

Articles
How To Store Blood Worms
Modified: January 6, 2024
Learn how to store blood worms properly with our informative articles. Find essential tips, tricks, and guidelines to maintain their freshness and nutritional value.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
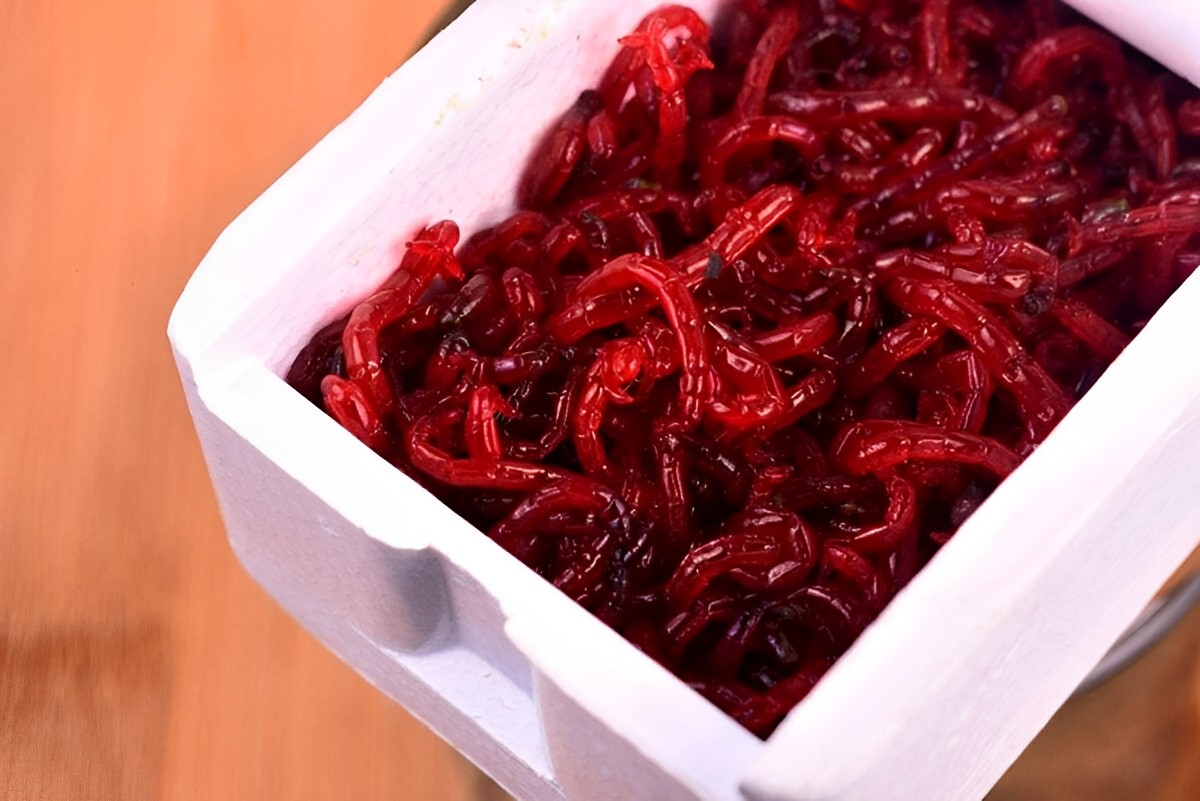
Blood worms, scientifically known as Chironomus plumosus, are a popular live food source for aquarium fish and other aquatic pets. These tiny red worms are high in protein and essential nutrients, making them a nutritious and natural diet option for many aquatic creatures.
If you’re an aquarium hobbyist or have aquatic pets that feed on blood worms, it’s crucial to understand the importance of proper blood worm storage. Keeping blood worms in optimal conditions ensures their longevity and nutritional value, maximizing their benefits for your aquatic pets.
In this article, we will guide you through the process of storing blood worms correctly. We will cover topics such as choosing the right container, preparing the storage container, maintaining the blood worms’ health, monitoring water quality, and tips for avoiding contamination.
Proper blood worm storage not only prolongs the worms’ lifespan but also helps maintain their nutritional content. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure that your blood worms remain fresh, healthy, and readily available for feeding your aquatic pets.
So, let’s dive into the details and learn how to store blood worms effectively!
Key Takeaways:
- Proper storage of blood worms is crucial for maintaining their freshness, nutritional value, and availability as a food source for aquatic pets. Choosing the right container, maintaining water quality, and avoiding contamination are key to successful storage.
- By following the guidelines for blood worm storage, you can ensure their longevity and nutritional benefits for your aquatic pets. Proper feeding, monitoring water quality, and preventing contamination are essential for maintaining a healthy environment for the blood worms.
Read more: How To Store Live Worms
Importance of Proper Blood Worm Storage
Proper blood worm storage is crucial for maintaining the worms’ freshness, viability, and nutritional value. When stored incorrectly, blood worms can deteriorate quickly, losing essential nutrients and becoming unfit for consumption by aquatic pets. Here are some of the key reasons why proper storage is important:
1. Extended shelf life: By storing blood worms correctly, you can extend their shelf life and ensure a readily available food source for your aquatic pets. This is particularly essential if you purchase blood worms in bulk or have a large number of aquatic pets to feed.
2. Prolonged nutritional content: Blood worms are highly nutritious, providing essential proteins and amino acids that are vital for the health and growth of aquatic animals. Proper storage helps preserve these nutrients for a longer period, ensuring that your pets receive the maximum nutritional benefits from their diet.
3. Economic value: Blood worms can be relatively expensive, especially if you buy them frequently. By storing them properly, you can avoid unnecessary wastage and save money in the long run.
4. Convenience: Having a consistent supply of blood worms on hand saves you time and effort. Proper storage ensures that you always have a readily available food source for your aquatic pets, eliminating the need for frequent trips to the store.
5. Preventing contamination: Incorrectly stored blood worms can attract bacteria and other pathogens, leading to contamination of the worms and potentially harming your aquatic pets. Proper storage methods help minimize the risk of contamination, ensuring the health and safety of your pets.
To reap these benefits, it’s essential to understand and implement the right techniques for blood worm storage. In the next sections, we will discuss in detail the steps you need to take to store blood worms effectively. From choosing the right container to monitoring water quality and avoiding contamination, these guidelines will help you maintain the freshness and nutritional value of your blood worms.
Choosing the Right Container
Selecting the right container is the first step in proper blood worm storage. The container you choose should meet specific criteria to ensure the worms’ longevity and prevent any unwanted contamination. Here are some factors to consider when choosing the right container:
1. Size: The container should be spacious enough to provide ample room for the blood worms to move and thrive. Avoid overcrowding the container, as this can lead to stress and lower their overall quality.
2. Material: It is best to choose a container made of non-toxic materials that won’t leach harmful chemicals into the water. Opt for glass or plastic containers that are labeled safe for aquarium or food storage.
3. Transparency: Transparent or translucent containers allow you to monitor the activity of the blood worms without disturbing them. This is especially important when checking for signs of decomposition or contamination.
4. Lid or Cover: The container should have a fitted lid or cover to prevent the escape of the blood worms and to minimize evaporation. This will also help in maintaining the necessary humidity levels for the worms’ survival.
5. Airtightness: While a lid or cover is essential, it’s important to ensure that the container is not completely airtight. Blood worms require oxygen to survive, and insufficient airflow can lead to anoxic conditions, which can be detrimental to their health.
6. Easy access: Choose a container with an opening or design that allows for easy access to the blood worms. This will simplify feeding and maintenance tasks, reducing stress for both you and the worms.
7. Ease of cleaning: Blood worm containers should be easy to clean and disinfect to prevent the buildup of bacteria or other contaminants. Look for containers with smooth surfaces that are easy to scrub and rinse.
Remember to label the container to avoid any accidental mix-ups or confusion with other stored items. By selecting the right container, you create an optimal environment for your blood worms and set the stage for successful long-term storage. In the next section, we will explore the steps involved in preparing the storage container for your blood worms.
Preparing the Storage Container
Preparing the storage container for your blood worms is a crucial step in ensuring their long-term survival and maintaining their nutritional value. Follow these steps to properly prepare the container:
1. Clean the container: Before using the container, thoroughly clean it with warm water and a mild detergent or aquarium-safe cleaning solution. Rinse it well to remove any traces of soap or cleaning agents that could be harmful to the blood worms.
2. Rinse with dechlorinated water: After cleaning, rinse the container with dechlorinated water to remove any remaining residue and chemicals. Chlorine and chloramine, commonly found in tap water, can be toxic to aquatic organisms.
3. Condition the container: To create a suitable environment for the blood worms, condition the container by adding dechlorinated water and allowing it to sit for 24 hours. This allows any residual chlorine or chemicals to dissipate and ensures the water reaches room temperature.
4. Provide substrate: Blood worms naturally reside in muddy or sandy areas, so providing a substrate in the container can mimic their natural habitat. Add a layer of fine sand or a commercial aquarium substrate to the bottom of the container. This helps prevent the blood worms from getting injured and provides a place for them to burrow and hide.
5. Optimize water quality: Before introducing the blood worms, make sure the water conditions are suitable. Test the water for parameters such as pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels to ensure they are within the acceptable range for the specific species of aquatic pets you have.
6. Establish biological filtration: Blood worm storage containers can benefit from the presence of beneficial bacteria that aid in maintaining water quality. If you have an established aquarium or filter system, you can transfer some established filter media or substrate to help kick-start the biological filtration process in the container.
7. Provide hiding spots: Blood worms are naturally prey for many species of fish and other aquatic pets. To help reduce stress and provide hiding spots for the blood worms, add some decorations such as small rocks, PVC pipes, or artificial plants to the container.
Once the container is prepared, it’s time to introduce the blood worms. Be sure to handle the worms gently and transfer them carefully to avoid any damage. In the next sections, we will explore how to keep the blood worms alive and maintain their health and nutritional value through proper care and maintenance.
Keeping the Blood Worms Alive
Maintaining the blood worms’ health and ensuring their longevity is crucial for providing a continuous and reliable food source for your aquatic pets. Here are some essential guidelines for keeping the blood worms alive:
1. Feeding: Blood worms need to be fed regularly to sustain their health. You can feed them a variety of foods, such as fish food flakes, algae wafers, or specialized blood worm food. Feed them small amounts at a time to avoid overfeeding, which can lead to water quality issues.
2. Water quality: Regularly monitor and maintain optimal water quality parameters in the storage container. Keep the water clean by performing weekly water changes of about 10-20% and removing any uneaten food or waste. Maintaining good water quality is vital for the blood worms’ health and overall well-being.
3. Temperature: Blood worms thrive in cooler water temperatures. Keep the storage container at a temperature between 50°F to 65°F (10°C to 18°C). Avoid exposing the container to extreme temperature fluctuations, as this can stress the blood worms and affect their survival.
4. Lighting: While blood worms do not require strong lighting, you can provide them with a dim light source. A low-intensity aquarium light or ambient room lighting is sufficient. Avoid exposing the container to direct sunlight, as this can lead to temperature fluctuations and unwanted algae growth.
5. Aeration and oxygenation: Blood worms require adequate oxygen levels to survive. Ensure proper aeration and oxygenation in the storage container by using an air pump and air stone. This will help maintain oxygen levels and prevent the water from becoming stagnant.
6. Avoid overcrowding: Overcrowding the container with too many blood worms can lead to stress, competition for resources, and reduced oxygen levels. To avoid overcrowding, ensure that the container has ample space and maintain a suitable population of blood worms based on the size of the container.
7. Minimize disturbances: Blood worms are sensitive to sudden disturbances and excessive handling. Minimize unnecessary disturbances or vibrations around the container to reduce stress on the worms.
By following these guidelines, you can create an optimal environment for the blood worms, keeping them alive, healthy, and thriving. In the next sections, we will discuss other factors to consider, such as temperature and lighting requirements, monitoring water quality, and tips for avoiding contamination.
Store blood worms in the refrigerator at a temperature between 38-45°F (3-7°C) to keep them fresh. Use a small container with a lid and change the water every 2-3 days.
Read more: How To Store Period Blood
Temperature and Lighting Requirements
Maintaining appropriate temperature and lighting conditions is crucial for the well-being and survival of blood worms. Here are the key factors to consider regarding temperature and lighting requirements:
Temperature:
Blood worms are cold-water organisms and thrive in temperatures between 50°F to 65°F (10°C to 18°C). It is important to keep the storage container within this temperature range to ensure the worms remain healthy and active. Fluctuations in temperature can stress the blood worms and negatively impact their overall well-being. Avoid exposing the container to direct sunlight or placing it near heat sources, as this can cause sudden temperature changes. Use a reliable thermometer to monitor the water temperature regularly and make necessary adjustments to maintain the ideal range.
Lighting:
Blood worms do not require intense lighting like some plant species, but having a properly lit environment can benefit them. In general, blood worms prefer low to moderate levels of light. You can provide ambient room lighting or use a low-intensity aquarium light to provide a subtle illumination for the container. Having a consistent light source can help regulate the worms’ biological rhythms and mimic their natural habitat. However, avoid exposing the container to direct sunlight, as it can lead to temperature fluctuations and promote unwanted algae growth.
To maintain a suitable lighting schedule, provide around 8-12 hours of light per day. You can use a timer to automate the lighting cycle and ensure a consistent photoperiod for the blood worms. Remember to switch off the lights during the night hours to allow for a natural day-night cycle.
It is important to note that prolonged exposure to bright light may cause stress and encourage the formation of algae in the container. If you notice excessive algae growth, adjust the lighting intensity or duration to strike a balance that supports the blood worms’ well-being without promoting algae proliferation.
Maintaining the proper temperature and lighting conditions not only promotes the blood worms’ health and longevity but also helps in preserving their nutritional content. In the next section, we will discuss the importance of feeding and maintaining the blood worms to maximize their overall quality and nutritional benefits.
Feeding and Maintaining the Blood Worms
Feeding and maintaining the blood worms properly is essential for their health and overall quality. These guidelines will help ensure that your blood worms receive the necessary nutrition and remain in optimal condition:
Feeding:
Blood worms require a regular and balanced diet to thrive. You can feed them a variety of foods to provide a range of nutrients. Commercial blood worm food, fish food flakes, freeze-dried or frozen plankton, and specialized invertebrate foods are all suitable options. It is important to offer a varied diet to ensure that the blood worms receive a wide spectrum of nutrients.
Feed the blood worms small amounts of food at least once or twice daily. It is ideal to provide only what they can consume within a few minutes. Overfeeding can lead to water quality problems and uneaten food accumulation, which can negatively impact the worms’ health.
Observe the blood worms during feeding time to ensure they are actively consuming the food. Remove any uneaten food after feeding to avoid water contamination. Regularly monitor the water quality parameters and adjust the feeding frequency and amount accordingly.
Maintaining Water Quality:
Regularly monitor and maintain optimal water quality in the blood worm storage container. Conduct routine water tests to ensure that the pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels are within the acceptable range for the specific species of aquatic pets you have.
Perform weekly water changes of about 10-20% to remove accumulated waste and maintain good water quality. Use dechlorinated water at room temperature during water changes to prevent shocks to the blood worms. While changing the water, take the opportunity to siphon the substrate gently to remove any debris and uneaten food.
Maintain a consistent and suitable filtration system in the container to help remove waste and maintain water clarity. A sponge filter or a small hang-on-back filter can be beneficial in ensuring good water quality for the blood worms.
Routine Care:
Regular observation and care are crucial for maintaining the blood worms’ health. Keep an eye out for any signs of stress or illness, such as color changes, excessive lethargy, or abnormal behavior. If you notice any issues, take prompt action to identify and resolve the underlying cause.
Gently stir the substrate occasionally to prevent debris buildup and improve water circulation. This will help maintain proper oxygen levels and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
Avoid introducing chemical treatments or medications directly into the blood worm storage container unless specifically instructed by a veterinarian. Chemical additives can be harmful to the blood worms and may disrupt their delicate ecosystem.
By following these feeding and maintenance practices, you can ensure that the blood worms remain healthy, vibrant, and of high nutritional value for your aquatic pets. In the next section, we will discuss the importance of monitoring water quality and tips for avoiding contamination in the blood worm storage container.
Monitoring Water Quality
Monitoring the water quality in the blood worm storage container is essential for the health and well-being of the blood worms themselves, as well as the aquatic pets that will consume them. Here are some key factors to consider when monitoring water quality:
pH Levels:
Maintaining the proper pH level is important, as extreme pH fluctuations can stress the blood worms and affect their overall health. Ideally, the pH should be within the range of 6.5 to 7.5, which is generally suitable for most aquatic pets. Monitor the pH using a reliable aquarium pH test kit and adjust if necessary using pH buffers or adjusters specifically designed for aquarium use.
Ammonia, Nitrite, and Nitrate Levels:
Ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate are waste products that can accumulate in the water and harm the blood worms if present in high concentrations. Regularly test the water for these parameters using appropriate test kits. Ideally, ammonia and nitrite levels should be kept at or near zero, while nitrate levels should be below 20 ppm. Perform regular water changes, maintain a good filtration system, and avoid overfeeding to help control these parameters.
Temperature:
As mentioned earlier, maintaining the proper temperature is crucial for the blood worms’ well-being. Use a reliable aquarium thermometer to monitor and ensure that the water temperature stays within the recommended range of 50°F to 65°F (10°C to 18°C). Sudden temperature fluctuations can stress the blood worms and lead to negative health effects.
Water Clarity:
Regularly assess the water clarity in the blood worm storage container. Cloudy or murky water can be an indication of poor water quality or excessive waste accumulation. If the water becomes cloudy, perform a water change and check the filtration system for any issues. Maintaining clear water helps ensure a healthy environment for the blood worms and reduces the risk of contamination.
Observation and Behavior:
Keep a close eye on the blood worms’ behavior and appearance. Healthy blood worms should be active, have vibrant colors, and display normal feeding behavior. If you notice any signs of lethargy, abnormal behavior, or changes in color, it may indicate a problem with water quality or the overall health of the blood worms. Address any issues promptly to maintain optimal living conditions for the blood worms.
By regularly monitoring these water quality factors and taking appropriate actions when necessary, you can ensure a clean and suitable environment for the blood worms. In the final section, we will discuss tips for avoiding contamination in the blood worm storage container, further ensuring the health and well-being of the blood worms and your aquatic pets.
Avoiding Contamination
Contamination in the blood worm storage container can have detrimental effects on the health of the worms and your aquatic pets. Taking precautions and implementing good practices can help minimize the risk of contamination. Here are some tips to consider:
Handle with Clean Hands:
When handling the blood worms or performing maintenance tasks in the storage container, make sure to wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. This helps prevent the transfer of any harmful substances, such as chemicals, lotions, or oils, that can contaminate the water and harm the blood worms.
Use Dechlorinated Water:
Always use dechlorinated water for the blood worm storage container. Chlorine and chloramine in tap water can be harmful to the blood worms and disrupt their delicate ecosystem. Treat tap water with a suitable dechlorinator or allow it to sit for 24 hours to allow the chlorine to dissipate naturally before using it in the container.
Avoid Cross-Contamination:
To prevent the spread of diseases or parasites, avoid cross-contamination between the blood worm storage container and other aquatic environments. Use separate equipment, such as nets and siphons, for the blood worm storage container to prevent the transfer of potential contaminants.
Properly Store and Handle Food:
If you are using live or frozen food to feed the blood worms, ensure that the food is properly handled and stored to prevent contamination. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for storage and handling. Thaw frozen food completely before offering it to the blood worms, and remove any uneaten food promptly to prevent water pollution.
Clean and Disinfect Equipment:
Regularly clean and disinfect equipment used in and around the blood worm storage container. This includes nets, syringes, and any other tools that come into contact with the water or the blood worms. Use a mild bleach solution or aquarium-safe cleaning agents to eliminate potential contaminants.
Prevent and Control Algae Growth:
Algae can quickly grow and negatively impact water quality and the overall health of the blood worms. To prevent excessive algae growth, ensure the storage container is not exposed to direct sunlight. Maintain proper lighting levels and duration, control the nutrient levels in the water through regular water changes, and consider using algae-controlling products or algae-eating organisms if necessary.
By implementing these practices, you can minimize the risk of contamination and provide a clean and healthy environment for the blood worms. Regular monitoring of water quality, observing the blood worms’ behavior, and addressing any issues promptly will further help maintain their overall well-being. With proper care and attention, your blood worms will thrive and serve as nutritious feed for your aquatic pets.
Read more: How To Store Blood In A Vial
Conclusion
Proper storage of blood worms is essential for maintaining their vitality, nutritional value, and availability as a food source for your aquatic pets. By following the guidelines discussed in this article, you can create an optimal environment for the blood worms, ensuring their longevity and overall health.
Choosing the right container, preparing it correctly, and providing suitable conditions such as temperature and lighting are key factors in successful blood worm storage. Feeding the blood worms a varied diet and maintaining good water quality through regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial for their well-being.
Avoiding contamination in the blood worm storage container is vital to prevent harm to the worms and potential negative effects on your aquatic pets. By handling with clean hands, using dechlorinated water, preventing cross-contamination, properly storing and handling food, and regularly cleaning and disinfecting equipment, you can minimize the risk of contamination and maintain a healthy environment.
Remember to observe the blood worms regularly for any signs of stress or illness, and promptly address any issues that arise. Proper monitoring of water quality and taking appropriate actions, such as performing water changes and controlling algae growth, can significantly contribute to the overall health and well-being of the blood worms.
In conclusion, by following the guidelines provided in this article, you can ensure the proper storage of blood worms and maximize their nutritional value for your aquatic pets. Providing a clean and suitable environment will not only benefit the blood worms but also contribute to the health and vitality of your aquatic ecosystem. With proper care and attention, you can enjoy the benefits of having a sustainable and nutritious food source for your beloved aquatic pets.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Blood Worms
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Store Blood Worms”