

Articles
How Does A Refrigerator Compressor Work
Modified: October 29, 2024
Learn how a refrigerator compressor works in this informative article. Understand the principles behind cooling and the role of the compressor in keeping your food fresh.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Refrigerators are an essential appliance in every household, keeping our food fresh and preserving it for longer. But have you ever wondered how a refrigerator actually works? At the heart of this ingenious cooling system lies the refrigerator compressor, a crucial component that plays a vital role in maintaining the desired temperature inside the appliance.
In this article, we will explore the inner workings of a refrigerator compressor, its components, and the step-by-step process of refrigeration. We will also discuss the different types of compressors and common issues that may arise, along with troubleshooting tips.
Understanding how a refrigerator compressor operates can not only help you appreciate the functionality of this everyday appliance but also empower you with the knowledge to troubleshoot any potential problems.
So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of refrigerator compressors and discover the magic behind keeping our food fresh and cool.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the refrigeration cycle and the components of a refrigerator compressor can empower you to troubleshoot common issues and appreciate the intricate workings of this essential appliance.
- Different types of compressors, such as reciprocating, rotary, screw, scroll, and centrifugal, offer unique advantages and are suited for specific applications, contributing to the efficiency and performance of refrigeration systems.
Read more: How Does A AC Compressor Work
Basics of Refrigeration
Before we delve into the specifics of how a refrigerator compressor works, it’s important to understand the basic principles of refrigeration. Refrigeration is the process of removing heat from a space to lower its temperature, thus creating a cool environment.
This cooling process is achieved through a cycle of evaporation and condensation of a refrigerant, a substance with low boiling and freezing points. The refrigerant, such as Freon or R-134a, circulates through the refrigerator’s system, absorbing heat from the inside and releasing it outside, therefore cooling the interior.
When the refrigerator is turned on, the refrigerant enters the evaporator coil located inside the appliance. As it enters, it has a low pressure and temperature. The warm air from within the refrigerator comes into contact with the cold evaporator coil, causing the refrigerant to absorb the heat from the air.
As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it evaporates and changes from a liquid to a gas. This gas then flows into the compressor, where it is compressed, resulting in an increase in temperature and pressure.
From the compressor, the high-pressure gas travels to the condenser coil located on the exterior of the refrigerator. Here, the heat from the gas is released into the surrounding environment, causing the refrigerant to condense back into a liquid state.
After the condensation process, the liquid refrigerant travels through an expansion valve, where its pressure is reduced, creating a low-pressure and low-temperature environment. The refrigerant then re-enters the evaporator coil, and the cycle repeats.
This continuous cycle of evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion allows the refrigerator to maintain a cool temperature inside, while expelling the heat generated by the cooling process to the outdoors.
Now that we have grasped the basics of refrigeration, let’s move on to understanding the components of a refrigerator compressor and their functions.
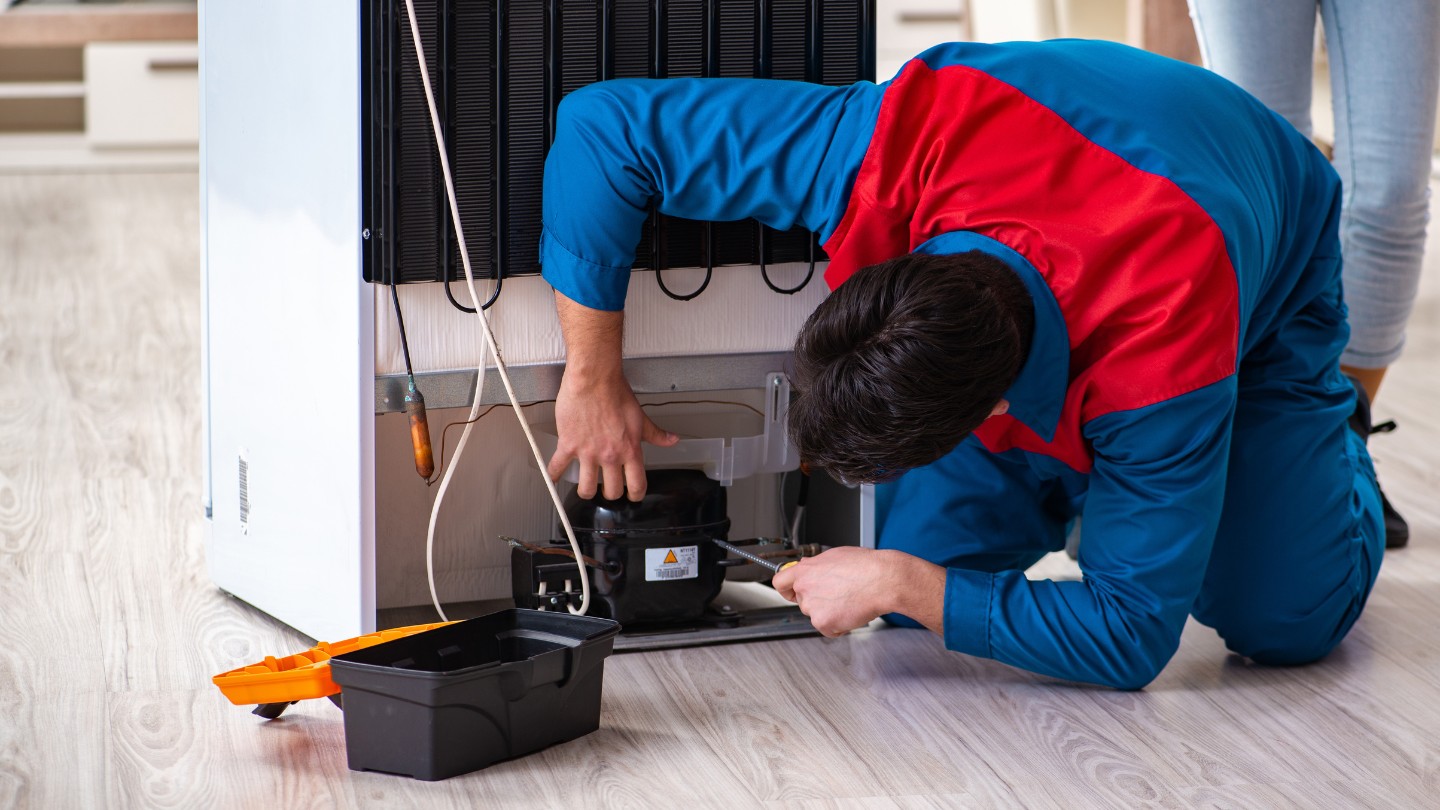
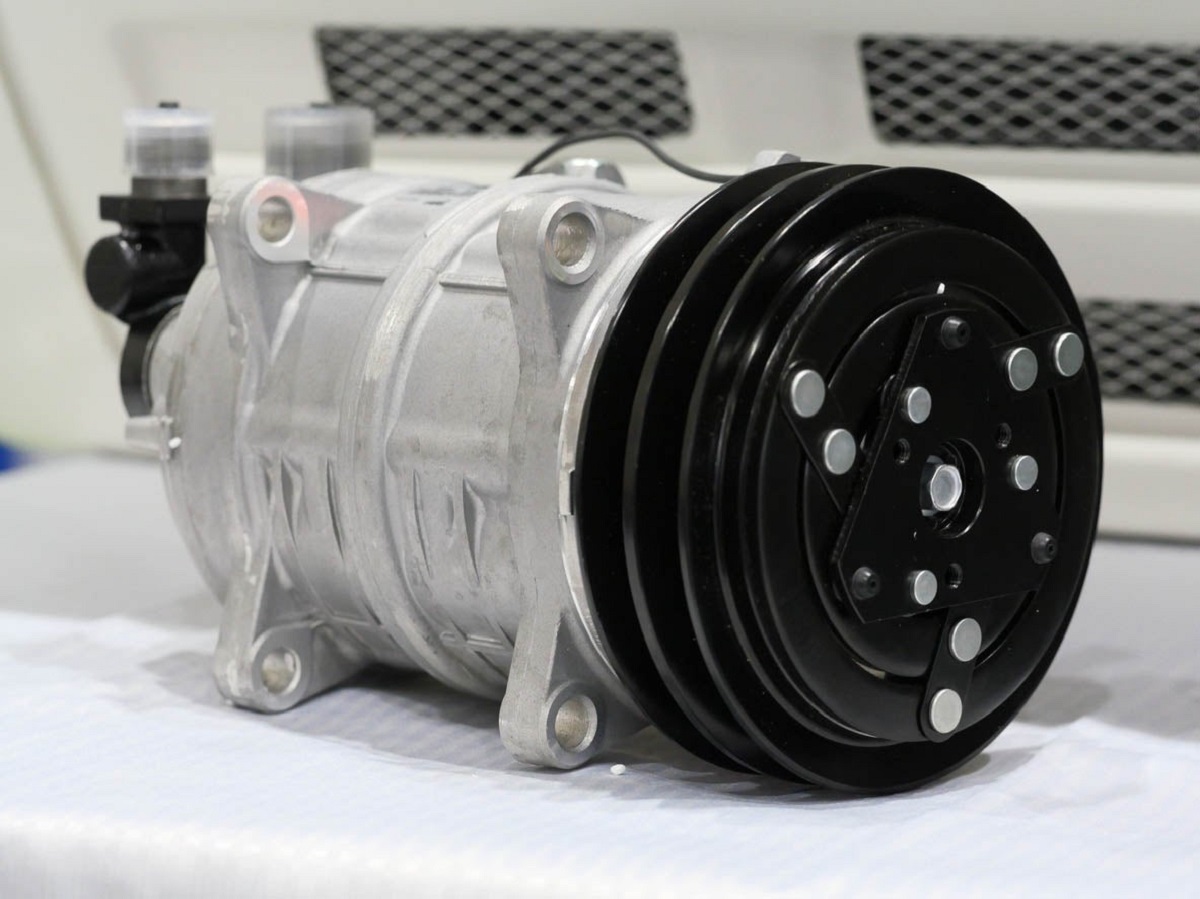
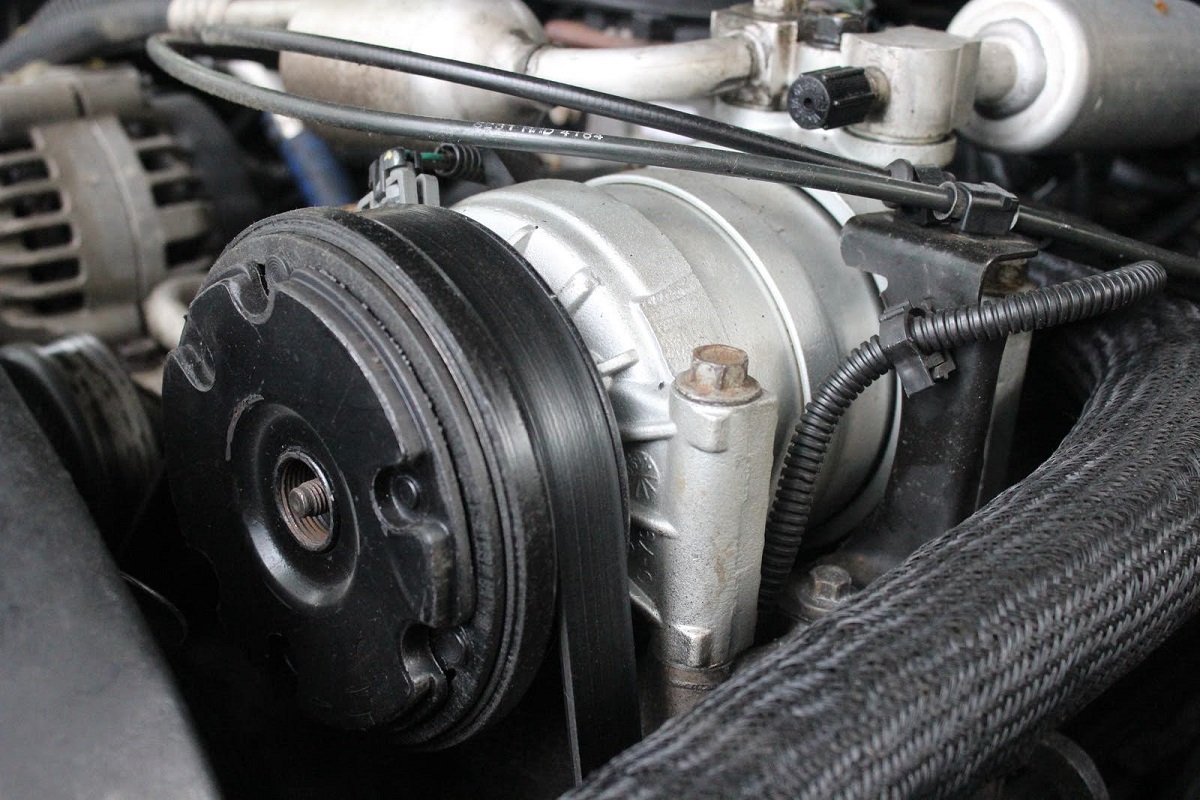
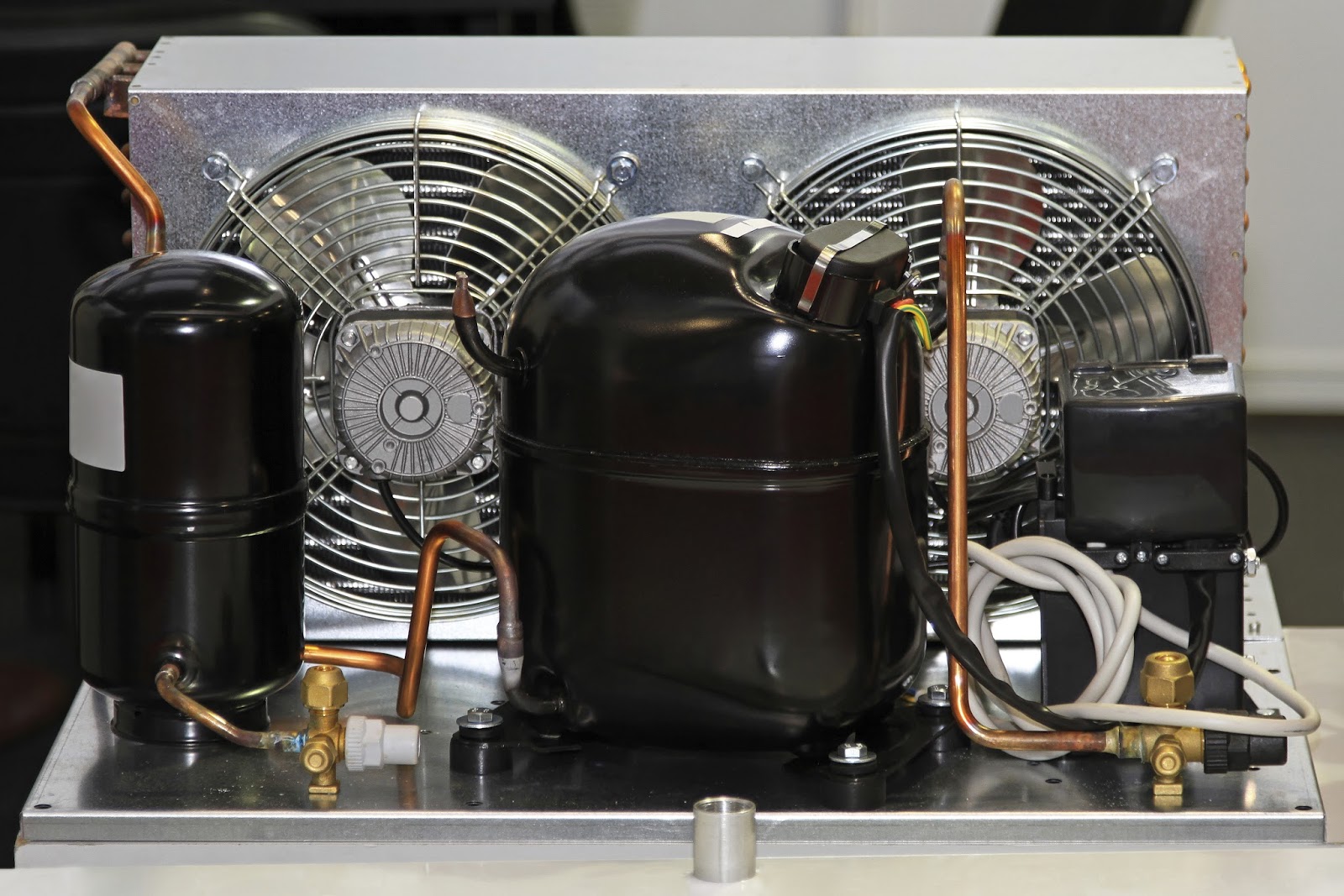
Components of a Refrigerator Compressor
The refrigerator compressor is the workhorse of the cooling system, responsible for circulating the refrigerant and maintaining the desired temperature inside the appliance. It consists of several important components working together to ensure efficient operation. Let’s take a closer look at these components:
- Electric Motor: The compressor is powered by an electric motor, which supplies the necessary energy to drive the refrigerant through the system. The motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, allowing the compressor to compress the refrigerant gas.
- Compressor Pump: The pump is the main component of the compressor. It is responsible for increasing the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas by compressing it. The pump sucks in the low-pressure gas from the evaporator and delivers it to the condenser.
- Piston: The compressor’s pump is often driven by a piston. The piston moves up and down inside a cylinder, creating a pumping action that compresses the refrigerant gas. As the piston moves downward, it draws in the gas from the evaporator. When the piston moves upward, it compresses the gas and pushes it to the condenser.
- Valves: The compressor is equipped with intake and discharge valves. These valves ensure the flow of refrigerant gas in the desired direction. The intake valve allows the low-pressure gas to enter the pump, while the discharge valve enables the compressed gas to exit the pump and flow towards the condenser.
- Refrigerant Lines: The compressor is connected to the rest of the refrigeration system through refrigerant lines. These lines transport the refrigerant gas between the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve in a closed-loop system. The lines are typically made of copper or aluminum for their excellent heat transfer properties.
These components work harmoniously to facilitate the compression and circulation of the refrigerant gas, ensuring efficient cooling inside the refrigerator. Now that we understand the individual parts of the compressor, let’s move on to explore the working principle of a refrigerator compressor.
Working Principle of a Refrigerator Compressor
The working principle of a refrigerator compressor is based on the concept of compression and expansion of the refrigerant gas. It operates in a continuous cycle, also known as the refrigeration cycle, to remove heat from the interior of the refrigerator and maintain a cool temperature.
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how a refrigerator compressor works:
- Step 1: Evaporation: The process begins with the evaporator coil inside the refrigerator. The low-pressure and low-temperature refrigerant gas enters the evaporator coil. As the warm air from the interior of the refrigerator passes over the coil, the refrigerant absorbs the heat from the air and evaporates, changing from a liquid to a gas.
- Step 2: Compression: The evaporated refrigerant gas is now in a gaseous state and flows into the compressor. The compressor’s electric motor drives a piston, creating a high-pressure environment that compresses the gas. As the gas is compressed, its temperature and pressure increase significantly.
- Step 3: Condensation: The high-pressure and high-temperature gas exits the compressor and moves into the condenser coil located on the back or bottom of the refrigerator. The condenser coil dissipates the heat from the gas, causing it to condense back into a liquid state. This heat exchange occurs as the surrounding air or a fan cools the condenser coil.
- Step 4: Expansion: The liquid refrigerant, now in a high-pressure state, passes through an expansion valve. The expansion valve restricts the flow of refrigerant, causing a drop in pressure and temperature. This drop in pressure and temperature prepares the refrigerant for the next cycle.
- Step 5: Evaporation (Repeat): The low-pressure liquid refrigerant now enters the evaporator coil again, restarting the cycle. The cycle continues as long as the refrigerator is running, extracting heat from the interior and releasing it to the condenser. This continuous cycle maintains the desired temperature inside the refrigerator and keeps the food fresh and cool.
It’s important to note that the compressor plays a crucial role in this refrigeration cycle by compressing the gas and maintaining the necessary pressure for efficient heat exchange. The efficiency of the compressor directly impacts the overall performance of the refrigerator.
Now that we have a better understanding of how a refrigerator compressor works, let’s explore the different types of compressors commonly used in refrigeration systems.
When the refrigerator thermostat detects that the temperature inside the fridge is too high, it sends a signal to the compressor to start. The compressor then pumps refrigerant gas through the system, which absorbs heat from inside the fridge and releases it outside, cooling the interior.
Step-by-Step Process of Refrigeration
The process of refrigeration involves a series of steps that work together to remove heat from the interior of a refrigerator and maintain a cool temperature. Understanding the step-by-step process can help us appreciate the complexity of the refrigeration cycle. Let’s take a closer look at each of these steps:
- Step 1: Evaporation: The refrigeration cycle begins with the evaporation of the refrigerant inside the evaporator coil. The low-pressure liquid refrigerant enters the coil and absorbs heat from the surrounding air. As a result, the refrigerant evaporates and changes from a liquid to a gas state. This evaporation process extracts heat from the interior of the refrigerator, causing the temperature inside to decrease.
- Step 2: Compression: After evaporation, the gaseous refrigerant enters the compressor. The compressor, powered by an electric motor, compresses the gas, increasing its pressure and temperature. By compressing the gas, the compressor raises its energy level, allowing it to transfer heat more effectively in subsequent steps.
- Step 3: Condensation: The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas then flows into the condenser coil, usually located on the exterior of the refrigerator. As the gas comes into contact with the cooler air or a fan, it starts to condense back into a liquid form. This process releases the heat absorbed from the evaporator, effectively transferring it to the surrounding environment.
- Step 4: Expansion: Once the refrigerant condenses into a high-pressure liquid, it passes through an expansion valve. The expansion valve serves as a restriction point that causes a drop in pressure and temperature. This drop prepares the refrigerant for the next cycle by reducing its energy level and allowing it to enter the evaporator as a low-pressure liquid.
- Step 5: Evaporator (Repeat): The low-pressure liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator coil again, restarting the refrigeration cycle. The refrigerant evaporates, absorbing heat from the interior of the refrigerator, and the process continues as long as the refrigerator is running.
By constantly repeating this refrigeration cycle, the refrigerator efficiently removes heat from the inside, keeping the temperature low and preserving food freshness. The compressor plays a critical role in this process by compressing the refrigerant gas, raising its energy level, and ensuring the efficient transfer of heat.
Now that we have a clear understanding of the step-by-step process of refrigeration, let’s explore the different types of refrigeration compressors commonly used in refrigerators.
Types of Refrigerator Compressors
Refrigerators employ different types of compressors, each with its own advantages and operating mechanisms. Let’s explore some of the most common types of refrigerator compressors:
- Reciprocating Compressor: This type of compressor features a piston-driven mechanism, where the piston moves back and forth inside a cylinder to compress the refrigerant gas. Reciprocating compressors are known for their durability and reliability, making them a popular choice for residential refrigerators.
- Rotary Compressor: Rotary compressors operate by rotating a roller inside a cylinder, compressing the refrigerant gas. These compressors provide quiet operation and are more energy-efficient than reciprocating compressors. They are commonly used in smaller refrigerators and air conditioning systems.
- Screw Compressor: Screw compressors use two interlocking screws to compress the refrigerant gas. They are known for their high capacity and efficiency, making them suitable for commercial refrigeration applications and industrial cooling systems.
- Scroll Compressor: Scroll compressors feature two spiral-shaped scrolls, one stationary and the other orbiting, to compress the refrigerant gas. They are highly efficient and provide smooth and quiet operation. Scroll compressors are commonly found in high-end refrigerators and air conditioning units.
- Centrifugal Compressor: Centrifugal compressors use centrifugal force to compress the refrigerant gas. They are typically used in large-scale industrial and commercial refrigeration systems due to their high capacity and energy efficiency.
Each type of compressor has its own set of advantages and considerations. Factors such as size, capacity requirements, noise levels, efficiency, and cost play a role in determining the most suitable compressor for a particular application.
It’s worth noting that manufacturers continue to innovate and develop new compressor technologies to improve energy efficiency and overall performance. As a result, newer refrigerators may employ advanced compressor designs such as inverter compressors, which provide variable speed operation and further enhance energy savings.
Now that we have explored the types of compressors used in refrigerators, let’s discuss some common issues that may arise with these compressors and ways to troubleshoot them.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While refrigerator compressors are designed to be reliable, they can occasionally encounter issues that affect the cooling performance of the appliance. Here are some common problems that you may encounter with a refrigerator compressor, along with troubleshooting tips:
- Compressor Not Running: If you notice that the compressor is not running at all, first check if the refrigerator is properly plugged in and the power supply is working. Ensure that the temperature control settings are correctly adjusted. If the compressor is receiving power but still not running, there may be a fault in the electrical components or a malfunctioning start capacitor or overload protector. In such cases, it is advisable to seek professional assistance for repair or replacement.
- Compressor Running Continuously: If the compressor runs continuously without cycling off, it may indicate that there is an issue with the temperature control or thermostat. Check if the temperature control is set at the appropriate level and adjust it if necessary. Dirty condenser coils or a faulty condenser fan can also cause the compressor to run continuously. Clean the condenser coils and ensure that the condenser fan is functioning properly. If the issue persists, it is best to consult a technician for further diagnosis and repair.
- Compressor Short Cycling: Short cycling refers to a situation where the compressor turns on and off frequently within a short period. This can be caused by various factors, including a malfunctioning temperature control, a blocked condenser coil, or a refrigerant leak. Clean the condenser coil and check for any signs of refrigerant leakage. If the issue persists, it is recommended to have a professional technician inspect and repair the compressor.
- Loud or Strange Noises: Unusual noises coming from the compressor, such as clicking, banging, or grinding sounds, can indicate a mechanical problem. These noises may be caused by a faulty motor or compressor components. It is recommended to turn off the refrigerator and contact a technician for inspection and repair. Ignoring such noises may lead to further damage and costly repairs.
- Inadequate Cooling: If your refrigerator is not adequately cooling, it can be due to a variety of factors. First, check the temperature settings and adjust if needed. Ensure that the condenser coils are clean and free of debris, which can impede heat transfer. A malfunctioning compressor may also be the cause of inadequate cooling. If you have ruled out other possible causes, it is best to consult a professional technician for diagnosis and repair.
Note that troubleshooting and repairing a refrigerator compressor can be complex and potentially hazardous. It is always advisable to seek the assistance of a qualified technician if you are unsure or unfamiliar with the troubleshooting process.
Understanding these common issues and troubleshooting techniques can help you address minor problems with your refrigerator compressor and potentially avoid unnecessary expenses. In case of any major issues, professional help is recommended to ensure the safe and effective operation of your appliance.
Now, let’s conclude our exploration of refrigerator compressors.
Conclusion
Refrigerator compressors are the heart of cooling systems, responsible for maintaining the desired temperature inside the appliance. Understanding how these compressors work and the step-by-step process of refrigeration can give us a deeper appreciation for the functionality of our refrigerators.
The refrigeration cycle, which involves evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion, allows the compressor to cool the interior of the refrigerator while expelling heat to the surroundings. The components of a compressor, including the electric motor, pump, piston, valves, and refrigerant lines, work in harmony to ensure efficient operation.
There are various types of compressors used in refrigerators, such as reciprocating, rotary, screw, scroll, and centrifugal compressors. Each type has its own advantages and is suited for specific applications.
While refrigerator compressors are generally reliable, issues can arise that impact their performance. Common problems, including the compressor not running, running continuously, short cycling, making loud or strange noises, and inadequate cooling, can be addressed through troubleshooting techniques. However, it is vital to seek professional assistance for complex or potentially hazardous repairs.
By understanding how refrigerator compressors work and being aware of common issues, you can better maintain and care for your appliance. Regular cleaning, proper temperature control, and prompt attention to any abnormalities will help ensure the longevity and efficiency of your refrigerator.
Now that you’ve gained insights into the fascinating world of refrigerator compressors, you can apply this knowledge to make informed decisions about purchasing, maintaining, and troubleshooting your refrigerator. By appreciating the intricate workings of these essential appliances, you can continue to enjoy fresh, cool food for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does A Refrigerator Compressor Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Does A Refrigerator Compressor Work”