Home>Articles>How To Tell What Is The Power On An Electrical Cord


Articles
How To Tell What Is The Power On An Electrical Cord
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn how to determine the power rating of an electrical cord in this informative article. Discover the key factors to consider for safe and efficient usage.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Electrical cords are essential components of our modern lives. Whether it’s for powering up our electronic devices, appliances, or tools, understanding the power rating of an electrical cord is crucial for their safe and efficient use. The power rating indicates the maximum amount of electrical power that the cord can handle, ensuring that it can deliver the necessary electricity without overheating or causing damage.
In this article, we will explore different methods to determine the power rating of an electrical cord. We will discuss visual cues on the cord itself, inspecting the plug, reading the label, and using a multimeter. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to determine the power rating of an electrical cord.
Key Takeaways:
- Visual cues like cord thickness and plug type provide clues to an electrical cord’s power rating, but reading the label or using a multimeter is essential for accurate determination.
- Understanding power ratings ensures safe and efficient use of electrical cords. Always prioritize safety and consider consulting a professional electrician for testing assistance.
Read more: How To Tell Age Of Electrical Cord
Understanding Electrical Cords
Electrical cords, also known as power cords or extension cords, are flexible cables that transmit electrical power from a power source to a device. They have a conductive wire encased in an insulating layer, typically made of rubber or thermoplastic, to prevent electrical shocks and protect the wire from damage. Understanding the different components of an electrical cord is essential for determining its power rating.
There are two main types of electrical cords: non-grounded (two-prong) and grounded (three-prong) cords. Non-grounded cords have two prongs – a live (hot) wire and a neutral wire, while grounded cords have an additional prong, which is the ground wire. The ground wire provides an extra layer of safety by redirecting any electrical current in case of a fault or short circuit.
Electrical cords come in various lengths, typically ranging from a few feet to several yards. The length of the cord plays a role in its power rating, as longer cords have a higher resistance, which can potentially lead to a drop in voltage and affect the performance of the connected device.
The power rating of an electrical cord is determined by the ampere rating and the voltage rating. The ampere rating, measured in amperes (A), indicates the maximum current that the cord can safely carry without overheating. The voltage rating, measured in volts (V), represents the maximum voltage that the cord can withstand.
It is essential to understand that using an electrical cord with a power rating lower than what is required by a device can lead to overheating and damage to both the cord and the device. On the other hand, using a cord with a higher power rating than necessary is generally safe, as the device will only draw the amount of power it needs.
Now that we have a basic understanding of electrical cords, let’s explore how to identify the power rating of a cord using visual cues, inspecting the plug, reading the label, and using a multimeter.
Identifying the Power Rating
When it comes to determining the power rating of an electrical cord, there are a few visual cues that can help provide some information. One of the first things to look for is the thickness or gauge of the cord. Thicker cords generally have a higher power rating as they can handle a larger current load without overheating. However, it’s important to note that the gauge alone is not sufficient to determine the precise power rating.
Another visual cue is the condition of the cord itself. Examine the cord for any wear and tear, fraying, or exposed wires. Damaged cords may not be able to handle the same power rating as a cord in good condition, so it’s crucial to assess the overall integrity of the cord before using it.
The plug attached to the electrical cord can also provide some information about the power rating. Look for any markings or labels on the plug, which may indicate the maximum power rating the cord can handle. However, keep in mind that not all plugs may have this information, so it’s not always a reliable method.
Inspecting the plug for the presence of a grounding prong is also important. Grounded cords, which have an extra prong, are generally designed to handle higher power loads than non-grounded cords.
While visual cues can give you some indication of the power rating, they are not foolproof methods. To get a more accurate measurement of the power rating, it’s best to rely on other techniques such as reading the label or using a multimeter.
In the next sections, we will explore these methods in more detail to help you accurately determine the power rating of an electrical cord. By understanding how to identify the power rating, you can ensure the safe and efficient use of your electrical devices and appliances.
Visual Cues on the Electrical Cord
When trying to determine the power rating of an electrical cord, there are several visual cues you can look for on the cord itself. These cues can give you a general idea of the cord’s capabilities, although they may not provide precise information. Let’s explore some of these visual cues:
1. Thickness or Gauge: The thickness or gauge of the cord can give you a rough indication of its power rating. Typically, thicker cords can handle higher power loads without overheating. For example, cords with a lower gauge number, such as 12 or 10 gauge, are generally thicker and can handle heavier loads than cords with a higher gauge number, such as 16 or 18 gauge. However, it’s important to note that the gauge alone is not the sole determinant of the power rating, and other factors need to be considered.
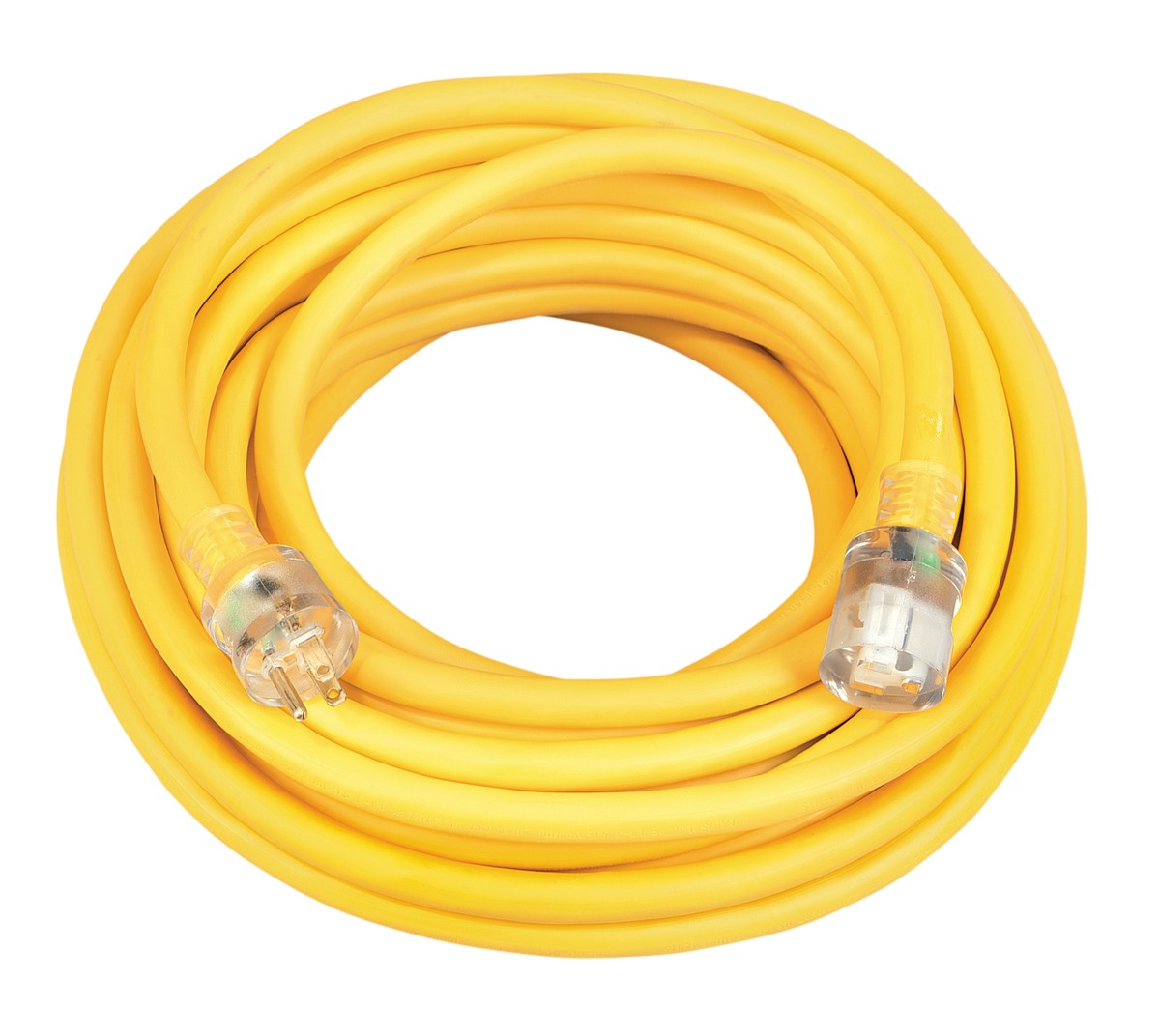
2. Color Coding: Some electrical cords have color-coded insulation, which can provide a clue about their power rating. For example, cords with yellow insulation are often used for heavy-duty applications and can handle higher power loads. However, color coding can vary between manufacturers, so it’s essential to refer to other methods for a more accurate determination.
3. Markings or Labels: Look for any markings or labels on the cord that may indicate its power rating. These markings may include information such as maximum current rating (in amperes) or voltage rating (in volts). This information can give you a better understanding of the cord’s capabilities. However, not all cords may have these markings, especially older ones, so it’s not always a reliable method.
4. Branding or Logo: In some cases, reputable brands or manufacturers may have specific characteristics or features associated with their cords that indicate higher quality and power handling capabilities. Keep an eye out for any branding or logo on the cord that may suggest a higher power rating.
While visual cues can provide some insight into the power rating of an electrical cord, they are not definitive measures. To obtain accurate information, it’s essential to refer to other methods such as reading the label or using a multimeter. These methods will give you a more precise understanding of the power rating and ensure the safe and efficient use of the electrical cord.
Look for the voltage and amperage rating printed on the electrical cord. The power can be calculated by multiplying the voltage by the amperage.
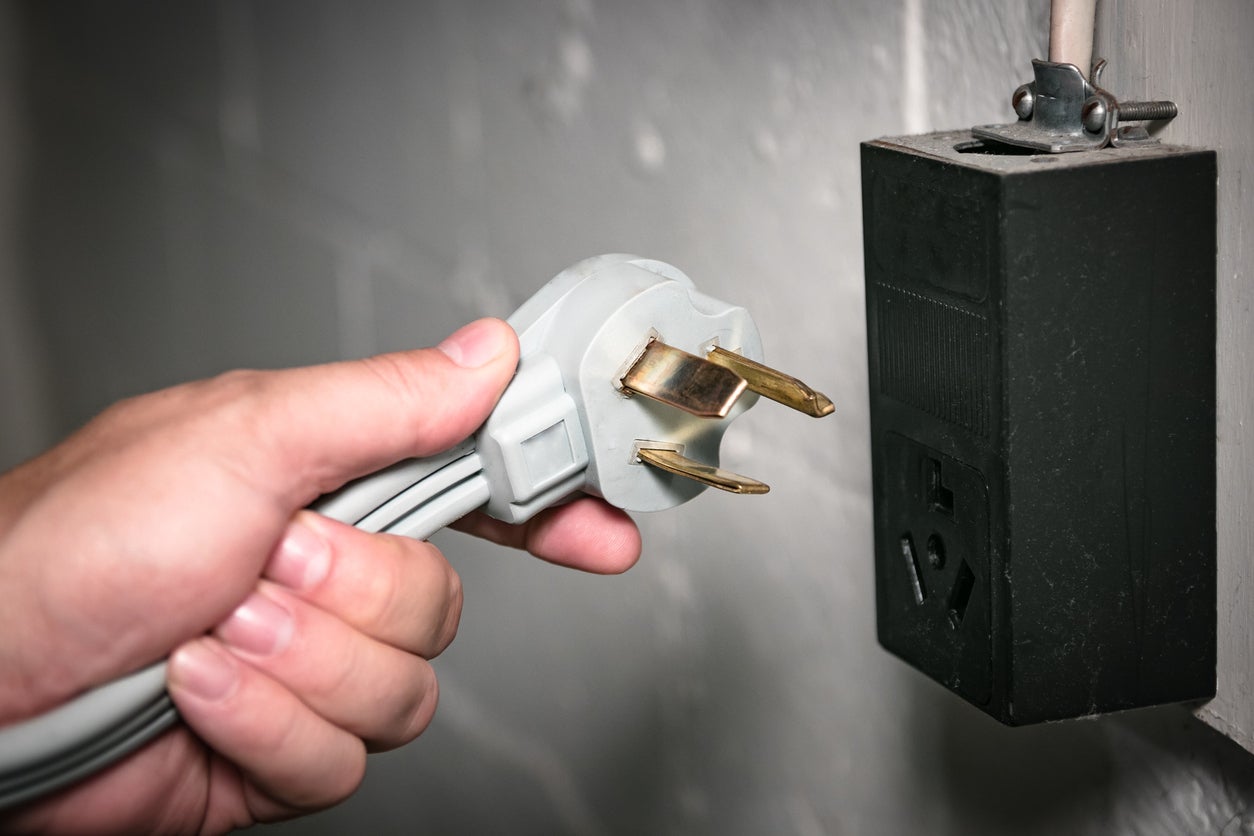
Inspecting the Plug
When determining the power rating of an electrical cord, inspecting the plug can provide valuable information. The plug is the component that connects the cord to the power source or device. Here are some steps to inspect the plug:
1. Plug Type: Start by identifying the type of plug attached to the cord. There are different plug types used in different regions or countries. For example, in North America, the most common plug type is the NEMA 5-15, which is a three-pronged plug with two flat parallel blades and a grounding pin. Understanding the plug type will help ensure compatibility with the power outlet.
2. Grounding Prong: Check if the plug has a grounding prong. Grounded cords have three prongs – two for live and neutral wires and one for the ground wire. The presence of a grounding prong indicates that the cord is designed to handle higher power loads. In contrast, non-grounded cords have only two prongs and may have a lower power rating.
3. Condition: Inspect the plug for any signs of damage or wear. Check for frayed wires, loose connections, or bent prongs. Damaged plugs may not be able to handle the same power rating as a plug in good condition. If you notice any damage, it’s advisable to replace the plug or the entire cord to ensure safety.
4. Markings: Look for any markings or labels on the plug that provide information about the cord’s power rating. Some plugs may have imprinted ampere or voltage ratings. However, not all plugs have these markings, so it’s important to use other methods for a more accurate determination.
Inspecting the plug can give you an idea of the power rating of the electrical cord, but it may not provide precise information. To obtain accurate and specific power rating details, it’s best to explore other methods such as reading the label or using a multimeter.
Next, we will discuss how to read the label on the cord, which is another reliable method to determine the power rating of an electrical cord.
Read more: How To Tell What Gauge An Extension Cord Is
Reading the Label
One of the most reliable methods for determining the power rating of an electrical cord is to read the label attached to it. Many cords, especially newer ones, come with a label that provides essential information about their power capabilities. Here’s how to read and interpret the label:
1. Maximum Ampere Rating: Look for the maximum ampere rating (sometimes denoted as “A” or “Amps”) on the label. This indicates the maximum current that the cord can safely carry without overheating. It is essential to match the power requirements of your device with the ampere rating of the cord to ensure safe and efficient usage.
2. Voltage Rating: Check for the voltage rating (typically denoted as “V” or “Volts”) on the label. This represents the maximum voltage that the cord can handle. Make sure the voltage requirements of your device align with or fall within the voltage rating of the cord to prevent electrical damage or malfunction.
3. Certification Marks: Look for any certification marks or logos on the label, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories), ETL (Intertek Group), or CSA (Canadian Standards Association). These marks indicate that the cord has undergone testing and meets specific safety standards.
4. Length: The label may also specify the length of the cord. While the length does not directly indicate the power rating, it is worth considering as longer cords may have higher resistance, leading to potential voltage drop and affecting the performance of connected devices.
If you cannot locate a label on the cord or the label has faded or become illegible, it’s best to err on the side of caution and assume that the power rating is unknown. In such cases, it’s advisable to consider other methods, such as using a multimeter, to determine the power rating accurately.
By reading the label on the electrical cord, you can obtain vital information about its power rating, current-carrying capacity, and voltage compatibility. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions when selecting and using the cord for various devices and appliances.
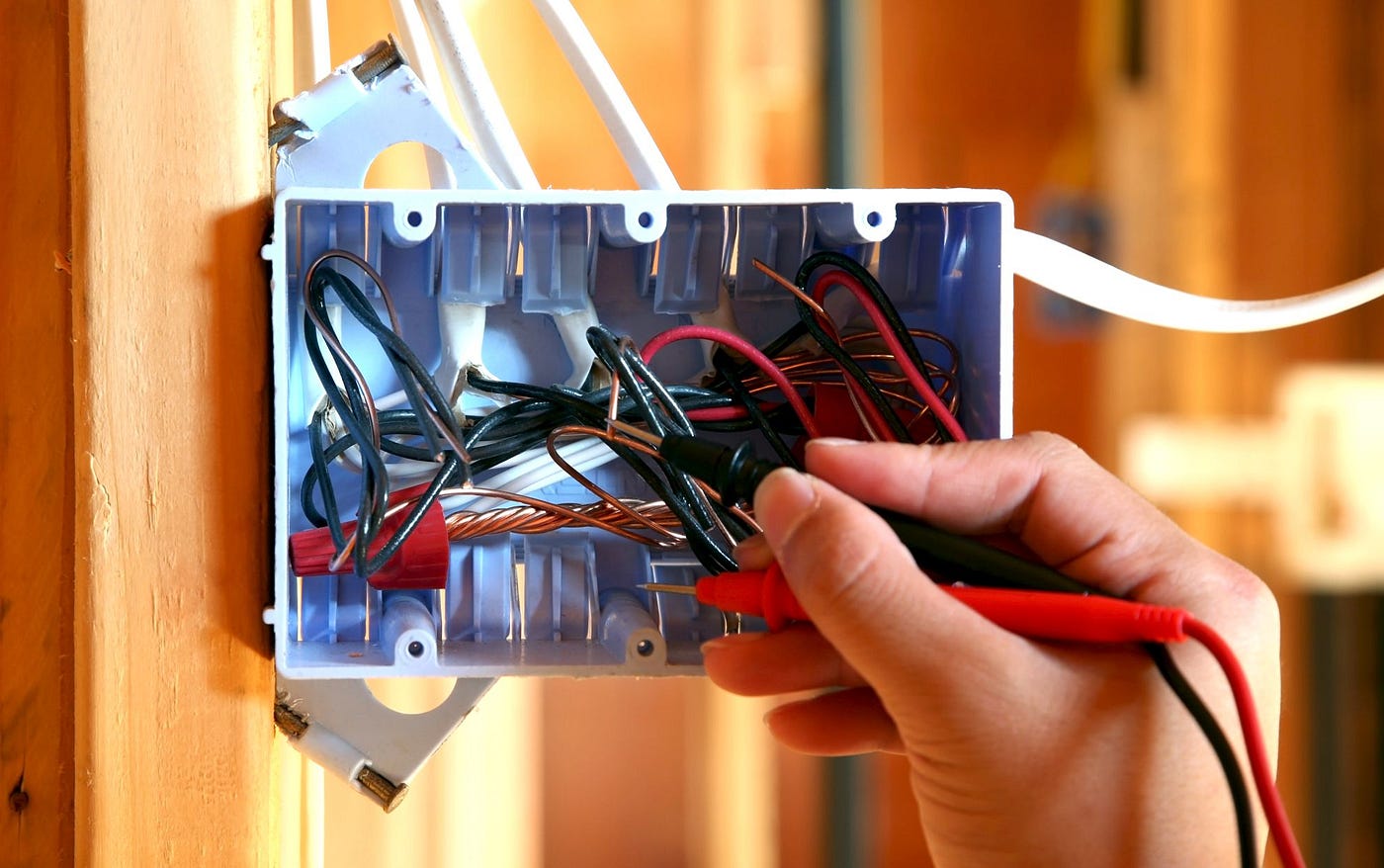
Using a Multimeter
When it comes to accurately determining the power rating of an electrical cord, using a multimeter is one of the most reliable methods. A multimeter is a versatile tool that can measure various electrical properties, including voltage, current, and resistance. Here’s how to use a multimeter to determine the power rating of an electrical cord:
1. Set the Multimeter: Begin by setting the multimeter to the appropriate mode for measuring resistance (ohms). Consult the user manual of your multimeter to locate and select the resistance mode.
2. Turn off the Power: Before proceeding, make sure the device or appliance connected to the cord is turned off and unplugged from the power source. This step ensures your safety during the measurement process.
3. Insert the Probes: Insert the probes of the multimeter into the corresponding slots of the cord’s plug. The black probe is to be inserted into the neutral/prong slot, and the red probe is to be inserted into the live/hot prong slot. Ensure a firm and secure connection between the probes and the prongs to get an accurate reading.
4. Read the Resistance: Once the probes are properly inserted, the multimeter will display the resistance value of the cord. The resistance reading will help you determine the power rating, as thicker cords with lower resistance can handle higher power loads.
5. Compare with Reference Chart: Consult a reference chart or the manufacturer’s specifications to match the resistance reading with the approximate power rating. Different cord materials and gauges have varying resistance values. By comparing the measured resistance to the reference values, you can estimate the power rating of the cord.
Using a multimeter allows for a more precise measurement of the power rating of an electrical cord. However, it is important to note that this method requires some technical knowledge and caution. If you are not familiar with using a multimeter or uncertain about the process, it is advisable to seek assistance from a professional electrician.
By utilizing a multimeter, you can accurately determine the power rating of an electrical cord and ensure its safe usage with devices and appliances.
Conclusion
Determining the power rating of an electrical cord is essential for the safe and efficient operation of devices and appliances. By understanding how to identify the power rating using visual cues, inspecting the plug, reading the label, and using a multimeter, you can make informed decisions and avoid potential hazards.
Visual cues such as the thickness or gauge of the cord, color coding, markings, and branding can provide some indication of the power rating. Inspecting the plug for the type, grounding prong, condition, and markings can also offer valuable insights. However, these visual cues may not provide precise information and should be supplemented with other methods.
Reading the label attached to the cord is a reliable way to determine the power rating. Look for the maximum ampere and voltage ratings, certification marks, and length information. These details will help you match the capability of the cord with the power requirements of your devices.
For a more precise measurement, using a multimeter can give you an accurate reading of the cord’s resistance, which is directly related to its power handling capabilities. By comparing the resistance value with a reference chart, you can estimate the power rating of the cord more accurately.
Remember, always prioritize safety when working with electrical cords. Consider consulting a professional electrician if you are unsure about any aspect of determining the power rating or if you need assistance with testing equipment.
By utilizing these methods and understanding the power rating of electrical cords, you can ensure the proper utilization of your devices, prevent damage to equipment, and promote a safe electrical environment in your home or workspace.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Tell What Is The Power On An Electrical Cord
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Tell What Is The Power On An Electrical Cord”