Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Is A Dot Matrix Printer


Smart Home Devices
What Is A Dot Matrix Printer
Published: January 10, 2024
Discover the benefits and uses of dot matrix printers for smart home devices. Learn how they can enhance your home automation system. Explore the best options for your needs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of dot matrix printers! In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating realm of dot matrix printers, exploring their history, inner workings, advantages, disadvantages, common uses, and more. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a history buff, or simply curious about this iconic printing technology, join us on a journey through the evolution and impact of dot matrix printers.
Dot matrix printers have left an indelible mark on the history of printing, and their legacy continues to influence modern printing technologies. Let’s unravel the story behind these resilient and versatile machines, gaining insights into their unique capabilities and the niche they continue to occupy in various industries and applications.
Key Takeaways:
- Dot matrix printers, with their unique impact printing method, are durable and versatile, making them ideal for industrial environments, point-of-sale systems, and financial institutions where multipart forms and reliable output are essential.
- Despite the rise of modern inkjet and laser printers, dot matrix printers continue to thrive in niche markets, serving specific industries with their robustness, ability to withstand harsh conditions, and cost-effective printing solutions.
Read more: What Is Alexa Echo Dot
History of Dot Matrix Printers
The history of dot matrix printers dates back to the early days of computer technology. In the 1970s, as the demand for affordable and efficient printing solutions grew, the dot matrix printer emerged as a revolutionary alternative to traditional impact and daisy wheel printers. The concept of dot matrix printing originated from the need to produce high-quality text and graphics using a matrix of individual dots.
One of the pioneering companies in the development of dot matrix printers was Centronics, which introduced the first commercially successful dot matrix printer, the Centronics 101, in 1970. This innovative device utilized a grid of pins to create characters and graphics by striking an inked ribbon against the paper, leaving behind a series of closely spaced dots. The impact of these pins on the ribbon transferred ink to the paper, resulting in printed output.
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, dot matrix printers gained widespread popularity due to their reliability, durability, and ability to produce carbon copies. They became the preferred choice for businesses, government agencies, and home users, offering a cost-effective solution for printing documents, invoices, labels, and more. As technology advanced, dot matrix printers evolved to incorporate improved print heads, faster speeds, and enhanced graphics capabilities, further solidifying their position in the printing landscape.
Despite the advent of inkjet and laser printers, dot matrix printers continued to thrive in specific niches, such as industrial settings, point-of-sale systems, and environments requiring multipart forms and continuous paper. Their ability to withstand harsh conditions, print on various paper types, and produce legible carbon copies made them indispensable in sectors such as logistics, manufacturing, and finance.
Today, while dot matrix printers have become less prevalent in mainstream consumer markets, they remain integral to certain industries where their unique capabilities outshine those of other printing technologies. The rich history and enduring relevance of dot matrix printers underscore their enduring legacy in the ever-evolving world of printing.
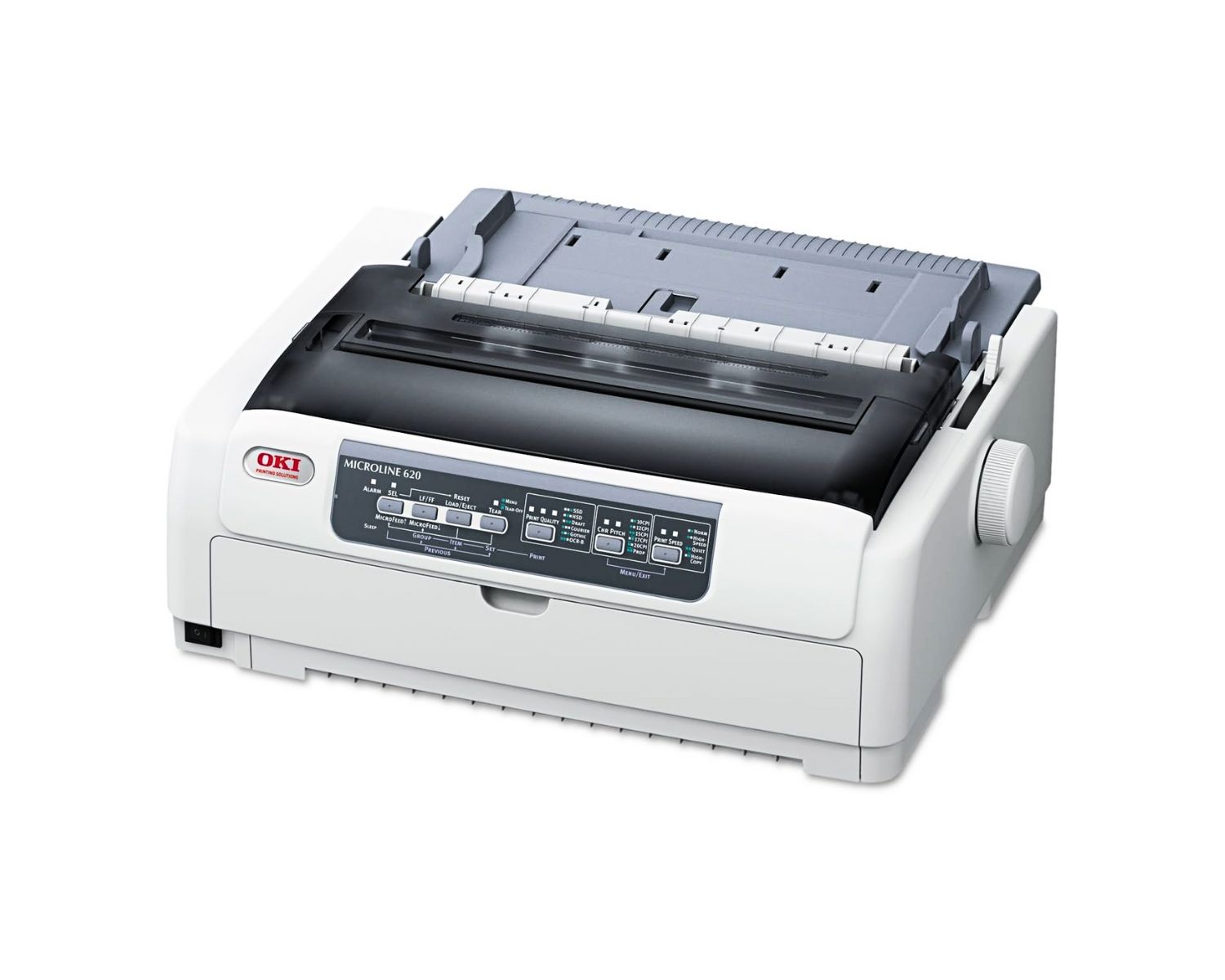
How Dot Matrix Printers Work
Dot matrix printers operate on a fascinating principle that involves the precise coordination of tiny pins to create characters, graphics, and images on paper. Unlike modern inkjet and laser printers, dot matrix printers rely on impact printing, where a matrix of pins strikes an inked ribbon to produce a pattern of dots on the paper.
At the heart of a dot matrix printer is the print head, which contains a grid of closely spaced pins arranged in a matrix formation. The most common configurations are 9-pin, 18-pin, or 24-pin, with higher pin counts enabling greater print quality and detail. When a print command is initiated, the print head moves horizontally across the paper, while the paper advances vertically, allowing the pins to strike the inked ribbon at precise locations to form characters and images.
Each pin in the print head can be individually activated, allowing for the creation of various dot patterns. By striking the inked ribbon against the paper, the pins leave behind a series of closely spaced dots, forming alphanumeric characters, symbols, and graphics. The impact of the pins on the ribbon transfers ink to the paper, resulting in the desired output.
Dot matrix printers are capable of producing both text and graphics with varying levels of quality, depending on the pin count and print density. The use of multipart forms, continuous paper, and carbon copies is one of the key strengths of dot matrix printers, making them ideal for applications requiring multiple copies of documents or forms.
Another notable feature of dot matrix printers is their adaptability to different paper types, including multipart forms, continuous stationery, and single sheets. This versatility allows them to excel in environments where specialized printing requirements are prevalent, such as in industrial settings, logistics, and point-of-sale systems.
Despite the rise of modern printing technologies, dot matrix printers continue to be valued for their robustness, ability to operate in harsh conditions, and cost-effectiveness in specific applications. Their unique method of operation and enduring relevance in niche markets highlight the enduring appeal of dot matrix printers in the ever-changing landscape of printing technology.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dot Matrix Printers
Dot matrix printers, with their distinctive impact printing mechanism, offer a unique set of advantages and disadvantages compared to other types of printers. Understanding these characteristics is essential for evaluating their suitability for specific printing needs.
Advantages:
- Robustness: Dot matrix printers are known for their durability and ability to withstand challenging operating conditions. This makes them well-suited for industrial environments and applications where reliability is paramount.
- Multi-Part Forms: One of the key strengths of dot matrix printers is their capability to produce multipart forms and carbon copies, making them indispensable for tasks requiring duplicate or triplicate documents.
- Versatility: Dot matrix printers can handle a variety of paper types, including continuous stationery, multipart forms, and single sheets, catering to diverse printing requirements in specialized industries.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In certain scenarios, dot matrix printers offer a cost-effective solution for high-volume printing needs, especially when the demand for multipart forms or continuous stationery is prevalent.
- Reliable in Harsh Environments: Their robust construction and impact printing method make dot matrix printers reliable in environments where dust, moisture, and other harsh conditions may affect the performance of other printer types.
Read more: What Are The Black Dots On Car Windows
Disadvantages:
- Print Quality: While dot matrix printers excel in producing multipart forms and carbon copies, their print quality for high-resolution graphics and images is limited compared to modern inkjet and laser printers.
- Noisy Operation: The impact printing mechanism of dot matrix printers results in audible noise during operation, which may be a consideration in environments where noise levels need to be minimized.
- Speed: Although some dot matrix printers offer reasonable speeds, they generally lag behind modern inkjet and laser printers in terms of overall printing speed, especially for high-quality output.
- Limited Color Options: Dot matrix printers predominantly produce monochrome output, limiting their suitability for applications requiring full-color printing.
- Ongoing Maintenance: The need for regular ribbon replacement and maintenance of the print head is a consideration for users of dot matrix printers, adding to the overall cost of ownership.
By weighing these advantages and disadvantages, businesses and individuals can make informed decisions regarding the adoption of dot matrix printers, particularly in scenarios where their unique strengths align with specific printing requirements.
Common Uses of Dot Matrix Printers
Despite the proliferation of modern inkjet and laser printers, dot matrix printers continue to play a vital role in various industries and applications, leveraging their unique capabilities to meet specific printing needs. From industrial settings to specialized printing requirements, dot matrix printers have found enduring relevance in the following common uses:
1. Industrial Environments
Dot matrix printers are well-suited for industrial applications where robustness, reliability, and the ability to operate in challenging conditions are essential. They are commonly utilized in manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and logistics centers for printing labels, invoices, shipping documents, and other essential paperwork.
2. Point-of-Sale Systems
In retail and hospitality environments, dot matrix printers are employed in point-of-sale (POS) systems to generate receipts, order tickets, and transaction records. Their ability to produce multipart forms and carbon copies makes them ideal for capturing transaction details and providing duplicate copies for customers and business records.
Read more: What Are The Buttons On Alexa Echo Dot
3. Financial Institutions
Due to their capability to produce multipart forms and continuous stationery, dot matrix printers remain prevalent in financial institutions for printing checks, deposit slips, account statements, and other critical documents that require duplicate copies for record-keeping and customer transactions.
4. Manufacturing and Logistics
Within the manufacturing and logistics sectors, dot matrix printers are utilized for printing shipping labels, inventory tags, packing slips, and other documentation essential for tracking and managing goods throughout the supply chain. Their reliability and ability to produce legible output on various paper types make them indispensable in these environments.
5. Specialized Applications
Dot matrix printers are also employed in specialized applications that require multipart forms, such as medical record-keeping, data logging, and industrial automation. Their versatility in handling multipart forms, continuous stationery, and carbon copies makes them well-suited for tasks that demand duplicate documentation and reliable print output.
While the prevalence of dot matrix printers in mainstream consumer markets has diminished, their enduring presence in these common uses underscores their continued relevance in specific industries and applications. The unique strengths of dot matrix printers, including their robustness, ability to produce multipart forms, and reliability in challenging environments, position them as indispensable tools in niche printing requirements.
Conclusion
The evolution of dot matrix printers has woven a rich tapestry of innovation, resilience, and enduring relevance in the realm of printing technology. From their early days as pioneers of impact printing to their continued presence in specialized industries and applications, dot matrix printers have left an indelible mark on the landscape of printing solutions.
While modern inkjet and laser printers have become ubiquitous in homes and offices, the unique strengths of dot matrix printers, including their robustness, ability to produce multipart forms, and reliability in challenging environments, position them as indispensable tools in niche printing requirements. Their enduring legacy is a testament to their adaptability and unwavering relevance in specific sectors where their capabilities outshine those of other printing technologies.
As we reflect on the journey of dot matrix printers, it becomes evident that their impact extends far beyond their mechanical components and printing capabilities. They embody a legacy of resilience, versatility, and adaptability, serving as a testament to the enduring value of purpose-driven technology in an ever-changing world.
Whether in industrial environments, point-of-sale systems, financial institutions, or specialized applications, dot matrix printers continue to play a vital role, meeting the specific printing needs of diverse sectors with unwavering reliability and precision. Their ability to produce legible output on various paper types, withstand harsh conditions, and fulfill the demand for multipart forms and carbon copies reinforces their position as indispensable assets in the printing landscape.
As the technological landscape continues to evolve, the legacy of dot matrix printers serves as a reminder that innovation is not solely defined by the latest advancements, but also by the enduring relevance and adaptability of proven technologies in meeting specialized needs. The story of dot matrix printers is a testament to the enduring value of purpose-driven technology and the timeless impact of innovation in shaping the world of printing.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Dot Matrix Printer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is A Dot Matrix Printer”