

Articles
How Does Carbon Monoxide Detector Work
Modified: October 28, 2024
Discover how carbon monoxide detectors work and protect your home in this informative article
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that can be extremely dangerous and even fatal if inhaled in high concentrations. It is produced by the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels such as gas, oil, coal, and wood. Sources of carbon monoxide in our homes can include faulty gas appliances, blocked chimneys, and poorly ventilated areas.
Since carbon monoxide is undetectable by human senses, it is crucial to have a reliable and effective way to monitor its presence in our environment. This is where carbon monoxide detectors come into play.
Carbon monoxide detectors are devices specifically designed to detect the presence of CO gas in indoor environments and alert occupants to potential danger. These devices are an essential part of home safety systems, providing early warning signs that allow residents to evacuate and seek fresh air before the gas reaches harmful levels.
In this article, we will dive into the workings of carbon monoxide detectors and explore their importance in safeguarding our homes and loved ones.
Key Takeaways:
- Carbon monoxide detectors are crucial for early detection of the “silent killer” gas, providing peace of mind, protection while sleeping, and compliance with regulations, safeguarding homes and loved ones from potential danger.
- Understanding the basic components, sensor technology, alert mechanisms, and proper maintenance of carbon monoxide detectors is essential for ensuring optimal functionality and reliable detection of CO gas, contributing to a safer living environment.
Understanding Carbon Monoxide
Before delving into the details of carbon monoxide detectors, it is crucial to understand what carbon monoxide is and why it is so dangerous.
Carbon monoxide is a toxic, odorless gas that is produced whenever fuel is burned incompletely. It is often referred to as the “silent killer” due to its stealthy nature and the fact that it cannot be detected by human senses alone. When inhaled, carbon monoxide enters the bloodstream and binds to hemoglobin, reducing its ability to carry oxygen to vital organs and tissues.
Exposure to high levels of carbon monoxide can cause a range of symptoms, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Prolonged exposure or extremely high concentrations of carbon monoxide can lead to severe health complications or even death.
It is important to note that carbon monoxide can be produced by a variety of everyday household items, including gas stoves, furnaces, water heaters, fireplaces, and even vehicles. Ensuring that these devices are properly maintained, vented, and used in well-ventilated areas is crucial in minimizing the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Now that we have a basic understanding of carbon monoxide and its potential dangers, let’s explore why carbon monoxide detectors are vital in protecting ourselves and our homes from this deadly gas.
Importance of Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Carbon monoxide detectors play a crucial role in keeping our homes and families safe from the dangers of carbon monoxide poisoning. Here are several reasons why they are of utmost importance:
- Early Detection: Carbon monoxide detectors are designed to detect even the smallest levels of CO gas in the air. This early detection allows occupants to be alerted before the gas reaches dangerous concentrations, providing valuable time to evacuate, ventilate the area, and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Protection While Sleeping: Carbon monoxide poisoning often occurs during sleep when people may not be aware of the presence of the gas. Installing carbon monoxide detectors in bedrooms and on each floor of the house ensures that occupants are protected throughout the night, even when they are unaware of potential danger.
- Peace of Mind: Having carbon monoxide detectors installed in your home provides peace of mind, knowing that you and your loved ones are being protected against this deadly gas. It allows you to sleep soundly at night and go about your daily activities without worrying about the unseen threat of carbon monoxide.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many cities and states have regulations requiring the installation of carbon monoxide detectors in residential buildings. By having these detectors in place, you not only ensure the safety of your household but also comply with legal requirements.
- Preventing Property Damage: Carbon monoxide can also damage property over time. High concentrations of CO gas can cause corrosion of metal fixtures and appliances, compromising their functionality and lifespan. Detecting CO gas early with carbon monoxide detectors can prevent costly repairs and replacements.
- Protecting Vulnerable Individuals: Certain individuals, such as elderly people, young children, pregnant women, and those with pre-existing health conditions, are more susceptible to the harmful effects of carbon monoxide. Installing carbon monoxide detectors is crucial in protecting these vulnerable individuals and ensuring their well-being.
Given the dangers posed by carbon monoxide and the importance of early detection, installing carbon monoxide detectors in your home is a wise and responsible decision. In the next section, we will explore the basic components that make up these life-saving devices.
Basic Components of a Carbon Monoxide Detector
Carbon monoxide detectors are designed with several key components that work together to detect the presence of CO gas and alert occupants to potential danger. Understanding these components is essential in comprehending how these devices operate. The basic components of a carbon monoxide detector include:
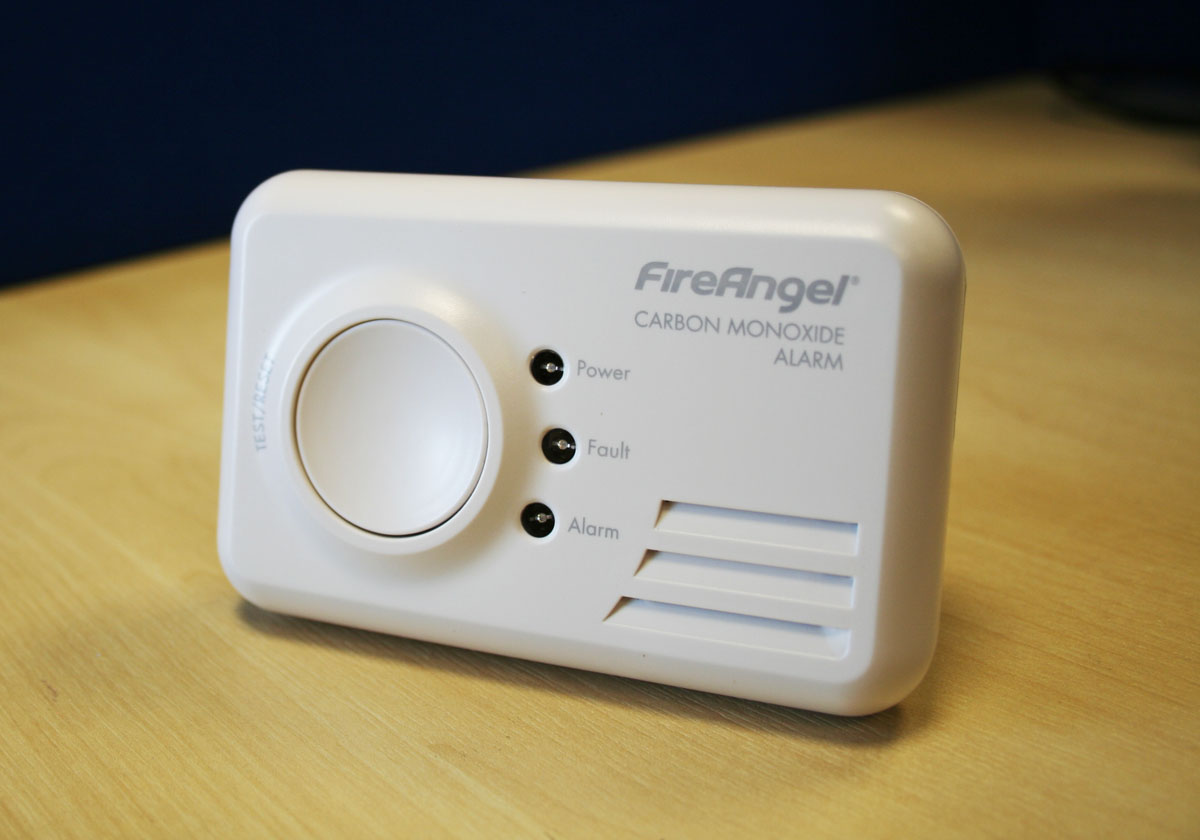
- Sensor: The sensor is the heart of the carbon monoxide detector. It is responsible for detecting the presence of CO gas in the surrounding environment. There are two main types of sensors used in carbon monoxide detectors: electrochemical sensors and biomimetic sensors. Electrochemical sensors work by generating an electrical current when exposed to CO gas, while biomimetic sensors use a gel-based material that changes color when exposed to CO gas.
- Alarm: The alarm is the component that alerts occupants to the presence of carbon monoxide in the air. Once the sensor detects CO gas, it triggers the alarm to emit a loud sound or a combination of sound and light signals, depending on the model. The alarm is designed to be loud enough to wake sleeping individuals and grab their attention in emergency situations.
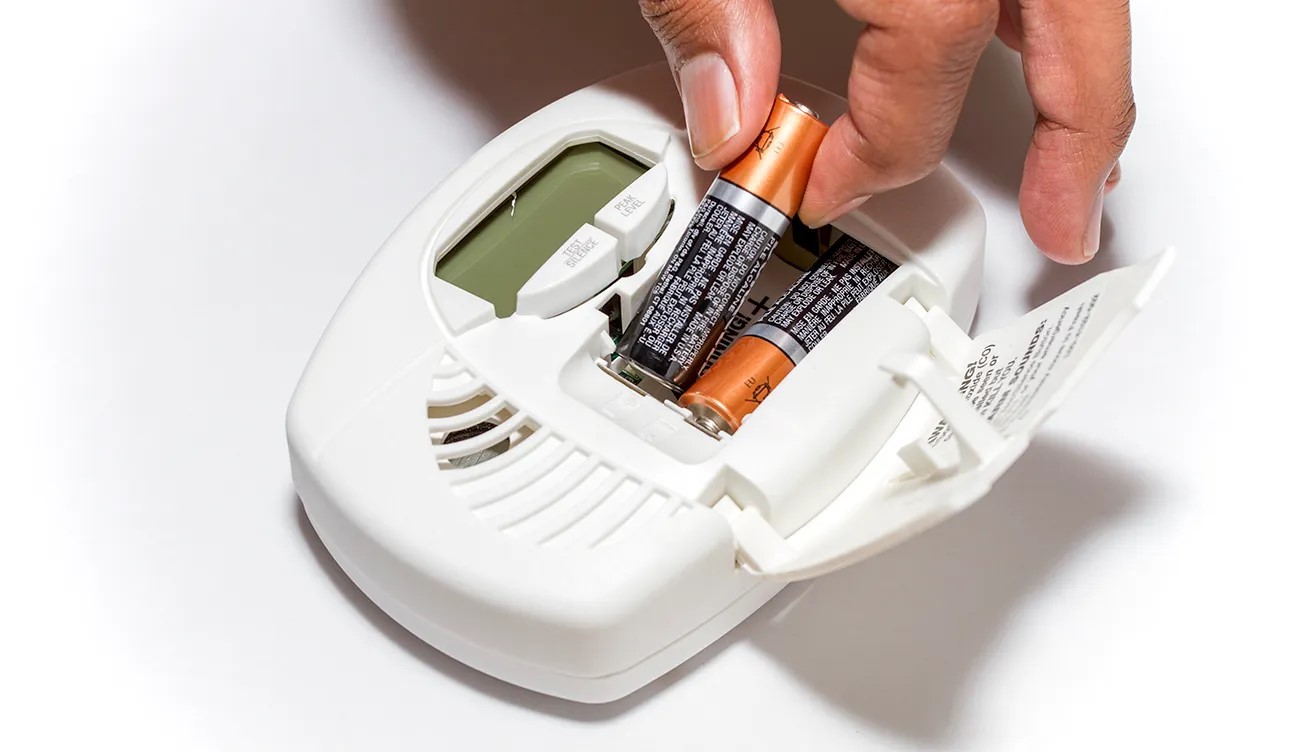
- Power Source: Carbon monoxide detectors require a power source to operate. They are typically powered by batteries, with some models offering the option of direct plug-in power. It is important to regularly check and replace the batteries to ensure the detector is functioning properly. Some carbon monoxide detectors have a built-in power backup in case of power outages.
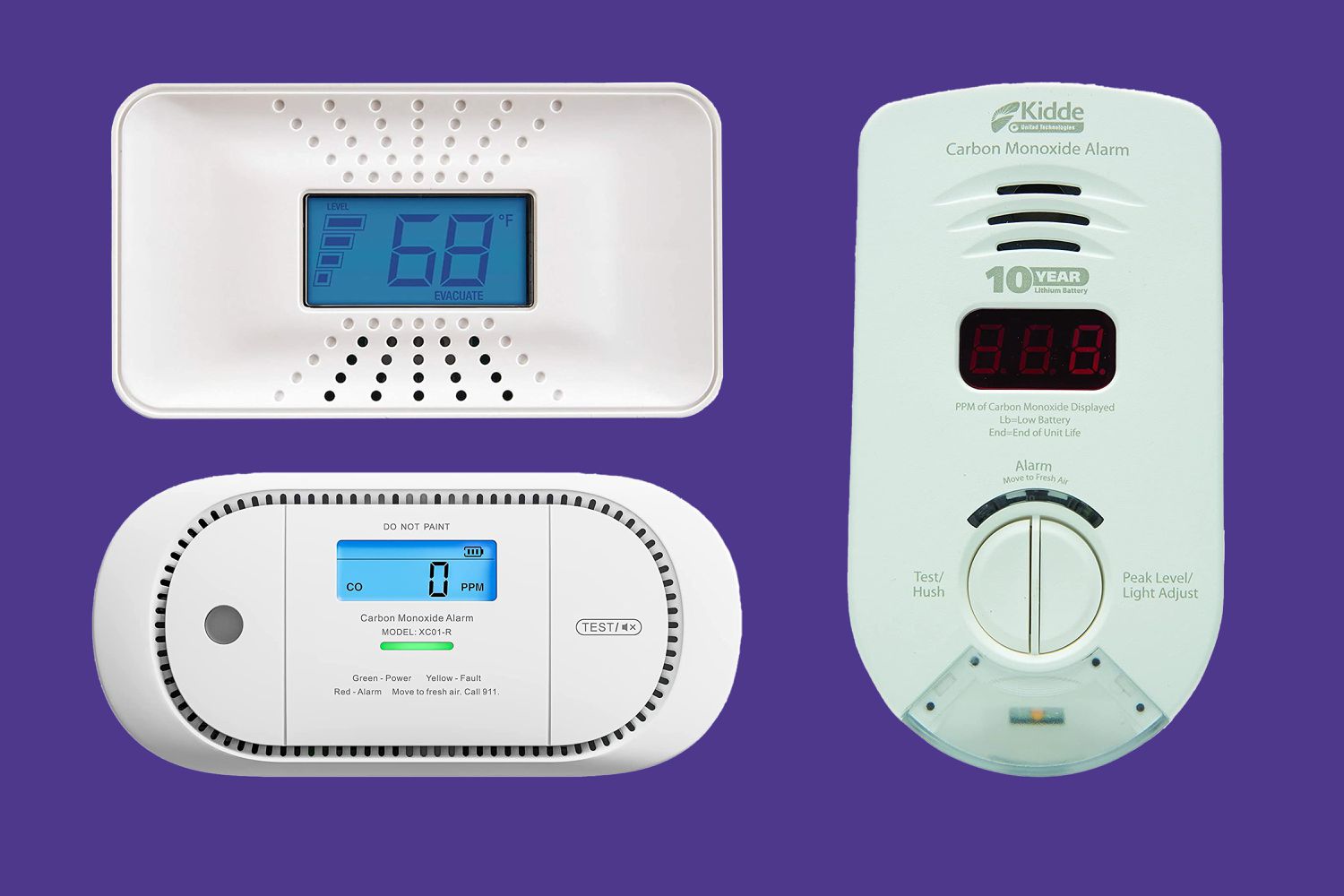
- Display/Indicator: Many carbon monoxide detectors come equipped with a display or indicator that provides valuable information about the concentration of CO gas in the air. This can include numerical readings, color-coded lights, or even digital screens that show the detected levels of carbon monoxide. This feature helps occupants understand the severity of the situation and take appropriate action.
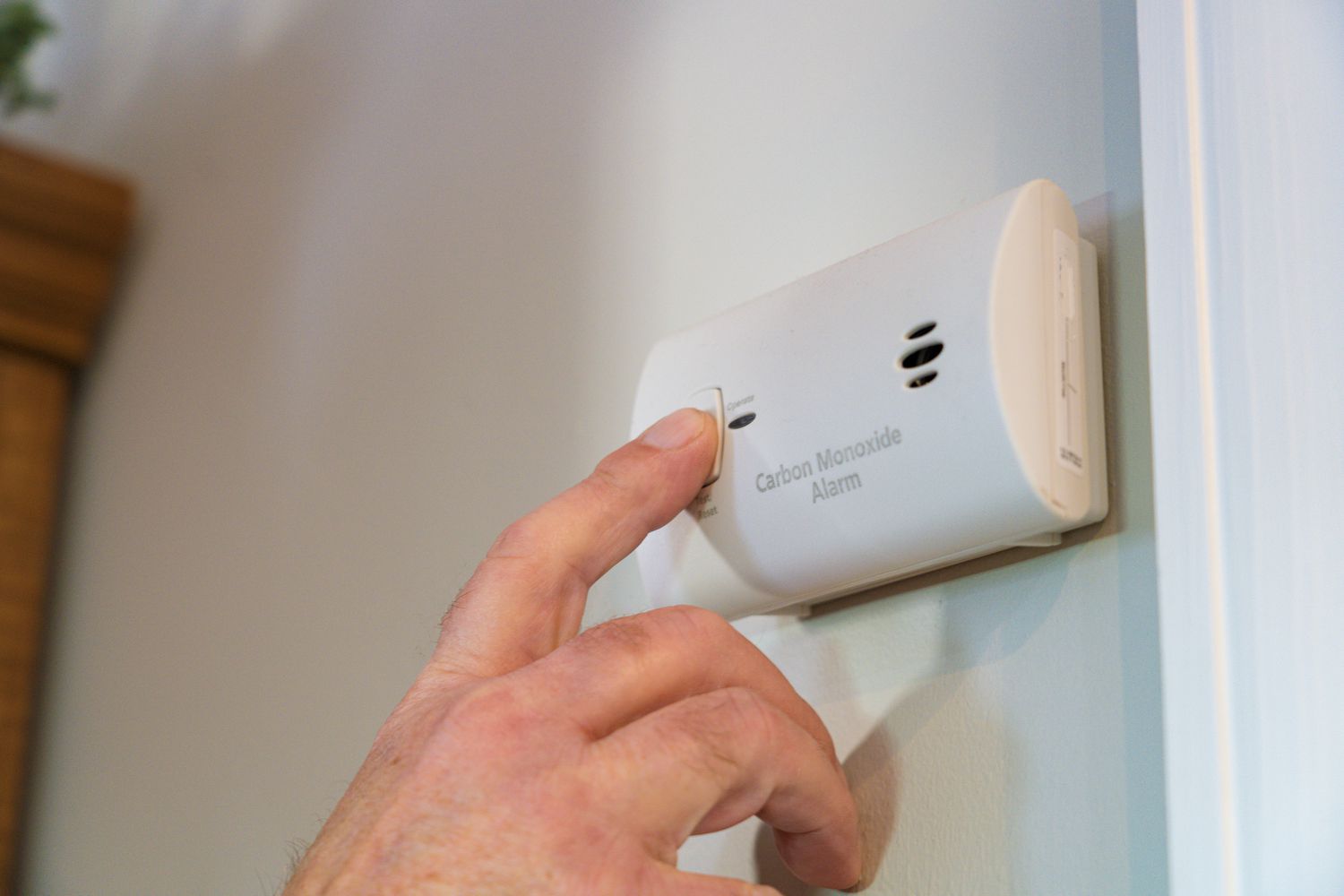
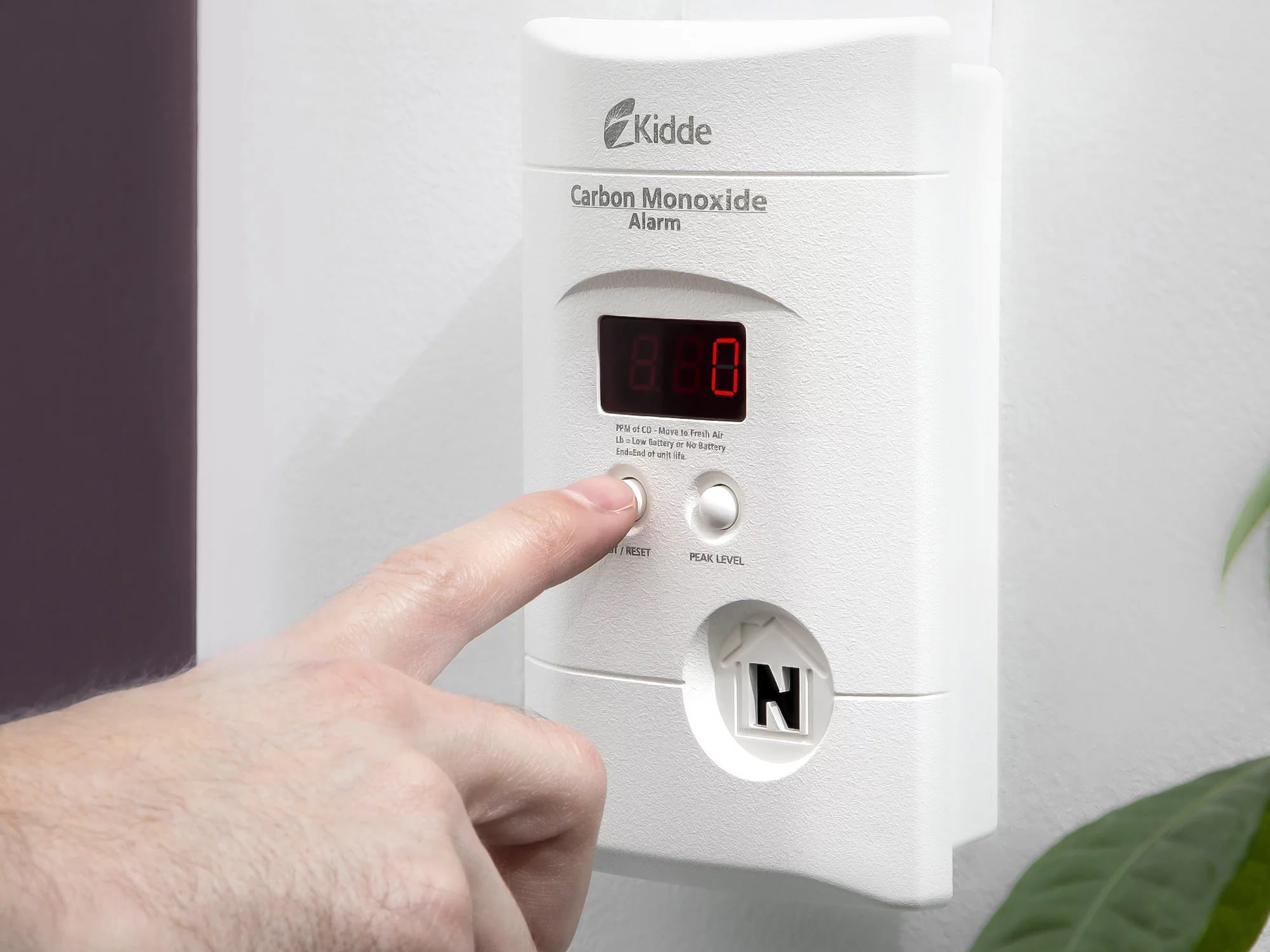
- Test/Silence Button: A test button allows homeowners to check the functionality of the carbon monoxide detector regularly. By pressing this button, the detector should initiate a self-test, ensuring that all components are working correctly. Some detectors also include a silence button that temporarily disables the alarm, useful in non-emergency situations such as cooking mishaps that may trigger false alarms.
- Interconnectivity: Some advanced carbon monoxide detectors offer interconnectivity capabilities. This means that multiple detectors can be linked together, allowing them to communicate and synchronize alarms. When one detector detects carbon monoxide, all interconnected detectors will sound their alarms, providing widespread notification throughout the home.
These basic components work together to provide effective carbon monoxide detection in residential and commercial settings. In the next section, we will explore the different sensor technologies used in carbon monoxide detectors, which play a crucial role in their detection capabilities.
Sensor Technology Used in Carbon Monoxide Detectors
The sensor is a critical component of a carbon monoxide detector, responsible for detecting and measuring the presence of CO gas in the surrounding environment. There are two main sensor technologies used in carbon monoxide detectors: electrochemical sensors and biomimetic sensors.
Electrochemical Sensors: Electrochemical sensors utilize a chemical reaction to detect carbon monoxide gas. They consist of a sensing electrode and a reference electrode immersed in an electrolyte solution. When exposed to CO gas, an electrochemical reaction occurs, generating an electric current that can be measured. The more carbon monoxide present, the greater the current produced. Electrochemical sensors are highly accurate, responsive, and have a long lifespan. They are commonly used in professional-grade and high-end residential carbon monoxide detectors.
Biomimetic Sensors: Biomimetic sensors mimic the natural response of living organisms to detect carbon monoxide. These sensors use a gel-based material that changes color when exposed to CO gas. The gel contains a pigment that undergoes a chemical reaction in the presence of carbon monoxide, resulting in a color change. The intensity of the color change corresponds to the level of CO gas present. Biomimetic sensors are cost-effective and provide reliable detection. They are commonly found in lower-cost residential carbon monoxide detectors.
Both types of sensors have their advantages and trade-offs. Electrochemical sensors offer high accuracy and longevity but can be more expensive. Biomimetic sensors provide cost-effective detection but may have slightly lower accuracy and shorter lifespans. Regardless of the sensor technology, it is crucial to ensure that carbon monoxide detectors are regularly tested and calibrated according to the manufacturer’s instructions to maintain their reliability and accuracy.
Now that we understand the sensor technology used in carbon monoxide detectors, let’s explore how these detectors are able to detect the presence of CO gas in the air.
Carbon monoxide detectors work by using a chemical reaction to measure the presence of CO gas. When CO is detected, the alarm is triggered to alert you of the danger. Make sure to test your detector regularly to ensure it is functioning properly.
Read more: What Does A Carbon Monoxide Detector Do
How Carbon Monoxide Detectors Detect CO Gas
Carbon monoxide detectors are specifically designed to detect and measure the presence of carbon monoxide (CO) gas in the surrounding environment. By doing so, they provide early warning signs to occupants, allowing them to take necessary actions to prevent harm. Let’s explore how carbon monoxide detectors detect CO gas:
Sensor Detection: Carbon monoxide detectors use specialized sensors, such as electrochemical or biomimetic sensors, to detect the presence of CO gas in the air. These sensors are designed to react to the presence of carbon monoxide molecules by generating an electrical current or changing color. The sensors are highly sensitive and can detect even small amounts of CO gas.
Monitoring Air Quality: Carbon monoxide detectors continuously monitor the air quality in their vicinity. When CO gas is present, the sensors produce a response that triggers the alarm system. The sensitivity of the detectors can be adjusted to detect varying levels of CO concentration, ensuring accurate and timely detection of potential danger.
Threshold Levels: Carbon monoxide detectors are typically set to trigger the alarm when CO gas reaches certain threshold levels. These levels are based on safety standards and guidelines established by regulatory bodies. When the detected CO levels reach or exceed these thresholds, the alarm is activated to alert occupants of the potential danger.
Sound and Visual Alarms: When carbon monoxide is detected, carbon monoxide detectors utilize both sound and visual alarms to alert occupants. The sound alarm emits a loud, distinctive noise that is designed to be attention-grabbing and wake individuals from sleep. Some detectors also incorporate visual indicators, such as flashing lights or a digital display, to provide additional visual cues of the detected CO levels.
Interconnected Systems: In larger residential or commercial settings, carbon monoxide detectors may be interconnected. This means that when one detector detects CO gas, it triggers the alarms of all interconnected detectors throughout the building. This interconnected system provides an effective means of notifying occupants in multiple areas, ensuring everyone is aware of the potential danger.
It is essential to note that carbon monoxide detectors are designed to detect CO gas, not smoke or other gases. They should not be mistaken for smoke detectors or gas detectors, which serve different purposes. To ensure comprehensive safety, it is recommended to have both carbon monoxide detectors and smoke detectors installed in your home.
Now that we understand how carbon monoxide detectors detect the presence of CO gas, let’s explore the various alert mechanisms that these devices employ to notify occupants in case of danger.
Alert Mechanisms in Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Carbon monoxide detectors are equipped with various alert mechanisms to notify occupants in the event of elevated levels of carbon monoxide (CO) gas. These alert mechanisms are designed to be highly noticeable and attention-grabbing to ensure that individuals can take immediate action to protect themselves. Let’s explore the different alert mechanisms commonly found in carbon monoxide detectors:
Sound Alarm: The most common alert mechanism in carbon monoxide detectors is a sound alarm. When the sensors detect dangerous levels of CO gas, the alarm is triggered, emitting a loud and distinctive sound. This sound is designed to be attention-grabbing and can vary in intensity and tone depending on the model. The loud alarm is crucial for waking individuals during sleep and notifying occupants throughout the home.
Flashing Lights: In addition to sound alarms, some carbon monoxide detectors feature flashing lights as an additional alert mechanism. These flashing lights can provide visual cues, especially for individuals with hearing impairments or in situations where the noise may not be as audible, such as when wearing headphones or in a noisy environment.
Verbal Alerts: Certain advanced carbon monoxide detectors may include a verbal alert feature. These detectors are equipped with a voice synthesizer that can audibly announce the presence of carbon monoxide, providing clear and concise instructions to occupants. Verbal alerts can be particularly helpful for individuals with visual impairments or in situations where immediate action may be required.
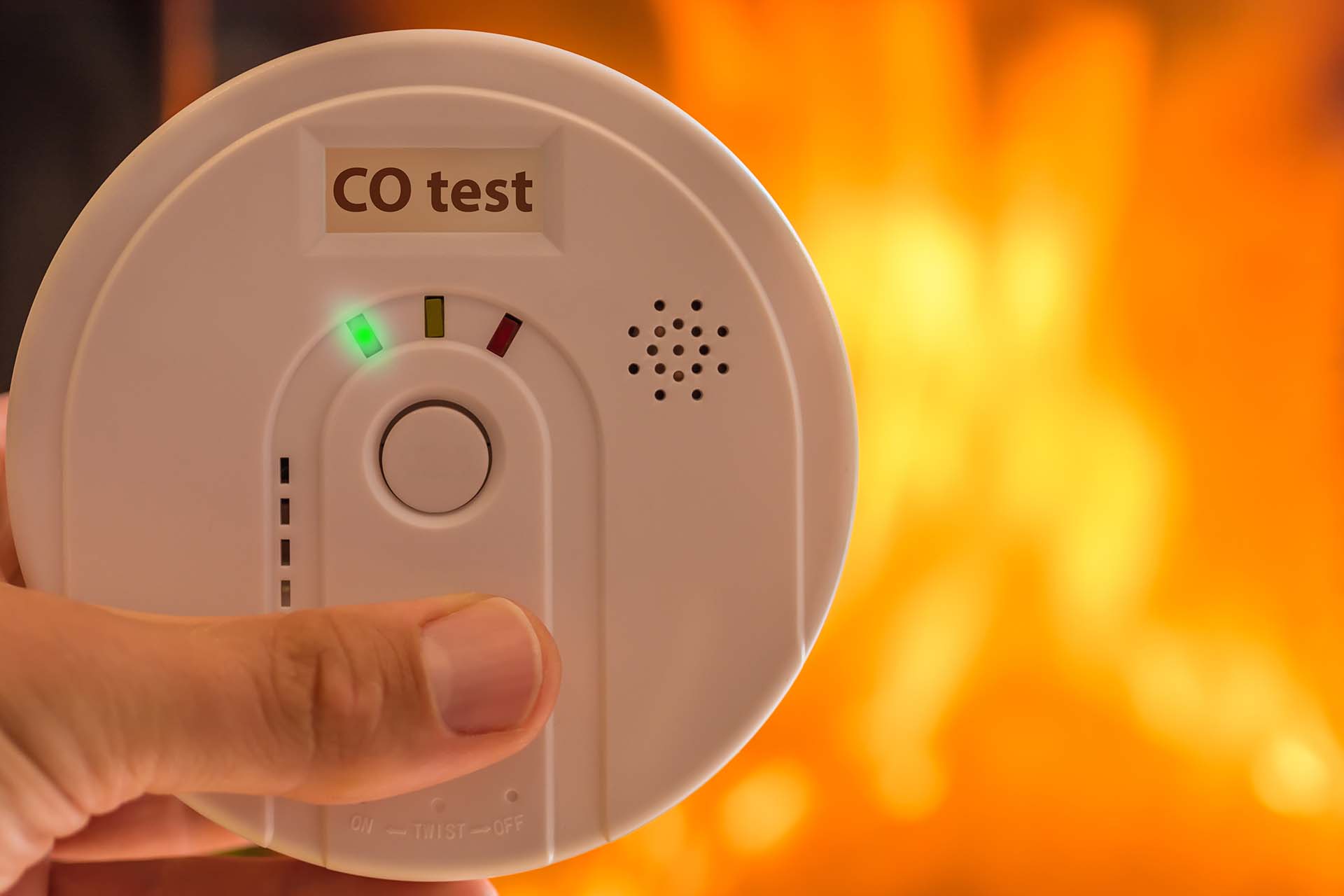
Digital Display: Some carbon monoxide detectors come with a digital display that provides visual information about the detected levels of carbon monoxide gas. This display may show the exact parts per million (ppm) of CO gas present in the air. A rising number on the display indicates an increasing level of danger, allowing occupants to gauge the severity of the situation and take appropriate action.
Mobile Notifications: With advancements in smart home technology, some carbon monoxide detectors can now send mobile notifications to occupants’ smartphones or connected devices. When carbon monoxide is detected, an alert is sent via a dedicated app, allowing individuals to receive immediate notifications even when they are not at home. This feature provides an extra layer of safety and peace of mind for homeowners.
It is essential to familiarize yourself with the alert mechanisms of your specific carbon monoxide detector and ensure that they are functioning properly. Regularly test the alarms and replace batteries as instructed by the manufacturer to ensure that the detectors are in optimal working condition.
In the next section, we will explore the importance of proper placement and installation of carbon monoxide detectors in your home.
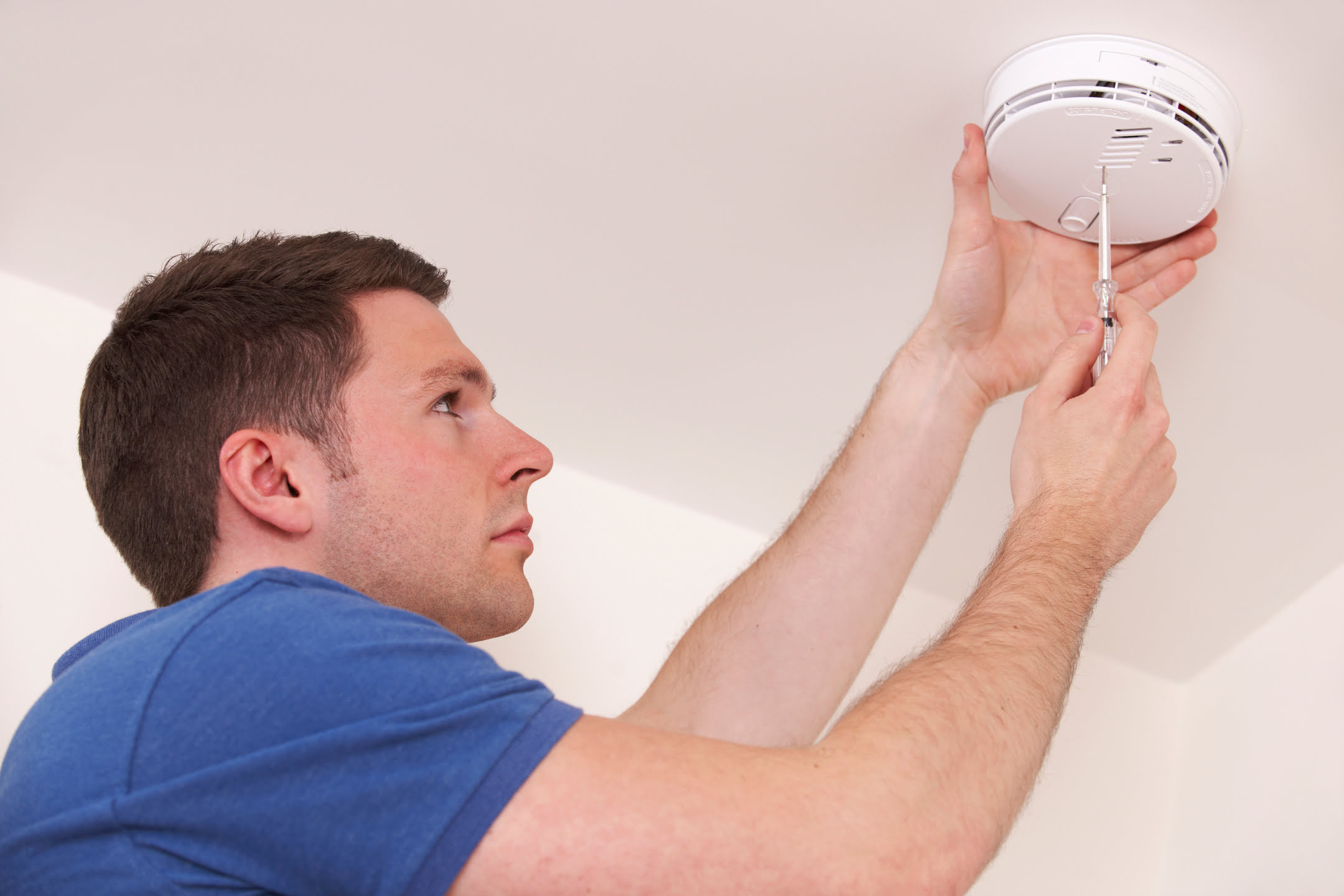
Placement and Installation of Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Proper placement and installation of carbon monoxide detectors are crucial for their effective operation and ensuring the safety of occupants. Here are some guidelines to consider when installing carbon monoxide detectors in your home:
Install on Every Level: It is recommended to have carbon monoxide detectors installed on every level of your home, including the basement and attic. Carbon monoxide can easily travel between floors, so having detectors on each level ensures comprehensive coverage throughout the entire house.
Place Near Bedrooms: Install carbon monoxide detectors near sleeping areas to provide immediate protection while individuals are most vulnerable. Bedrooms should always have a detector installed, even if other areas on the same level have detectors. If you have multiple bedrooms, it is wise to have a detector in each room or in the adjacent hallway.
Mount at the Correct Height: Carbon monoxide detectors should be mounted at a recommended height for optimal detection. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific model, but generally, the detectors should be mounted at a height of around 5 feet (1.5 meters) from the floor. This allows the detector to sense the CO gas at the breathing level of individuals.
Keep Away from Obstacles: Avoid placing carbon monoxide detectors near objects that may obstruct airflow or inhibit their proper functioning. Keep them away from curtains, furniture, or any other obstructions that could block the path of CO gas reaching the detector.
Follow Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Each carbon monoxide detector may have specific installation guidelines provided by the manufacturer. It is essential to thoroughly read and follow these recommendations to ensure proper installation and functionality of the detector. This includes any instructions regarding wiring, power source, mounting options, or interconnection with other detectors.
Consider Additional Areas: In addition to bedrooms and living areas, consider installing carbon monoxide detectors in other areas where CO gas sources are present. This includes near gas-powered appliances (such as water heaters, furnaces, and stoves), fireplaces, and attached garages. These areas often have a higher likelihood of carbon monoxide buildup, so having detectors installed provides added protection.
Maintain Regular Testing: Once the carbon monoxide detectors are installed, it is important to regularly test their functionality. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for testing, which may involve pressing a test button or using a carbon monoxide test kit. Test the detectors monthly and replace batteries as needed to ensure they are in proper working condition.
By following these placement and installation guidelines, you can ensure that carbon monoxide detectors are positioned optimally to detect any potential CO gas threats in your home. In the next section, we will explore the importance of regular maintenance and testing of carbon monoxide detectors.
Maintenance and Testing of Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Regular maintenance and testing of carbon monoxide detectors are essential to ensure their proper functioning and reliability. Here are some important guidelines to follow for the maintenance and testing of carbon monoxide detectors:
Read the Manufacturer’s Instructions: Start by thoroughly reading and understanding the manufacturer’s instructions that come with your specific carbon monoxide detector. These instructions will provide valuable information on maintenance requirements and testing procedures.
Test Monthly: It is recommended to test your carbon monoxide detectors at least once a month. Testing verifies that the detectors are functioning correctly and can effectively alert occupants in the event of elevated CO levels. Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer for testing, which typically involve pressing a test button to initiate the test sequence.
Replace Batteries: Carbon monoxide detectors are typically battery-powered. Regularly check the batteries and replace them as needed, following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Some detectors may have a low-battery indicator that alerts you when the batteries need to be replaced. It is generally recommended to replace the batteries at least once a year, even if they still have some remaining power.
Clean Regularly: Dust, debris, and other particles can accumulate on the sensors of carbon monoxide detectors, potentially affecting their accuracy and sensitivity. Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the exterior of the detector regularly. Avoid using any liquid cleaners or solvents, as they may damage the sensors or other internal components.
Replace According to Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Carbon monoxide detectors have a limited lifespan, typically between 5 to 10 years depending on the model. After this time, the sensors may become less reliable, and the overall performance of the detector can decline. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding when to replace your carbon monoxide detectors to ensure ongoing safety and effectiveness.
Respond to Alarms: If the carbon monoxide detector sounds an alarm, take immediate action. Treat each alarm as a serious matter, even if you do not notice any symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning. Evacuate the premises, seek fresh air, and contact emergency services to assess and resolve the issue causing the alarm activation.
Carbon Monoxide Test Kit: Consider using a carbon monoxide test kit periodically to verify the accuracy of your carbon monoxide detectors. These test kits release a small amount of CO gas in a controlled manner to confirm that the detectors can detect it and trigger the alarms. Follow the instructions provided with the test kit and consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for your detectors.
By following these maintenance and testing guidelines, you can ensure that your carbon monoxide detectors are properly maintained, reliable, and ready to provide early warning signs of potential carbon monoxide dangers in your home.
Now that we have explored the importance of maintenance and testing, let’s conclude our discussion on carbon monoxide detectors.
Read more: Why Does Carbon Monoxide Detector Beeps
Conclusion
Carbon monoxide detectors are an essential component of home safety systems, providing early detection and warning signs of carbon monoxide gas in our indoor environments. These detectors play a critical role in protecting ourselves and our loved ones from the dangers of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Understanding the nature of carbon monoxide and its potential hazards is crucial in realizing the importance of carbon monoxide detectors. This odorless, colorless gas can be produced by a variety of everyday household items, such as gas appliances and fireplaces, making it imperative to have a reliable means of detection.
We have explored the basic components of carbon monoxide detectors, including the sensor technology used to detect CO gas, as well as the alert mechanisms employed to notify occupants in case of danger. We have also discussed the significance of proper placement and installation of carbon monoxide detectors throughout the home, as well as the importance of regular maintenance and testing.
By following guidelines and recommendations for placement, installation, maintenance, and testing, we can ensure that our carbon monoxide detectors are in optimal working condition, providing accurate detection and timely alerts. This gives us peace of mind and confidence that we are taking necessary precautions to keep our homes and our loved ones safe.
Remember, carbon monoxide detectors are not a substitute for preventive measures such as regular maintenance of gas appliances, proper ventilation, and usage practices. However, they act as an additional layer of protection, providing early warning signs and precious time to take appropriate actions in case of elevated CO gas levels.
Stay vigilant and prioritize the safety of your household by installing carbon monoxide detectors today. These small, life-saving devices can make a significant difference in preventing carbon monoxide-related accidents and ensuring the well-being of your family.
Always consult the guidelines provided by the manufacturer for your specific carbon monoxide detectors and adhere to local regulations regarding installation and maintenance. With proper care, maintenance, and awareness, we can mitigate the risks associated with carbon monoxide and create a safer living environment for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does Carbon Monoxide Detector Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Does Carbon Monoxide Detector Work”