: The air-cooled condenser is the most common type found in residential and commercial air conditioning systems. It utilizes outdoor air to dissipate heat from the refrigerant. This type of condenser consists of a condensing coil and a fan that blows air over the coil to cool the refrigerant. Air-cooled condensers are cost-effective, easy to install, and suitable for most climate conditions.
- Water-Cooled Condenser: As the name suggests, water-cooled condensers use water as the heat exchange medium. They require a water source, such as a cooling tower or a water supply line, to carry away the heat from the refrigerant. Water-cooled condensers are typically used in larger commercial or industrial applications where air-cooled units may not be feasible or efficient.
- Evaporative Condenser: Evaporative condensers combine the principles of both air-cooled and water-cooled condensers. They use water and air to cool the refrigerant. The condensing coil is surrounded by a wetting media, and as air passes through, water evaporates, removing heat from the coil. Evaporative condensers are efficient in hot and dry climates where water is readily available.
- Hybrid Condenser: Hybrid condensers combine different heat exchange technologies to maximize energy efficiency. For example, a hybrid condenser may use air-cooling during mild weather conditions and switch to water-cooling during peak load periods. This type of condenser is designed to optimize energy consumption and reduce operating costs.
- Remote Condenser: Remote condensers are typically used in commercial or industrial applications where the cooling unit is located far away from the condenser. The condenser is placed outside the building, and refrigerant lines connect it to the indoor unit. Remote condensers allow for flexibility in system design and can accommodate larger cooling capacities.
It is important to consult with a professional HVAC technician or contractor to determine the most suitable type of air conditioner condenser for your specific needs and installation requirements. Factors such as climate, available space, and budget should be taken into consideration to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
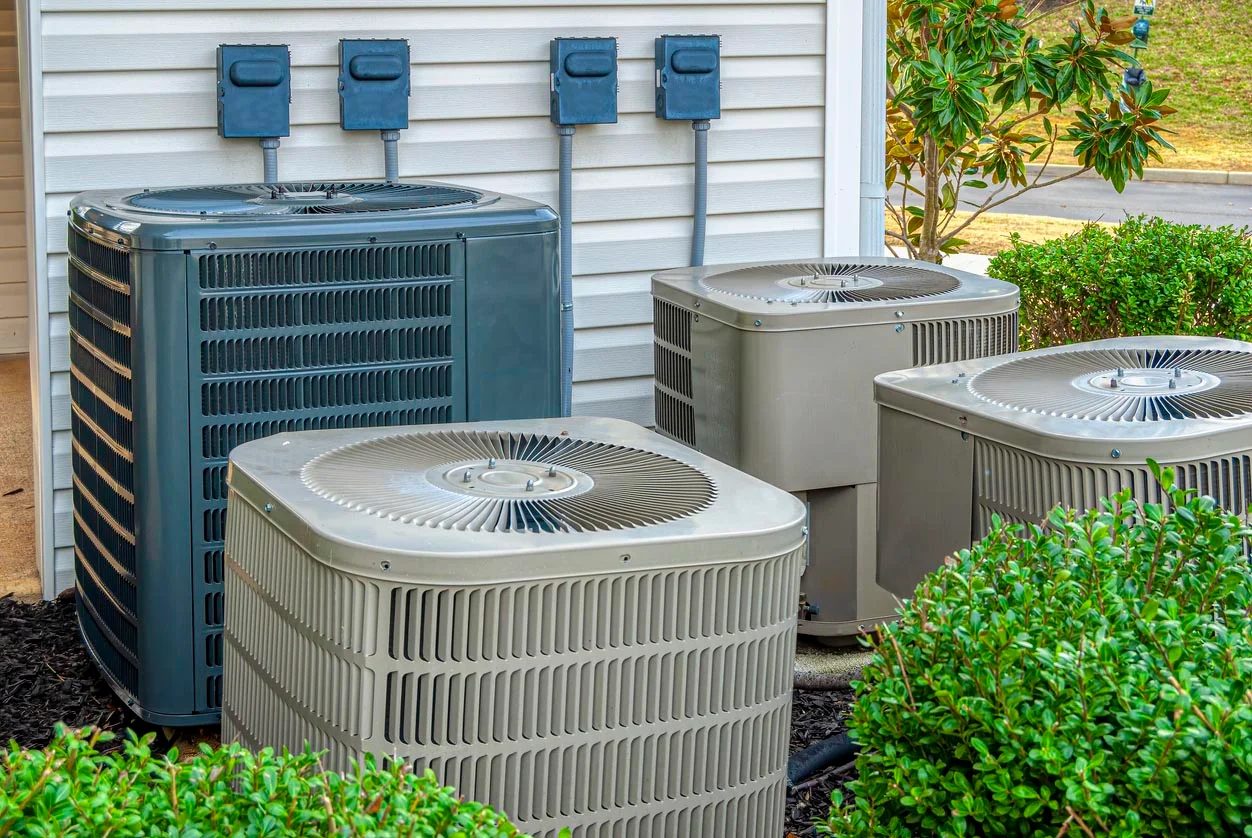
The air conditioner condenser is the outdoor unit of the air conditioning system. It releases heat from the refrigerant to the outside air, allowing the refrigerant to cool down and circulate back into the indoor unit to continue the cooling process. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the condenser coils, can help improve the efficiency and lifespan of the air conditioner.
How an Air Conditioner Condenser Works
The air conditioner condenser is a crucial component of the cooling system that plays a vital role in the heat transfer process. Understanding how an air conditioner condenser works can provide insights into its operation and the overall functioning of the air conditioning system. Let’s dive into the workings of an air conditioner condenser:
The process begins with the compressor, which compresses the low-pressure refrigerant vapor, raising its temperature and pressure. The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant then flows to the condenser.
Once inside the condenser, the refrigerant enters the condensing coils, which are typically made of copper or aluminum. These coils are designed to maximize surface area to facilitate efficient heat transfer. As the hot refrigerant flows through the condensing coils, it releases heat energy to the surrounding air.
The condenser fan, positioned near the condensing coils, plays a crucial role. It draws outdoor air over the coils, aiding the heat transfer process. As the fan blows air across the condensing coils, it carries away the heat from the refrigerant, allowing it to cool down and liquefy.
As the heat is removed from the refrigerant, it undergoes a phase change from a high-pressure gas to a high-pressure liquid state. This liquid refrigerant, now cooled down, continues its journey and is directed back to the indoor unit for further cooling.
To ensure efficient operation, the condenser fan and motor work in tandem. The motor powers the fan, allowing it to move air effectively over the condensing coils, optimizing heat transfer and cooling capacity.
It’s important to note that the outdoor temperature and airflow can impact the condenser’s efficiency. If the outdoor temperature is high or if the airflow is restricted, the condenser may struggle to release heat effectively. Regular maintenance, including cleaning the condensing coils and ensuring proper airflow, is essential to keep the condenser operating optimally.
The condenser is a crucial component in the air conditioning system, working in conjunction with other parts like the compressor and evaporator. By dissipating heat from the indoor unit to the outdoor environment, the condenser helps create a comfortable and cool living space.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips for Air Conditioner Condensers
Maintaining your air conditioner condenser is essential for its efficient operation and longevity. By following these maintenance and troubleshooting tips, you can ensure that your condenser continues to perform optimally, keeping your home cool and comfortable:
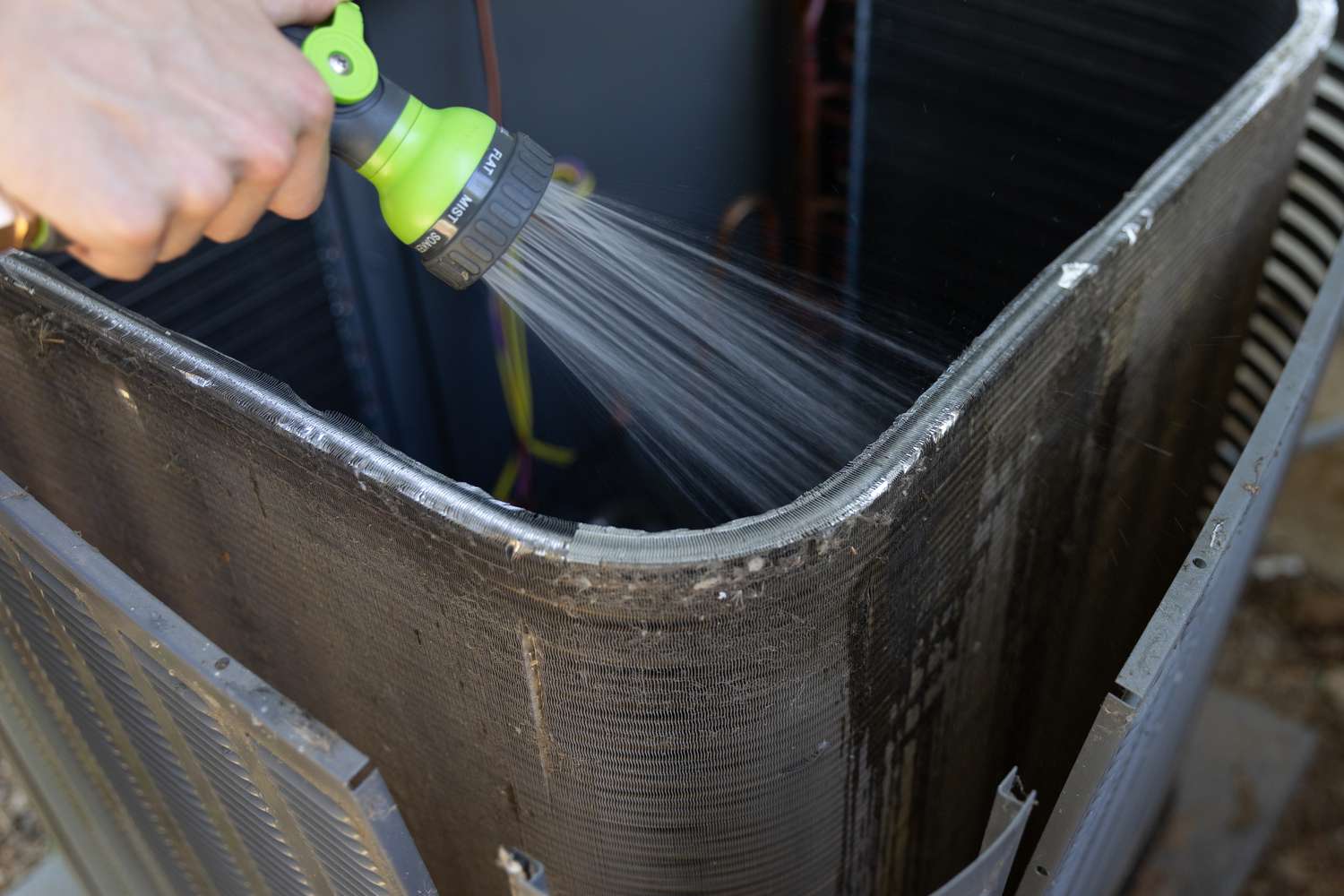
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the condensing coils clean and free from dirt, debris, and vegetation. Use a soft brush or a vacuum cleaner to gently remove any buildup on the coils. This will help maintain proper airflow and heat transfer.
- Clean the Condenser Fan: Ensure that the condenser fan is clean and in good working condition. Remove any dirt or debris that may have accumulated on the fan blades. A dirty or damaged fan can impede airflow and affect the condenser’s performance.
- Check for Refrigerant Leaks: Inspect the refrigerant lines and fittings for any signs of leaks, such as oil stains or hissing sounds. If you suspect a refrigerant leak, contact a professional HVAC technician to locate and repair the leak and recharge the refrigerant if necessary.
- Inspect Electrical Connections: Regularly check the electrical connections and terminals to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or faulty connections can lead to electrical issues and system malfunctions.
- Check the Condenser Fan Motor: Ensure that the condenser fan motor is functioning properly. Listen for any unusual noises, vibrations, or overheating. If you notice any problems, it’s best to have a qualified technician inspect and repair the motor.
- Maintain Proper Airflow: Keep the area around the condenser clear of obstructions, such as tall grass, shrubs, or debris. Maintain a distance of at least two feet around the unit to allow for proper airflow. Restricted airflow can cause the condenser to work harder and may lead to system inefficiencies.
- Check the Condensate Drain: Ensure that the condensate drain line is clear and free from obstructions. A clogged drain can lead to water backup and damage the unit. Regularly clean the drain and consider using a condensate line treatment to prevent buildup.
- Inspect and Replace Filters: Check and replace the air filters regularly to maintain good indoor air quality and improve system efficiency. Dirty filters can restrict airflow, making the condenser work harder to cool the air.
- Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on the performance of your air conditioner condenser. If you notice a decrease in cooling capacity, uneven cooling, or an increase in energy consumption, it may indicate a problem that requires professional attention.
It’s important to note that some maintenance tasks, such as refrigerant recharge or motor repairs, should be performed by qualified HVAC technicians. Regular professional maintenance is recommended to ensure the longevity and optimal functioning of your air conditioner condenser.
Common Issues with Air Conditioner Condensers and How to Fix Them
While air conditioner condensers are reliable and durable, they can experience issues over time. Understanding the common problems that can occur with condensers and knowing how to troubleshoot and fix them can help you avoid unnecessary expenses and keep your cooling system running smoothly. Here are some common issues with air conditioner condensers and how to fix them:
- Dirty Condenser Coils: Accumulated dirt, dust, and debris on the condenser coils can impede heat transfer and reduce the condenser’s efficiency. Fix: Regularly clean the condenser coils using a soft brush or vacuum cleaner. Ensure the power is turned off before attempting any cleaning.
- Blocked Condenser Fins: Bent or blocked condenser fins can restrict airflow and hinder heat dissipation. Fix: Use a fin comb or a soft brush to carefully straighten bent fins. Remove any debris or obstructions blocking the fins.
- Condenser Fan Issues: A malfunctioning condenser fan can cause poor heat transfer and system efficiency. Fix: Check the fan motor for issues such as worn-out bearings or faulty wiring. Replace the fan motor if necessary.
- Refrigerant Leaks: Refrigerant leaks can lead to reduced cooling capacity and damage to the condenser. Fix: If you suspect a refrigerant leak, contact a professional HVAC technician to locate and repair the leak and recharge the refrigerant if needed.
- Faulty Capacitor: A faulty capacitor can cause the condenser fan or compressor to stop working. Fix: Check the capacitor for signs of bulging or leaking. If it appears faulty, have it replaced by a professional technician.
- Electrical Issues: Loose connections, faulty wiring, or tripped breakers can cause the condenser to malfunction or not start at all. Fix: Inspect electrical connections and tighten any loose wires. Reset tripped breakers or replace faulty ones.
- Frozen Condenser: If the refrigerant levels are too low or airflow is restricted, the condensing coil can freeze, reducing cooling efficiency. Fix: Check the refrigerant levels and ensure proper airflow. Thaw the condenser by turning off the system and allowing it to defrost.
- Blocked Condensate Drain: A clogged condensate drain can cause water backup and potential damage to the unit. Fix: Clear any blockage from the condensate drain using a brush or suction. Consider using a condensate line treatment to prevent future clogs.
- Overheating: Overheating of the condenser can be caused by restricted airflow, malfunctioning fan motor, or dirty coils. Fix: Ensure proper airflow around the condenser by clearing any obstructions. Clean the coils and check the fan motor for issues.
- Insufficient Cooling: If the condenser is running but not providing adequate cooling, it may indicate problems with the compressor or refrigerant levels. Fix: Have a professional technician inspect the compressor and check refrigerant levels. They can diagnose and address the issue accordingly.
Remember, some of these issues require expert assistance. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with performing any troubleshooting or repairs, it’s best to seek the help of a qualified HVAC technician to ensure the proper diagnosis and resolution of the problem.
Energy Efficiency and Air Conditioner Condensers
Energy efficiency is a key consideration when it comes to air conditioning systems, and the air conditioner condenser plays a significant role in determining the overall energy efficiency of the system. An energy-efficient condenser not only helps reduce electricity consumption but also contributes to a greener and more sustainable environment. Let’s explore some factors related to energy efficiency and air conditioner condensers:
SEER Ratings: The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) is a measure of an air conditioner’s cooling efficiency. The SEER rating indicates the amount of cooling produced per unit of energy consumed. A higher SEER rating indicates greater energy efficiency. When selecting an air conditioner condenser, look for models with higher SEER ratings to ensure optimal energy efficiency.
Size and Capacity: Choosing the right size and capacity of the condenser is crucial for energy efficiency. An undersized condenser may struggle to cool the space adequately, leading to increased energy consumption as it works harder to meet the demand. Conversely, an oversized condenser may short-cycle, frequently turning on and off, which can decrease energy efficiency. Consult with an HVAC professional to determine the appropriate size and capacity for your specific cooling needs.
Proper Installation: Correct installation of the condenser is essential for optimal energy efficiency. Improper installation, such as incorrect refrigerant charge or inadequate airflow, can significantly impact the performance and efficiency of the system. Ensure that the condenser is installed by a qualified technician following manufacturer guidelines and industry best practices.
Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the air conditioner condenser is crucial for maintaining energy efficiency. Clean condenser coils, a well-functioning fan, and proper airflow are vital for effective heat transfer and optimal performance. Additionally, changing air filters regularly and inspecting electrical connections can help improve energy efficiency and prolong the lifespan of the condenser.
Smart Thermostats and Controls: Utilizing smart thermostats and controls can enhance energy efficiency by allowing you to program temperature settings, adjust cooling schedules, and monitor energy usage. These devices can help optimize comfort while minimizing energy waste, ensuring that the condenser operates efficiently.
Location and Shading: The location of the condenser can impact energy efficiency. Choose a location that is shaded or shielded from direct sunlight, as reducing heat exposure can improve cooling efficiency. Additionally, ensure that there is sufficient clearance around the condenser for proper airflow, as obstructions can impede its performance.
By considering these energy efficiency factors and implementing appropriate measures, you can ensure that your air conditioner condenser operates efficiently, reducing energy consumption, and saving on electricity bills. It’s important to consult with HVAC professionals to guide you in making informed decisions regarding energy-efficient condensers and optimizing the overall cooling system’s efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of the air conditioner condenser and its role in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment is crucial for any homeowner or HVAC professional. The condenser is responsible for dissipating heat, converting refrigerant, and facilitating the cooling process. By properly maintaining the condenser and addressing any issues that arise, you can ensure the efficient and reliable operation of your air conditioning system.
In this article, we explored the definition of an air conditioner condenser and its components, delving into its functions and the various types available. We also discussed how the condenser works, transferring heat energy from the indoor unit to the outdoor environment. Additionally, we provided maintenance and troubleshooting tips to help you keep your condenser in top shape.
We emphasized the importance of regular cleaning, checking electrical connections, and monitoring performance to ensure the condenser operates optimally. We also discussed common issues that can occur with condensers, providing troubleshooting steps to address these problems when they arise.
Finally, we discussed the role of energy efficiency in air conditioner condensers. By choosing high SEER-rated models, ensuring proper sizing and installation, and implementing smart thermostats and controls, you can maximize energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
In conclusion, by understanding the workings of the air conditioner condenser and implementing proper maintenance and energy-efficient practices, you can prolong the lifespan of your cooling system, minimize energy consumption, and enjoy a comfortably cooled home for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is An Air Conditioner Condenser
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.