Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Is The Difference Between Modem And Wi-Fi Router


Smart Home Devices
What Is The Difference Between Modem And Wi-Fi Router
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover the variances between a modem and Wi-Fi router to enhance your smart home devices. Learn how they function and optimize your network.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
**
Introduction
**
In the era of interconnectedness and digital innovation, the home network has become a hub for various smart devices, enabling seamless communication and access to a wealth of online resources. At the heart of this network are two essential components: the modem and the Wi-Fi router. While both are integral to establishing a reliable and high-speed internet connection, they serve distinct functions that are crucial for the smooth operation of a modern smart home.
Understanding the difference between a modem and a Wi-Fi router is essential for optimizing home networking capabilities and ensuring a stable and efficient internet connection. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the distinct roles of these devices, highlighting their unique functionalities and shedding light on the key differences between them. By gaining insight into the inner workings of modems and Wi-Fi routers, you will be better equipped to harness the full potential of your home network and elevate your digital lifestyle.
Key Takeaways:
- Modems connect your home to the internet, while Wi-Fi routers distribute the internet connection to all your devices wirelessly, making it easy for you to go online without any cables.
- Modems and Wi-Fi routers have different jobs – modems link your home to the internet, and Wi-Fi routers spread the internet connection to all your devices without using cables.
Read more: What Is The Best Cable Modem Wi-Fi Router
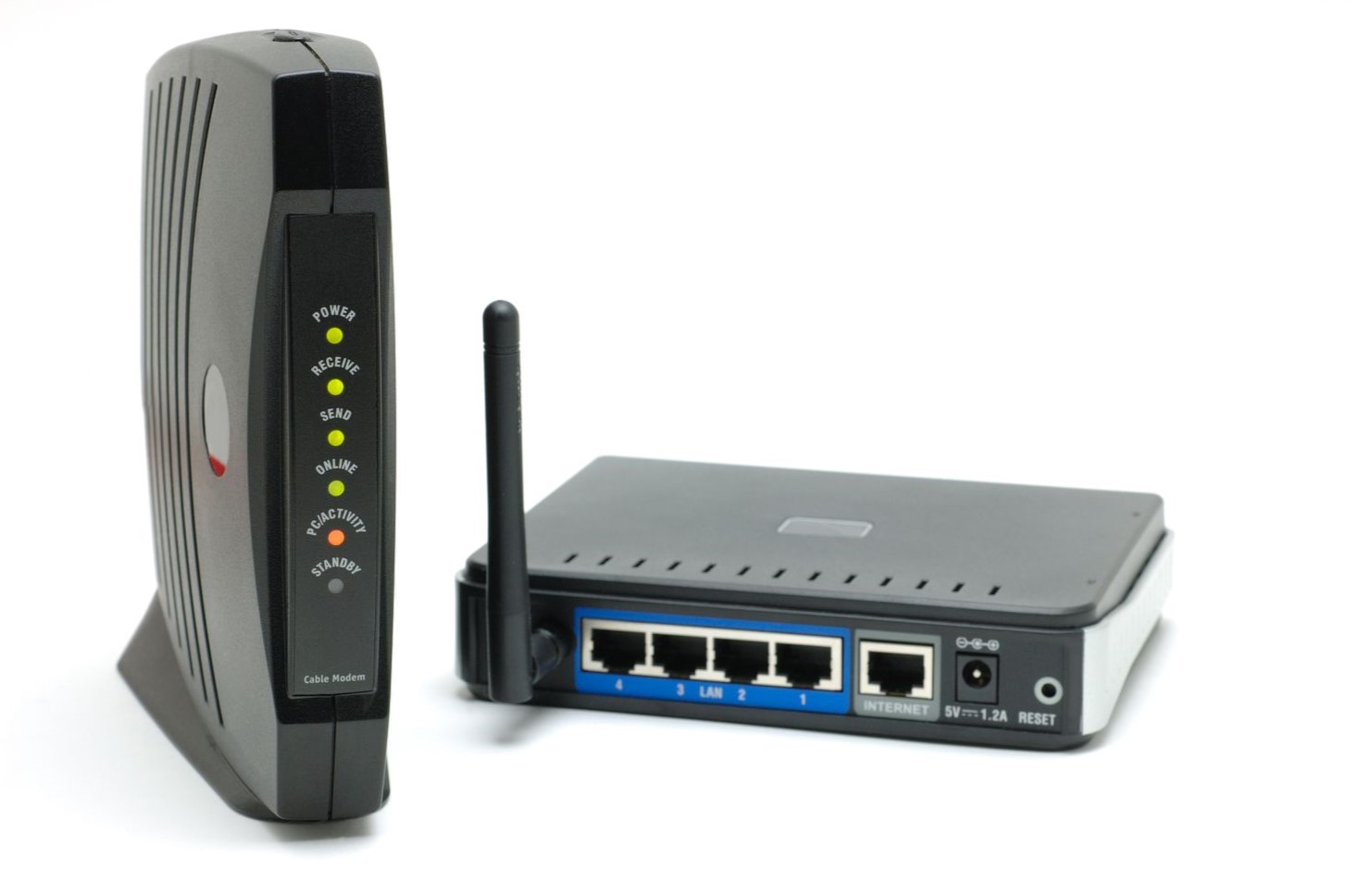
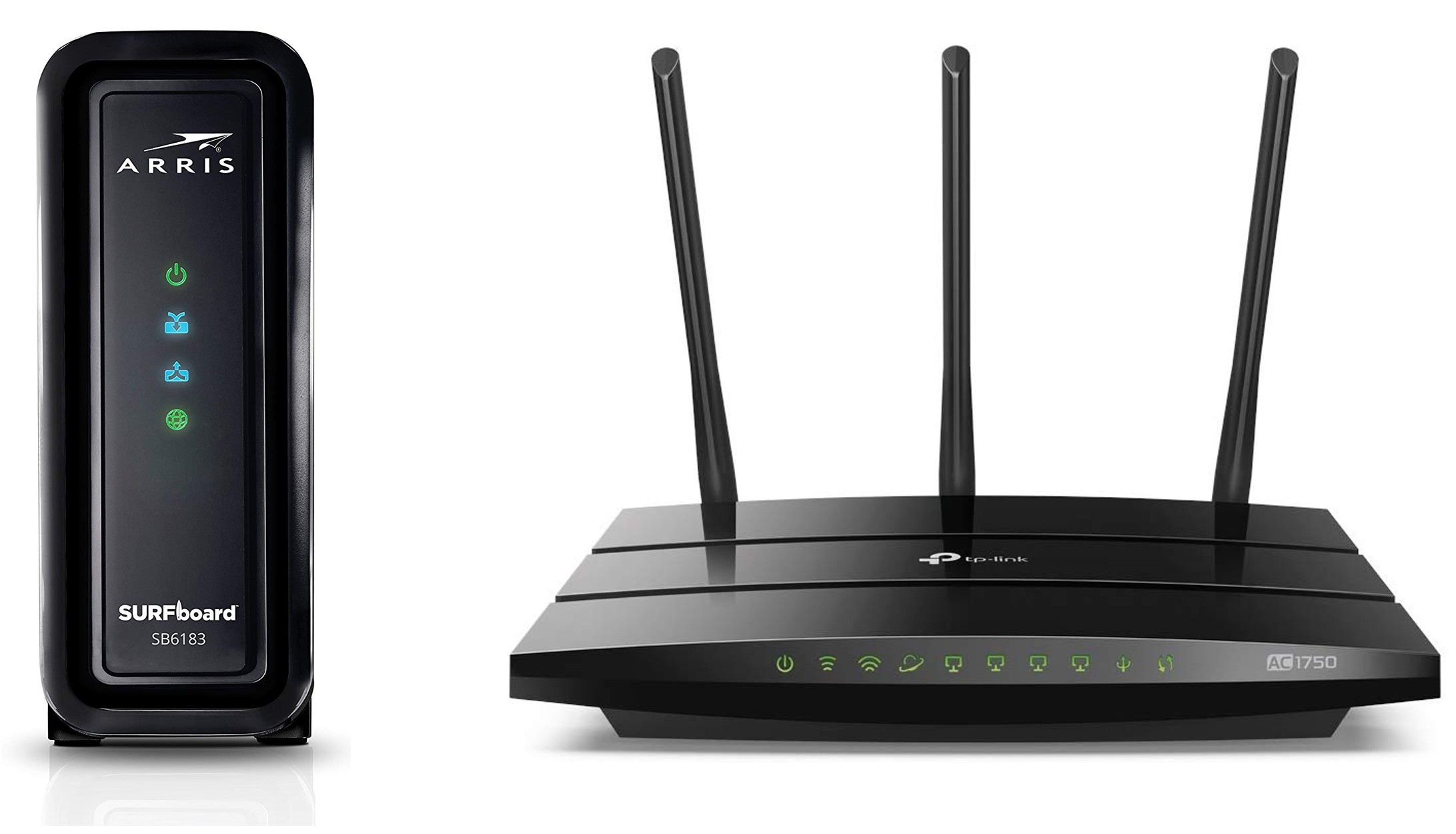
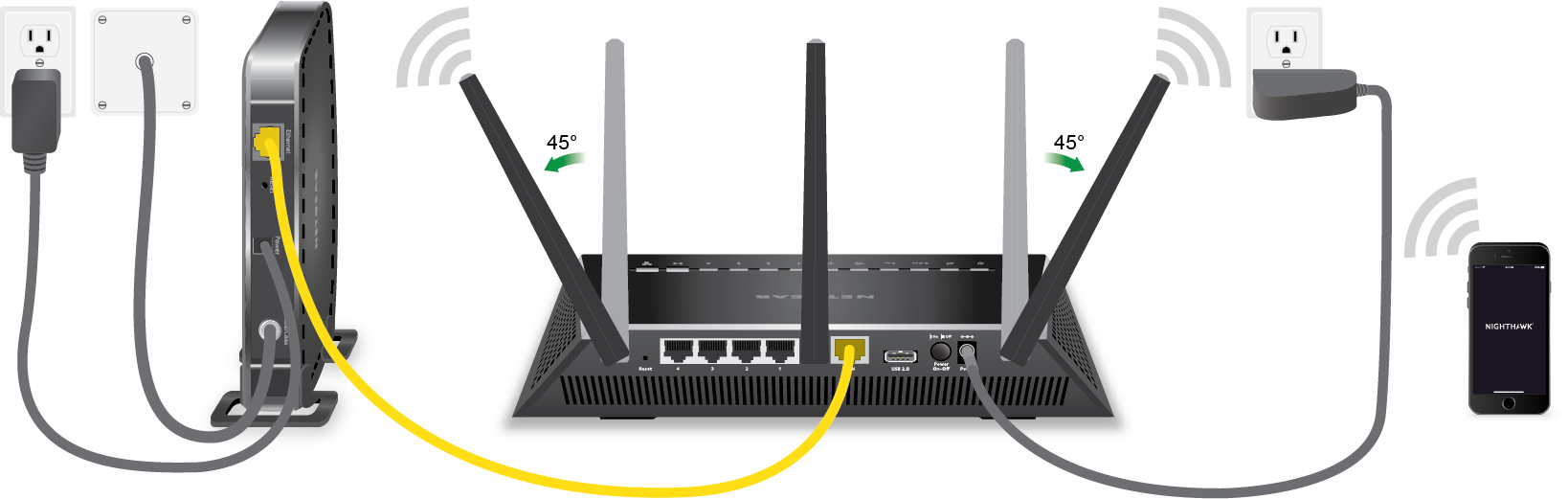
Function of a Modem
At the core of every home internet connection lies the modem, a device that plays a pivotal role in establishing a link between your home network and your Internet Service Provider (ISP). The term “modem” is derived from “modulator-demodulator,” reflecting its primary function of modulating and demodulating analog signals to facilitate the transmission of digital data over communication channels.
When you initiate an online activity, such as browsing the web or streaming content, your requests are transmitted as digital data packets. These packets are then converted into analog signals by the modem, allowing them to be transmitted over the physical infrastructure of your ISP’s network. Conversely, when data is received from the internet, the modem demodulates the analog signals back into digital data packets that can be interpreted by your devices.
Modems come in various types, including DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), cable, fiber-optic, and satellite modems, each tailored to accommodate specific types of internet connections. For instance, DSL modems are designed to work with telephone lines, while cable modems are optimized for cable television infrastructure. Fiber-optic modems leverage optical fibers to transmit data at incredibly high speeds, making them ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications.
It’s important to note that a modem solely facilitates the transfer of data between your home network and your ISP, acting as a gateway to the internet. However, it does not possess the capability to distribute this internet connection to multiple devices within your home. This is where the Wi-Fi router comes into play, functioning as a crucial intermediary that enables wireless connectivity and network distribution.
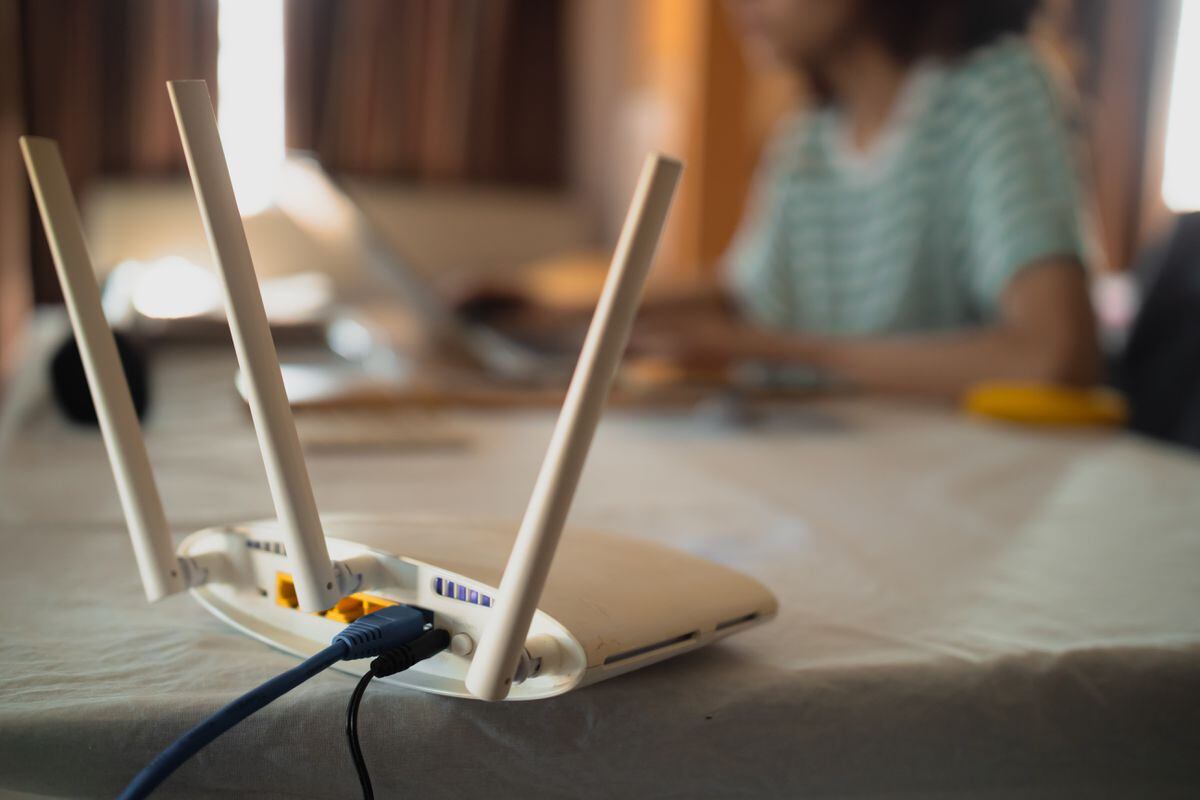
Function of a Wi-Fi Router
While the modem establishes the primary link between your home network and the internet, the Wi-Fi router serves as a pivotal component responsible for distributing this internet connection to a multitude of devices within your household. In essence, the Wi-Fi router acts as a central hub, facilitating wireless communication between your various smart devices and the modem, thereby enabling seamless access to the internet.
One of the key functions of a Wi-Fi router is to create a local area network (LAN) within your home, allowing devices such as smartphones, laptops, smart TVs, and IoT gadgets to connect to the internet without the need for physical cables. This is achieved through the wireless access point integrated into the router, which emits Wi-Fi signals that can be picked up by compatible devices within its range.
Furthermore, Wi-Fi routers are equipped with advanced security features such as encryption protocols and firewalls, safeguarding your home network from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats. This ensures that your personal data and online activities remain protected, contributing to a secure and reliable online experience.
Modern Wi-Fi routers often incorporate dual-band or tri-band technology, allowing them to operate on multiple frequencies simultaneously. This not only enhances the overall network performance but also enables the segregation of devices based on their bandwidth requirements, thereby optimizing the distribution of internet resources.
Moreover, many contemporary Wi-Fi routers are equipped with advanced features such as Quality of Service (QoS) settings, which enable users to prioritize specific types of internet traffic, ensuring that bandwidth-intensive applications such as video streaming and online gaming receive optimal network resources.
By seamlessly integrating the modem’s internet connection with a wireless network and providing advanced networking features, the Wi-Fi router plays a crucial role in transforming your home into a digitally connected and efficient ecosystem.
A modem connects your home to the internet, while a Wi-Fi router allows multiple devices to connect to the internet wirelessly. Think of the modem as the gateway to the internet, and the router as the traffic cop directing internet traffic to different devices.
Key Differences Between Modem and Wi-Fi Router
While both the modem and the Wi-Fi router are integral components of a home network, they serve distinct functions and exhibit fundamental differences in their operation and capabilities. Understanding these disparities is essential for optimizing your home networking setup and ensuring a seamless internet experience. Here are the key differences between modems and Wi-Fi routers:
- Primary Function: The primary function of a modem is to establish a connection between your home network and your Internet Service Provider (ISP), facilitating the transmission of data to and from the internet. In contrast, a Wi-Fi router functions as a central hub that distributes the internet connection received from the modem to multiple devices within your household, enabling wireless connectivity and local area network (LAN) creation.
- Wired vs. Wireless Connectivity: Modems typically provide a wired connection to the internet, allowing devices to connect directly via Ethernet cables. On the other hand, Wi-Fi routers enable wireless connectivity, emitting Wi-Fi signals that allow compatible devices to connect to the internet without physical cables.
- Network Distribution: While a modem only facilitates the transmission of data to and from the internet, a Wi-Fi router is equipped with the capability to create a local network and distribute the internet connection to multiple devices, enabling seamless connectivity throughout your home.
- Security Features: Modems generally do not include advanced security features beyond basic firewall functionalities. In contrast, Wi-Fi routers are equipped with robust security measures such as encryption protocols, firewalls, and guest network capabilities, ensuring the protection of your home network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Wireless Access Point: A modem does not include a wireless access point, meaning it cannot emit Wi-Fi signals for wireless device connectivity. Conversely, a Wi-Fi router is specifically designed to serve as a wireless access point, allowing devices to connect to the internet without physical cables.
- Advanced Networking Features: Wi-Fi routers often incorporate advanced networking features such as dual-band or tri-band technology, Quality of Service (QoS) settings, and device prioritization, enabling optimized network performance and resource allocation. Modems, in contrast, focus solely on facilitating the transfer of data between your home network and the ISP.
By comprehending these fundamental differences, you can effectively harness the capabilities of both the modem and the Wi-Fi router, ensuring a robust and efficient home network that caters to the diverse connectivity needs of modern smart homes.
Conclusion
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the significance of modems and Wi-Fi routers in shaping our connected lifestyles cannot be overstated. These two devices, each with its distinct functions and capabilities, form the backbone of our home networks, enabling seamless internet connectivity and empowering the myriad smart devices that enhance our daily lives.
By understanding the unique roles of modems and Wi-Fi routers, you are better equipped to optimize your home network, ensuring reliable and efficient internet access for all your connected devices. The modem serves as the gateway to the internet, establishing the crucial link between your home network and your Internet Service Provider, while the Wi-Fi router acts as a central hub, distributing this internet connection to a multitude of devices wirelessly.
Moreover, recognizing the disparities between these devices allows you to make informed decisions when setting up or upgrading your home network. Whether it’s selecting the appropriate modem for your specific type of internet connection or choosing a Wi-Fi router with advanced networking features to cater to your household’s connectivity needs, a deeper understanding of these devices empowers you to create a robust and tailored home network.
As we embrace the era of smart homes and interconnected devices, the synergy between modems and Wi-Fi routers plays a pivotal role in shaping our digital experiences. By harnessing the capabilities of these devices, you can create a seamless and efficient home network that not only meets your current connectivity requirements but also adapts to the ever-evolving demands of the digital age.
In essence, the modem and Wi-Fi router, with their distinct yet complementary functionalities, form the cornerstone of a modern home network, paving the way for a connected lifestyle that seamlessly integrates the digital world into our daily routines.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Difference Between Modem And Wi-Fi Router
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.















0 thoughts on “What Is The Difference Between Modem And Wi-Fi Router”