

Articles
What Is A Steamer Clam
Modified: August 28, 2024
Discover the best articles on steamer clams, including tips for cooking, cleaning, and enjoying these delicious shellfish. Learn more about steamer clams today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Steamer clams, also known as soft-shell clams or longneck clams, are a popular and delicious seafood delicacy. They are a type of bivalve mollusk, belonging to the family Myidae. Steamer clams are found in coastal areas and estuaries, where they burrow in sandy or muddy substrates.
These clams are highly valued for their tender and succulent meat, which is commonly enjoyed steamed, boiled, or baked. In addition to being a delectable treat, steamer clams offer various health benefits and play a vital role in marine ecosystems.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of steamer clams, exploring their anatomy, habitat, behavior, culinary uses, and more. Join us as we uncover the secrets of these amazing bivalves.
Key Takeaways:
- Steamer clams, also known as soft-shell clams, are prized for their tender meat and play a vital role in marine ecosystems as filter feeders, contributing to water quality and ecosystem health.
- From their culinary appeal to their health benefits, steamer clams offer a versatile and valuable resource. Conservation efforts and responsible harvesting practices are essential to ensure their sustainability for future generations.
Read more: Where To Buy Steamer Clams Near Me
Definition of a Steamer Clam
A steamer clam is a type of bivalve mollusk characterized by its soft-shell and elongated neck. They are scientifically classified as Mya arenaria and are commonly found along the North American Atlantic coast, from Labrador to Georgia.
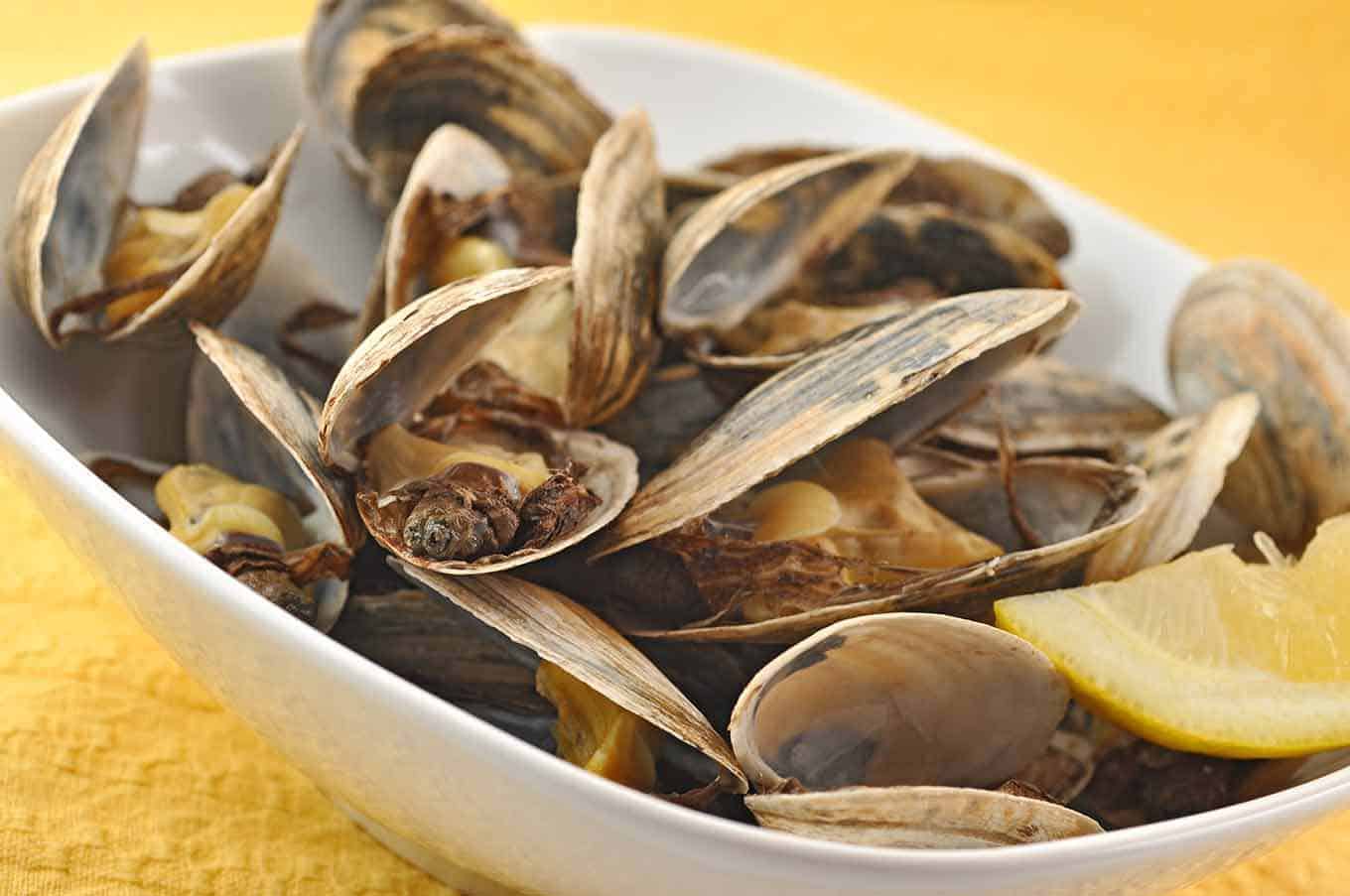
These clams get their name from the method of cooking that is commonly used to prepare them. Steaming is the preferred cooking technique, as it helps to retain the natural flavors and preserve the tender texture of the meat.
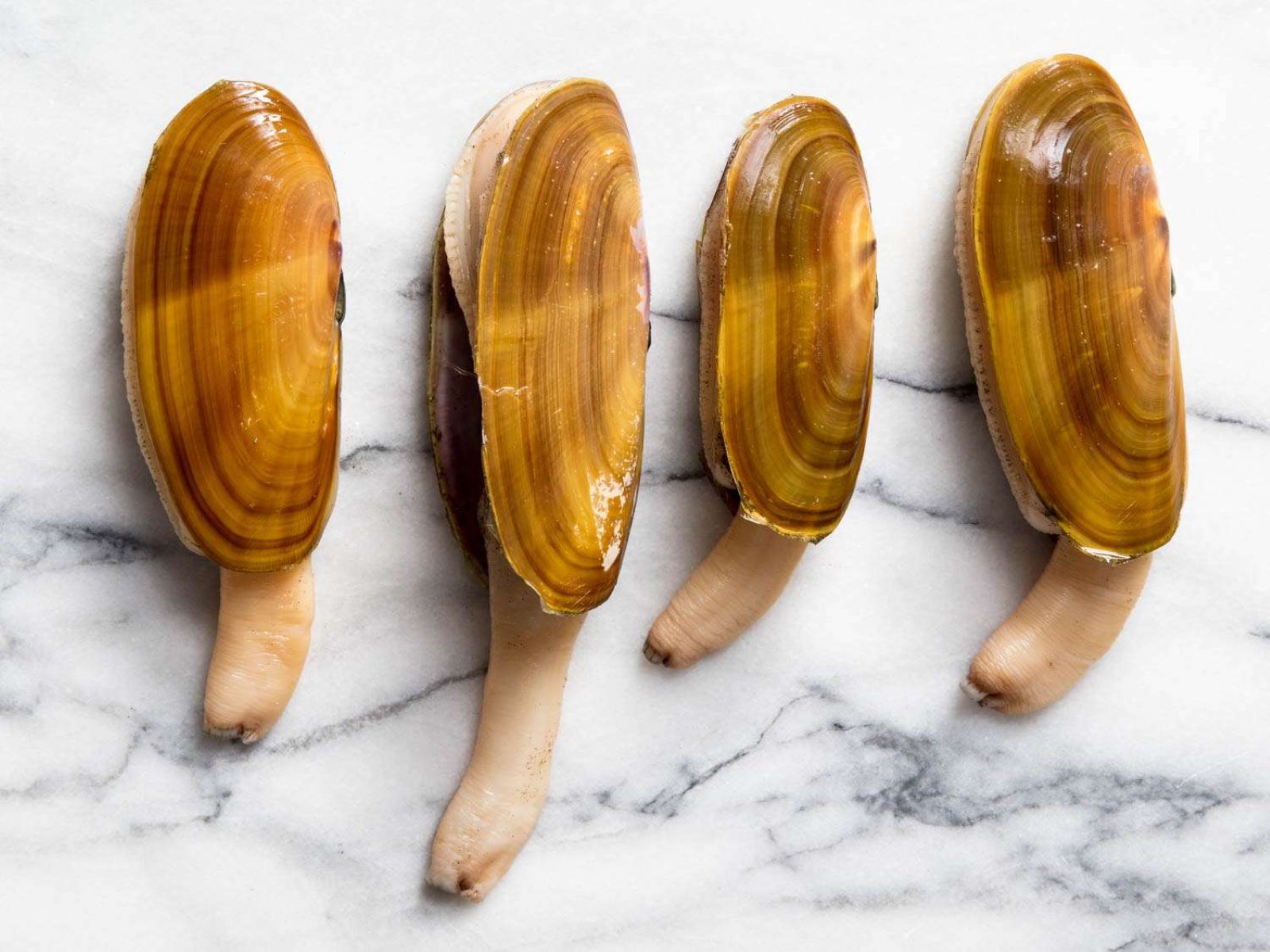
Steamer clams have a thin, brittle shell that is typically gray or white in color. The shell is elongated and oblong, with a slightly rounded back. The size of a steamer clam can vary, but they usually measure between 3 to 6 inches in length. The neck, or siphon, of a steamer clam is long and slender, enabling it to extend out of the sand in search of food and oxygen.
Unlike other clam species, steamer clams are known for their ability to burrow deep into the sediment, using their muscular foot. This allows them to anchor themselves securely and protect themselves from predators.
Steamer clams are often mistaken for other species, such as hard-shell clams or geoducks, due to their similar appearance. However, they can be distinguished by their soft shells and longer, more pronounced necks.
Anatomy of a Steamer Clam
Understanding the anatomy of a steamer clam is key to appreciating the remarkable adaptations and functions of this unique mollusk.
The shell of a steamer clam is a protective exoskeleton composed of two halves, or valves, connected by a hinge. The shell is made up of calcium carbonate and is relatively thin compared to other clam species. The outer surface of the shell is usually smooth, with concentric ridges and markings.
When examining the inside of a steamer clam shell, you will find a series of intricate features. Near the hinge, there is a prominent adductor muscle, which is responsible for opening and closing the shell. This muscle is highly developed in steamer clams, allowing them to burrow and withstand the pressures of the surrounding sediment.
Below the adductor muscle, you will find the visceral mass, which contains the digestive, circulatory, and reproductive organs of the clam. The visceral mass is protected by a thin, transparent membrane called the mantle.
One of the most distinctive features of a steamer clam is its long, retractable neck, also known as the siphon. The siphon serves multiple functions, including respiration, ingestion of food particles, and the expulsion of waste. It can extend out of the burrow and into the water column to filter feed.
Streamer clams have a well-developed foot, which is a muscular organ used for locomotion and burrowing into the sediment. The foot is also responsible for anchoring the clam in position and preventing it from being washed away by currents.
Along the mantle, you will find gills, which are crucial for respiration and filter feeding. The gills help the clam extract oxygen from the water and filter out microscopic food particles, such as phytoplankton and organic detritus.
The presence of these various anatomical features enables steamer clams to thrive in their sandy or muddy habitats, as they can adapt and survive in environments with fluctuating water conditions and limited food resources.
Habitat and Distribution
Steamer clams are primarily found along the North American Atlantic coast, spanning from Labrador in Canada to Georgia in the United States. They are commonly encountered in coastal areas, estuaries, and shallow bays, where they can burrow into sandy or muddy substrates.
These clams are well-adapted to a wide range of habitat conditions, including areas with varying levels of salinity, water temperature, and tidal flow. They thrive in areas where there is a mix of fresh and saltwater, such as brackish marshes and tidal flats.
Steamer clams are most abundant in areas with fine sediments, as they require loose, sandy or muddy substrates to burrow and anchor themselves. They can be found in intertidal zones, where the clam beds may be exposed at low tide and submerged at high tide.
When it comes to depth, steamer clams are typically found in shallower waters, ranging from the low intertidal zone to a few meters below the surface. However, they have been known to occur at depths of up to 30 meters in certain areas.
In terms of distribution, while steamer clams have a wide range along the North American Atlantic coast, their abundance and density can vary depending on local habitat conditions. They are more common in regions with suitable sandy or muddy substrates and optimal water quality.
It is important to note that steamer clam populations can be influenced by various factors, including habitat degradation, pollution, predation, and harvesting activities. Proper management and conservation efforts are crucial in ensuring the sustainability and preservation of steamer clam populations for future generations.
Feeding and Behavior
Steamer clams are filter feeders, meaning they obtain their food by extracting small particles from the water column. They have a specialized feeding mechanism that allows them to filter out organic matter, plankton, and other microscopic organisms.
The feeding process begins with the clam extending its long siphon, or neck, out of its burrow and into the water. The siphon acts like a snorkel, allowing the clam to take in water. As the water flows into the clam’s body, the gills trap tiny food particles and filter out any sediment or debris.
The filtered particles are then transported to the clam’s mouth, where they are ingested and digested. Steamers primarily feed on phytoplankton, bacteria, and small organic detritus, utilizing their specialized gills and cilia to capture and transfer the food to their digestive system.
While filter feeding is their primary method of obtaining nutrients, steamer clams are also capable of extending their siphons to engulf larger food items, such as small crustaceans and worms, if the opportunity presents itself.
In terms of behavior, steamer clams are generally sedentary creatures. They spend the majority of their time buried in the substrate, with only their siphons exposed to the water column. This strategy provides protection from predators and helps them conserve energy.
When disturbed or threatened, steamer clams have a fascinating and effective defense mechanism. They can rapidly retract their siphon and foot into their shell, sealing themselves off from the surrounding environment. This enables them to avoid predation and stay hidden from potential threats.
Steamer clams also play a crucial role in the estuarine ecosystem. As filter feeders, they help maintain water quality by filtering and removing excess nutrients and organic matter from the water. Their activities also contribute to the cycling of nutrients and the overall health of the ecosystem.
While they may not be the most active creatures, steamer clams have adapted remarkable feeding strategies and behaviors that allow them to thrive in their unique coastal habitats.
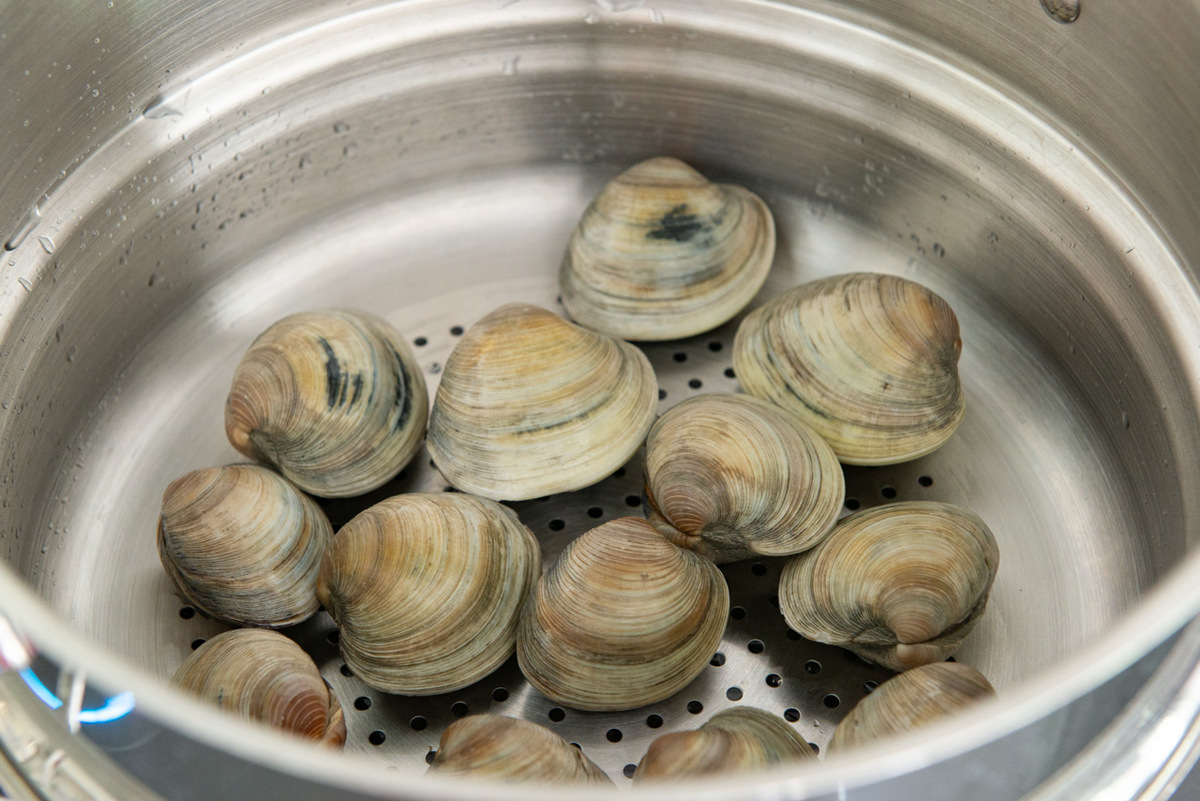
When cooking steamer clams, make sure to discard any clams that do not open after cooking, as they may be unsafe to eat.
Read also: 15 Amazing Clam Steamer Pot for 2024
Uses of Steamer Clams
Steamer clams have been enjoyed as a culinary delicacy for centuries, and their uses extend beyond just their delicious taste. Let’s explore some of the various ways in which steamer clams are utilized:
- Gastronomy: One of the primary uses of steamer clams is as a food source. They are highly prized for their tender meat, which has a subtle, briny flavor. Steamer clams are commonly steamed, boiled, or baked, and can be served on their own or incorporated into various dishes like clam chowder, pasta, or seafood stews.
- Culinary Industry: Steamer clams play a significant role in the culinary industry, serving as a staple ingredient in many seafood dishes. They are sought after by seafood restaurants, fish markets, and gourmet food suppliers, catering to both local and international consumers.
- Seafood Markets: The commercial demand for steamer clams has led to the development of a thriving seafood market. These clams are harvested, processed, and made available in fresh, frozen, or canned forms to meet consumer needs and preferences.
- Tradition and Culture: In coastal communities, steamer clams hold cultural significance and are often featured in traditional recipes and festive occasions. They are a part of culinary traditions that are passed down through generations, enriching the cultural heritage of these communities.
- Economic Importance: The harvesting and sale of steamer clams provide economic benefits to coastal regions. It supports local fishing communities, creates employment opportunities, and contributes to the overall economy through revenue generated from the seafood industry.
- Tourism and Recreational Activities: Steamer clam populations can attract recreational fishers, clam diggers, and tourists who enjoy foraging for these delectable bivalves. This not only fosters tourism but also enables individuals to connect with nature and experience the thrill of finding their own food.
- Education and Research: Steamer clams serve as valuable subjects for scientific research and educational purposes. Their biology, behavior, and ecological interactions provide insights into marine ecosystems, helping researchers understand the delicate balance of coastal habitats.
These are just a few examples of the diverse uses of steamer clams. Their culinary appeal, economic importance, and cultural significance make them a versatile and valuable resource.
Harvesting and Cooking Steamer Clams
Harvesting and cooking steamer clams require careful techniques to ensure their freshness and flavor. Let’s take a closer look at the process of harvesting and cooking these delectable mollusks:
Harvesting: Steamer clams can be harvested through various methods, including handpicking, raking, or using specialized tools such as clam guns or clam rakes. It is important to check local regulations and obtain the necessary permits before harvesting, as there may be restrictions on size limits and harvesting seasons to ensure sustainable practices. Clammers typically target lower tides, as the exposed clam beds make it easier to locate and dig up the clams from the sand or mud.
Cleaning and Preparing: Once harvested, it is crucial to rinse off any excess sediment or debris from the clams. This can be done by gently scrubbing the shells under cool running water. It is important to discard any clams with cracked or broken shells, as they may be compromised and should not be consumed.
Cooking Methods: Steamer clams are most commonly cooked by steaming, although boiling and baking are also popular methods. To steam clams, place them in a pot with a small amount of water or broth, cover, and cook over medium heat until the shells open. This usually takes around 6 to 10 minutes. Discard any clams that do not open during the cooking process, as they may be unsafe to eat. Boiling clams is another option, wherein the clams are submerged in boiling water for a few minutes until the shells open. Baking clams involves placing them on a baking sheet and cooking in a preheated oven until the shells open.
Serving Suggestions: Steamed clams can be enjoyed on their own, dipped in melted butter or clarified broth. They are also a popular ingredient in various recipes, such as clam chowder, pasta dishes, or seafood stews. The tender meat of steamer clams pairs well with flavors like garlic, lemon, parsley, and white wine. It is important to handle cooked clams gently to avoid damaging the delicate meat.
Storage and Shelf Life: Fresh live steamer clams should be consumed as soon as possible after harvesting or purchase to ensure optimal taste and quality. If not cooking immediately, they can be stored in the refrigerator in a container covered with a damp cloth or paper towel. It is recommended to consume cooked clams within one to two days.
By following proper harvesting and cooking techniques, you can fully enjoy the flavors and textures of steamer clams. Whether savored on their own or incorporated into your favorite recipes, these bivalves are sure to delight seafood lovers.
Health and Nutritional Benefits
Steamer clams not only satisfy our taste buds, but they also offer several health and nutritional benefits. Let’s explore the ways in which these delicious bivalves can contribute to a healthy diet:
Nutrient-Rich: Steamer clams are packed with essential nutrients. They are an excellent source of lean protein, which is vital for muscle growth, repair, and overall body function. They are also rich in essential minerals like iron, zinc, and selenium, which play key roles in various bodily functions, including immune function, cognitive health, and energy production.
Low in Fat and Calories: Steamer clams are naturally low in fat and calories, making them a nutritious choice for those looking to maintain a healthy weight. They provide a satisfying and filling meal without adding excessive calories or unhealthy fats.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These clams are a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are essential for heart health and brain function. Omega-3 fatty acids have been associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, inflammation, and cognitive decline.
B Vitamins: Steamer clams contain several B vitamins, including vitamin B12, which is necessary for red blood cell production and maintaining a healthy nervous system. They also provide vitamins B3 (niacin), B6, and folate, which are important for energy metabolism, DNA synthesis, and nervous system function.
Mineral Richness: Apart from iron and zinc, steamer clams are a significant source of other minerals, such as potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium. These minerals contribute to maintaining healthy bones, regulating blood pressure, and supporting proper muscle function.
Antioxidant Properties: Steamer clams contain antioxidants, including vitamin C and selenium, which help combat oxidative stress and protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants are important for overall health and may contribute to a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Benefits for Brain Health: The omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients found in steamer clams have been linked to improved cognitive function and a reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline. They may also play a role in supporting mood and mental well-being.
It’s important to note that while steamer clams offer numerous health benefits, individuals with shellfish allergies or certain medical conditions should exercise caution and consult with a healthcare professional before consuming them.
By incorporating steamer clams into a balanced diet, you can enjoy their delicious taste while reaping the nutritional rewards they offer.
Conservation and Sustainability
Conservation and sustainability are crucial for maintaining healthy steamer clam populations and preserving their habitats for future generations. Here are some key considerations and practices related to the conservation and sustainable management of steamer clams:
Regulations and Monitoring: Many coastal regions have implemented regulations to manage the harvesting of steamer clams. These regulations may include restrictions on the size and number of clams that can be harvested, as well as designated harvesting seasons or areas. Monitoring efforts help ensure compliance with these regulations and assess the health of the clam populations.
Harvesting Practices: Sustainable harvesting practices are essential to prevent overexploitation and minimize environmental impact. Clammers should avoid targeting areas with high densities of juvenile clams, as they contribute to the growth and replenishment of the population. Additionally, implementing techniques such as handpicking or using manual tools instead of heavy machinery can help minimize habitat disturbance.
Habitat Preservation: Protecting and preserving the habitat of steamer clams is critical for their long-term survival. Coastal areas and estuaries where clams thrive should be conserved to maintain the necessary sandy or muddy substrates. Preservation efforts should also focus on maintaining water quality, reducing pollution, and minimizing habitat degradation caused by factors such as coastal development and climate change.
Research and Monitoring: Continuous research and monitoring of steamer clam populations and their habitats are essential to gather data on population trends, reproductive biology, and the impacts of environmental changes. This information can help inform management practices and guide conservation efforts.
Community Engagement: Engaging local communities, clammers, and stakeholders in the conservation and management of steamer clams is crucial. Promoting awareness and providing education about sustainable harvesting practices, habitat preservation, and the importance of conserving these valuable resources can foster a sense of responsibility and ensure the long-term sustainability of steamer clam populations.
Partnering with Researchers and Conservation Organizations: Collaboration between researchers, conservation organizations, and governmental agencies is vital in implementing effective management strategies and ensuring the sustainable use and conservation of steamer clams. Sharing knowledge, data, and best practices can help make informed decisions and promote the long-term viability of steamer clam populations.
By adopting sustainable harvesting practices, preserving important habitats, and actively involving stakeholders in conservation efforts, we can contribute to the preservation of steamer clams and the delicate ecosystems they inhabit. This will allow future generations to continue enjoying the culinary and ecological benefits these bivalves offer.
Read more: How To Store Cooked Clams
Conclusion
Steamer clams, with their unique attributes and delectable taste, have captivated seafood lovers for centuries. These soft-shell bivalves, found along the North American Atlantic coast, offer a myriad of benefits and play essential roles in coastal ecosystems.
From their elongated necks to their ability to burrow deep in the substrate, steamer clams have adapted remarkable features that allow them to thrive in sandy or muddy habitats. As filter feeders, they contribute to maintaining water quality by filtering out organic matter and excess nutrients.
The culinary uses of steamer clams are diverse, making them an integral part of gastronomy. From clam chowder to pasta dishes, their tender meat adds a delectable flavor to various recipes. The economical value of steamer clams supports local fishing communities and contributes to the seafood industry.
Beyond their taste and economic significance, steamer clams offer significant health benefits. They are low in fat and calories, rich in lean protein, minerals like iron and zinc, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins. These nutrients contribute to overall health, brain function, and heart health.
Ensuring the conservation and sustainability of steamer clams requires responsible harvesting practices, habitat preservation, and community engagement. By implementing regulations, monitoring populations, and educating stakeholders, we can protect these valuable resources and their habitats for future generations to enjoy.
In conclusion, steamer clams are more than a delicious seafood delicacy – they are living organisms with ecological importance and numerous benefits. By appreciating and safeguarding these remarkable bivalves, we can continue to relish their flavors and contribute to the preservation of our valuable coastal ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Steamer Clam
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is A Steamer Clam”