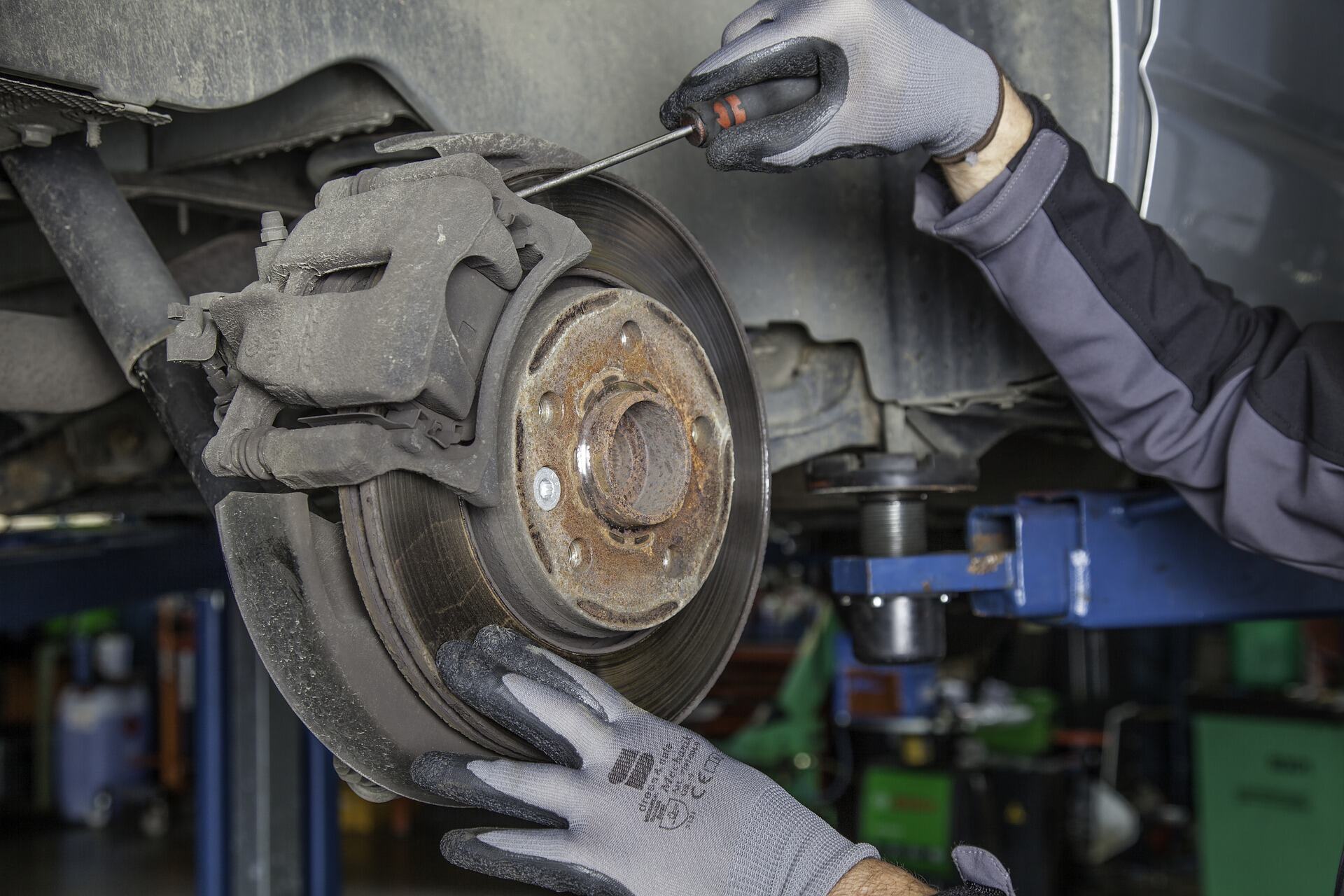


Articles
What Causes Seized Calipers
Modified: October 22, 2024
Discover the common causes of seized calipers in this informative article. Learn how to prevent and fix this issue to ensure optimal braking performance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to road safety, a crucial component of any vehicle’s braking system is the brake caliper. Responsible for applying pressure to the brake pads, the caliper plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient stopping power. However, in some cases, calipers can become seized, compromising the effectiveness of the braking system and posing a serious risk.
Understanding the root causes of seized calipers is essential for vehicle owners and mechanics alike. By identifying the underlying issues, they can take appropriate measures to rectify the problem and ensure optimal performance and safety on the road. In this article, we will explore the common reasons behind seized calipers and how they can be addressed.
Key Takeaways:
- Regular maintenance, including brake fluid replacement and lubrication, is crucial to prevent seized calipers caused by contamination, corrosion, and lack of lubrication. Stay proactive to ensure optimal brake performance and safety.
- Addressing symptoms of seized calipers promptly through professional intervention and regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of calipers and maintain the efficiency of the braking system. Prioritize safety by staying vigilant and proactive.
Read more: What Are Calipers
Understanding Brake Calipers
Before we discuss the causes of seized calipers, it is important to have a basic understanding of how brake calipers function. Located near each wheel, calipers house the brake pads and are responsible for squeezing them against the rotor, generating the necessary friction to slow down or stop the vehicle.
Most modern vehicles use either sliding calipers or fixed calipers. Sliding calipers have pistons on only one side, allowing the caliper to slide back and forth to apply pressure evenly on the brake pads. Fixed calipers, on the other hand, have pistons on both sides and apply pressure simultaneously. Regardless of the type, calipers play a critical role in the braking system.
Common Symptoms of Seized Calipers
When a brake caliper becomes seized, several warning signs may indicate the problem. Recognizing these symptoms early on can help prevent further damage and ensure your safety on the road. Here are some common symptoms of seized calipers:
1. Uneven braking: If you notice that your vehicle pulls to one side while braking, it could be a sign of a seized caliper. When a caliper becomes stuck or fails to release properly, it causes uneven pressure on the brake pads, resulting in uneven braking performance.
2. Overheating: A seized caliper can generate excessive heat due to constant friction between the pad and rotor. If you feel a burning smell or notice smoke coming from the wheels after driving, it may indicate a seized caliper that needs attention.
3. Reduced braking power: Seized calipers can significantly impact the braking performance of your vehicle. You may experience a longer stopping distance or the need to apply more pressure on the brake pedal to achieve the desired braking effect.
4. Vibration and pulsation: When a caliper seizes, it can lead to uneven wear on the brake pads and rotor. This uneven wear can cause vibrations or pulsations in the brake pedal when applying the brakes, indicating a potential issue with the caliper.
5. Increased fuel consumption: A seized caliper can cause excessive drag on the wheel, leading to increased fuel consumption. If you notice a sudden decrease in fuel efficiency, it is worth checking the calipers for any signs of seizing.
Brake Fluid Contamination
Contaminated brake fluid is one of the common causes behind seized calipers. Over time, brake fluid can become contaminated with moisture, debris, and dirt, which can lead to corrosion and rust within the caliper assembly.
Moisture is a significant threat to the brake system as it promotes the oxidation process, resulting in rust formation. When rust accumulates inside the caliper, it can cause the piston or slide pins to become stuck, preventing proper movement and causing the caliper to seize.
Contaminated brake fluid can also lead to the deterioration of the rubber seals inside the caliper. As the seals degrade, they can allow moisture and debris to enter the caliper, further exacerbating the problem.
Regular brake fluid flushes and replacements are essential to prevent contamination and maintain the integrity of the caliper assembly. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for brake fluid replacement to ensure the longevity and proper functioning of the calipers.
Corrosion and Rust
Corrosion and rust are common culprits behind seized calipers. The brake calipers are exposed to various environmental elements, including moisture, road salt, and debris, which can contribute to the development of corrosion and rust.
When the caliper or its components are corroded or covered in rust, it can impede the movement of the pistons or slide pins. As a result, the caliper may become seized, preventing it from properly engaging or disengaging the brake pads.
Corrosion and rust can also lead to the degradation of the caliper’s housing, causing it to seize in place. This can be particularly problematic in areas with harsh climates or where road salt is used during the winter months.
Regular maintenance and inspection of the brake calipers can help identify any signs of corrosion or rust formation. Taking preventative measures, such as applying protective coatings or using anti-corrosion products, can help mitigate the risk of seizing due to corrosion.
If corrosion or rust is identified on the caliper, it is crucial to address the issue promptly. Cleaning and lubricating the affected areas or replacing the caliper altogether may be necessary to restore proper functionality and avoid further damage to the braking system.
One common cause of seized calipers is corrosion and rust buildup. To prevent this, regularly inspect and clean the calipers, and consider using a high-quality, corrosion-resistant brake fluid.
Read more: What Is A Core Charge For Calipers
Lack of Lubrication
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation of brake calipers. When there is a lack of lubrication, friction can increase, leading to heat buildup and potential seizure of the caliper components.
The pistons and slide pins within the caliper require lubrication to ensure free movement. Over time, without proper lubrication, these components can become dry and stiff, making it difficult for the caliper to engage or disengage the brake pads effectively.
Furthermore, the lack of lubrication can cause increased wear and tear on the caliper parts, leading to accelerated deterioration. This can result in the caliper seizing or failing to function correctly.
Regular maintenance of the brake calipers should include lubrication of the appropriate components using a high-quality, heat-resistant brake caliper grease. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding the type and frequency of lubrication to prevent seizing and ensure optimal performance.
In cases where the lack of lubrication has already caused the caliper to seize, professional intervention may be required. Mechanics can disassemble the caliper, clean out any debris or corrosion, and properly lubricate the components to restore full functionality.
Ensuring that the brake calipers are adequately lubricated will not only help prevent seizing but also extend the lifespan of the caliper and contribute to the overall performance and safety of the braking system.
Stuck Piston or Slide Pins
One of the primary reasons behind seized calipers is a stuck piston or slide pins. Calipers with sliding mechanisms rely on the smooth movement of the pistons or slide pins to apply and release pressure on the brake pads.
If the piston or slide pins become stuck due to corrosion, rust, or lack of lubrication, the caliper can seize and fail to function properly. The stuck piston may not retract fully, keeping the brake pads in constant contact with the rotor and causing excess friction and heat buildup.
Similarly, if the slide pins, which allow the caliper to move freely, become seized, it can restrict the caliper’s movement and prevent it from properly engaging or disengaging the brake pads. This can lead to uneven brake pad wear and compromised braking performance.
Regular inspection and lubrication of the piston and slide pins are essential to prevent them from sticking. Lubricating these components with proper brake caliper grease can help maintain their smooth operation and reduce the risk of caliper seizure.
In cases where the piston or slide pins are already stuck, professional intervention may be necessary. Skilled mechanics can disassemble the caliper, inspect the piston or slide pins for any signs of damage or corrosion, and take appropriate measures to restore their functionality.
Taking proactive measures to ensure the smooth movement of the piston and slide pins will not only help prevent caliper seizure but also contribute to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the braking system.
Overheating and Brake Fade
Overheating of the brake system can lead to brake fade, a phenomenon where the braking performance deteriorates due to the inability of the brakes to effectively dissipate heat. This can contribute to the seizing of calipers.
When the calipers are subjected to excessive heat, such as during prolonged and aggressive braking or driving in mountainous terrain, the high temperatures can cause the brake fluid to boil. The formation of gas bubbles in the brake fluid, known as vapor lock, can lead to a loss of hydraulic pressure and compromised braking efficiency.
As the calipers and other brake components heat up, the increased friction between the brake pads and rotor can also generate excessive heat. This can lead to the expansion of the caliper components, such as the pistons, causing them to seize and impede proper brake pad movement.
To prevent overheating and brake fade, it is important to use high-quality brake pads and ensure sufficient airflow to the brakes. This can be achieved by maintaining proper clearance between the brake components, maintaining adequate brake fluid levels, and avoiding excessive and aggressive braking.
If caliper seizure due to overheating is suspected, it is crucial to address the issue promptly. Allow the brakes to cool down before inspecting for any signs of damage or deformation. If necessary, professional assistance may be required to restore the caliper’s functionality and ensure effective braking performance.
Regular maintenance of the entire braking system, including calipers, pads, rotors, and brake fluid, will help prevent overheating, reduce the risk of caliper seizure, and maintain optimal brake performance.
Neglected Maintenance and Debris Buildup
Neglected maintenance and debris buildup are significant factors that can contribute to the seizing of brake calipers. Over time, if the calipers are not properly maintained, various issues can arise, leading to caliper seizure.
One of the common problems is the buildup of dirt, dust, and road debris within the caliper assembly. This can prevent the caliper’s moving parts, such as the pistons or slide pins, from functioning smoothly, causing them to become stuck or seized.
Additionally, if the calipers are not regularly inspected and maintained, small problems may go unnoticed and eventually escalate. Minor issues, such as rubber seal degradation or corrosion, can worsen over time, leading to caliper seizure and compromised braking performance.
Regular cleaning and inspection of the brake system, including the calipers, play a vital role in preventing debris buildup. Cleaning the calipers and removing any accumulated dirt or debris can help ensure free movement of the caliper components.
Routine maintenance should also include checking the condition of the rubber seals, which can deteriorate over time. If any signs of damage or wear are detected, replacing the seals promptly can help avoid further problems and potential caliper seizure.
Furthermore, regular brake system maintenance should include checking the level and condition of the brake fluid. Contaminated or deteriorated brake fluid can lead to caliper issues, as discussed earlier. Regular fluid flushes and replacements can help prevent contaminants from affecting the caliper’s functionality.
By prioritizing proper maintenance and addressing any signs of debris buildup or damage promptly, vehicle owners can reduce the risk of caliper seizure and ensure the longevity and optimal performance of their brake calipers.
Read more: What Are The Two Types Of Calipers
Conclusion
Seized calipers can pose a serious safety risk and compromise the effectiveness of a vehicle’s braking system. Understanding the causes behind caliper seizure is crucial in order to prevent and address the issue.
Common causes of seized calipers include brake fluid contamination, corrosion and rust, lack of lubrication, stuck pistons or slide pins, overheating, and neglected maintenance leading to debris buildup. These factors can hinder the smooth operation of the caliper components, causing them to become stuck or seize.
Regular maintenance and inspection of the brake system, including the calipers, is essential in preventing caliper seizure. This includes routine cleaning, lubrication, and replacement of brake fluid. Checking for signs of corrosion, rust, and wear on the caliper components is also important. Prompt action and professional intervention may be necessary if caliper seizure is suspected.
By staying proactive and addressing any caliper issues promptly, vehicle owners can ensure the optimal performance and safety of their braking system. Regular maintenance not only prevents caliper seizure but also extends the lifespan of the calipers and other brake system components.
Remember, the brake calipers are a critical component of the braking system, and any signs of caliper seizure should not be ignored. If you experience any symptoms such as uneven braking, overheating, reduced braking power, vibration, or increased fuel consumption, it is essential to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic.
Your safety on the road relies on the proper functioning of your vehicle’s braking system, and maintaining healthy brake calipers is a vital part of that. So, stay vigilant, prioritize maintenance, and take swift action to address any issues to ensure a smooth and safe driving experience.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Causes Seized Calipers
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “What Causes Seized Calipers”