

Articles
How Do Digital Calipers Work
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover how digital calipers work and their importance in precision measurements. Read our informative articles to understand their features and applications.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Digital calipers are a vital tool in various industries, providing precise and accurate measurements for a wide range of applications. With their advanced technology and user-friendly interface, they have revolutionized the way measurements are taken. In this article, we will delve into the workings of digital calipers, exploring their components, working principles, and applications.
Whether you’re a machinist, carpenter, engineer, or hobbyist, understanding how digital calipers work can help you make more informed decisions and achieve greater precision in your work. So, let’s dive into the world of digital calipers and uncover their fascinating inner workings.
First, let’s start with a brief overview of digital calipers.
Key Takeaways:
- Digital calipers provide precise and reliable measurements through advanced sensor technology and versatile measurement modes, making them indispensable across industries and hobbies.
- Understanding the working principles, components, and limitations of digital calipers is crucial for maximizing their accuracy, precision, and longevity in various applications.
Read more: How Do You Read Calipers
Overview of Digital Calipers
Digital calipers, also known as electronic calipers, are measuring instruments that provide precise and accurate measurements of length, thickness, depth, and diameter. They are an evolution of traditional vernier calipers and offer several advantages over their analog counterparts.
One of the key features of digital calipers is their digital display, which provides instant and accurate readings. This eliminates the need for manual interpretation and reduces the chances of human error. The digital display typically shows measurements in millimeters (mm), inches (in), or both, depending on the user’s preference.
Digital calipers come in various sizes, with the most common being 6-inch and 8-inch models. They are constructed using high-quality materials such as stainless steel, ensuring durability and resistance to wear and tear.
In addition to their measurement capabilities, digital calipers often include features such as zero-setting, hold function, and data output. These features allow users to perform various tasks efficiently and simplify data collection.
Now that we have a general understanding of digital calipers, let’s explore their key components.
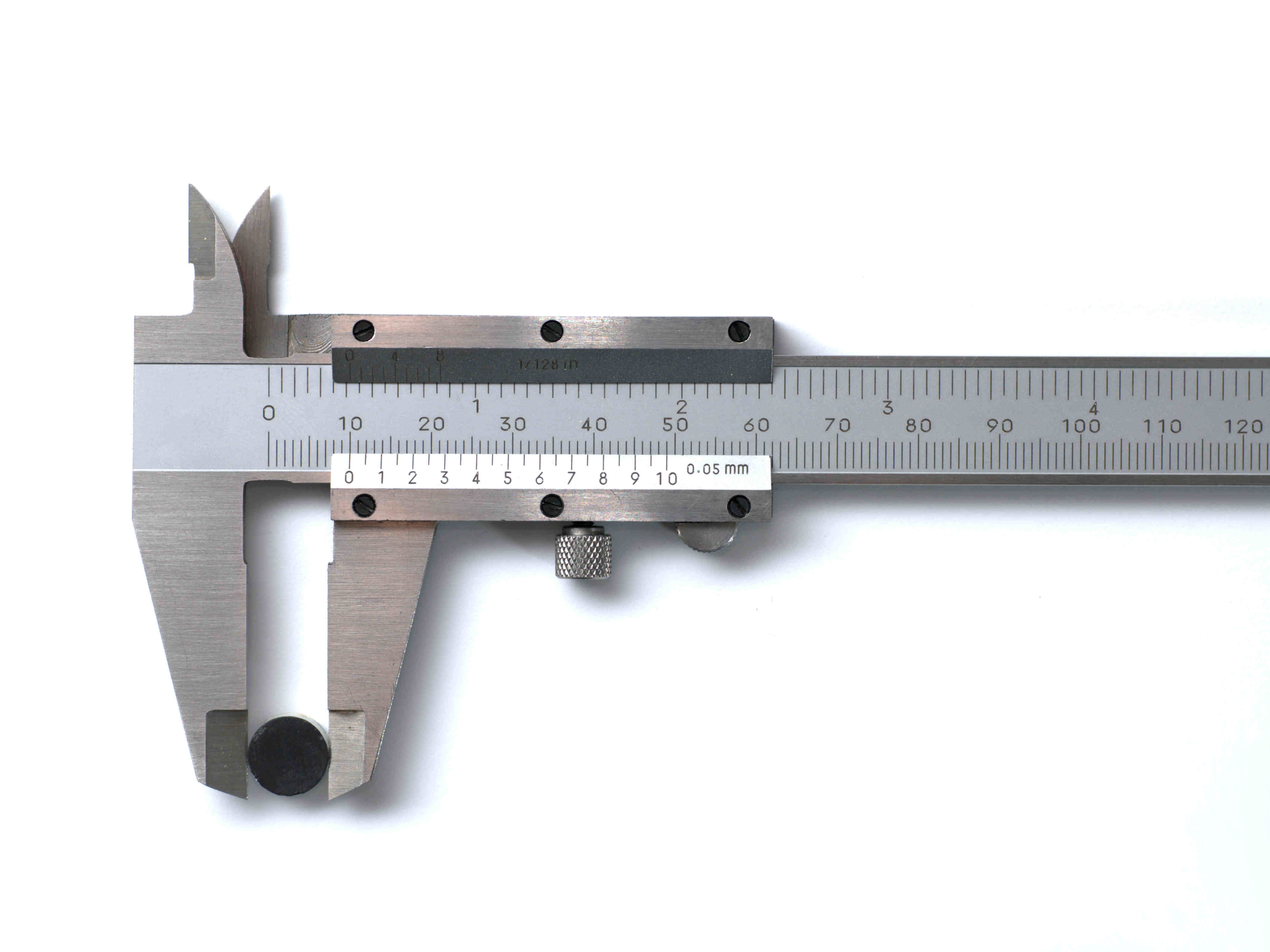
Components of Digital Calipers
Digital calipers consist of several key components that work together to provide precise and accurate measurements. Let’s take a closer look at these components:
- Measuring Jaws: The measuring jaws are the two arms of the caliper that come in contact with the object being measured. These jaws are usually made of hardened stainless steel to ensure durability and resistance to wear. The upper jaw is fixed, while the lower jaw is movable, allowing for easy adjustment and measurement.
- Scale: The scale is the linear measurement scale engraved on the upper part of the caliper. It allows users to read measurements up to the maximum range of the caliper. The scale is usually marked in millimeters (mm) and inches (in), providing versatility for different measurement systems.
- Slider: The slider is the part of the caliper that moves along the scale when the lower jaw is adjusted. It is connected to the digital sensor and transmits the measurement data for display.
- Digital Sensor: The digital sensor is the heart of the digital caliper. It is responsible for converting the linear movement of the slider into a digital signal for measurement display. The digital sensor uses advanced technology, such as capacitive or inductive sensors, to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Display: The display is where the measurement readings are shown. It is usually an LCD screen that provides clear and easy-to-read measurements. The display may also include additional features, such as buttons for zero-setting, mode selection, and data hold.
- Battery Compartment: Many digital calipers are powered by batteries, typically button cells. The battery compartment is where the batteries are inserted to supply power to the caliper. Some models also offer rechargeable battery options for convenience.
These components work seamlessly together to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. Now that we understand the components, let’s move on to explore the working principles of digital calipers.
Working Principles of Digital Calipers
The working principles of digital calipers are based on the conversion of linear movement into digital signals. Let’s explore how these calipers operate:
When the lower jaw of the caliper is adjusted to measure an object, the slider moves along the scale. As the slider moves, it activates the digital sensor, which converts the linear movement into electrical signals. The digital sensor utilizes advanced technologies, such as capacitive or inductive sensors, to detect the position of the slider precisely.
These electrical signals are then processed by the internal circuitry of the caliper. The circuitry translates the signals into a digital format that can be displayed on the screen. The digital display shows the precise measurement reading, providing instant feedback to the user.
In addition to the measurement display, digital calipers often offer other features that enhance usability and efficiency. These features may include zero-setting, allowing the user to set the reference point for measurements, and a data hold function, which freezes the displayed measurement for easy recording and comparison.
Furthermore, some digital calipers have the capability to output measurement data for further analysis or documentation. They can be connected to a computer or data logging device using a cable or wireless connection. This feature is especially valuable in industries that require data recording and analysis.
The working principles of digital calipers ensure precise and accurate measurements with minimal human error. The combination of digital sensors, internal circuitry, and advanced technology guarantees reliable results for various applications.
Now that we have a good understanding of how digital calipers work, let’s delve into the digital sensor technology used in these instruments.
Digital Sensor Technology
The digital sensor technology used in digital calipers plays a crucial role in their precision and accuracy. Two commonly used sensor technologies in digital calipers are capacitive sensors and inductive sensors. Let’s explore these technologies:
1. Capacitive Sensors: Capacitive sensors work by measuring the change in capacitance between two conductive plates. When the lower jaw of the caliper moves, the distance between the plates changes, resulting in a change in capacitance. This change is detected and converted into a digital signal, which is then displayed as the measured value. Capacitive sensors are known for their high accuracy and reliability.
2. Inductive Sensors: Inductive sensors utilize the principle of electromagnetic induction. When the lower jaw of the caliper moves, it changes the proximity between a coil and a metal target on the slider. This change in proximity induces a current in the coil, which is then converted into a digital signal. Inductive sensors are valued for their robustness and resistance to environmental influences.
The choice between capacitive and inductive sensors depends on factors such as the application requirements and the desired level of accuracy. Both sensor technologies offer precise and reliable measurements, ensuring the performance of digital calipers in various industries.
It is worth noting that some digital calipers may utilize hybrid sensor technologies, combining the benefits of capacitive and inductive sensors. This hybrid approach may further enhance the accuracy and versatility of the calipers.
Now that we have covered the digital sensor technology, let’s move on to explore the different measurement modes available in digital calipers.
When using digital calipers, make sure to keep the measuring surfaces clean and free of debris to ensure accurate measurements. Regular maintenance and calibration are also important for reliable performance.
Read more: Why Do Calipers Stick
Measurement Modes of Digital Calipers
Digital calipers offer various measurement modes, allowing users to adapt to different measurement requirements. Let’s explore the common measurement modes available in these instruments:
- External Measurement: This mode is used to measure the external dimensions of an object, such as the width or diameter. The user places the object between the measuring jaws, ensuring a firm and stable contact, and reads the measurement displayed on the digital screen.
- Internal Measurement: In this mode, the user can measure the internal dimensions of an object, such as the inner diameter or width. The caliper’s jaws are adjusted to fit inside the object, and the measurement is displayed on the screen.
- Depth Measurement: Digital calipers also provide a depth measurement mode, allowing users to measure the depth of holes, slots, or recesses. The lower jaw is extended beyond the upper jaw, and the caliper is inserted into the hole or slot until the desired depth is reached. The depth measurement is then displayed on the screen.
- Step Measurement: This mode is used to measure the difference in height between two surfaces or steps. The user places the caliper on the lower surface and moves the slider until the upper jaw contacts the higher surface. The height difference is displayed on the screen.
Some digital calipers also offer additional measurement modes, such as tolerance setting, which allows users to set upper and lower limits for measurements. The caliper will indicate if a measurement falls within or outside the specified tolerance range.
By offering these measurement modes, digital calipers provide versatility and adaptability to different measurement scenarios. They simplify the measuring process and allow users to obtain accurate and reliable measurements in various applications.
Now that we understand the different measurement modes, let’s explore the concepts of accuracy and precision in digital calipers.
Accuracy and Precision of Digital Calipers
Accuracy and precision are two important factors to consider when using digital calipers for measurements. While they are related, they have distinct meanings:
Accuracy: In the context of digital calipers, accuracy refers to how closely the measured value corresponds to the true value of the object being measured. It represents the calibration and reliability of the caliper’s measurements. Accurate digital calipers provide measurements that are close to the actual dimensions of the object.
Precision: Precision, on the other hand, refers to the repeatability and consistency of the measurements. It indicates the degree to which repeated measurements of the same object yield similar results. A precise digital caliper produces consistent readings when measuring the same object multiple times.
Manufacturers usually provide information about the accuracy and precision of their digital calipers. This information is typically expressed as an accuracy rating, often denoted as “+/-X” or “±X”, where X represents a value in millimeters or inches. For example, an accuracy rating of +/-0.01 mm means that the caliper can provide measurements within a range of 0.01 mm accuracy.
It is important to note that accuracy and precision can be affected by various factors, such as environmental conditions, user technique, and the quality of the caliper itself. To maintain accuracy and precision, calibrating the digital caliper regularly is recommended. Calibrating involves comparing the measurements of the caliper against a known standard to ensure its accuracy and make any necessary adjustments.
When using digital calipers, it is essential to understand both the accuracy and precision of the instrument. Depending on the requirements of your application, you may prioritize one over the other. For applications that require highly precise measurements, it is crucial to choose a caliper with a high precision rating.
Now that we have explored accuracy and precision, let’s move on to discuss the common applications of digital calipers.
Common Applications of Digital Calipers
Digital calipers find widespread use in various industries and professions due to their accuracy, precision, and versatility. Let’s explore some of the common applications where digital calipers are essential tools:
- Engineering and Manufacturing: In engineering and manufacturing fields, digital calipers are invaluable for measuring dimensions of components, parts, and prototypes. They are used in machining, metalworking, 3D printing, and quality control processes to ensure precise and accurate measurements for a proper fit and functionality.
- Woodworking and Carpentry: Woodworkers and carpenters rely on digital calipers to measure dimensions such as thickness, width, and depth of materials. They are particularly useful for ensuring accurate joinery, setting up milling machines, and creating precise cuts for furniture making and cabinetry.
- Automotive and Aerospace: In automotive and aerospace industries, digital calipers are used for various applications, including measuring engine components, brake parts, and body panel thickness. They play a crucial role in maintaining quality standards and ensuring precise fitment of parts.
- Jewelry and Gemology: Digital calipers are widely used in jewelry making and gemology to measure gemstones, diamonds, and metal components. Their precise measurements allow jewelers to create exquisite pieces and ensure proper stone settings.
- Medical and Dental: Digital calipers are utilized in medical and dental fields for measurements during surgeries, orthodontic procedures, and prosthesis fabrication. They provide accurate measurements for precise fitting and alignment of implants, braces, and other medical devices.
- Hobbyists and DIY Enthusiasts: Digital calipers are popular among hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts for various projects such as model making, electronics assembly, and woodworking. They help hobbyists achieve precise measurements and ensure accurate assembly and alignment.
These are just a few examples of the wide-ranging applications of digital calipers. They are versatile tools that find utility in almost any field that involves precise dimensional measurements.
Before concluding, let’s briefly discuss the limitations and considerations when using digital calipers.
Limitations and Considerations
While digital calipers are highly accurate and reliable tools, there are certain limitations and considerations to keep in mind when using them:
- Measurement Range: Digital calipers have a limited measurement range, typically ranging from a few inches to around 20 inches. It is important to choose a caliper that suits the measurement needs of your specific application.
- Environmental Factors: Extreme temperatures, humidity, and magnetic fields can affect the performance of digital calipers. It is important to store and use them in controlled environments to maintain accuracy and prevent damage.
- Battery Life: Digital calipers rely on batteries for power. It is essential to keep spare batteries on hand and monitor the battery life to ensure uninterrupted operation. Some models offer low battery indicators to alert users when the battery needs to be replaced.
- Proper Usage: To obtain accurate measurements, it is crucial to use digital calipers correctly. Ensure the object being measured is clean, properly aligned with the measuring jaws, and securely held to prevent any movement or slippage during measurement.
- Calibration: Digital calipers should be calibrated regularly to maintain their accuracy and precision. This can be done by comparing the measurements against a known standard or with the help of calibration services or tools.
- Physical Limitations: Digital calipers have a limited level of physical robustness. Dropping or mishandling the caliper can damage its internal components, affect accuracy, or cause malfunction. Handle the caliper with care to prevent any damage.
Considering these limitations and taking proper precautions will help maximize the performance and longevity of your digital calipers. It is important to refer to the manufacturer”s guidance and user manuals for specific usage instructions and maintenance guidelines.
To conclude, digital calipers are highly versatile and accurate tools that find applications across various industries and hobbies. Their ability to provide precise and reliable measurements makes them indispensable for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Whether you’re a machinist, woodworker, jeweler, or medical professional, digital calipers will undoubtedly enhance your measurement capabilities, improve accuracy, and streamline your processes.
As technology continues to advance, digital calipers will likely evolve further, offering enhanced features and greater measurement capabilities. So, embrace the digital revolution in caliper technology and take advantage of the power and precision these tools provide.
Read more: Why Do Calipers Lock Up
Conclusion
Digital calipers have revolutionized the way we measure and ensure precision in various industries and hobbies. With their advanced technology, accurate measurements, and user-friendly features, they have become indispensable tools for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
In this article, we explored the inner workings of digital calipers, including their components, working principles, and measurement modes. We also discussed the importance of accuracy and precision in these tools and their common applications in engineering, woodworking, jewelry making, and more.
However, it’s important to remember that like any tool, digital calipers have their limitations and considerations. From being mindful of environmental factors to regular calibration, proper usage ensures optimal performance and longevity.
As technology continues to advance in the field of digital calipers, we can expect even more precise measurements, additional features, and further convenience in the future.
So, whether you’re a professional in the manufacturing industry, a hobbyist working on DIY projects, or someone who values precision in their work, digital calipers are an indispensable tool that will provide accurate and reliable measurements time and time again.
Embrace the digital revolution in measurement and unleash your potential for greater precision and accuracy with digital calipers!
Frequently Asked Questions about How Do Digital Calipers Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Do Digital Calipers Work”