

Articles
What Is An Electrical Cord?
Modified: March 1, 2024
Discover the importance of electrical cords and how they play a vital role in ensuring safety and efficiency. Read informative articles on the topic.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of electrical cords! In our modern era, we are surrounded by a vast array of electronic devices and appliances that require power to function. But have you ever wondered how these devices receive the necessary electrical supply? That’s where the humble electrical cord comes into play.
An electrical cord, also known as a power cord or electric cord, is a flexible cable that is used to connect electrical devices to power sources. Whether it’s charging your smartphone, running your blender, or plugging in your television, electrical cords play a crucial role in delivering the electricity needed to power your daily life.
In this article, we will explore the different types of electrical cords, their components, how they work, safety considerations, and their common uses. Let’s dive in and unravel the fascinating world of electrical cords!
Key Takeaways:
- Electrical cords are the unsung heroes of our modern world, delivering the power that keeps our devices and appliances running smoothly, but it’s crucial to prioritize safety and proper usage to prevent accidents and ensure longevity.
- From indoor power supply to outdoor use, electrical cords are versatile and essential for a wide range of applications, making our lives more convenient and enabling us to enjoy the benefits of electricity in various settings.
Read more: What Is An Electrical Cord Choke
Definition of an Electrical Cord
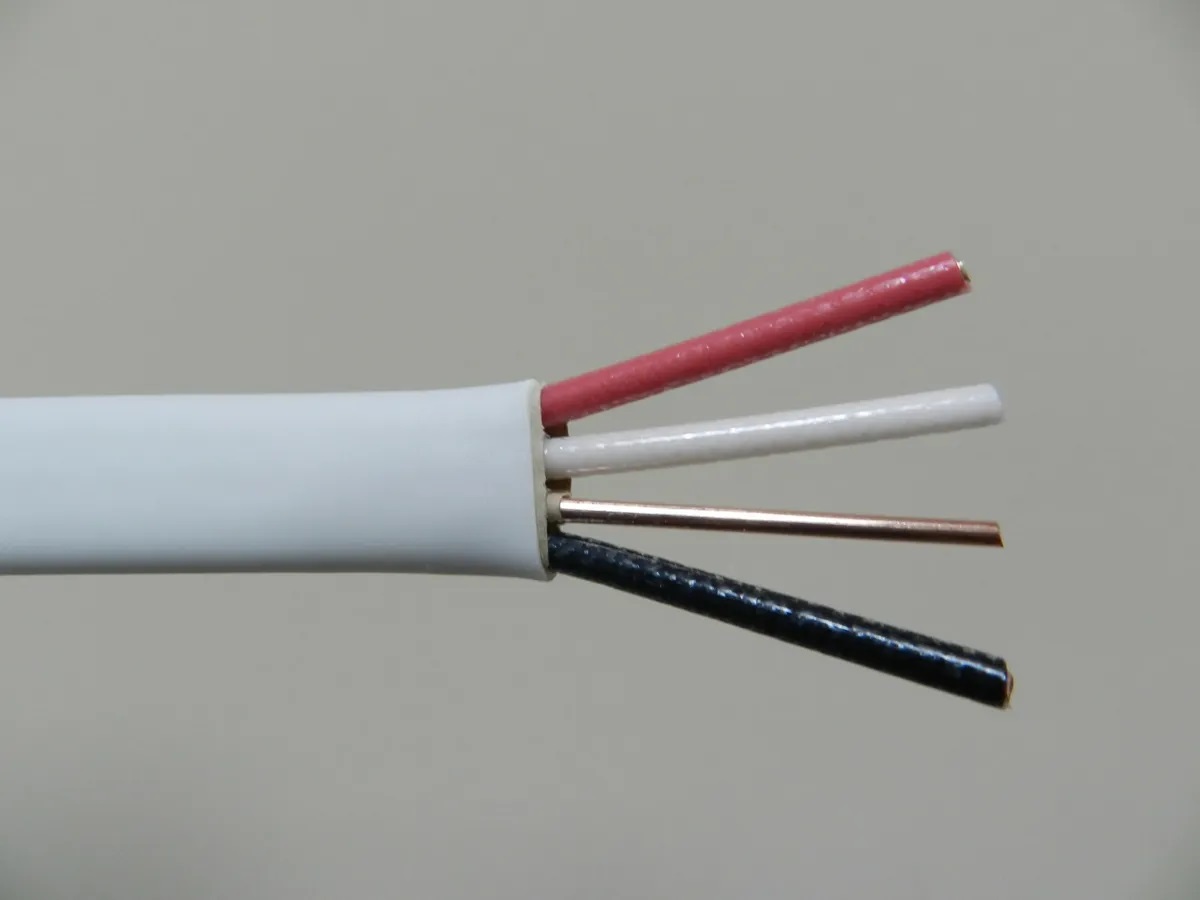
An electrical cord is a flexible cable that provides a means of connecting electrical devices to a power supply. It serves as a pathway for the flow of electricity from the power source to the device, allowing it to operate efficiently. The cord usually consists of multiple conductive wires encased in insulation, with connectors on each end for easy plug-in and disconnection.
Electrical cords come in various lengths, thicknesses, and configurations to accommodate different power requirements and usage scenarios. They are designed to be versatile and portable, allowing users to connect their devices to a power source without the need for intricate wiring procedures.
One end of the electrical cord features a plug, which is inserted into a compatible electrical outlet or power source. The other end is equipped with a receptacle or connector that interfaces with the device, enabling the transfer of electrical energy. The plug and receptacle may have different shapes and configurations depending on the region or country’s electrical standards.
The cords are typically made from durable materials that can withstand physical stress and resist damage from environmental factors like heat, moisture, and friction. The insulation surrounding the wires ensures that the electrical current remains contained and prevents potential shocks or short circuits.
It’s important to note that not all cords are created equal. The capacity to handle electrical current can vary depending on the cord’s gauge or thickness. Thicker cords with a lower gauge can accommodate higher power loads and are suitable for heavy-duty electrical equipment. On the other hand, thinner cords with a higher gauge are better suited for low-power devices.
In summary, an electrical cord is a vital component in our everyday lives, providing the necessary link between electrical devices and power sources. With their versatility and convenience, they make it possible for us to enjoy the benefits of electricity safely and efficiently.
Types of Electrical Cords
Electrical cords come in a variety of types and configurations, each designed to serve a specific purpose and meet different power requirements. Let’s explore some of the common types of electrical cords:
Standard Extension Cords:
Standard extension cords are perhaps the most widely recognized type of electrical cord. They are typically used to extend the reach of power outlets, allowing flexibility in positioning electrical devices. These cords are available in various lengths and gauge sizes to accommodate different power needs. Standard extension cords are commonly used in homes, offices, and other indoor environments.
Power Strips:
Power strips are a convenient way to expand the number of available outlets in a single location. They feature multiple outlets along with a cord, allowing users to plug in multiple devices simultaneously. Power strips often come with surge protection features to safeguard connected devices from voltage spikes and surges. They are commonly used in home entertainment centers, computer setups, and offices where multiple devices need to be powered.
Read more: What Are Cloth Covered Electrical Cords
Surge Protectors:
Surge protectors, also known as surge suppressors, are specialized electrical cords designed to protect electronic devices from voltage surges. These surges, which can occur due to lightning strikes or fluctuations in the power grid, can potentially damage sensitive electronics. Surge protectors feature built-in circuitry that detects and diverts excess voltage away from connected devices. They are commonly used with computers, televisions, and other valuable electronics.
Appliance Cords:
Appliance cords are specifically designed for use with large electrical appliances such as refrigerators, washers, dryers, and dishwashers. These cords are typically thicker and have higher gauge sizes to handle the higher power demands of these appliances. Appliance cords are often equipped with a molded plug and are built to be durable and heat-resistant.
Outdoor Extension Cords:
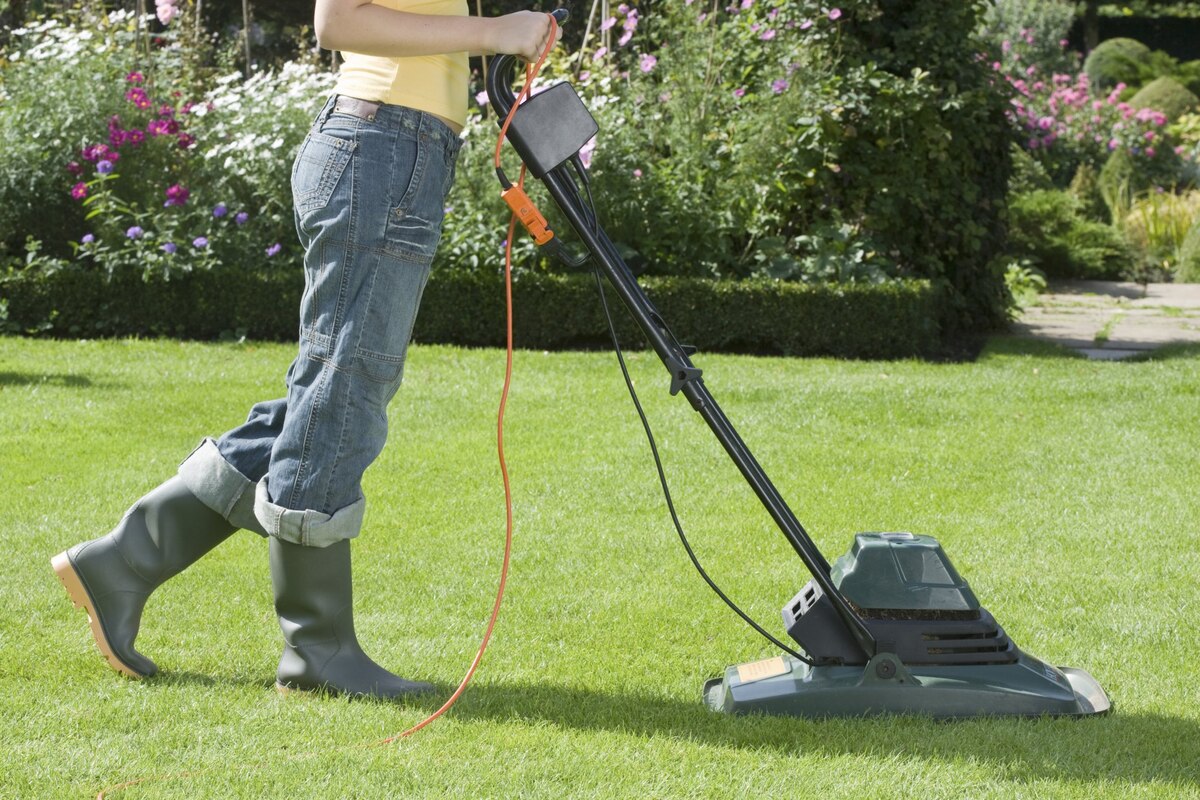
Outdoor extension cords are designed to withstand the environmental conditions encountered outside. They are usually weatherproof and have additional features such as water resistance and UV protection. These cords allow for powering outdoor equipment like lawnmowers, hedge trimmers, and holiday lights, providing electrical connectivity in outdoor spaces.
These are just a few examples of the many types of electrical cords available. It’s important to select the right cord for the intended purpose and ensure that it meets the necessary safety standards and power requirements.
Components of an Electrical Cord
An electrical cord may seem like a simple, flexible cable, but it consists of several important components that work together to ensure safe and efficient electricity transfer. Let’s take a closer look at the key components of an electrical cord:
Wire:
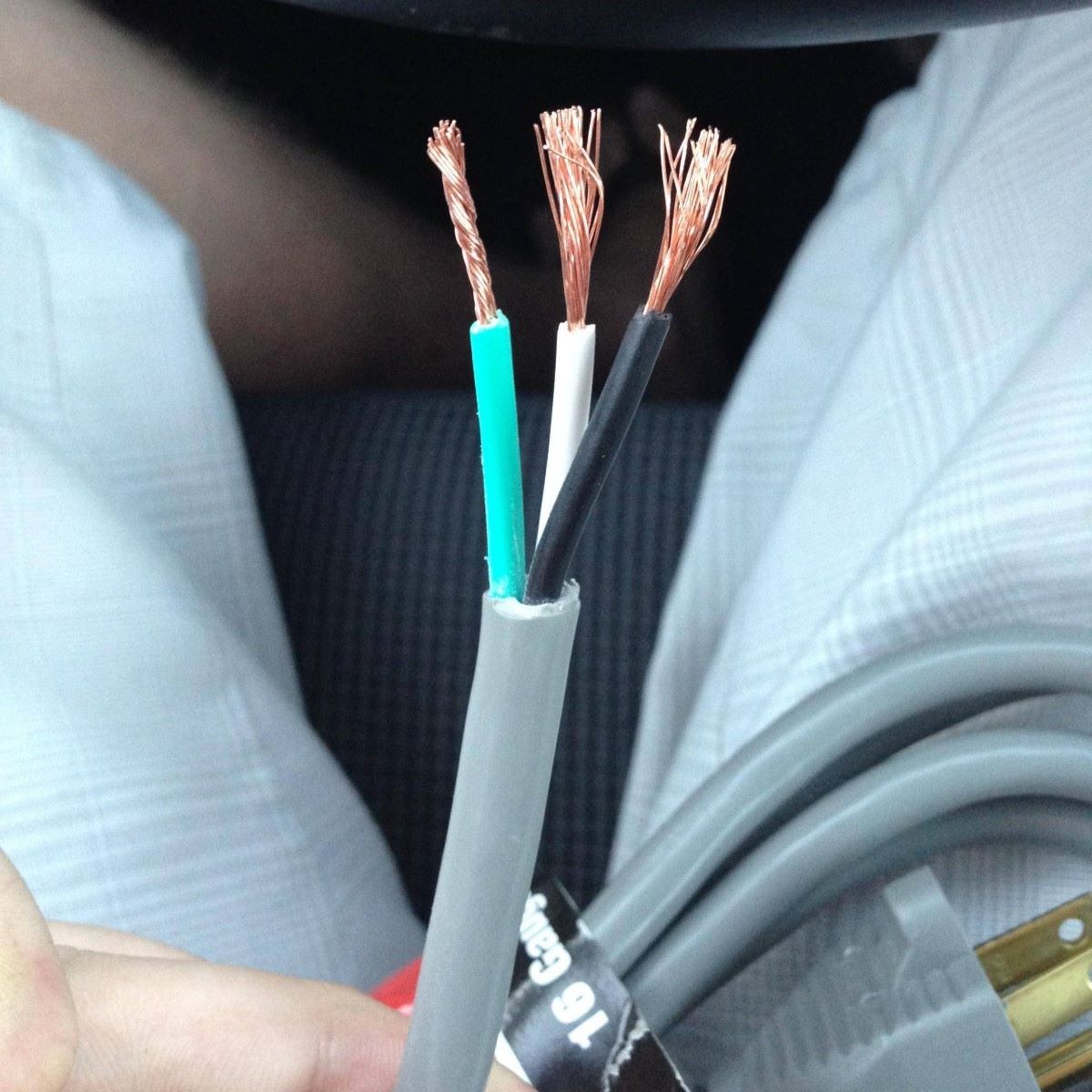
The wire is the core component of an electrical cord and serves as the pathway for the flow of electricity. It is typically made of copper or aluminum, which are excellent conductors of electricity. The wire’s gauge, or thickness, determines its ability to carry current. Thicker wires with lower gauge sizes can handle higher power loads more effectively.
Insulation:
Insulation surrounds the wires and acts as a protective barrier. It is usually made of materials such as PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) or rubber, which provide insulation against electrical shocks. The insulation also protects the wires from damage caused by abrasion, moisture, and heat. The color of the insulation may vary depending on the purpose and standards set by regulatory authorities.
Plug and Receptacle:
The plug and receptacle are the connecting ends of the electrical cord. The plug, also known as the male connector, is inserted into an electrical outlet or power source. The receptacle, also called the female connector, interfaces with the device or appliance that requires power. Different countries may have different plug and receptacle designs based on their specific electrical standards.
Grounding:
Grounding is a crucial safety feature in many electrical cords. It involves providing a dedicated ground wire that serves as a path for electrical current to flow into the ground. Grounding helps protect against electrical shock by redirecting excess current away from the user or device. Grounded cords typically have three prongs on the plug: live, neutral, and ground.
Read more: What Is The End Of An Electrical Cord Called
Cord Locks or Connectors:
Cord locks or connectors are additional components that enhance the usability and versatility of electrical cords. Cord locks, such as cord grips or strain reliefs, are used to secure the cord and prevent accidental disconnections. Connectors, like twist-lock or snap-lock connectors, provide a secure and reliable connection between the cord and the device or power source.
By combining these components, electrical cords provide a safe and efficient way to deliver electricity to various devices and appliances. It’s important to ensure that all components are in good condition and meet the required safety standards for optimal performance and peace of mind.
How Electrical Cords Work
Electrical cords may seem like a simple part of our daily lives, but they play a crucial role in delivering the power needed to operate our devices. Let’s explore how electrical cords work and facilitate the flow of electricity:
Electric Current Flow:
Electricity flows through an electrical cord in the form of electric current. Electric current is the movement of electric charge, usually carried by electrons, through a conductive path. When a device is plugged into an electrical cord and connected to a power source, the flow of electric current is established, allowing the device to receive the necessary electrical energy.
Conductors and Insulators:
Electrical cords are designed with conductive materials, typically copper or aluminum, which are excellent conductors of electricity. Conductors allow the flow of electric current with minimal resistance. However, to prevent unwanted flow or electrical shocks, the conductors are insulated. The insulation, typically made of materials like PVC or rubber, acts as a barrier, preventing the electric current from coming into contact with other conductive objects or people.
Read more: What Type Of Electrical Cord To Bury
Plug and Receptacle Connections:
The plug and receptacle connections are critical elements in the functionality of electrical cords. The plug, when inserted into a compatible outlet, establishes a connection with the power source. The prongs on the plug make contact with the corresponding slots in the outlet, allowing the flow of electric current from the power source to the cord. The receptacle, on the other end of the cord, connects to the device or appliance, completing the circuit and enabling the electrical energy to power the device.
To ensure proper and safe electrical connectivity, it’s important to use plugs and receptacles that match the electrical standards of your region. Compatibility between the plug and receptacle ensures a secure connection and minimizes the risk of electrical hazards.
By understanding the principles of electric current flow, the importance of conductors and insulators, and the significance of plug and receptacle connections, we can appreciate the functionality of electrical cords. They provide a reliable and efficient pathway for the flow of electricity, allowing our devices to function seamlessly and make our lives easier.
Safety Considerations with Electrical Cords
While electrical cords are convenient and necessary for powering our devices, it is essential to prioritize safety when using them. Here are some important safety considerations to keep in mind:
Overloading and Overheating:
One of the primary safety concerns with electrical cords is overloading. Overloading occurs when too many devices are plugged into a single cord or when a device draws more power than the cord can handle. This can lead to overheating, which increases the risk of the cord melting, catching fire, or causing electrical damage. Avoid overloading by distributing the load among multiple circuits and using cords capable of handling the required power.
Proper Usage and Handling:
Using electrical cords appropriately is crucial for safety. Avoid using damaged or frayed cords that expose the wires. Always grip the plug head when inserting or removing cords from outlets to prevent damage. Do not pull on the cord itself, as this can strain the connections and cause internal damage. Additionally, do not run cords through doorways, windows, or under rugs where they can be pinched or damaged.
Read more: What To Do With A Frayed Electrical Cord
Cord Maintenance and Inspection:
Regularly inspect electrical cords for any signs of wear and tear, such as cuts, fraying, or damaged insulation. Replace any defective cords immediately to avoid electrical hazards. Keep cords away from sharp objects and corrosive materials that can cause damage. Clean cords regularly to remove dust, debris, or any build-up that can affect their performance or create a safety risk.
Avoiding Trip Hazards:
Tripping over electrical cords can result in injuries and damage. Keep cords out of high-traffic areas and secure them with cord covers or tape to reduce the risk of tripping. When using cords outdoors, make sure they are safely positioned and protected from being stepped on or run over by vehicles or equipment.
Electrocution and Shock Prevention:
To prevent the risk of electrocution or electric shock, never touch electrical cords or appliances with wet hands. When unplugging cords, grasp the plug head, not the cord, to avoid accidental shocks. Ensure that outlets and electrical cords are protected by ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in areas where water is present, such as kitchens and bathrooms. It’s also important to teach children about electrical safety and the proper handling of cords.
By following these safety considerations, we can mitigate potential hazards associated with electrical cords and ensure a safe and secure environment when using electrical devices.
Common Uses of Electrical Cords
Electrical cords play a vital role in providing power to various devices and appliances, both indoors and outdoors. Let’s explore some of the common uses of electrical cords:
Read more: What Electrical Cord Do I Need For My RV
Indoor Power Supply:
One of the primary uses of electrical cords is to supply power indoors. From lamps and televisions to computers and kitchen appliances, electrical cords enable us to conveniently plug in the devices we use daily. Whether it’s charging our phones or running household appliances, electrical cords ensure a steady flow of electricity to keep our indoor spaces functioning smoothly.
Outdoor Power Supply:
Electrical cords also extend their functionality to outdoor environments. Outdoor extension cords enable us to power tools and equipment in garden spaces, workshops, or construction sites. Whether it’s mowing the lawn, trimming hedges, or operating power tools, electrical cords provide the flexibility to work outdoors without worrying about the proximity of power outlets.
Electronic Devices and Appliances:
Electrical cords are indispensable companions for our electronic devices and appliances. From smartphones and laptops to televisions and gaming consoles, these devices require electrical cords to connect them to power sources. Likewise, kitchen appliances like blenders, microwaves, and coffee makers rely on electrical cords to deliver the necessary electricity for their operation.
Construction and DIY Projects:
In construction sites and DIY projects, electrical cords are essential for powering tools and equipment. From drills and saws to power sanders and nail guns, these tools often require electrical cords to carry the necessary electrical power. Construction extension cords are designed to withstand demanding conditions and provide reliable power to construction equipment and tools.
Read more: What Does SO Stand For Electrical Cord
Entertainment and Events:
Electrical cords are an integral part of entertainment setups and event planning. Whether it’s setting up sound systems, lighting fixtures, or stage equipment, electrical cords ensure that the necessary power is delivered to create memorable experiences. In event venues, extension cords and power strips are used to supply electricity to various equipment, including audiovisual systems, decorative lighting, and stage production equipment.
Electrical cords have become an essential part of our daily lives, enabling us to power our devices, operate equipment, and create memorable experiences. With their versatility and convenience, electrical cords make it possible for us to enjoy the benefits of electricity in various settings and applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrical cords are more than just mere cables – they are the lifeline that powers our devices and appliances, connecting them to the electrical energy they need to function. These cords come in various types, each serving a specific purpose. Standard extension cords provide flexibility in reaching distant power outlets, while power strips and surge protectors extend the number of available outlets and provide protection from voltage spikes. Appliance cords are specially designed for larger appliances, and outdoor extension cords withstand the rigors of outdoor use.
Understanding the components of an electrical cord, such as the wire, insulation, plug and receptacle, grounding, and cord locks or connectors, helps us appreciate the technology that goes into their design and construction. By ensuring the proper flow of electric current and providing safety measures like insulation and grounding, electrical cords enable us to power our devices safely and efficiently.
However, safety should always be a top priority when using electrical cords. Being aware of the risks of overloading, overheating, and improper usage is essential in preventing accidents. Regular maintenance and inspection of cords, as well as avoiding trip hazards, are crucial steps to ensure their longevity and prevent potential hazards.
Electrical cords find wide applications in both indoor and outdoor settings. They power our electronic devices and appliances, provide electricity for construction and DIY projects, and play a crucial role in entertainment and event planning.
As we wrap up our exploration of electrical cords, it is important to remember to use them responsibly and safely. Choosing the right type of cord for the intended purpose, following proper handling techniques, and regularly inspecting and maintaining cords will help ensure their safe and efficient operation.
So the next time you plug in your smartphone or use an electrical appliance, take a moment to appreciate the role that electrical cords play in delivering the power that keeps our modern world running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is An Electrical Cord?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.








0 thoughts on “What Is An Electrical Cord?”