
Articles
What Is Heat Exchanger In HVAC
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn about heat exchangers in HVAC systems with our informative articles. Stay updated on how heat exchangers work and their importance in maintaining efficient heating and cooling in your home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, there are many components that work together to provide optimal comfort and efficiency. One such crucial component is the heat exchanger.
A heat exchanger plays a vital role in the HVAC system, enabling the transfer of heat between two fluids without mixing them. It allows for the efficient heating or cooling of air, which is then distributed throughout a residential or commercial space.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of heat exchangers in HVAC systems, their importance, types, functionality, benefits, and common maintenance issues. By gaining a better understanding of heat exchangers, you will be well-equipped to make informed decisions and ensure the smooth operation of your HVAC system.
Key Takeaways:
- Heat exchangers are vital for efficient heat transfer in HVAC systems, leading to energy conservation, improved indoor air quality, and cost savings. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Understanding the types and benefits of heat exchangers is essential for maintaining comfort and energy efficiency in residential and commercial buildings. Proper maintenance practices help prevent common issues and ensure efficient HVAC operation.
Read more: What Is A Heat Exchanger Espresso Machine
Definition of a Heat Exchanger in HVAC
A heat exchanger in HVAC is a device that facilitates the transfer of heat energy between two fluids, typically air and a refrigerant, without allowing them to mix. It is an integral component of HVAC systems, enabling the efficient heating or cooling of air before it is distributed throughout a building.
The primary purpose of a heat exchanger is to transfer thermal energy from one fluid to another, ensuring that the conditioned air is at the desired temperature. In cooling mode, the heat exchanger extracts heat from the indoor air and transfers it to the refrigerant, which is then released to the outside environment. In heating mode, the process is reversed, with the heat exchanger absorbing heat from the refrigerant and transferring it to the air.
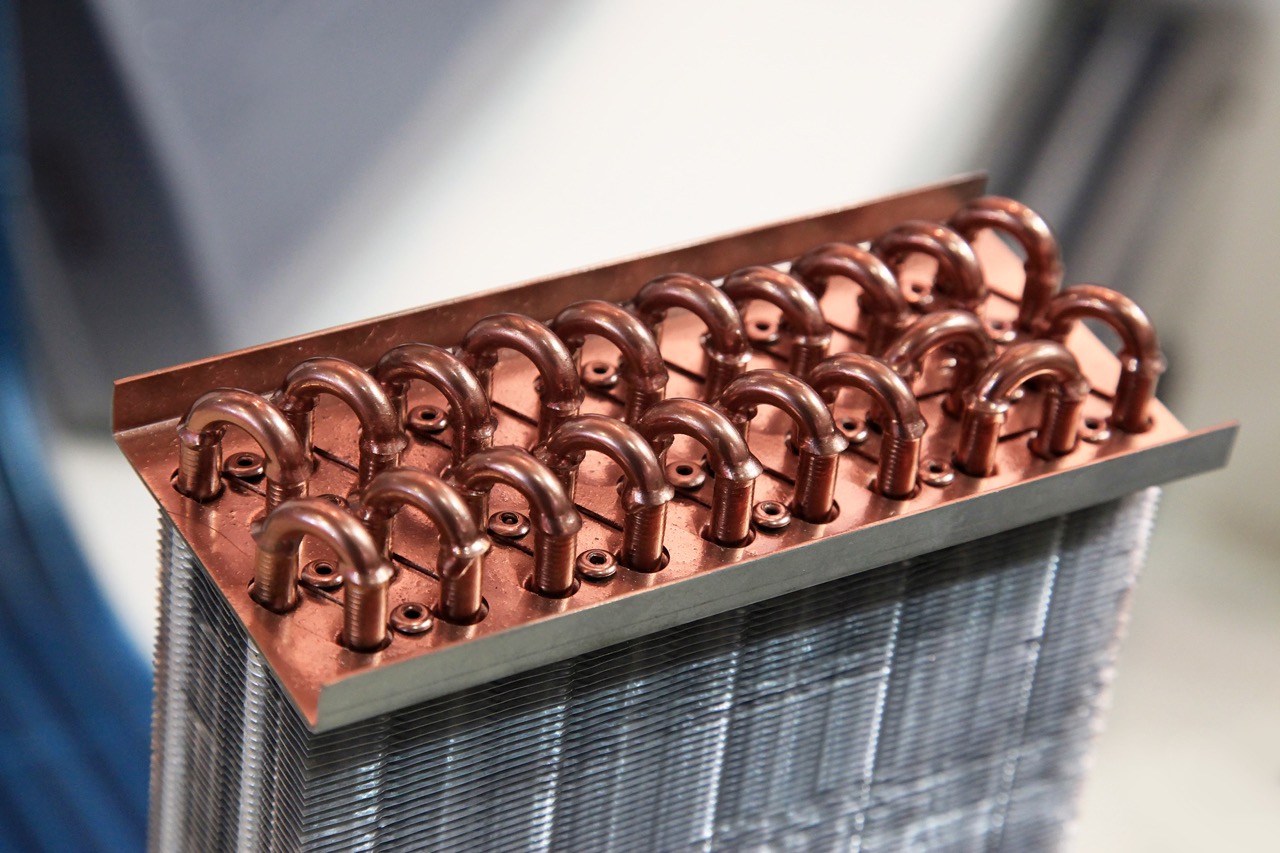
Heat exchangers typically consist of a series of metal tubes or plates that provide a large surface area for the transfer of heat. The two fluids, in separate channels, flow in opposite directions, maximizing heat transfer efficiency. The metal walls between the channels act as a barrier, allowing heat to be transferred through conduction while preventing the fluids from mixing.
There are various types of heat exchangers used in HVAC systems, including air-to-air, air-to-water, water-to-water, and plate heat exchangers. Each type has its own design and application, depending on the specific requirements of the HVAC system.
Overall, heat exchangers play a critical role in maintaining the desired temperature in HVAC systems. They ensure that heat is efficiently transferred between the air and refrigerant, resulting in optimized comfort and energy efficiency. Understanding the function and importance of heat exchangers is essential for anyone involved in the design, installation, or maintenance of HVAC systems.
Importance of Heat Exchangers in HVAC Systems
Heat exchangers are integral components of HVAC systems and play a vital role in ensuring optimal comfort and energy efficiency. Here are some key reasons why heat exchangers are important in HVAC systems:
1. Efficient Heat Transfer:
Heat exchangers enable the efficient transfer of heat between the air and the refrigerant in HVAC systems. By maximizing heat transfer rates, heat exchangers help to quickly and effectively heat or cool the air, providing a comfortable indoor environment.
2. Energy Conservation:
Heat exchangers help to conserve energy by transferring heat from one fluid to another without wasting it. In cooling mode, the heat exchanger extracts heat from the indoor air and transfers it to the refrigerant, allowing the system to cool the air more efficiently. In heating mode, the heat exchanger absorbs heat from the refrigerant and transfers it to the air, reducing energy consumption by utilizing existing heat.
Read more: What Is A Heat Pump In HVAC
3. Temperature Control:
Heat exchangers play a crucial role in maintaining the desired temperature in HVAC systems. By efficiently transferring heat, they help to achieve precise temperature control, ensuring that the indoor environment remains comfortable and suitable for occupants.
4. Improved Indoor Air Quality:
Heat exchangers also contribute to improved indoor air quality. In modern HVAC systems, heat exchangers are often equipped with air-to-air heat recovery systems. These systems recover heat from the outgoing air and use it to preheat the incoming fresh air. By doing so, heat exchangers help to remove contaminants and odors from the indoor air, resulting in cleaner and healthier indoor environments.
5. Cost Savings:
By enhancing energy efficiency and reducing the workload on the HVAC system, heat exchangers can lead to significant cost savings. More efficient heat transfer means less energy consumption, resulting in lower utility bills for building owners and occupants.
In summary, heat exchangers are crucial components of HVAC systems that enable efficient heat transfer, conserve energy, control indoor temperature, improve indoor air quality, and provide cost savings. Understanding the importance of heat exchangers helps to emphasize their role in maintaining optimal HVAC performance and comfort.
Types of Heat Exchangers Used in HVAC
Heat exchangers used in HVAC systems come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. Here are the most common types of heat exchangers used in HVAC:
Read more: What Is Emergency Heat On HVAC
1. Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers:
As the name suggests, air-to-air heat exchangers transfer heat between two streams of air. They are commonly used in ventilation systems to extract heat from the outgoing air and transfer it to the incoming fresh air, improving energy efficiency while maintaining a comfortable indoor environment.
2. Air-to-Water Heat Exchangers:
These heat exchangers transfer heat between air and water. They are commonly used in residential and commercial HVAC systems that utilize hydronic heating or cooling, where hot or cold water circulates through radiators or underfloor heating systems to regulate indoor temperature.
3. Water-to-Water Heat Exchangers:
Water-to-water heat exchangers transfer heat between two streams of water. They are widely used in HVAC systems that involve water-based heat transfer, such as geothermal systems or hydronic heating systems. These heat exchangers facilitate the transfer of heat from a heat source, such as a ground loop or boiler, to the heating or cooling distribution system.
4. Plate Heat Exchangers:
Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin metal plates stacked together with alternating channels for the two fluids. These heat exchangers provide a large surface area for heat transfer, making them highly efficient. They are commonly used in HVAC systems for applications that require high heat transfer rates and compact designs.
Read more: Swimming Pool Heat Exchanger: How It Works
5. Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers:
Shell and tube heat exchangers are widely used in HVAC systems that involve large heat transfer capacities. They consist of a shell (outer vessel) with multiple tubes inside. One fluid flows through the tubes, while the other flows outside the tubes in the shell. These heat exchangers are robust and versatile, suitable for various HVAC applications.
Each type of heat exchanger has its own advantages and suitability for specific HVAC applications. The choice of heat exchanger depends on factors such as the type of HVAC system, heating or cooling requirements, available space, and cost considerations. Consulting with an HVAC professional can help determine the most appropriate heat exchanger for a specific application.
How Heat Exchangers Work in HVAC Systems
Heat exchangers play a crucial role in the operation of HVAC systems by facilitating the transfer of heat between two fluids. Understanding how heat exchangers work is essential to grasp the overall functioning of an HVAC system. Here’s a breakdown of how heat exchangers work in HVAC systems:
1. Heat Transfer:
The primary function of a heat exchanger is to transfer thermal energy from one fluid to another. In HVAC systems, heat exchangers transfer heat between the air and a refrigerant, or between two streams of air. This transfer of heat is essential to heat or cool the air before it is distributed throughout a building.
2. Fluid Separation:
Heat exchangers ensure that the two fluids being exchanged, such as air and refrigerant, do not mix. They consist of separate channels or passages for each fluid, with metal walls acting as a barrier between them. This separation prevents cross-contamination and ensures that the two fluids remain distinct throughout the heat transfer process.
Read more: Why Is My HVAC Not Heating
3. Surface Area for Heat Transfer:
Heat exchangers are designed to maximize the surface area available for heat transfer. This is achieved through the use of multiple tubes, plates, or fins within the heat exchanger. The increased surface area allows for more efficient heat transfer between the two fluids, resulting in effective heating or cooling of the air.
4. Fluid Flow and Direction:
Heat exchangers control the flow and direction of the fluids being exchanged to optimize heat transfer. The fluids typically flow in opposite directions within the heat exchanger, known as counterflow or crossflow. This arrangement ensures efficient heat transfer by maximizing the temperature difference between the two fluids.
5. Conduction of Heat:
Heat transfer within a heat exchanger occurs through conduction. The thermal energy of the hotter fluid is conducted through the metal walls of the heat exchanger and transferred to the cooler fluid. The metal walls act as a conductor, allowing the heat to transfer across the barrier between the two fluids.
By efficiently transferring heat between the air and refrigerant or between two streams of air, heat exchangers help to condition the air before it is distributed throughout a building. This process ensures that the air reaches the desired temperature, providing comfort to occupants and optimizing energy efficiency.
It’s important to note that heat exchangers require proper maintenance to ensure their continued operation and performance. Regular cleaning and inspections can help prevent issues such as fouling or leakage, which can impair heat transfer and affect the overall efficiency of the HVAC system.
Benefits of Using Heat Exchangers in HVAC Systems
Heat exchangers are essential components of HVAC systems, providing several benefits that contribute to comfort, energy efficiency, and cost savings. Here are some key benefits of using heat exchangers in HVAC systems:
1. Energy Efficiency:
One of the primary benefits of heat exchangers is their ability to improve energy efficiency in HVAC systems. By transferring heat between fluids, heat exchangers help to optimize the heating or cooling process. This reduces the workload on the HVAC system, resulting in lower energy consumption and decreased utility bills.
2. Improved Indoor Comfort:
Heat exchangers play a vital role in maintaining optimal indoor comfort. By efficiently heating or cooling the air before it is distributed throughout a building, heat exchangers ensure a pleasant and consistent indoor temperature. This leads to increased occupant satisfaction and productivity.
3. Enhanced Air Quality:
Many modern HVAC systems use heat exchangers equipped with air-to-air heat recovery systems. These systems recover heat from the outgoing air and use it to preheat the fresh air entering the building. This process not only improves energy efficiency but also aids in removing contaminants and pollutants from the air, resulting in improved indoor air quality.
4. Cost Savings:
Using heat exchangers in HVAC systems can lead to significant cost savings. By improving energy efficiency, heat exchangers reduce the amount of energy required to heat or cool the air. This translates into lower energy bills, allowing building owners to save money in the long run.
Read more: What Is Central Heating
5. Environmentally Friendly:
Heat exchangers promote sustainability and environmental friendliness. By reducing energy consumption, they contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions and help combat climate change. Additionally, heat exchangers that incorporate air-to-air heat recovery systems minimize the need for mechanical ventilation, thereby conserving energy and reducing the overall environmental impact.
6. Versatility and Compatibility:
Heat exchangers come in various types and designs, allowing them to be versatile and compatible with different HVAC applications. Whether it’s air-to-air, air-to-water, or water-to-water heat transfer, there is a heat exchanger suitable for the specific requirements of each HVAC system.
Overall, the benefits of using heat exchangers in HVAC systems are numerous. From energy efficiency and improved indoor comfort to cost savings and environmental friendliness, integrating heat exchangers into HVAC systems is a smart choice for both residential and commercial buildings.
Common Issues and Maintenance of Heat Exchangers in HVAC
Heat exchangers are crucial components of HVAC systems, and proper maintenance is essential to ensure their efficient operation. Here are some common issues that can arise with heat exchangers in HVAC systems and important maintenance practices:
1. Fouling and Build-up:
Over time, heat exchangers can accumulate dirt, dust, debris, and other contaminants, resulting in fouling or build-up. This can hinder heat transfer efficiency and reduce the overall performance of the HVAC system. Regular cleaning of the heat exchanger’s surfaces and fins is necessary to remove any accumulated debris.
Read more: What Is Heat Insulation
2. Corrosion:
Corrosion is a common issue with heat exchangers, especially those exposed to moisture or certain chemicals. Corrosion can weaken the heat exchanger, leading to leaks and reduced heat transfer efficiency. Implementing corrosion-resistant materials for the construction of heat exchangers and conducting periodic inspections can help prevent and address corrosion issues.
3. Leakage:
Leaks in heat exchangers can result from corrosion, excessive pressure, or mechanical damage. Leaks can significantly impact heat transfer and compromise the overall performance of the HVAC system. Regular inspections should be carried out to identify and address any leaks promptly.
4. Blocked or Restricted Airflow:
Blockages or restrictions in the airflow through the heat exchanger can occur due to debris, dirt, or improper installation. This can impede heat transfer and reduce the system’s efficiency. Regular visual inspections and cleaning of air filters and the heat exchanger can help prevent or address these issues.
5. Insufficient Airflow:
Inadequate airflow through the heat exchanger can affect heat transfer and compromise the HVAC system’s performance. This can be caused by issues such as a faulty blower motor or clogged ductwork. Regular inspection and maintenance of the HVAC system’s components, including the blower motor and ductwork, are necessary to ensure proper airflow.
Read more: What Is A Heat Lamp
6. Lack of Maintenance:
Failure to perform regular maintenance on heat exchangers can lead to various issues. Routine inspections, cleaning, and maintenance tasks, such as replacing air filters, lubricating parts, and checking for signs of wear and tear, are crucial to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the heat exchanger.
To maintain heat exchangers in HVAC systems, it is recommended to follow manufacturer guidelines and consult with HVAC professionals for regular inspections and maintenance. Regular cleaning, monitoring for signs of issues such as leaks or corrosion, and addressing these problems promptly can help ensure the efficient operation of heat exchangers and prolong their lifespan.
Conclusion
Heat exchangers are essential components of HVAC systems, enabling the efficient transfer of heat between fluids to heat or cool the air before it is distributed throughout a building. Understanding the definition, importance, types, operation, benefits, and maintenance of heat exchangers is crucial for a well-functioning HVAC system.
Heat exchangers contribute to energy efficiency by optimizing heat transfer and reducing the workload on the HVAC system. They enhance indoor comfort by ensuring precise temperature control and improved indoor air quality through heat recovery systems. Additionally, heat exchangers offer cost savings, promote environmental sustainability, and provide compatibility and versatility for various HVAC applications.
However, it is essential to address common issues and perform regular maintenance to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of heat exchangers. Regular cleaning, inspecting for corrosion or leaks, checking for blockages or inadequate airflow, and following manufacturer guidelines are crucial maintenance practices for heat exchangers.
In conclusion, heat exchangers are integral components in HVAC systems that play a vital role in maintaining comfort and energy efficiency. They provide benefits such as energy savings, improved indoor comfort, enhanced air quality, cost savings, environmental friendliness, and versatility. Proper maintenance helps prevent common issues and ensures the efficient operation of heat exchangers, contributing to the overall performance of HVAC systems.
By understanding the importance and functioning of heat exchangers and implementing regular maintenance, you can ensure a properly functioning HVAC system that provides optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and cost savings for residential and commercial buildings.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Heat Exchanger In HVAC
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.








0 thoughts on “What Is Heat Exchanger In HVAC”