

Articles
How Does A Well Water Pump Work
Modified: March 1, 2024
Discover the inner workings of a well water pump and gain valuable knowledge about well water systems. Read our informative articles on how a well water pump operates.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of well water systems, where a reliable and efficient well water pump plays a crucial role in providing clean and fresh water to homes and buildings. Whether you live in a rural area or choose to have a well for your water supply, understanding how a well water pump works is essential.
A well water pump is a device that extracts water from underground sources, such as wells or boreholes, and delivers it to your faucets, showers, and other household appliances. It operates using mechanical and electrical components, working tirelessly to ensure a steady flow of water for your daily needs.
In this article, we will explore the basics of well water systems, the components of a well water pump, the working principle behind its operation, the different types of pumps available, installation and maintenance tips, and troubleshooting common issues that may arise. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how a well water pump functions and how to keep it in optimal condition.
So, let’s dive in and uncover the inner workings of this vital piece of equipment that keeps our taps flowing with fresh water.
Key Takeaways:
- Well water pumps are essential for providing a reliable and consistent water supply to homes and buildings, and understanding their components and working principle is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
- Proper installation, regular maintenance, and timely troubleshooting of common issues are essential for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of well water pumps, ensuring a continuous supply of clean and fresh water for everyday needs.
Read more: How Long Does A Well Water Pump Last
Basics of Well Water Systems
A well water system consists of several key components that work together to provide a continuous supply of water. Understanding these basic components is essential in comprehending the functioning of a well water pump.
Well: The well is the source of the water supply. It is a hole drilled into the ground, typically reaching an aquifer or underground water source. Wells can vary in depth depending on the location and water table levels.
Well Casing: The well casing is a pipe inserted into the well to protect the well walls from collapsing and to prevent contamination of the water supply. It is usually made of metal or PVC and extends above the ground level.
Foot Valve: The foot valve is a one-way valve located at the bottom of the well. It allows water to enter the well but prevents it from flowing back down. This valve helps maintain prime suction and prevents the pump from losing its prime.
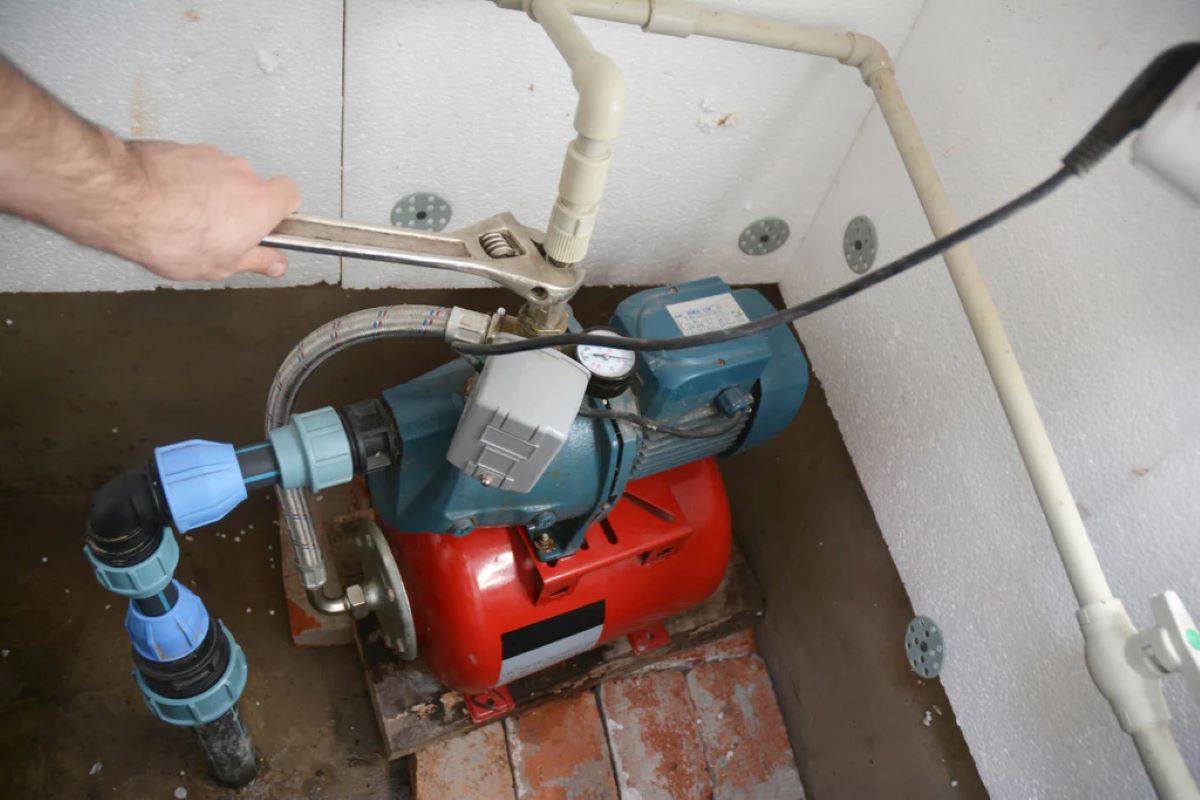
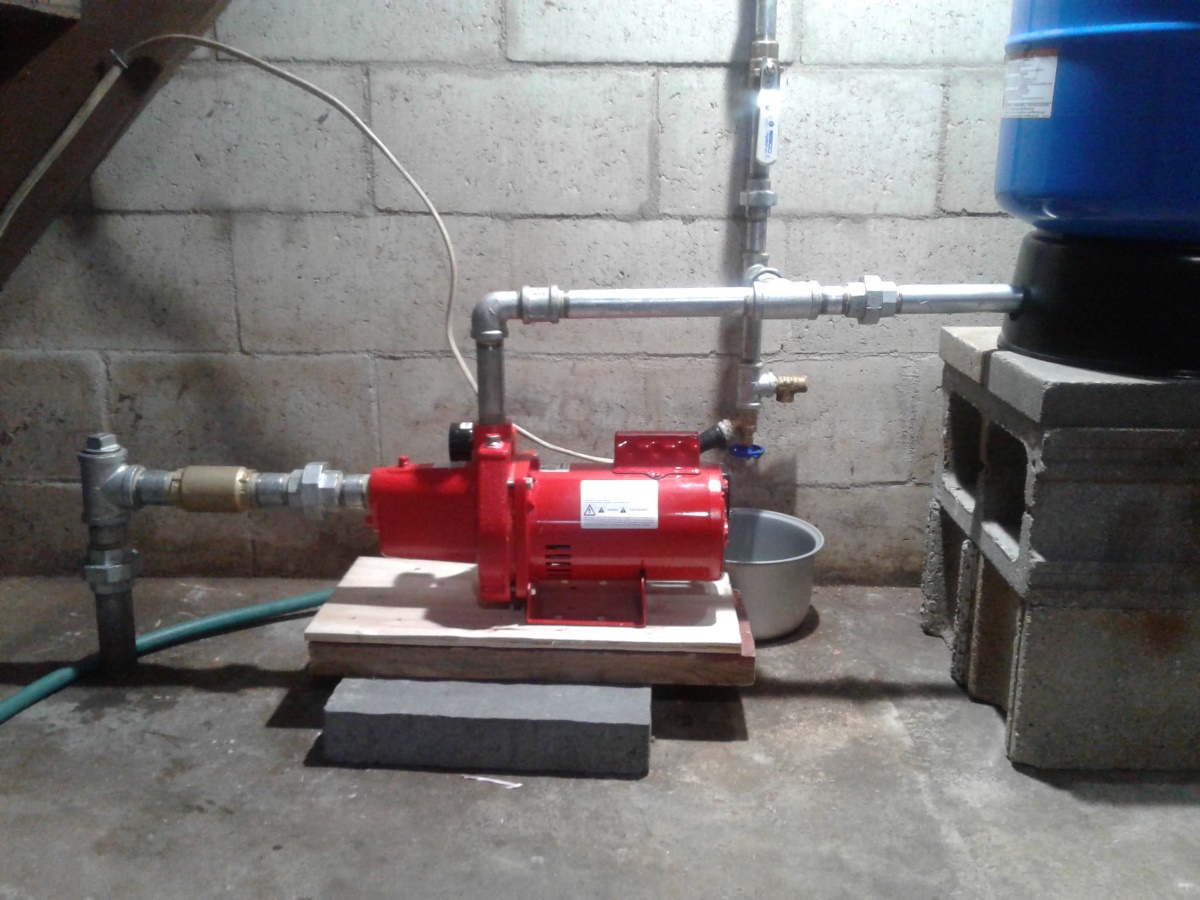
Pump: The pump is the heart of the well water system and is responsible for extracting water from the well and delivering it to the desired point of use. There are different types of pumps available, which we will discuss in detail later.
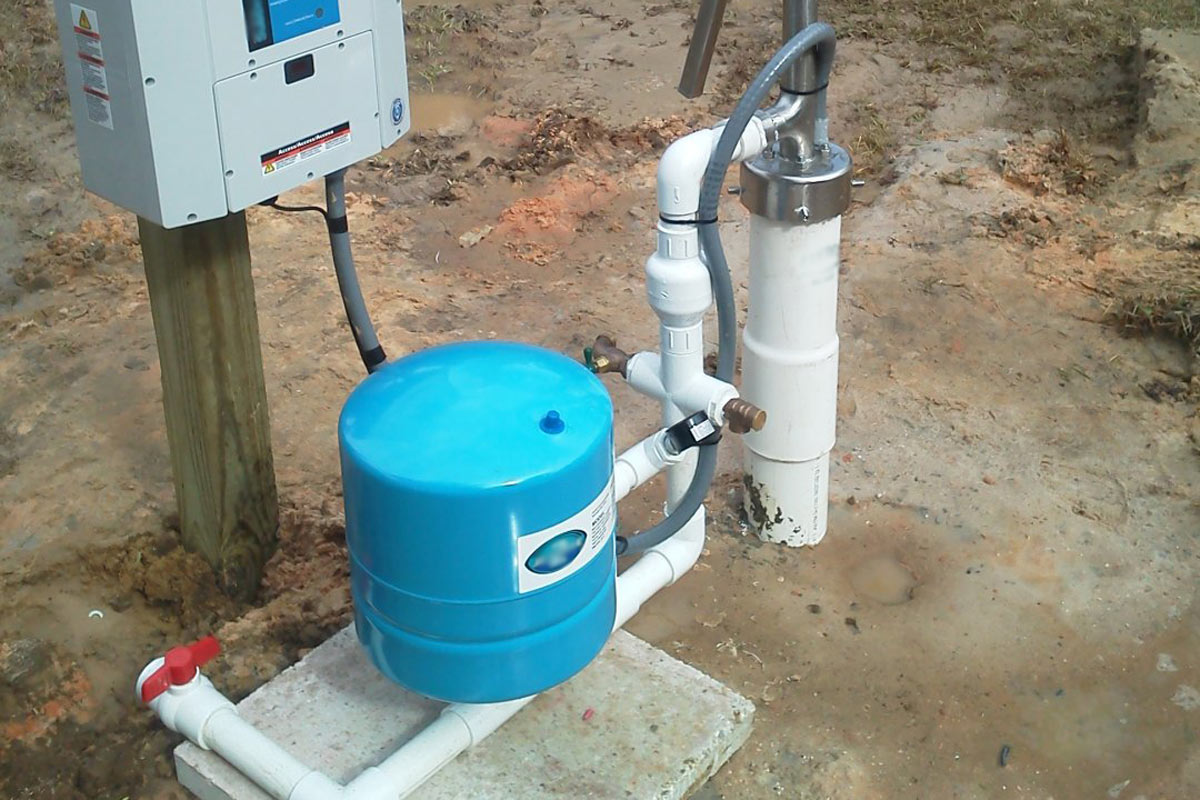
Pressure Tank: The pressure tank acts as a storage vessel for the water pumped from the well. It helps maintain a consistent water pressure throughout the system by using compressed air to push the water out when needed.
Pressure Switch: The pressure switch is an electrical device that monitors the water pressure in the pressure tank. It automatically activates the pump when the pressure drops below a certain level and shuts it off when the desired pressure is reached.
Piping and Plumbing: The piping and plumbing connections transport water from the pump to the desired outlets, such as faucets, showers, and appliances throughout your home or building.
By understanding these basic components and how they work together, you’ll be able to grasp the overall functioning of a well water system and appreciate the importance of a well water pump in maintaining a reliable water supply.
Components of a Well Water Pump
A well water pump is composed of various components that work in harmony to extract water from the well and deliver it to your taps and appliances. Understanding these components will give you a better insight into the inner workings of a well water pump.
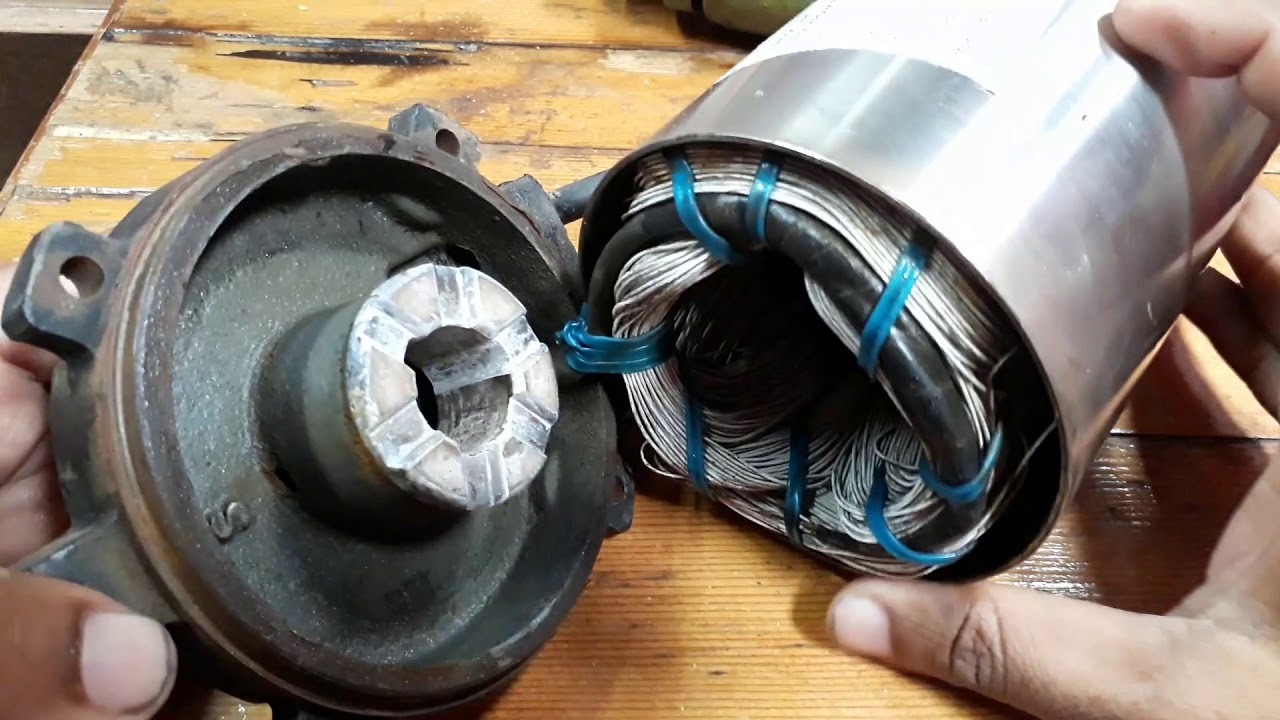
Motor: The motor is the powerhouse of the pump, providing the necessary energy to drive the pump’s operation. It is typically an electric motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, allowing the pump to function.
Impeller: The impeller is a rotating component inside the pump that is responsible for creating centrifugal force. As the impeller spins, it pushes water towards the pump’s outlet, generating the necessary pressure to move the water through the system.
Diffuser: The diffuser is a stationary component located after the impeller. It helps direct the flow of water and converts the high-velocity flow from the impeller into pressure. The diffuser plays a crucial role in increasing the efficiency of the pump.
Check Valve: The check valve, also known as a non-return valve, is a one-way valve that prevents water from flowing back into the well once it has been pumped out. It ensures that the water moves only in the desired direction and maintains the prime of the pump.
Control Box: In some well water pump systems, a control box is used to regulate the pump’s operation. It contains electrical controls that monitor the motor’s performance, adjust the pump’s speed, and protect it from damage due to electrical issues.
Pressure Gauge: The pressure gauge is a device that measures the water pressure in the system. It is typically installed on the pressure tank and provides a visual indication of the current pressure level. This allows you to monitor the system’s performance and ensure optimal pressure for your water supply.
Well Cap: The well cap is a protective cover that sits on top of the well casing, keeping out contaminants, debris, and animals. It usually has a vent to allow air circulation and may have openings for electrical cables and plumbing connections.
These components work together to create the necessary pressure and flow to extract water from the well and distribute it throughout the water system. Understanding their functions and how they interact will help you troubleshoot issues and ensure the proper functioning of your well water pump.
Working Principle of a Well Water Pump
Understanding the working principle of a well water pump is essential for comprehending its functionality and operation. The process involves a series of steps that enable the extraction and delivery of water from the well to your taps and appliances.
When the pump is activated, the motor begins to rotate, powering the pump’s internal components. As the impeller spins, it creates centrifugal force, pushing water towards the pump’s outlet. The impeller sucks water in through an inlet, typically located at the bottom of the pump housing.
Once inside, the water is propelled towards the diffuser, where it undergoes a change in flow direction. The diffuser helps convert the high-velocity flow from the impeller into pressure by gradually expanding the flow area. This pressure buildup is essential for the water to flow through the pipes and reach the desired outlets with sufficient force.
From the pump, the water is pushed into the piping system, which delivers it to various faucets, showers, and appliances throughout your home or building. The pressure tank plays a vital role in this process by acting as a storage vessel. As water is pumped into the tank, air inside the tank compresses, creating pressure. The compressed air forces the water out of the tank and into the system when a tap is opened.
The pressure switch constantly monitors the pressure in the tank. When the pressure drops below a pre-set level, the switch activates the pump to replenish the water supply. Once the desired pressure is reached, the switch shuts off the pump until it is needed again.
The check valve, located after the pump, ensures that water flows only in one direction, preventing backflow into the well or system. This helps maintain the prime of the pump and prevents the loss of water pressure.
Overall, the well water pump uses mechanical and electrical components to create the necessary pressure and flow to extract water from the well and deliver it to your faucets. The constant monitoring of pressure ensures a continuous water supply and efficient operation of the pump.
Understanding the working principle allows you to troubleshoot minor issues, maintain the pump properly, and ensure a reliable supply of clean and fresh water for your everyday needs.
Regular maintenance of your well water pump is essential to ensure its proper functioning. This includes checking for any leaks, testing the pressure switch, and cleaning the pump and its components regularly.
Types of Well Water Pumps
When it comes to well water pumps, there are several types available, each designed to suit different well depths, flow rates, and system requirements. Understanding the different types of pumps will help you choose the most suitable one for your specific needs.
Submersible Pump: A submersible pump is a common type of well water pump that is fully submerged in the water well. It consists of a sealed motor and pump unit, which is placed at the bottom of the well. Submersible pumps are known for their efficiency and ability to deliver high water pressure, making them suitable for deep wells.
Jet Pump: Jet pumps are installed above the ground and are designed to draw water from the well using suction. They utilize the Venturi effect to create pressure, pulling water from the well into the pump and then pushing it up to the desired outlets. Jet pumps are commonly used in shallow to medium-depth wells.
Convertible Jet Pump: A convertible jet pump is similar to a standard jet pump but offers more versatility. It can be adjusted to function as either a shallow well or a deep well pump, depending on the depth of the water source. Convertible jet pumps are ideal for wells with varying water levels.
Centrifugal Pump: Centrifugal pumps are commonly used in irrigation systems but can also be utilized in well water systems. They work by using centrifugal force to push water outward from the center of the impeller. These pumps are not typically used in deep wells, as they are less efficient at generating high pressures.
Hand Pump: Hand pumps are manual pumps that operate by manually pumping a handle or lever to draw water from the well. They offer a reliable backup option in case of power outages or pump failures. Hand pumps are commonly used in rural areas or for emergency water supply.
Solar-Powered Pump: Solar-powered pumps use energy from the sun to power the pump’s motor. They are environmentally friendly and typically used in off-grid or remote locations where access to electricity is limited. Solar-powered pumps can be submersible or surface-mounted, depending on the specific application.
When choosing a well water pump, consider factors such as the depth of your well, desired flow rate, water usage requirements, and power sources available. Consulting with a professional can help determine the most suitable pump for your needs.
By selecting the right type of pump, you can ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and a reliable water supply for your home or building.
Read more: How Does Water Pump Work
Installation and Maintenance of Well Water Pumps
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of your well water pump. Following these guidelines will help you avoid potential issues and keep your pump running smoothly.
Installation:
- Consult a professional: It is recommended to hire a professional well pump installer for the installation process. They have the expertise and knowledge to ensure proper installation and adherence to local codes and regulations.
- Choose the right location: Select a suitable location for the pump and pressure tank, ensuring they are protected from extreme temperatures, direct sunlight, and potential damage.
- Well casing and foot valve: Ensure the well casing is properly sealed and the foot valve is installed correctly at the bottom of the well to prevent debris and contamination.
- Electrical connections: Follow electrical safety protocols and ensure that all electrical connections are properly installed and grounded. Consult a qualified electrician if needed.
- Prime the pump: For a submersible pump or jet pump, the pump needs to be primed before starting it. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific priming procedures.
Maintenance:
- Regular inspections: Schedule routine inspections to check for any signs of damage or leaks. Inspect the well, pressure tank, electrical connections, and pump components.
- Clean the well: Periodically clean the well to prevent debris and sediment buildup. Consult a professional well technician for proper cleaning techniques.
- Test the water quality: Arrange for water quality testing to ensure that the water supply remains safe and free from contamination.
- Check pressure and adjust settings: Monitor the pressure gauge and ensure that the pressure switch and control settings are appropriate for your specific water system.
- Lubrication and maintenance of moving parts: Some pumps may require periodic lubrication of bearings or other moving parts. Consult the pump manufacturer’s guidelines for proper lubrication and maintenance procedures.
- Replace worn-out components: Replace any worn-out or damaged components promptly to avoid further deterioration and potential pump failure.
It is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines and recommendations for installation and maintenance specific to your well water pump model. Regular maintenance and timely repairs will help extend the lifespan of your pump and ensure a consistent supply of clean water.
If you encounter any issues or if the pump requires major repairs, it is advisable to contact a qualified well pump professional for assistance. They have the expertise to diagnose and resolve problems efficiently.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Well Water Pumps
Well water pumps are essential for providing a reliable water supply, but like any mechanical device, they can encounter problems over time. Understanding common issues and their troubleshooting methods will help you address these problems promptly and ensure the proper functioning of your well water pump.
No Water:
- Check the power supply: Ensure that the pump’s electrical connection is intact and that there is power reaching the pump. Check circuit breakers and fuses.
- Check the pressure switch: Inspect the pressure switch to determine if it is malfunctioning. Adjust or replace the pressure switch if necessary.
- Check the foot valve or check valve: A faulty foot valve or check valve can prevent water from reaching the pump. Inspect them for proper functioning and replace if damaged.
- Check the well depth: If the water level in the well has dropped below the pump’s intake, it may not be able to draw water. Consider lowering the pump or installing a deeper well pump.
Low Water Pressure:
- Check the pressure tank: Inspect the pressure tank for proper pressure. If the tank is low on air or waterlogged, it can lead to low water pressure. Adjust the air pressure or replace the tank if necessary.
- Check for clogged pipes or filters: Buildup of sediment, debris, or mineral deposits in the pipes or filters can restrict water flow and cause low pressure. Clean or replace clogged pipes or filters.
- Check for leaks: Inspect the system for any leaks, both inside and outside the building. Leaks can affect water pressure. Repair or replace damaged pipes or fittings.
Pump Cycling Frequently:
- Check for waterlogged pressure tank: A waterlogged pressure tank can cause frequent cycling. Adjust the air pressure in the tank or replace it if needed.
- Check for leaks: Water leaks in the system can cause the pump to cycle frequently. Inspect and fix any leaks to prevent unnecessary pump cycling.
- Check for proper pressure switch settings: If the pressure switch is not adjusted correctly, it can cause frequent cycling. Make sure the pressure settings align with the desired pressure range.
Strange Noises:
- Check for a worn-out pump motor or impeller: A worn-out motor or impeller can produce strange noises. Consult a professional technician to determine if any components need to be replaced.
- Check for air in the system: Air trapped in the pipes or pressure tank can cause noises. Bleed the system or contact a technician to remove the air and restore proper function.
If you encounter more complex issues or if you are unsure about troubleshooting, it is recommended to seek the assistance of a professional well pump technician. They have the knowledge and experience to diagnose and repair any problems, ensuring the efficient operation of your well water pump.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a well water pump is a vital component of a well water system, responsible for extracting water from underground sources and delivering it to your faucets, showers, and appliances. Understanding the functioning and maintenance of a well water pump is essential for ensuring a reliable and consistent water supply.
We explored the basics of well water systems, including the well, well casing, foot valve, pump, pressure tank, pressure switch, and piping. These components work together to create pressure, move water through the system, and provide a steady flow of water to meet your daily needs.
Different types of well water pumps, such as submersible pumps, jet pumps, convertible jet pumps, centrifugal pumps, hand pumps, and solar-powered pumps, allow for flexibility in choosing the right pump for your specific well depth and flow rate requirements.
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial in ensuring the optimal performance of your well water pump. Following installation guidelines, conducting regular inspections, cleaning the well, testing water quality, and promptly addressing any issues that arise will help extend the lifespan of your pump and maintain an uninterrupted water supply.
By troubleshooting common issues such as no water flow, low water pressure, frequent pump cycling, and unusual noises, you can identify and resolve problems efficiently. However, it is always recommended to consult a professional well pump technician for complex issues or if you are unsure about the troubleshooting process.
In conclusion, a well water pump is an essential investment that requires proper care and attention. By understanding its operation, conducting regular maintenance, and addressing issues promptly, you can ensure a reliable and efficient water supply for years to come.
Remember, water is a precious resource, and a well water pump helps us harness its benefits. So take the necessary steps to keep your well water pump in good condition and enjoy the convenience of a steady flow of clean and fresh water whenever you need it.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does A Well Water Pump Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Does A Well Water Pump Work”