

Articles
How Does An Electric Water Pump Work
Modified: February 26, 2024
Learn how electric water pumps work with this informative article. Understand the inner workings of these efficient devices and their benefits.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
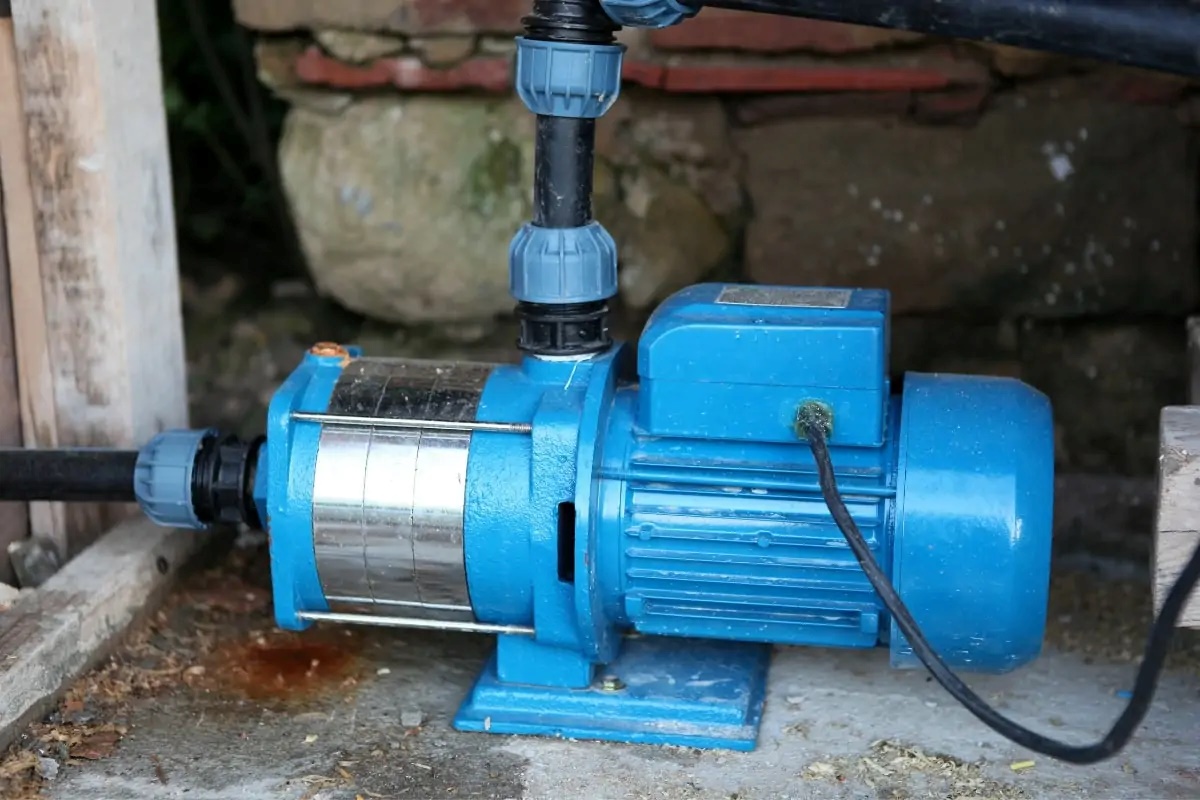
An electric water pump is a vital component in various industries and applications, playing a key role in circulating water and maintaining the efficient operation of systems. From residential water supply to industrial cooling systems, electric water pumps are relied upon for their ability to move water quickly and effectively. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of electric water pumps, their history, components, types, advantages, applications, and maintenance.
Electric water pumps provide a reliable and convenient solution for pumping water, especially when compared to traditional diesel or petrol-powered pumps. They use an electric motor to drive impellers or propellers, creating the necessary flow and pressure to move water from one location to another. While these pumps may seem like a relatively simple piece of equipment, their design and functionality involve several key components and principles.
Understanding how electric water pumps work is crucial for anyone involved in water management, plumbing, or system maintenance. Whether you are a homeowner looking to upgrade your water supply or a professional in the industry, this article aims to provide you with comprehensive insights into the fascinating world of electric water pumps.
Key Takeaways:
- Electric water pumps offer energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and versatile solutions for water movement in residential, agricultural, and industrial settings. Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for ensuring their reliable performance.
- Understanding the history, components, and working principle of electric water pumps is essential for maximizing their benefits. From residential water supply to firefighting, these pumps play a vital role in efficient water management.
Read more: How Does Water Pump Work
History of Electric Water Pumps
The history of electric water pumps dates back to the late 19th century, coinciding with the advent of electricity. Prior to the introduction of electric power, water pumps were predominantly powered by steam engines or hand-operated mechanisms.
The first electric water pumps were developed in the late 1800s when electricity became more widely available. These early electric pumps were relatively crude, often consisting of a simple motor attached to a centrifugal pump. However, they quickly gained popularity due to their convenience and efficiency compared to traditional pumps.
Advancements in electric motor technology throughout the 20th century led to significant improvements in electric water pumps. The introduction of more powerful and efficient motors allowed for higher flow rates and increased water pressure. Additionally, the development of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel and durable polymers improved the durability and longevity of electric water pumps.
As industries grew and technology advanced, electric water pumps found their way into a wide range of applications. From agricultural irrigation and wastewater treatment to HVAC systems and firefighting, electric water pumps became indispensable tools in various sectors.
In recent years, the rising demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly equipment has driven further innovation in electric water pump technology. Manufacturers have focused on developing pumps with variable speed drives and smart control systems to optimize energy consumption. These advancements have not only improved the efficiency and performance of electric water pumps but also reduced their environmental impact.
Today, electric water pumps are essential components in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Their continued development and integration with smart technologies are reshaping the way we manage and distribute water, providing sustainable and efficient solutions for a wide range of applications.
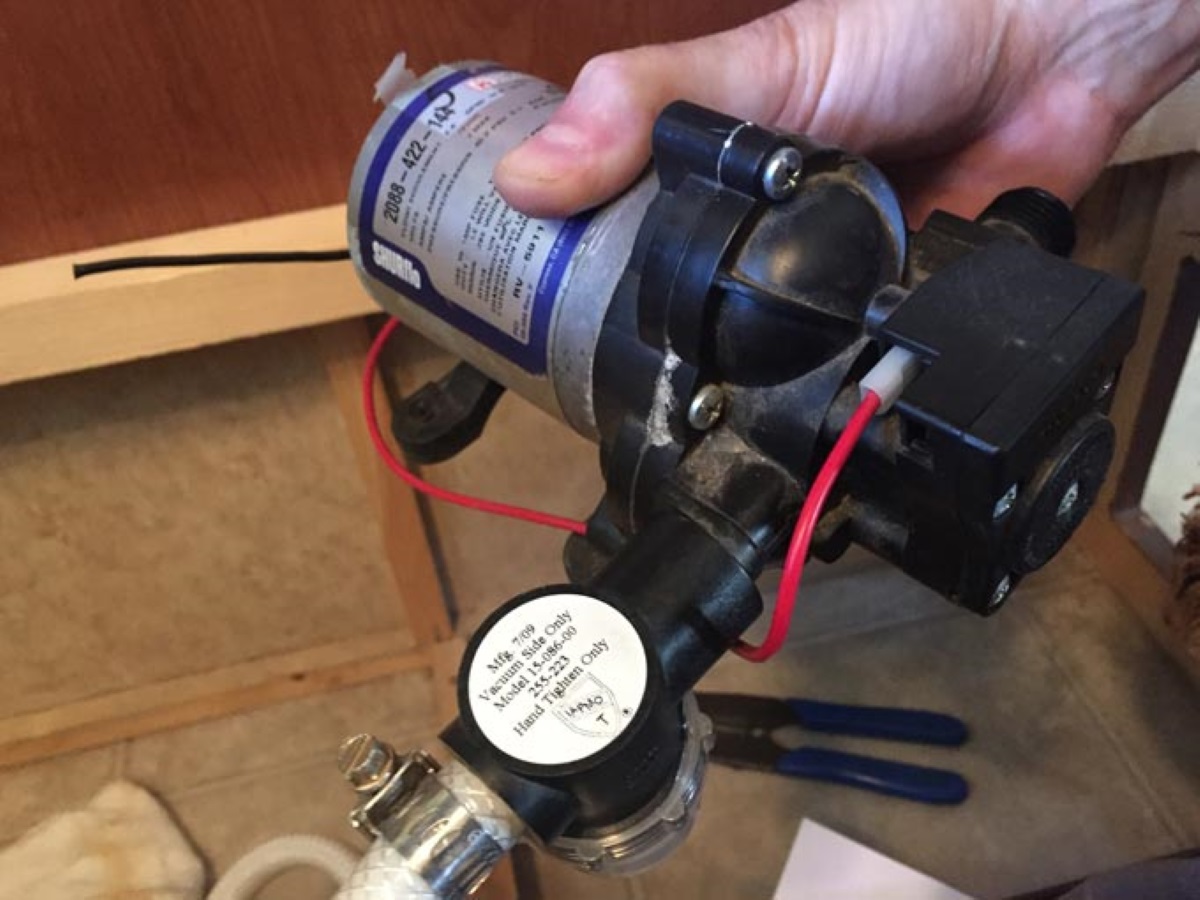
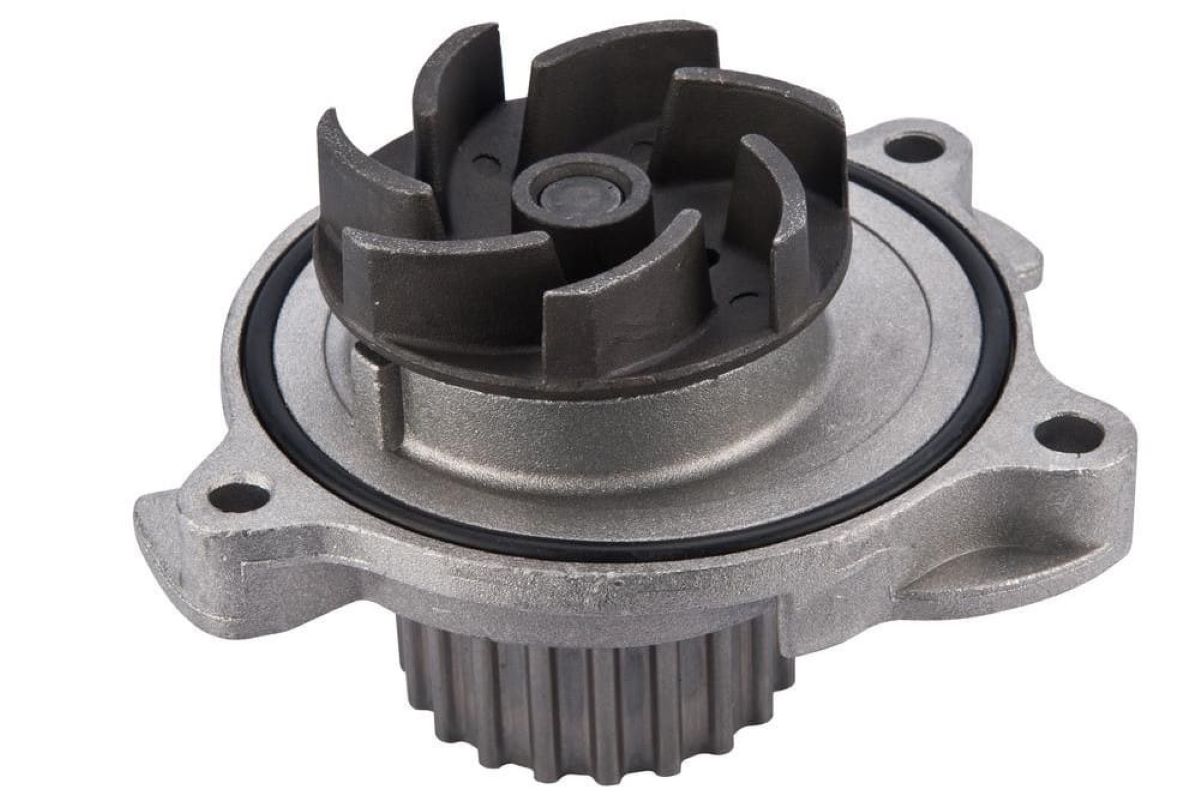
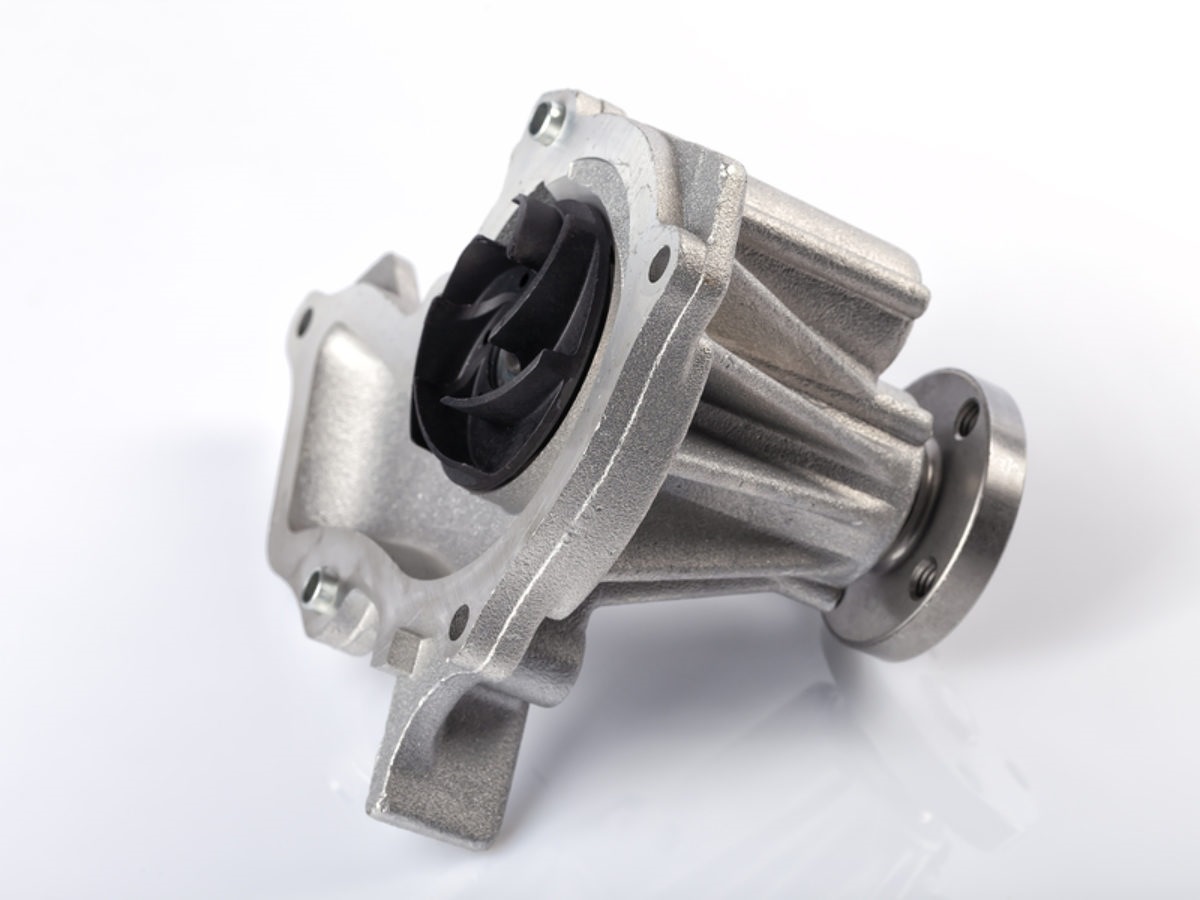
Components of an Electric Water Pump
An electric water pump is composed of several key components, each playing a crucial role in its functionality. Understanding these components is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance. Let’s take a closer look at the primary components of an electric water pump:
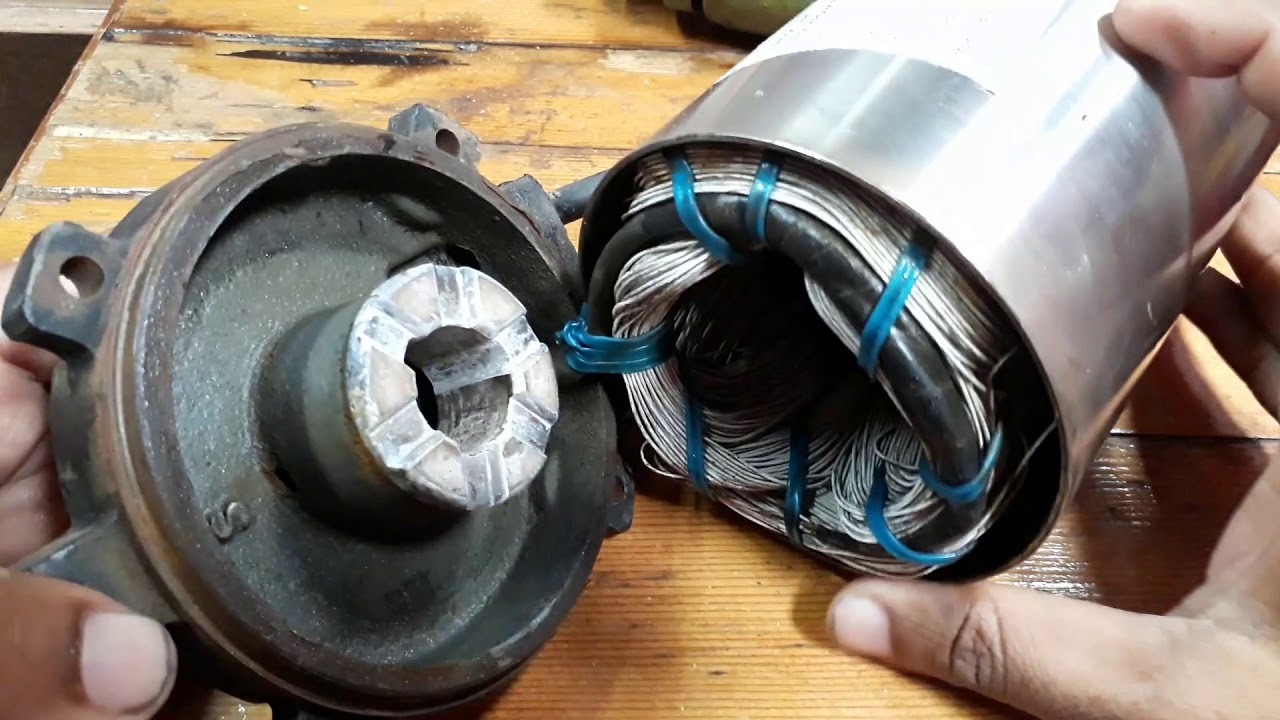
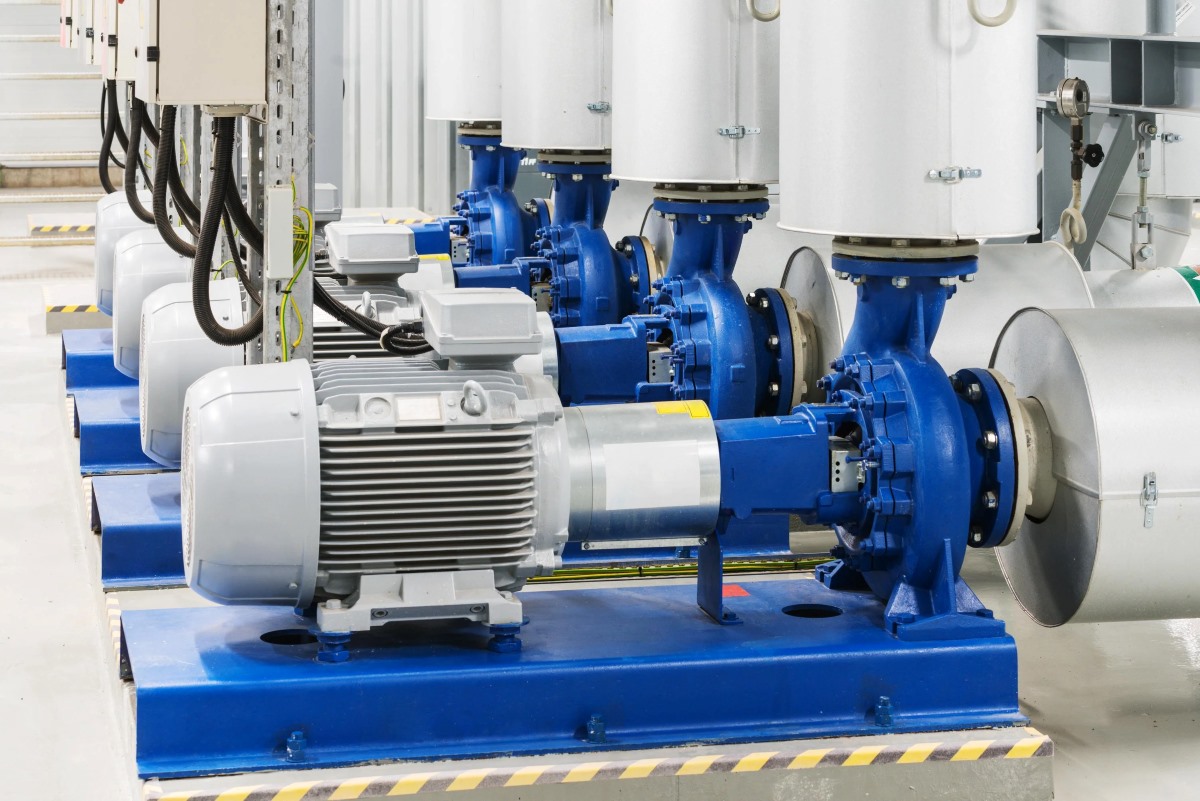
- Electric Motor: The electric motor is the heart of the water pump. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the impeller or propeller. Electric motors used in water pumps are typically either induction motors or brushless DC motors, depending on the specific application and requirements.
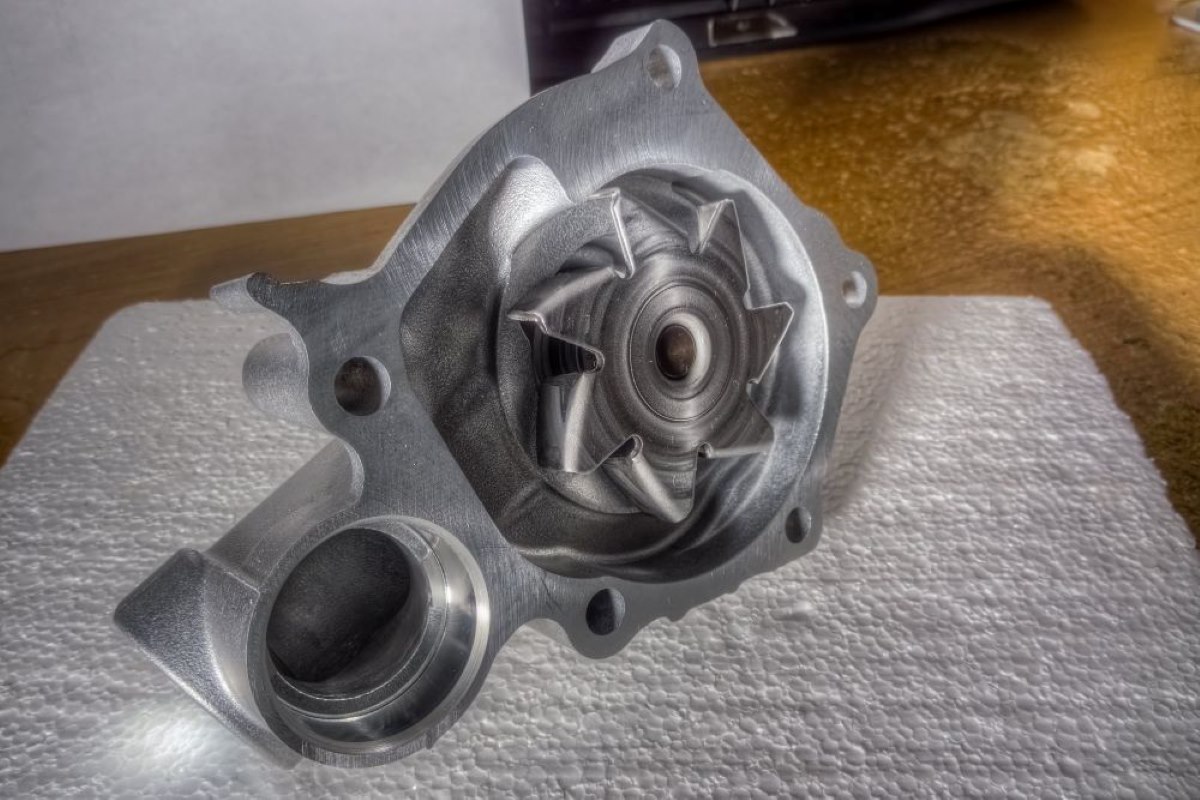
- Impeller/Propeller: The impeller or propeller is responsible for creating the flow and pressure necessary to move water. It consists of curved blades that push water in a specific direction. Depending on the pump type, the impeller may be housed inside a volute or diffuser to direct the flow of water.
- Volute/Diffuser: The volute or diffuser is a stationary casing surrounding the impeller. It helps to convert the kinetic energy imparted by the impeller into pressure energy, increasing the water’s pressure as it exits the pump.
- Inlet and Outlet Connection: These are the ports through which water enters and exits the pump. The size and type of connections depend on the pump’s capacity and intended application. In residential water supply pumps, these connections are typically threaded or flanged fittings.
- Seals and Gaskets: Seals and gaskets are used to prevent water leakage around rotating shafts or between pump components. Common types of seals include mechanical seals, O-rings, and gaskets made of materials compatible with the pumped fluid.
- Housing or Casing: The housing or casing encloses all the components of the pump and provides protection and support. It is usually made of durable materials such as cast iron, stainless steel, or high-quality plastics, depending on the pump’s intended application and environment.
- Control Panel: In some electric water pumps, particularly those used in commercial or industrial applications, a control panel is present. This panel houses the necessary controls, switches, and indicators for monitoring and managing the pump’s operation.
These components work together to create the necessary flow and pressure to move water efficiently. It is essential to regularly inspect and maintain these components to ensure the pump’s proper functioning and longevity.
Working Principle of an Electric Water Pump
The working principle of an electric water pump is based on the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy to move water from one location to another. Understanding this principle is crucial for comprehending the operation of electric water pumps. Let’s delve into the working principle of an electric water pump:
- Electricity Supply: The electric water pump is connected to an electrical power source, typically the grid or a generator. The power supply provides the necessary electrical energy to the electric motor of the pump.
- Motor Rotation: When the power supply is turned on, electricity flows to the electric motor, causing it to rotate. The motor is designed to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of magnetic fields, coils, and rotating components.
- Impeller/Propeller Action: As the motor rotates, it drives the impeller or propeller inside the pump. The rotation of the impeller creates a centrifugal force that pushes water away from the center of the pump, creating a low-pressure area near the impeller blades.
- Water Inflow: In response to the low-pressure area created by the rotating impeller, water from the source or reservoir flows into the pump through the inlet connection. The flow rate and volume of water entering the pump depend on the impeller design, speed of rotation, and the size and characteristics of the inlet connection.
- Centrifugal Force: As water enters the pump, it is pushed by the impeller’s centrifugal force towards the casing’s periphery. The curved blades of the impeller accelerate the water, imparting kinetic energy to it.
- Pressure Increase: The kinetic energy of the water is then converted into pressure energy as it passes through the volute or diffuser. The shape of the volute or diffuser guides the water flow and gradually increases its pressure while reducing its velocity.
- Water Discharge: The high-pressure water is then discharged from the pump through the outlet connection. It can be directed to the desired destination, such as a pipe network, irrigation system, or cooling apparatus.
This continuous process of the electric motor rotating the impeller, creating a low-pressure area, and subsequently pushing and pressurizing the water is what enables an electric water pump to function effectively. The specific flow rate, pressure, and efficiency of the pump depend on factors such as the pump’s design, motor power, impeller size, and the system’s hydraulic characteristics.
Understanding the working principle of an electric water pump is essential for troubleshooting common issues and optimizing its performance. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the impeller and checking for leaks, can help prolong the pump’s lifespan and ensure its consistent operation.
Types of Electric Water Pumps
Electric water pumps come in various types, each designed to meet specific requirements and applications. Understanding the different types of electric water pumps allows you to choose the most suitable option for your needs. Let’s explore some of the common types of electric water pumps:
- Centrifugal Pumps: Centrifugal pumps are the most widely used type of electric water pump. They work by converting rotational energy from the electric motor into kinetic energy by using an impeller to create centrifugal force. The kinetic energy then converts into pressure energy as water passes through the volute or diffuser. Centrifugal pumps are efficient for applications requiring high flow rates and moderate pressure, making them suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial use.
- Submersible Pumps: Submersible pumps are designed to be fully submerged in water, allowing them to pump water from deep wells or underground sources. They are hermetically sealed and often have built-in motors. Submersible pumps are commonly used for domestic water supply, irrigation, groundwater management, and wastewater drainage.
- Jet Pumps: Jet pumps are versatile electric water pumps that generate pressure through a combination of centrifugal force and the Venturi effect. They feature a nozzle and diffuser system that creates a vacuum, pulling water from the source and boosting its pressure. Jet pumps are commonly used for shallow wells, water supply systems, and residential applications.
- Booster Pumps: Booster pumps are designed specifically to increase water pressure in existing plumbing systems. They are often used in buildings or households with low water pressure, providing a boost to ensure adequate flow and pressure for showers, faucets, and other fixtures.
- Diaphragm Pumps: Diaphragm pumps utilize a flexible diaphragm to push and pull water, creating a pulsating action. They are self-priming and can handle liquids with solids or abrasive content, making them suitable for applications such as spraying, irrigation, and dewatering.
- Vertical Turbine Pumps: Vertical turbine pumps are used for pumping water from deep wells or reservoirs. They consist of multiple stages, each comprising an impeller and a diffuser. Vertical turbine pumps are widely used for irrigation, municipal water supply, and industrial applications that require high flow rates and significant lift.
- Peripheral Pumps: Peripheral pumps, also known as regenerative pumps, use a rotating impeller with numerous blades to generate pressure and flow. They are particularly effective in applications that require high pressure levels but lower flow rates, such as pressure boosting in residential buildings or small irrigation systems.
These are just a few examples of the types of electric water pumps available. The choice of pump depends on factors such as the application’s requirements, available power source, flow rate, pressure, and the characteristics of the water being pumped. Understanding the different types helps you select the most suitable pump for your specific needs.
Read more: How Does Hand Water Pump Work
Advantages of Electric Water Pumps
Electric water pumps offer numerous advantages over traditional pumps powered by diesel or petrol engines. These benefits make them a preferred choice in various applications. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of electric water pumps:
- Energy Efficiency: Electric water pumps are known for their high energy efficiency compared to combustion engine pumps. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy with minimal loss, resulting in less wasted energy and reduced operating costs.
- Environmentally Friendly: Electric water pumps produce fewer emissions compared to their combustion engine counterparts, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment. They help reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, making them a more sustainable choice.
- Lower Operating Costs: Electric water pumps generally have lower operating costs due to their higher energy efficiency and the relatively low cost of electricity compared to fuel. They are also easier to maintain as they have fewer mechanical components and require less frequent servicing.
- Quiet Operation: Electric water pumps generally operate more quietly than combustion engine pumps, making them suitable for residential areas, hospitals, schools, and other noise-sensitive environments. Their quieter operation minimizes disturbance and improves the overall comfort of the surroundings.
- Convenient and Easy to Use: Electric water pumps are easy to operate and require minimal setup. They can be conveniently connected to electrical power sources such as the grid or generators. Once connected, they can be controlled easily using switches or control panels.
- Reliable Performance: Electric water pumps offer reliable and consistent performance, especially when properly maintained. They are less prone to breakdowns and have a longer operational life compared to combustion engine pumps. This reliability is crucial, particularly in critical applications such as firefighting or industrial processes.
- Versatility: Electric water pumps are available in various sizes and types, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. From residential water supply to agricultural irrigation, municipal water systems, and industrial processes, electric water pumps can adapt to different scenarios.
- Safety: Electric water pumps do not involve the storage or handling of flammable fuels, reducing the risk of accidents or fires. Additionally, they eliminate the emission of hazardous fumes, ensuring safer working conditions for operators and reducing health and safety concerns.
These advantages make electric water pumps an attractive choice for many applications. Their energy efficiency, environmental friendliness, lower operating costs, and ease of use contribute to their growing popularity in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
An electric water pump works by using an electric motor to drive an impeller, which creates a flow of water through the pump. The impeller pushes the water through the pump, creating pressure and moving the water to its desired location.
Disadvantages of Electric Water Pumps
While electric water pumps offer numerous benefits, they also have some disadvantages to consider depending on the application and specific requirements. Understanding these drawbacks helps in making informed decisions. Let’s explore some of the main disadvantages of electric water pumps:
- Dependence on Electricity: Electric water pumps rely on a continuous and reliable supply of electricity to operate. In the event of power outages or disruptions, the pump may cease to function, leading to a temporary loss of water supply or system failure. Backup power sources or generators may be required in critical applications.
- Limited Mobility: Electric water pumps are stationary devices that require a fixed installation and power source. This limits their mobility and flexibility compared to portable pumps powered by petrol or diesel engines. If mobility is a requirement, alternative pump options may need to be considered.
- Initial Cost: Electric water pumps may have a higher initial cost compared to some types of traditional pumps. The cost of the electric motor, control panel (if needed), and the necessary electrical infrastructure can add to the overall expense. However, the lower operating and maintenance costs over time may offset the initial investment.
- Power Limitations: Electric water pumps may have limitations in terms of power availability. In areas with unreliable or insufficient electrical infrastructure, it may be challenging to operate electric pumps optimally. In such cases, alternative power sources or upgrading the electrical system may be necessary.
- Environmental Impact: While electric water pumps are more environmentally friendly than combustion engine pumps, they still rely on electricity, which may be generated from non-renewable sources. If the electricity grid in a certain region relies heavily on fossil fuels, the indirect environmental impact may be a consideration.
- Maintenance Requirements: Electric water pumps, like any mechanical equipment, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes inspecting and cleaning the impeller, replacing seals, and monitoring the electrical components. Failure to maintain the pump properly can lead to reduced efficiency and potential breakdowns.
- Size and Space: Electric water pumps may require a dedicated space for installation due to their size and the need for electrical connections. In situations where space is limited, such as in compact residential or commercial buildings, finding suitable installation locations can be a challenge.
- Specific Applications: Electric water pumps may not be the ideal choice for certain specialized applications. For example, in remote areas without access to electricity, alternative pump options like solar-powered pumps or hand-operated pumps may be more suitable.
Considering these disadvantages alongside the advantages allows for a well-informed decision when selecting an electric water pump. It is important to evaluate the specific requirements of the application, the availability of power, and the overall cost-effectiveness in the long run.
Applications of Electric Water Pumps
Electric water pumps find extensive use in a wide range of applications across various industries. They provide efficient and reliable water movement and circulation, making them indispensable in numerous settings. Let’s explore some of the common applications of electric water pumps:
- Residential Water Supply: Electric water pumps are commonly used for residential water supply, ensuring a consistent flow of water to households. Whether it’s for general consumption, watering the garden, or maintaining water pressure in multi-story buildings, electric water pumps play a vital role in maintaining a reliable water supply.
- Agricultural Irrigation: Electric water pumps are extensively used in agricultural irrigation systems. They efficiently distribute water to crops, ensuring optimal growth and yield. From small-scale farms to large agricultural operations, electric water pumps are key components in irrigation infrastructure.
- Industrial Processes: Electric water pumps are essential in various industrial processes that require water circulation or cooling. They play a crucial role in cooling towers, heat exchangers, boilers, and other equipment that need a constant flow of water to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
- Wastewater Management: Electric water pumps are used in wastewater treatment plants for the movement and treatment of sewage and wastewater. They enable the efficient transfer of water through the different stages of treatment, including pumping it into tanks, aerating systems, and filtration units.
- Fire Protection: Electric water pumps are vital components of fire protection systems. They provide the necessary water pressure and flow rate for firefighting activities, ensuring the availability of water in case of emergencies. Electric fire pumps are commonly installed in commercial buildings, warehouses, and high-rise structures.
- Swimming Pool and Pond Filtration: Electric water pumps are used in swimming pool and pond filtration systems to circulate and filter water. They help maintain water cleanliness and clarity by continuously moving the water through filters and removing debris and contaminants.
- Hydroponics and Aquaponics: Electric water pumps play a critical role in hydroponic and aquaponic systems, which involve growing plants in water-based environments. The pumps provide the necessary water circulation and nutrient distribution, ensuring the optimal growth and health of plants.
- Fountain and Water feature Display: Electric water pumps are essential components in fountains and decorative water features. They provide the necessary water flow and pressure to create captivating water displays, enhance aesthetics, and create soothing ambient sounds.
- Groundwater Extraction: Electric water pumps are commonly used to extract groundwater from wells and boreholes. They are employed in domestic, agricultural, and commercial settings to access and distribute water from underground sources.
- Construction and Dewatering: Electric water pumps play a crucial role in construction sites, particularly in dewatering applications. They are used to remove excess water from excavations, foundations, and underground structures, ensuring a dry and safe working environment.
These are just a few examples of the many applications where electric water pumps are utilized. From residential and agricultural use to industrial processes and water management, electric water pumps are versatile and vital tools in ensuring efficient water circulation and supply.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Electric Water Pumps
Maintaining and troubleshooting electric water pumps is crucial to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting can help identify and address issues before they escalate into major problems. Let’s explore some key maintenance practices and troubleshooting steps for electric water pumps:
Read more: How Does A Well Water Pump Work
Maintenance:
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect the pump for any signs of wear or damage. Check for leaks, loose connections, and any abnormal noise or vibrations during operation.
- Cleaning the Impeller: The impeller is a crucial component that can get clogged with debris or sediments over time. Clean the impeller periodically to ensure smooth water flow and prevent efficiency losses.
- Checking Seals and Gaskets: Inspect the seals and gaskets for any signs of leakage or wear. Replace them if necessary to prevent water leakage and ensure proper sealing.
- Monitoring Motor Temperature: Keep an eye on the motor’s temperature during operation. Excessive heat may indicate a problem such as overload or insufficient cooling. Ensure proper ventilation and address any issues promptly.
- Checking Electrical Connections: Regularly inspect the electrical connections and wiring to ensure they are secure and free from damage. Loose connections or frayed wires can affect the pump’s performance and pose safety hazards.
- Regular Lubrication: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding lubrication points, if applicable. Proper lubrication helps reduce friction and wear on moving parts, ensuring smooth operation.
- Schedule Professional Servicing: Consider periodic professional servicing from qualified technicians. They can perform more in-depth inspections, testing, and maintenance, ensuring the pump’s optimal performance.
Troubleshooting:
- No Power: If the pump does not start, check if there is a power supply issue. Verify that the power source is active and the electrical connections are secure.
- Low Water Pressure: Insufficient water pressure may indicate a clogged impeller, air trapped in the system, or an issue with the inlet valve. Clean the impeller, purge air from the system, and inspect the inlet valve for proper operation.
- Unusual Noise or Vibrations: Strange noises or excessive vibrations during pump operation may stem from a misaligned impeller, loose components, or worn bearings. Inspect and realign the impeller if necessary, tighten any loose components, and replace worn bearings.
- Water Leaks: Water leaks can occur due to damaged seals, gaskets, or cracked pump casings. Inspect and replace any faulty seals, gaskets, or damaged components to eliminate leaks.
- Pump Overheating: Pump overheating can be caused by motor overload, insufficient cooling, or clogged vents. Check for signs of overloading, ensure proper cooling ventilation, and clean any clogged vents or filters.
- Inconsistent Flow: Inconsistent water flow may indicate a problem with the impeller, clogged pipes, or a faulty pressure switch. Inspect and clean the impeller, check for pipe blockages, and test the pressure switch for proper functioning.
- Pump Cycling On and Off: Rapid on/off cycling can be caused by a malfunctioning pressure switch or incorrect settings. Adjust the pressure switch settings or replace it if necessary.
It is important to follow safety precautions and refer to the pump’s specific maintenance guidelines and the manufacturer’s recommendations. If unsure or if issues persist, consult a professional technician or contact the manufacturer for further guidance.
By practicing regular maintenance and promptly addressing any troubleshooting issues, you can ensure the efficient and reliable operation of your electric water pump for years to come.
Conclusion
Electric water pumps have revolutionized the way we manage and distribute water in various industries and applications. From residential water supply to agricultural irrigation, industrial processes, and firefighting, these pumps have become essential tools for efficient water movement and circulation.
Throughout this article, we have explored the history, components, working principle, types, advantages, applications, and maintenance of electric water pumps. We’ve learned that electric water pumps offer numerous benefits, including energy efficiency, environmental friendliness, lower operating costs, and ease of use. They provide reliable and consistent performance, contributing to the smooth functioning of systems and promoting a sustainable approach to water management.
We’ve also identified that electric water pumps are available in various types, catering to different requirements and scenarios. Whether it’s a centrifugal pump for residential use, a submersible pump for agricultural irrigation, or a booster pump for industrial applications, there is a suitable electric water pump for every need.
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of electric water pumps, we must emphasize the importance of proper maintenance practices. Regular inspections, cleaning the impeller, checking seals and gaskets, monitoring the motor’s temperature, and scheduling professional servicing are key elements of pump maintenance. Additionally, troubleshooting common issues promptly and effectively can prevent potential breakdowns and ensure smooth operation.
In conclusion, electric water pumps continue to play a vital role in water management and circulation. Their efficiency, reliability, and versatility make them indispensable in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. By understanding their inner workings, undertaking regular maintenance, and addressing any troubleshooting concerns, we can maximize the benefits of electric water pumps and ensure a continuous and efficient supply of water for various applications.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does An Electric Water Pump Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Does An Electric Water Pump Work”