Home>Home Appliances>Heating & Cooling>How Central Heating Works In The UK


Heating & Cooling
How Central Heating Works In The UK
Modified: February 17, 2024
Learn how central heating works in the UK and get expert tips for efficient heating and cooling systems. Find out everything you need to know about heating and cooling your home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Central heating is an essential aspect of modern living, especially in the UK, where the weather can be quite unpredictable. It provides a comfortable and consistent indoor temperature, ensuring that homes and businesses remain warm and cozy, regardless of the external conditions. Understanding how central heating works is crucial for homeowners and tenants, as it allows them to make informed decisions about their heating systems, troubleshoot issues, and ensure efficient operation.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of central heating systems, exploring their history, components, functionality, and maintenance requirements. By gaining insight into these aspects, readers will be better equipped to optimize their heating systems for enhanced comfort and energy efficiency.
Central heating systems have evolved significantly over the years, incorporating advanced technologies and energy-efficient solutions to meet the ever-growing demand for reliable and sustainable heating. Whether you reside in a bustling urban apartment or a quaint countryside cottage, the principles of central heating remain consistent, albeit with variations in system design and components.
As we embark on this journey through the realm of central heating, we will unravel the inner workings of these systems, shedding light on the various components, operational mechanisms, and common issues that may arise. Additionally, we will explore the different types of central heating systems available, each offering unique benefits and considerations for prospective users.
By the end of this guide, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of central heating, empowering them to make informed decisions about system installation, maintenance, and upgrades. Whether you are a homeowner, tenant, or heating professional, the knowledge gained from this exploration will prove invaluable in navigating the intricacies of central heating in the UK.
Key Takeaways:
- Central heating in the UK has a rich history, from Roman hypocausts to modern condensing boilers, reflecting a relentless pursuit of warmth, efficiency, and sustainability.
- Understanding the components, functionality, and maintenance of central heating systems empowers individuals to ensure optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and longevity for their heating systems.
Read more: Why Is Central Heating Not Working
History of Central Heating in the UK
Central heating has played a pivotal role in shaping the living conditions and comfort levels of households across the UK. The evolution of central heating systems can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where ingenious methods were employed to distribute heat within dwellings. In the UK, the historical progression of central heating reflects a fascinating journey of innovation and adaptation to the country's climatic demands.
During the Roman era, hypocaust systems were introduced, representing an early form of central heating. These intricate networks of underfloor heating utilized hot air from furnaces to warm the floors and walls of grand villas and bathhouses. The concept of circulating heated air through concealed channels laid the foundation for centralized heating methods that would emerge in subsequent centuries.
The medieval period witnessed the emergence of rudimentary central heating systems, often centered around large hearths or open fires located within the heart of dwellings. As architectural advancements led to the construction of grand manor houses and castles, central heating solutions evolved to accommodate the heating needs of expansive interiors. Elaborate chimneys and flues were integrated into these structures, facilitating the distribution of heat from centralized hearths to various chambers and living spaces.
The Industrial Revolution marked a significant turning point in the history of central heating, as advancements in engineering and manufacturing spurred the development of more efficient heating technologies. The introduction of coal-fired boilers and steam-based heating systems revolutionized the way heat was generated and distributed within residential and commercial premises. This era saw the proliferation of centralized heating infrastructure in urban centers, transforming the thermal comfort of densely populated areas.
In the 20th century, the widespread adoption of gas and oil-fired central heating systems brought about a new era of convenience and reliability. The integration of radiators, piped hot water, and thermostatic controls ushered in an era of unparalleled comfort and efficiency for UK households. The evolution of central heating continued with the advent of electric heating solutions, offering versatile and responsive heating options for modern homes.
Today, the UK's central heating landscape is characterized by a diverse array of heating technologies, including modern condensing boilers, heat pumps, and renewable energy systems. The historical trajectory of central heating in the UK reflects a relentless pursuit of innovation and sustainability, culminating in the integration of eco-friendly heating solutions that prioritize energy efficiency and environmental responsibility.
As we reflect on the historical evolution of central heating in the UK, it becomes evident that the quest for optimal comfort and warmth has been a driving force behind the continuous refinement of heating technologies. This rich tapestry of innovation and adaptation has shaped the modern central heating systems that grace homes and businesses across the UK, underscoring the enduring significance of heating in the fabric of everyday life.
Components of a Central Heating System
A central heating system comprises several essential components that work in harmony to deliver consistent warmth and comfort throughout a building. Understanding these components is crucial for homeowners and heating professionals, as it enables them to troubleshoot issues, optimize system performance, and make informed decisions about upgrades and maintenance. Let's explore the key elements that constitute a typical central heating system:
-
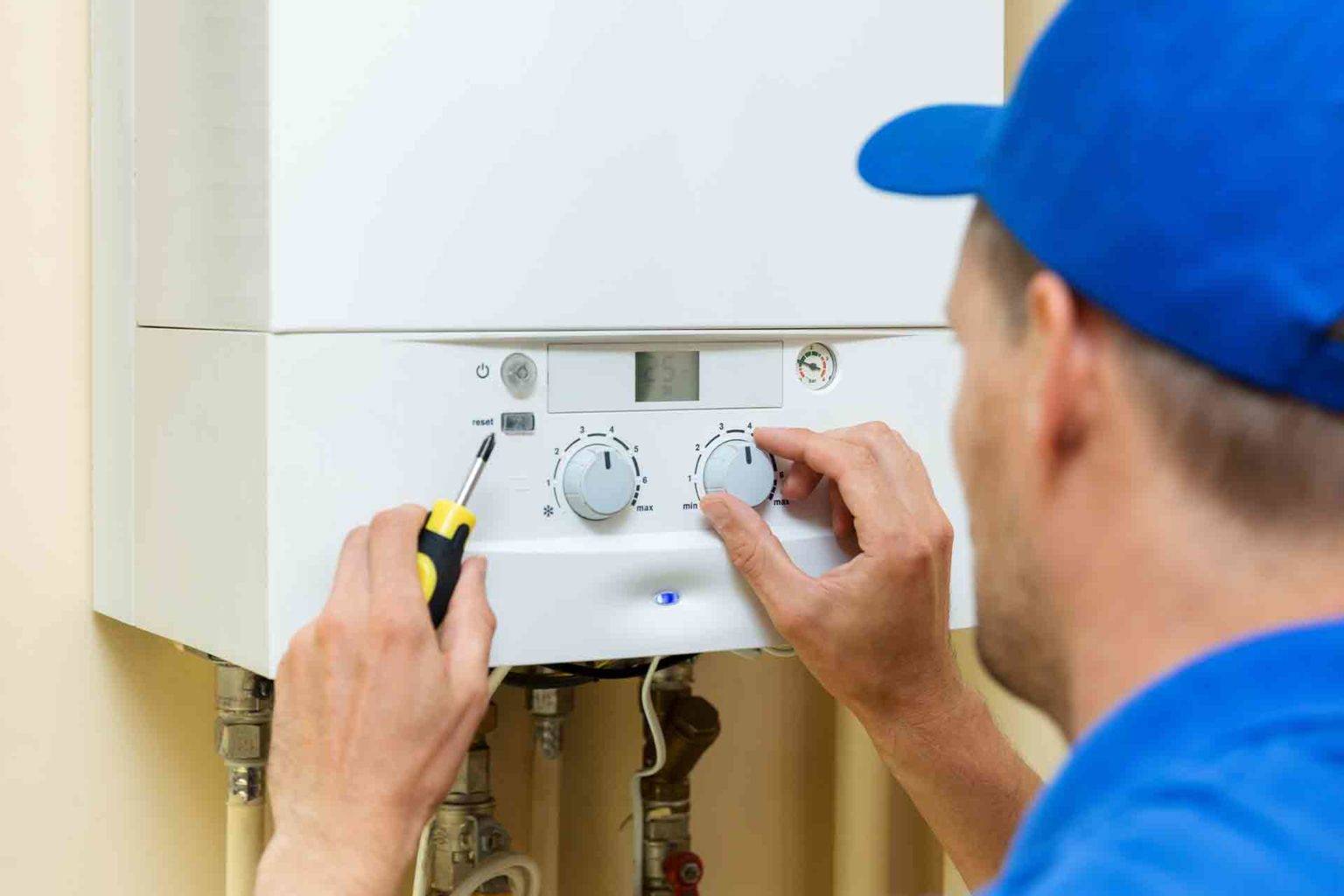
Boiler: At the heart of the central heating system lies the boiler, which serves as the primary heat source. Boilers are available in various types, including combi boilers, conventional boilers, and system boilers, each catering to specific heating and hot water requirements. The boiler generates heat by burning gas, oil, or utilizing electric resistance, and distributes it to the radiators and hot water cylinder.
-
Radiators: These heat exchangers are strategically positioned throughout the building to emit warmth and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Radiators come in diverse shapes and sizes, and their efficient operation is essential for even heat distribution. They are connected to the boiler via a network of pipes, allowing hot water to flow through them and release heat into the surrounding space.
-
Pipework: A network of pipes facilitates the circulation of hot water from the boiler to the radiators and hot water cylinder. The pipework is a critical component that ensures the seamless flow of heated water throughout the central heating system. Proper insulation of the pipes is essential to minimize heat loss and optimize energy efficiency.
-
Hot Water Cylinder: In systems that require a separate hot water supply, a hot water cylinder is utilized to store and distribute heated water for domestic use. This component is commonly found in conventional and system boiler setups, providing a reservoir of hot water for bathing, washing, and other household activities.
-
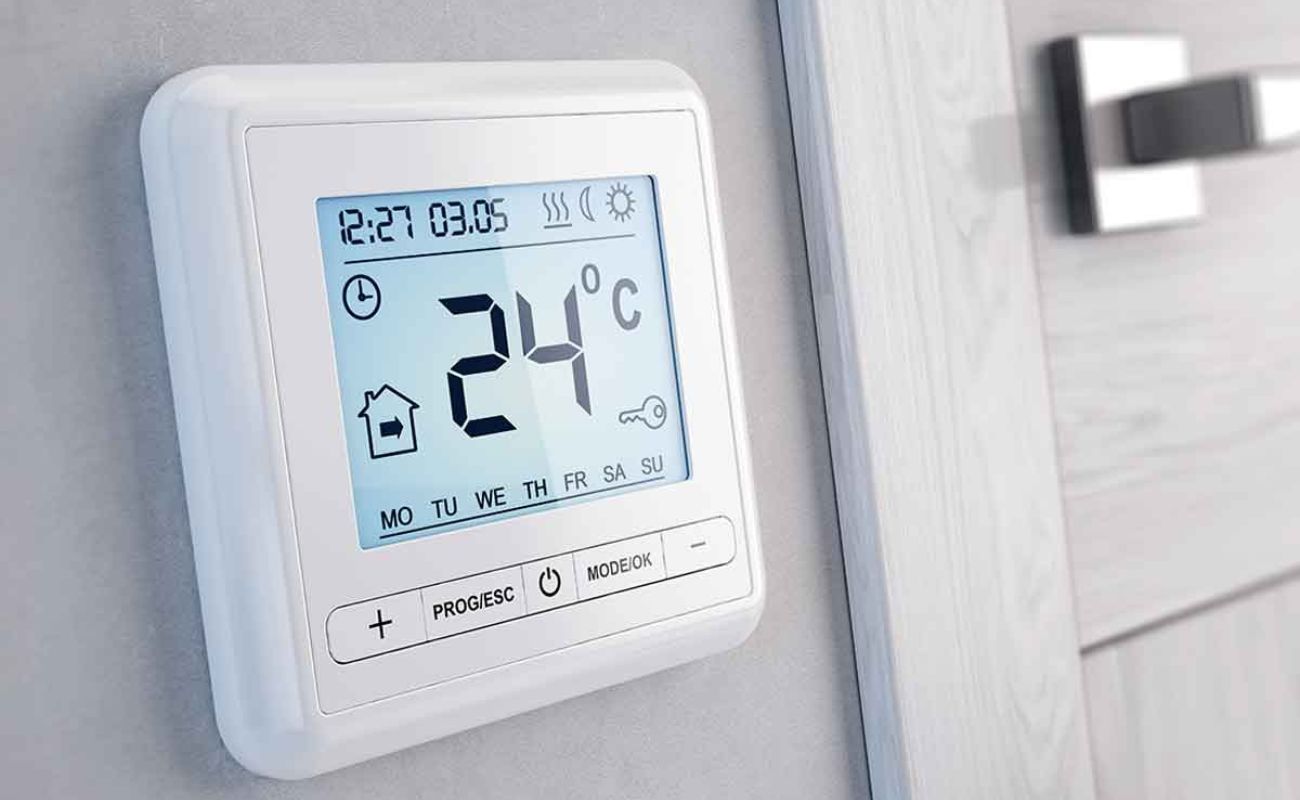
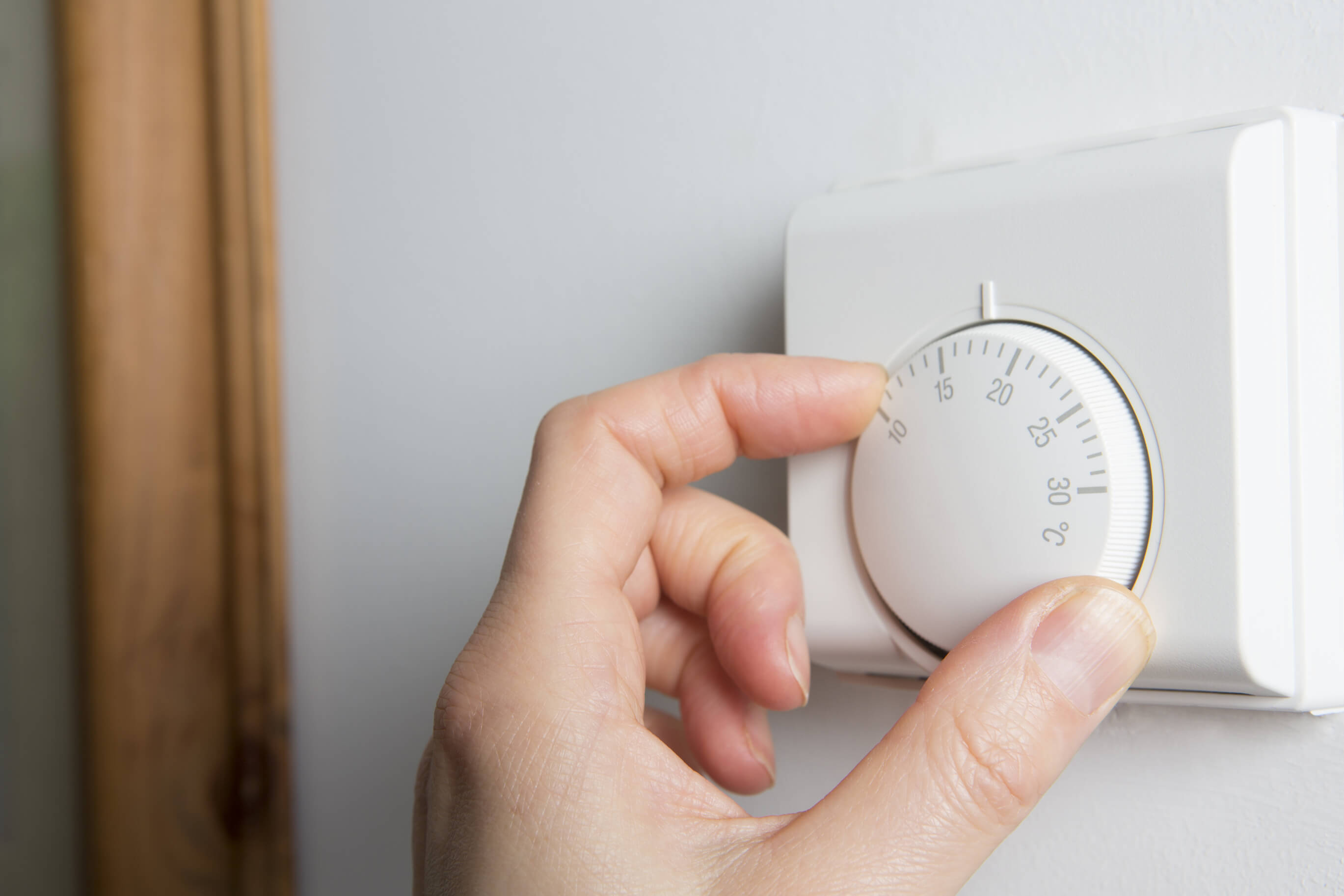
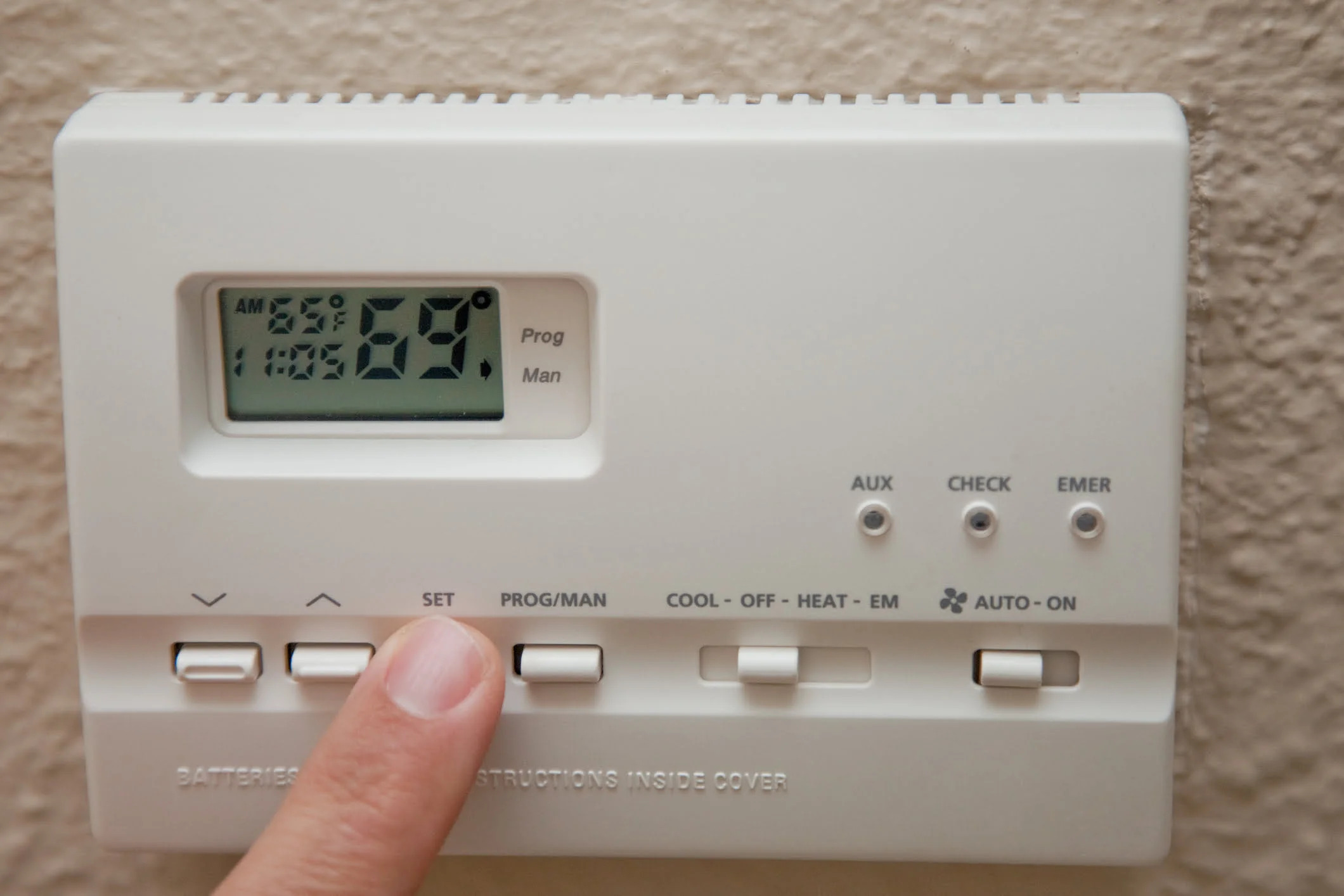
Thermostat and Controls: Central heating systems are equipped with thermostatic controls that regulate the temperature within the building. Thermostats allow users to set desired temperature levels and ensure that the heating system operates efficiently. Additionally, programmable timers and smart heating controls enable precise management of heating schedules, contributing to energy savings and personalized comfort.
-
Expansion Vessel: To accommodate the expansion of water as it heats up, central heating systems incorporate an expansion vessel. This component helps maintain optimal pressure within the system, preventing damage and ensuring safe and efficient operation of the boiler and associated components.
Understanding the role and interplay of these components is essential for maintaining a well-functioning central heating system. Regular inspection, maintenance, and, if necessary, professional servicing of these components are vital to ensure the longevity and efficiency of the heating system.
This comprehensive overview of the components of a central heating system provides valuable insight into the intricate network of elements that collaborate to deliver warmth and comfort to homes and businesses across the UK. By familiarizing themselves with these components, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the inner workings of their central heating systems and make informed decisions regarding their maintenance and optimization.
How Central Heating Systems Work
Central heating systems operate on the principle of generating heat at a central source and distributing it throughout a building to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. The process involves a series of interconnected components working in tandem to facilitate the efficient transfer of heat. Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of central heating systems provides valuable insight into their functionality and enables users to optimize their performance for enhanced comfort and energy efficiency.
The process begins with the activation of the central heating system, typically initiated through a thermostat or heating controls. Upon receiving the signal to generate heat, the boiler, which serves as the primary heat source, springs into action. Depending on the type of boiler—whether it be a combi boiler, conventional boiler, or system boiler—it utilizes gas, oil, or electricity to produce heat. This heat energy is then transferred to the water within the boiler, raising its temperature and creating hot water or steam.
Once the water is heated to the desired temperature, it is circulated through a network of pipework that connects the boiler to the radiators and, if applicable, the hot water cylinder. The heated water flows through the pipework under pressure, reaching the radiators positioned strategically throughout the building. As the hot water enters the radiators, it releases heat through a process of convection and radiation, warming the surrounding air and elevating the indoor temperature.
Simultaneously, if the central heating system incorporates a hot water cylinder, the heated water is directed to this component, where it is stored for domestic use. This ensures a readily available supply of hot water for bathing, washing, and other household activities, enhancing the overall functionality of the central heating system.
Throughout this process, the thermostat and heating controls play a crucial role in regulating the temperature within the building. The thermostat continuously monitors the ambient temperature and communicates with the boiler to maintain the desired level of warmth. Programmable timers and smart heating controls further enhance the system's efficiency by enabling users to customize heating schedules and optimize energy consumption based on their specific requirements.
In essence, central heating systems function as a cohesive network of components, orchestrating the generation, distribution, and regulation of heat to create a comfortable and consistent indoor environment. By comprehending the intricacies of how central heating systems work, individuals can proactively manage their heating systems, troubleshoot potential issues, and leverage energy-efficient practices to maximize comfort and minimize energy expenditure.
Types of Central Heating Systems
Central heating systems come in various configurations, each offering distinct advantages and considerations based on the specific heating and hot water requirements of a property. Understanding the different types of central heating systems is essential for homeowners and property managers, as it enables them to select the most suitable option for their needs and preferences. Let's explore the primary types of central heating systems commonly found in the UK:
-
Combi Boilers: Combi, short for combination, boilers are a popular choice for smaller properties and apartments where space is at a premium. These compact units integrate the functions of a central heating boiler and a hot water heater, providing on-demand heating and hot water without the need for a separate hot water cylinder. Combi boilers are renowned for their energy efficiency and rapid hot water delivery, making them an ideal choice for households with limited space and a preference for instant hot water.
-
Conventional Boilers: Also known as regular or traditional boilers, conventional boilers comprise a central heating boiler, a hot water cylinder, and an expansion tank. They are well-suited for larger properties with high hot water demand and multiple bathrooms. Conventional boilers deliver hot water to the taps and showers at mains pressure, ensuring consistent water flow. While they require additional space for the hot water cylinder and expansion tank, they offer excellent hot water performance and compatibility with existing heating systems.
-
System Boilers: System boilers feature a built-in expansion vessel and circulating pump, streamlining the installation process and reducing the space requirements compared to conventional boilers. They work in conjunction with an unvented hot water cylinder, providing ample hot water for larger households. System boilers are favored for their ease of installation and compatibility with solar thermal systems, offering a sustainable heating solution for environmentally conscious homeowners.
-
Heat Pumps: Heat pumps utilize renewable energy from the air, ground, or water to provide heating and hot water. They operate on the principle of extracting heat from the external environment and transferring it into the building. Air source heat pumps, ground source heat pumps, and water source heat pumps offer sustainable heating solutions, significantly reducing carbon emissions and energy costs. Heat pumps are particularly well-suited for well-insulated properties and can be integrated with underfloor heating systems for enhanced comfort.
-
Electric Heating Systems: Electric central heating systems encompass electric boilers, electric radiators, and electric storage heaters. They are a viable option for properties without access to gas or where renewable electricity sources are prevalent. Electric heating systems offer precise temperature control and are easy to install, making them a versatile choice for both new installations and retrofitting existing properties.
By familiarizing themselves with the characteristics and benefits of these central heating system types, individuals can make informed decisions when selecting a heating solution that aligns with their specific requirements, lifestyle, and environmental considerations. Each type of central heating system presents unique features and considerations, catering to diverse heating needs and preferences across residential and commercial properties.
Read more: Central Heating Radiators: How They Work
Benefits of Central Heating
Central heating systems offer a myriad of advantages that significantly enhance the comfort, convenience, and energy efficiency of residential and commercial properties. Understanding the benefits of central heating is instrumental in appreciating the value it brings to everyday living, especially in regions with fluctuating temperatures such as the UK.
-
Consistent Comfort: Central heating systems ensure a consistent and comfortable indoor temperature throughout the year, regardless of external weather conditions. By distributing heat evenly across various rooms, these systems create a cozy and inviting environment, promoting a sense of well-being and relaxation for occupants.
-
Energy Efficiency: Modern central heating systems are designed to optimize energy usage, resulting in reduced heating costs and environmental impact. Advanced technologies, such as condensing boilers and smart heating controls, enable precise temperature management and minimize energy wastage, contributing to sustainable living and lower utility bills.
-
Convenience and Control: Central heating systems offer unparalleled convenience and control, allowing users to tailor their heating schedules and preferences to suit their lifestyle. Programmable timers and smart thermostats empower individuals to regulate heating patterns, ensuring warmth when needed and conserving energy during periods of inactivity.
-
Hot Water Supply: For properties equipped with a hot water cylinder, central heating systems provide a reliable and readily available supply of hot water for bathing, washing, and domestic use. This eliminates the need for separate water heating solutions and ensures consistent hot water delivery throughout the property.
-
Versatile Heating Solutions: With a diverse range of central heating system types available, including combi boilers, conventional boilers, system boilers, heat pumps, and electric heating systems, individuals can select a solution that aligns with their specific heating and hot water requirements. This versatility enables tailored heating solutions for properties of varying sizes and usage patterns.
-
Enhanced Property Value: Properties equipped with efficient central heating systems often command higher market value and appeal to prospective buyers and tenants. The presence of a well-maintained and modern central heating system is a significant selling point, reflecting a commitment to comfort, energy efficiency, and long-term property maintenance.
-
Health and Well-being: Central heating systems contribute to improved indoor air quality and overall well-being by maintaining optimal temperature levels and reducing humidity. By creating a comfortable and healthy living environment, these systems support respiratory health and enhance the overall quality of life for occupants.
-
Adaptability to Renewable Energy: Many central heating systems are compatible with renewable energy sources, such as solar thermal systems and heat pumps, enabling environmentally conscious individuals to integrate sustainable heating solutions into their properties. This aligns with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly living and reduced carbon footprint.
In summary, the benefits of central heating extend far beyond mere warmth, encompassing energy efficiency, convenience, versatility, and overall well-being. By embracing the advantages offered by modern central heating systems, individuals can elevate their living standards, reduce their environmental impact, and enjoy a comfortable and sustainable lifestyle.
Common Issues with Central Heating Systems
Central heating systems, while indispensable for maintaining indoor comfort, are susceptible to a range of common issues that can disrupt their functionality and compromise heating performance. Understanding these prevalent issues is crucial for homeowners and property managers, as it enables them to identify and address potential problems in a timely manner, ensuring the uninterrupted operation of their heating systems.
-
Boiler Malfunctions: Boiler malfunctions represent a significant concern for central heating systems. Issues such as low pressure, ignition failures, and thermostat faults can lead to a loss of heating and hot water. Additionally, limescale buildup within the boiler can impede its efficiency, resulting in reduced heat output and increased energy consumption.
-
Radiator Cold Spots: Uneven heating across radiators, characterized by cold spots or inconsistent warmth, is a common issue in central heating systems. This can be attributed to air pockets within the radiators, sludge accumulation in the pipework, or imbalanced water flow, leading to suboptimal heat distribution.
-
Noisy Operation: Central heating systems may exhibit noisy operation, manifesting as banging, gurgling, or whistling sounds emanating from the boiler or radiators. These noises can indicate issues such as air ingress, pump malfunctions, or limescale deposits, necessitating prompt investigation and resolution.
-
Thermostat Inaccuracies: Inaccurate thermostat readings or unresponsive controls can disrupt the temperature regulation within the building, leading to discomfort and energy wastage. Calibration errors, sensor faults, or wiring issues can contribute to thermostat inaccuracies, requiring recalibration or replacement.
-
Pipework Leaks: Leaking pipework within the central heating system can result in water damage, reduced system pressure, and diminished heating performance. Corrosion, joint failures, or damaged seals can contribute to pipework leaks, necessitating immediate attention to prevent further complications.
-
Hot Water Supply Issues: Properties with hot water cylinders may encounter issues with inadequate hot water supply, inconsistent water temperature, or prolonged heating times. These issues can stem from cylinder insulation deficiencies, faulty immersion heaters, or sediment accumulation within the cylinder.
-
Pressure Fluctuations: Central heating systems may experience fluctuations in pressure, leading to operational inefficiencies and potential system shutdowns. Pressure loss can be attributed to leaks, bleeding of radiators, or faulty pressure relief valves, necessitating pressure re-adjustment and leak identification.
-
Inefficient Heating Controls: Outdated or malfunctioning heating controls, including timers, thermostats, and zone valves, can impede the efficient operation of the central heating system. Upgrading to smart heating controls or addressing control malfunctions is essential for optimizing energy usage and comfort levels.
By acknowledging these common issues with central heating systems, individuals can proactively monitor their heating systems, engage in preventive maintenance, and seek professional assistance when encountering persistent or complex issues. Timely intervention and regular servicing are instrumental in mitigating these issues, ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of central heating systems.
Regular maintenance of your central heating system is crucial to ensure it runs efficiently and safely. This includes bleeding radiators, checking boiler pressure, and scheduling annual servicing by a qualified engineer.
Maintenance and Servicing of Central Heating Systems
Maintenance and servicing are integral aspects of ensuring the optimal performance, longevity, and safety of central heating systems. Regular upkeep and professional servicing not only mitigate potential issues but also contribute to energy efficiency and cost savings. By adhering to a structured maintenance regimen and engaging qualified professionals for servicing, homeowners and property managers can safeguard their central heating systems against malfunctions and prolong their operational lifespan.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular maintenance plays a pivotal role in preserving the functionality and efficiency of central heating systems. It involves a series of proactive measures aimed at identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Maintenance tasks encompass inspecting and cleaning components, checking for leaks, optimizing system pressure, and verifying the accuracy of heating controls and thermostats. Additionally, the periodic removal of air pockets from radiators and the assessment of boiler performance are essential maintenance activities that contribute to the seamless operation of the heating system.
Read more: How Does Oil Central Heating Work
Professional Servicing
Engaging certified heating engineers for professional servicing is paramount in ensuring the comprehensive assessment and upkeep of central heating systems. Professional servicing involves in-depth inspections, performance evaluations, and component servicing to uphold the system's efficiency and safety standards. During servicing, engineers conduct thorough checks of the boiler, radiators, pipework, and heating controls, identifying and rectifying any underlying issues. Furthermore, professional servicing often includes the cleaning of heat exchangers, descaling of boilers, and the assessment of combustion efficiency, all of which contribute to optimized system performance.
Seasonal Considerations
Adhering to a seasonal maintenance schedule is essential for addressing the unique demands of central heating systems throughout the year. Preparing the system for the winter season involves inspecting and, if necessary, insulating external pipework to prevent freezing, ensuring the functionality of thermostats and controls, and verifying the integrity of the boiler's ignition and safety mechanisms. Conversely, post-winter maintenance focuses on addressing any wear and tear resulting from prolonged usage, optimizing system efficiency for the warmer months, and preparing the system for reduced heating demands.
User Responsibilities
In addition to professional servicing, homeowners and occupants play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of central heating systems. This includes regularly bleeding radiators to remove trapped air, monitoring system pressure, and promptly addressing any unusual noises or performance irregularities. Furthermore, adhering to manufacturer-recommended maintenance guidelines, such as replacing filters and scheduling periodic system checks, contributes to the overall health and efficiency of the central heating system.
By prioritizing maintenance and professional servicing, individuals can uphold the reliability, efficiency, and safety of their central heating systems, ensuring uninterrupted comfort and peace of mind throughout the year. Proactive maintenance not only minimizes the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns but also optimizes energy usage, resulting in cost savings and sustainable heating practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, central heating systems stand as indispensable pillars of comfort and convenience, particularly in the context of the UK's diverse climate. The evolution of central heating, from ancient hypocaust systems to modern condensing boilers and heat pumps, reflects a relentless pursuit of warmth, efficiency, and sustainability. The historical journey of central heating in the UK underscores the enduring significance of heating technologies in shaping the living standards and architectural landscapes of the nation.
By delving into the components, functionality, and maintenance requirements of central heating systems, individuals gain a profound understanding of the intricate network of elements that collaborate to deliver warmth and comfort. The diverse types of central heating systems, ranging from combi boilers to heat pumps, offer tailored solutions for properties of varying sizes and usage patterns, catering to the unique heating and hot water requirements of homeowners and businesses.
The benefits of central heating systems extend far beyond mere warmth, encompassing energy efficiency, convenience, and overall well-being. These systems provide consistent comfort, precise temperature control, and reliable hot water supply, contributing to enhanced property value and sustainable living practices. However, they are not without their challenges, as common issues such as boiler malfunctions, radiator cold spots, and thermostat inaccuracies necessitate proactive maintenance and professional servicing to ensure uninterrupted operation.
Maintenance and servicing emerge as critical facets of preserving the functionality and efficiency of central heating systems. By adhering to a structured maintenance regimen and engaging qualified professionals for servicing, homeowners and property managers can safeguard their central heating systems against malfunctions and prolong their operational lifespan. Seasonal considerations and user responsibilities further underscore the collaborative effort required to maintain the integrity of central heating systems.
In essence, central heating systems embody a harmonious fusion of innovation, comfort, and sustainability, enriching the lives of individuals and communities across the UK. By embracing the knowledge and insights presented in this guide, readers are empowered to navigate the complexities of central heating with confidence, ensuring optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and longevity for their heating systems. As central heating continues to evolve in tandem with technological advancements and environmental imperatives, its role as a cornerstone of modern living remains unwavering, shaping the warmth and well-being of generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Central Heating Works In The UK
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Central Heating Works In The UK”