

Articles
How Does Central AC Work
Modified: November 2, 2024
Learn how central AC works with this informative article. Discover the key components and processes involved in cooling your home efficiently.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In hot summer months, having a well-functioning central air conditioning (AC) system is essential for staying cool and comfortable. But have you ever wondered how exactly a central AC system works? Understanding the components and processes behind this technology can help you better appreciate its efficiency and reliability.
A central AC system is designed to cool your entire home or a specific area by removing heat from the indoor air and transferring it outside. It relies on a combination of mechanical and chemical processes to achieve this cooling effect. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of a central AC system, breaking down its components and explaining the air conditioning process.
By gaining insight into how your central AC system operates, you will be better equipped to troubleshoot any issues that may arise and make informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades. So, let’s dive in and discover the fascinating world of central air conditioning!
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the inner workings of a central AC system, from the compressor and condenser to the evaporator coil and refrigerant flow, empowers homeowners to troubleshoot issues and perform necessary maintenance tasks, ensuring optimal cooling efficiency and comfort.
- Proper maintenance, troubleshooting techniques, and professional assistance when needed are essential for the long-term functionality and performance of a central AC system. By following these guidelines, homeowners can enjoy a cool and comfortable indoor environment during hot summer months.
Read more: How Does Oil Central Heating Work
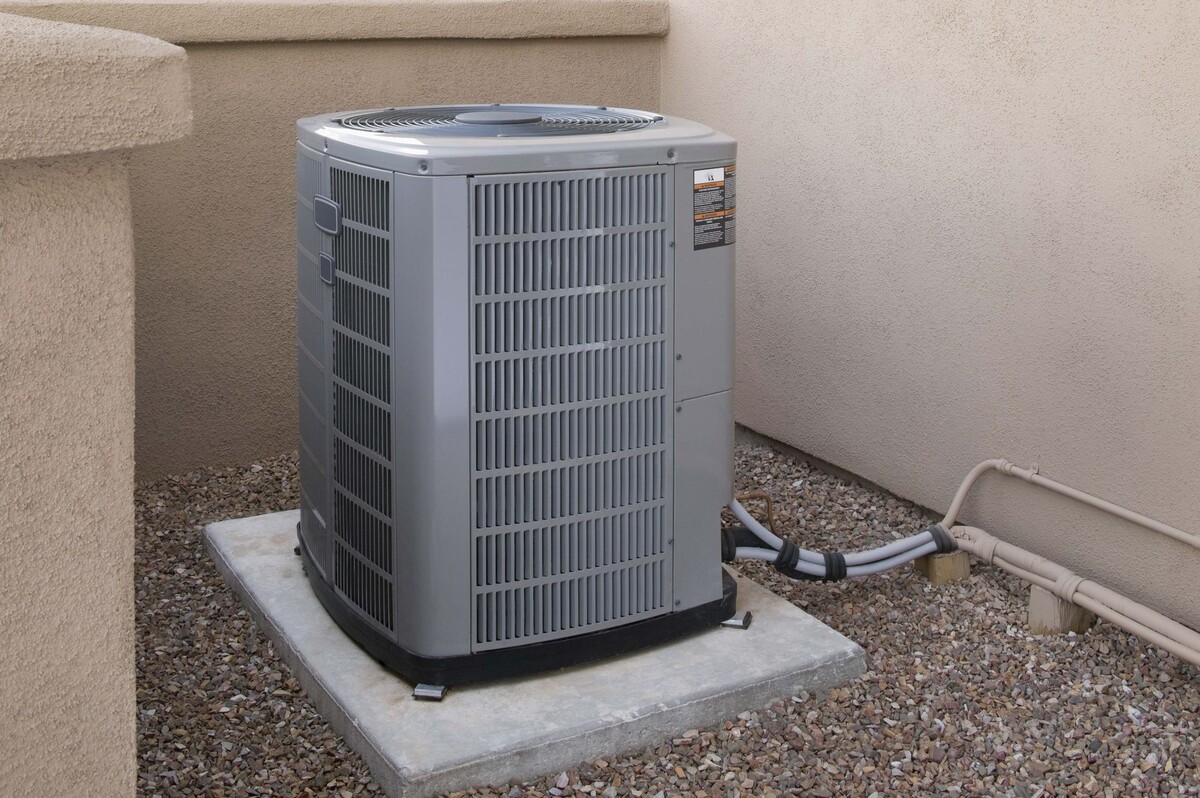
Components of a Central AC System
A central AC system consists of several key components that work together to cool the air in your home. These components include:
- 1. Compressor: The compressor is the heart of the AC system. It is responsible for pressurizing the refrigerant and propelling it through the system, creating the necessary pressure difference for heat transfer.
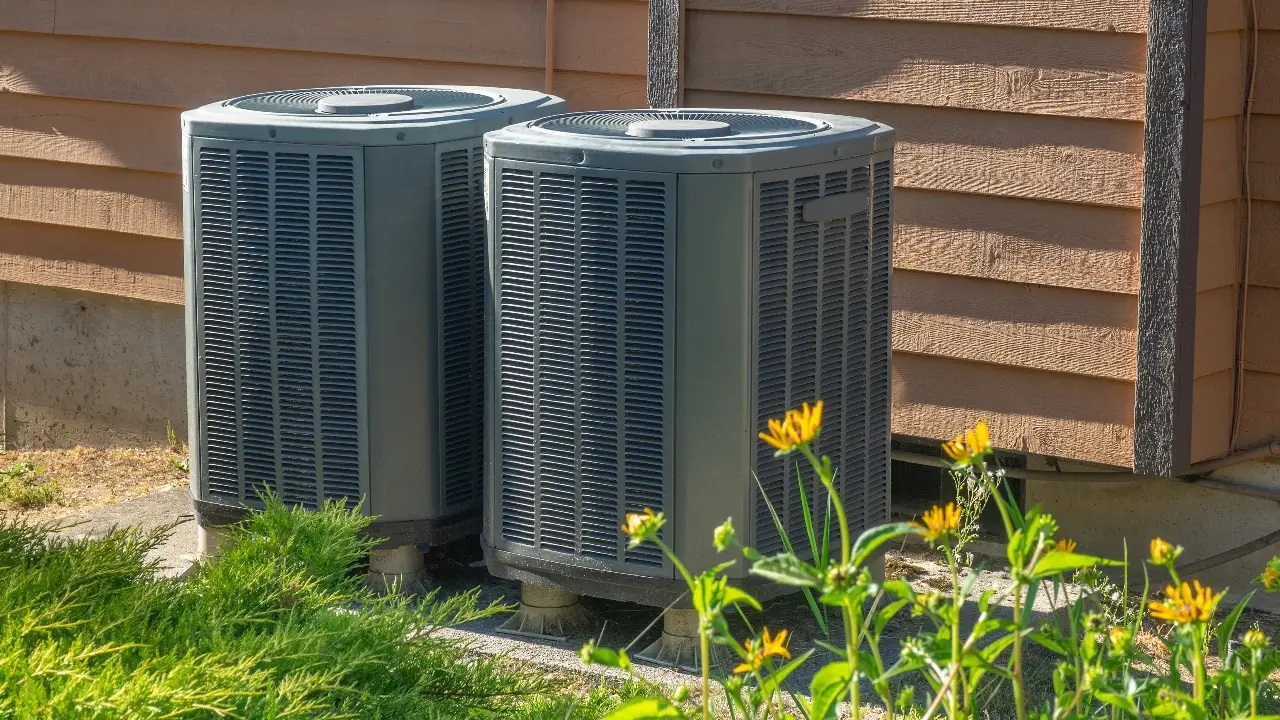
- 2. Condenser: The condenser is located on the outside of your home and acts as a heat exchanger. It receives the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant from the compressor and releases the heat into the surrounding air.
- 3. Evaporator Coil: The evaporator coil is located inside your home, typically in the air handler or furnace. Its function is to absorb heat from the indoor air as the refrigerant evaporates, cooling the air in the process.
- 4. Refrigerant: The refrigerant is a chemical compound that circulates through the AC system, absorbing and releasing heat as it changes between liquid and gas states. Common refrigerants used in AC systems include R-410A and R-22.
- 5. Air Handler: The air handler is responsible for circulating the cooled air throughout your home. It contains a blower fan that pushes the conditioned air through the ductwork and into the various rooms.
- 6. Ductwork: The ductwork consists of a network of pipes or channels that distribute the conditioned air from the air handler to different areas of your home. It ensures that each room receives an adequate supply of cool air.
- 7. Thermostat: The thermostat acts as the control center for your central AC system. It allows you to set the desired temperature and controls when the AC system turns on and off.
All of these components work together in a synchronized manner to cool your home efficiently. Understanding the role of each component is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining your central AC system. In the next section, we will delve into the air conditioning process to get a closer look at how these components interact.
Air Conditioning Process
The air conditioning process in a central AC system involves a series of steps to absorb heat from the indoor air and release it outside, resulting in a cool and comfortable environment. Let’s explore this process in detail:
- 1. Indoor Air Circulation: The first step in the air conditioning process is the circulation of indoor air. The blower fan in the air handler pulls warm air from the rooms through the return vents and directs it towards the evaporator coil.
- 2. Heat Absorption: As the warm air passes over the evaporator coil, the refrigerant inside the coil evaporates. This evaporation absorbs heat from the surrounding air, cooling it down in the process.
- 3. Refrigerant Compression: The now-gaseous refrigerant is drawn into the compressor, where it is pressurized. This compression increases the temperature and energy level of the refrigerant.
- 4. Heat Dissipation: The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant flows into the condenser coil located outside. As it moves through the narrow coil, the refrigerant releases heat to the outdoor air, causing it to condense back into a liquid state.
- 5. Refrigerant Expansion: The condensed liquid refrigerant then enters an expansion valve or metering device. This device reduces the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, preparing it for the next cycle.
- 6. Repeat Cycle: The cool liquid refrigerant returns to the evaporator coil, where the process starts all over again. The blower fan blows air over the chilled coil, and the refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air, continuing the cooling cycle.
By repeatedly cycling through these steps, the central AC system maintains a comfortable indoor temperature by removing heat from the air and expelling it outside. This process continues until the desired temperature set on the thermostat is reached.
Understanding this air conditioning process helps you appreciate the intricate workings of your central AC system, and it also highlights the importance of each component in achieving efficient cooling. Next, let’s take a closer look at two critical components of a central AC system: the compressor and condenser.
Compressor and Condenser
The compressor and condenser are two essential components in a central AC system that work together to remove heat from the indoor air and release it outside. Let’s explore these components in detail:
Compressor:
The compressor is often referred to as the “heart” of the central AC system. It plays a crucial role in the air conditioning process by compressing the refrigerant and creating the pressure difference needed for heat transfer. Here’s how it works:
- 1. Suction: The compressor starts by drawing in the low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant from the evaporator coil.
- 2. Compression: Once inside the compressor, the refrigerant is compressed, increasing both its pressure and temperature. This process raises the energy level of the refrigerant.
- 3. Ejection: The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant leaves the compressor and moves towards the condenser.
Condenser:
The condenser is located outside of your home and acts as a heat exchanger. It receives the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant from the compressor and facilitates the release of heat to the environment. Here’s how it works:
- 1. Heat Dissipation: As the refrigerant enters the condenser, it flows through a series of narrow metal coils or fins. These coils provide a large surface area for heat transfer. As the refrigerant travels through the coils, it releases heat to the surrounding air.
- 2. Fan Assisted: The condenser usually has a fan or fans that help in dissipating the heat. The fan blows outdoor air over the condenser coils, aiding in the removal of heat from the refrigerant.
- 3. Cooling: As the refrigerant releases heat and loses energy, it condenses back into a liquid state. It then moves towards the expansion valve to lower its pressure and temperature, preparing for the next cycle.
The compressor and condenser work together to ensure efficient heat transfer and cooling in your central AC system. The compressor’s function of pressurizing the refrigerant and the condenser’s role in dissipating heat are vital for the overall performance of the system.
Now that we have a better understanding of the compressor and condenser, let’s move on to exploring another critical component of a central AC system: the evaporator coil.
Evaporator Coil
The evaporator coil is a crucial component of a central AC system that is responsible for absorbing heat from the indoor air. It is typically located inside the air handler or furnace. Let’s take a closer look at how the evaporator coil functions:
The evaporator coil consists of a series of metal fins or tubes that contain the refrigerant. When the warm indoor air is drawn in by the blower fan, it passes over these coils, initiating the heat absorption process. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Air Circulation: The blower fan in the air handler pulls warm air from the rooms through the return vents and directs it towards the evaporator coil.
- Heat Transfer: As the warm air moves over the cold surface of the evaporator coil, heat is transferred from the air to the refrigerant inside the coils.
- Evaporation: The low-pressure refrigerant inside the evaporator coil starts to evaporate as it absorbs heat from the warm air. This evaporation process causes the refrigerant to change from a liquid to a gas state.
- Cooling: As the refrigerant evaporates, it cools down the metal fins or tubes of the evaporator coil, subsequently cooling the air passing over it.
- Condensate Removal: During the cooling process, moisture from the warm air condenses on the surface of the evaporator coil. This condensed water, known as condensate, drips down into a drain pan and is removed from the system.
The cooled air is then released back into your home through the supply vents, while the warm refrigerant gas from the evaporator coil travels to the compressor to start the next phase of the air conditioning process.
The efficient operation of the evaporator coil is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the coil and ensuring proper airflow, is essential to ensure its performance and prevent issues such as clogging or ice buildup. Keeping the evaporator coil in good condition helps optimize the cooling efficiency of your central AC system.
Now that we understand how the evaporator coil works, let’s move on to discussing another important aspect of the central AC system: the flow of refrigerant.
Regular maintenance of your central AC system, including cleaning or replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting ductwork, can help ensure efficient operation and extend the lifespan of the unit.
Read more: How Does A Central Air Conditioner Work?
Refrigerant Flow
The flow of refrigerant is a critical process in a central AC system as it allows for the transfer of heat and enables the cooling effect. Let’s explore how the refrigerant flows through the system:
The refrigerant begins its journey in the evaporator coil, where it absorbs heat from the indoor air and evaporates. As a low-pressure gas, it moves on to the compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature. From here, the refrigerant enters the condenser coil located outside, where it releases the absorbed heat to the outdoor air and condenses back into a liquid state.
But how does the refrigerant flow through the system exactly? Here’s a simplified breakdown of the refrigerant flow process:
- Evaporator Coil: The low-pressure refrigerant enters the evaporator coil, where it evaporates and absorbs heat from the warm indoor air.
- Compressor: The compressor sucks in the low-pressure gas refrigerant and compresses it, increasing its pressure as well as its temperature.
- Condenser Coil: The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant leaves the compressor and flows into the condenser coil, where it releases heat to the outdoor air and condenses back into a liquid state.
- Expansion Valve: The condensed liquid refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve or metering device. This device reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, preparing it for the next cycle.
- Evaporator Coil (again): The low-pressure refrigerant, after passing through the expansion valve, returns to the evaporator coil to absorb more heat and continue the cooling cycle.
This continuous cycle of evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the indoor air and release it outside, providing the cooling effect throughout your home.
It’s important to note that the type of refrigerant used in a central AC system can vary. Older systems may still use R-22 refrigerant, while newer systems typically use more environmentally friendly options such as R-410A. It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and ensure proper handling, disposal, and professional maintenance when it comes to refrigerant.
Having a clear understanding of the refrigerant flow in your central AC system not only helps you appreciate the cooling process but also enables you to troubleshoot issues and ensure optimal performance.
Now that we understand how the refrigerant flows through the system, let’s move on to discussing the crucial role of air distribution in a central AC system.
Air Distribution
In a central AC system, air distribution plays a vital role in ensuring that the cool air reaches every part of your home effectively and efficiently. Let’s delve into the process of air distribution and its components:
The process of air distribution begins once the air has been cooled and conditioned by the central AC system. Here’s how air distribution works:
- Air Handler: The air handler, typically located inside your home, is responsible for circulating the cooled air. It contains a blower fan that draws in the air and pushes it through the system.
- Ductwork: The conditioned air travels through a network of ducts, which are channels or pipes strategically placed throughout your home. These ducts serve as pathways for the air to flow into different rooms and areas.
- Supply Vents: The ductwork is connected to supply vents, which are the outlets through which the cool air is released into each room. These vents are strategically placed to ensure even distribution of cool air throughout your home.
- Return Vents: In addition to supply vents, return vents play a crucial role in air distribution. They draw in warm indoor air and circulate it back to the air handler, where it is cooled again before being distributed back into the rooms.
- Airflow Control: Dampers, or valves, are often installed within the ductwork to control the airflow to different rooms. By adjusting these dampers, you can regulate the amount of cool air entering individual areas, allowing for customized temperature control.
- Filtration: The ductwork may also contain air filters, which capture dust, allergens, and other particles, improving the air quality before it is distributed into your home.
Properly designed and installed ductwork, along with strategically placed supply and return vents, ensure that the cool air from your central AC system is effectively distributed throughout your home. If there are issues with air distribution, such as uneven cooling or weak airflow in certain rooms, it may be necessary to inspect and address potential problems with the ductwork or adjust the dampers.
Remember, maintaining a well-balanced airflow and properly functioning distribution system is essential for optimizing the cooling performance of your central AC system and ensuring a comfortable indoor environment.
Now that we understand the importance of air distribution, let’s move on to discussing another critical component of a central AC system: the thermostat and controls.
Thermostat and Controls
The thermostat and controls are integral to the operation of a central AC system, allowing you to set and maintain the desired temperature in your home. Let’s take a closer look at these components:
Thermostat:
The thermostat acts as the control center for your central AC system. It allows you to set the desired temperature and initiates the cooling process accordingly. Here are some key features of a thermostat:
- 1. Temperature Setting: The thermostat enables you to set the desired temperature by adjusting the temperature controls or using a digital interface.
- 2. Mode Selection: Many thermostats offer different operating modes such as cool, heat, fan-only, or auto. In the cool mode, the thermostat signals the AC system to cool the air. In the heat mode, it activates the heating system if available.
- 3. Programmable Features: Advanced thermostats may come with programmable features, allowing you to set specific temperature schedules for different times of the day. This feature helps optimize energy usage and maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
- 4. Temperature Sensors: Thermostats are equipped with temperature sensors that can accurately measure the ambient temperature in your home. Some thermostats may have multiple sensors to monitor temperature in different zones or rooms.
Controls:
In addition to the thermostat, central AC systems may have other controls that enhance their functionality and convenience. These controls can include:
- 1. Fan Controls: The fan control setting allows you to adjust the speed of the blower fan. You can choose to have the fan run continuously or only when the AC system is actively cooling the air.
- 2. Zone Controls: In larger homes or buildings with multiple cooling zones, zone controls provide the ability to regulate temperatures independently in different areas. This ensures personalized comfort and energy efficiency.
- 3. Remote Controls: Some AC systems come with remote controls that allow you to adjust settings from a distance, providing convenience and flexibility.
- 4. Smart Controls: With advancements in smart home technology, you can now control your central AC system using your smartphone or other smart devices. These controls offer features such as remote monitoring, temperature adjustments, and energy usage tracking.
The thermostat and controls in your central AC system allow you to maintain a comfortable indoor environment and effectively manage the cooling process. By utilizing programmable features, zoning controls, or smart technology, you can maximize energy efficiency while enjoying personalized comfort.
Now that we understand the role of the thermostat and controls, let’s move on to discussing the importance of maintenance and troubleshooting in keeping your central AC system running smoothly.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintaining your central AC system and being able to troubleshoot common issues is crucial for ensuring its optimal performance and longevity. Let’s explore the importance of maintenance and some troubleshooting tips for your AC system:
Maintenance:
Regular maintenance helps keep your central AC system operating efficiently and can prevent potential problems. Here are some maintenance tasks to keep in mind:
- 1. Regular Filter Replacement: It’s important to replace or clean the air filters regularly to maintain adequate airflow and prevent dust and dirt buildup, which can reduce system efficiency.
- 2. Coil Cleaning: Over time, the evaporator and condenser coils can accumulate dirt and debris. Regularly cleaning these coils helps maintain their efficiency and ensures proper heat transfer.
- 3. Check and Clean Ductwork: Inspecting the ductwork for leaks or blockages and cleaning the ducts can improve airflow and overall system performance.
- 4. Lubricate Moving Parts: Proper lubrication of motor bearings and other moving parts prevents excessive friction and extends their lifespan.
- 5. Check Refrigerant Levels: It’s important to have a professional inspect the refrigerant levels and adjust if necessary to ensure optimal cooling performance.
Troubleshooting:
While regular maintenance can minimize issues, it’s important to be able to troubleshoot common AC problems. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- 1. No Cooling: If your AC system is not cooling properly, check if the thermostat is set correctly and the air filters are clean. Additionally, check for any signs of refrigerant leaks or issues with the compressor or condenser unit.
- 2. Weak Airflow: Poor airflow can be caused by clogged air filters, blocked vents, or issues with the blower fan. Check and clean the filters, ensure vents are not blocked, and inspect the blower fan for any obstructions.
- 3. Uneven Cooling: If certain rooms or areas of your home are not cooling evenly, check for air leaks in the ductwork, adjust the dampers if applicable, and consider installing zoning controls for better temperature regulation.
- 4. Strange Noises: Unusual noises such as grinding, banging, or squealing could indicate issues with the fan motor, compressor, or other components. It’s best to have a professional inspect and repair any unusual noises.
- 5. Excessive Energy Consumption: If you notice a sudden increase in energy consumption, it could indicate a problem with system efficiency. Check for leaks, ensure adequate insulation, and consider a professional energy audit to identify potential areas of improvement.
Remember, if you are unsure about any maintenance tasks or troubleshooting procedures, it’s best to consult with a qualified HVAC professional. They can provide expert advice, perform necessary repairs, and help you maintain the optimal performance of your central AC system.
Now that we’ve covered maintenance and troubleshooting, let’s summarize what we’ve learned about the inner workings of a central AC system.
Read more: How Does A Central Heating System Work
Conclusion
Understanding the inner workings of a central air conditioning (AC) system can help you appreciate its efficiency and reliability while enabling you to troubleshoot issues and perform necessary maintenance tasks. We’ve explored the components and processes involved in a central AC system, from the compressor and condenser to the evaporator coil, refrigerant flow, air distribution, and the thermostat and controls.
Each component plays a vital role in the overall cooling process. The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, the condenser dissipates heat, the evaporator coil absorbs heat from the air, and the refrigerant flows through the system, undergoing changes in pressure and state. The cooled air is then efficiently distributed throughout your home via the air handler, ductwork, and supply vents.
The thermostat and controls give you the ability to set and maintain the desired temperature, while regular maintenance tasks, such as replacing air filters, cleaning coils, and checking refrigerant levels, ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
In the event of troubleshooting, it’s important to check for common issues such as improper thermostat settings, clogged filters, weak airflow, or unusual noises. By taking the necessary steps to address these problems or seeking professional help, you can keep your central AC system running smoothly.
Remember, regular maintenance, proper troubleshooting techniques, and professional assistance when needed are essential to ensure the long-term functionality and performance of your central AC system. By understanding how it works and following these guidelines, you can enjoy the comfort and coolness of your home during hot summer months.
So, sit back, relax, and enjoy the cool breeze knowing that you have a solid understanding of how your central AC system works and how to keep it operating at its best.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does Central AC Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Does Central AC Work”