Home>Articles>What Is The Difference Between Garden Soil And Potting Soil


Articles
What Is The Difference Between Garden Soil And Potting Soil
Modified: March 24, 2024
Discover the key distinctions between garden soil and potting soil for your gardening needs. Enhance your gardening success with expert advice on choosing the right soil for your plants.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Gardening is a rewarding and fulfilling hobby that allows individuals to connect with nature, beautify their surroundings, and even grow their own food. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, it’s important to understand the difference between garden soil and potting soil. These two types of soil have unique compositions and characteristics that can greatly impact the success of your plants.
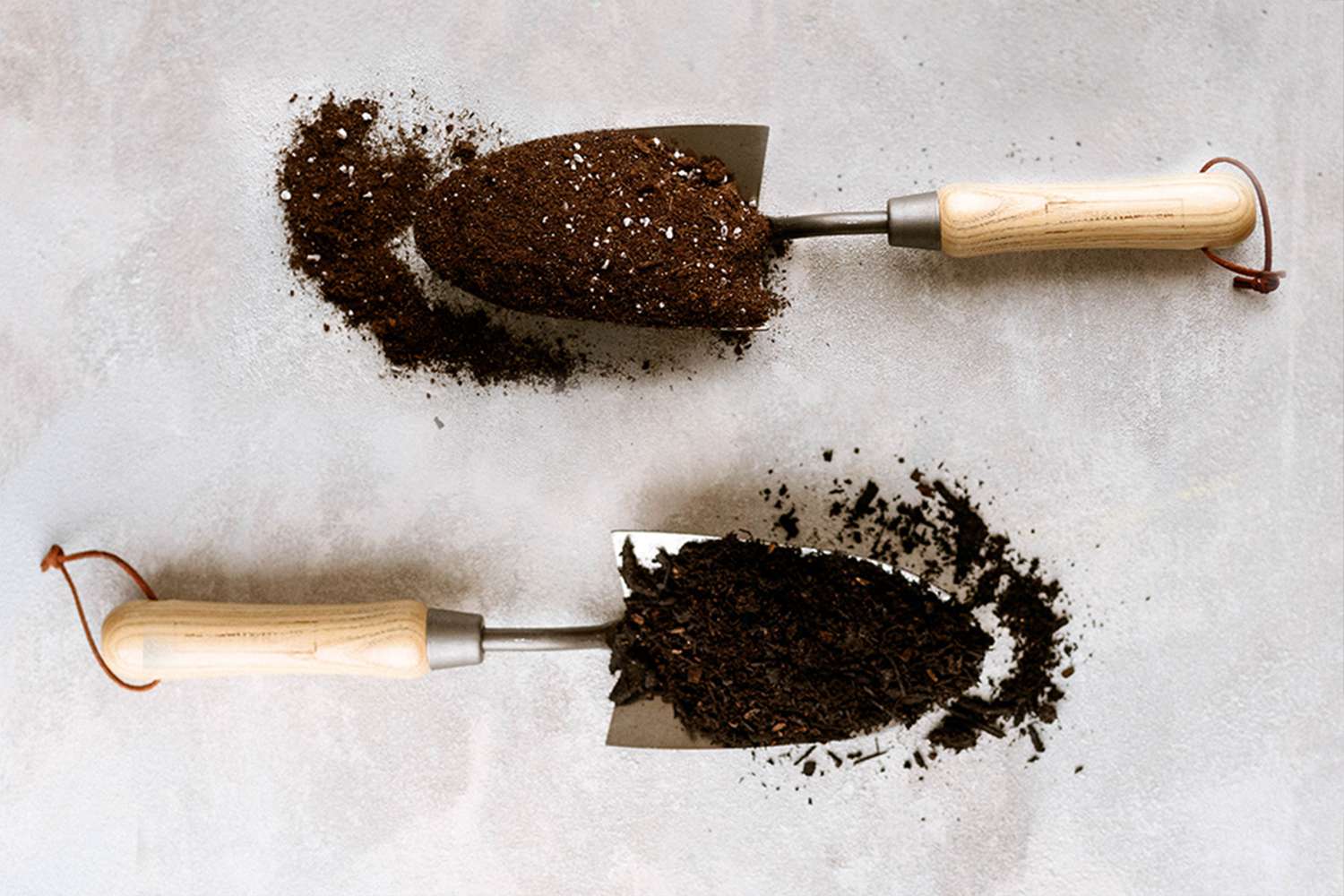
Garden soil, also known as topsoil or native soil, refers to the soil that naturally exists in your outdoor garden beds. It is a mixture of mineral particles, organic matter, water, and air. On the other hand, potting soil, also called potting mix or container soil, is specifically formulated to meet the unique needs of potted plants. It is typically a blend of organic matter, such as peat moss or coconut coir, and various additives to provide optimal growing conditions.
The key differences between garden soil and potting soil lie in their composition, nutrient content, drainage, pH level, sterilization, and usage. By understanding these distinctions, you can make informed decisions about which type of soil is best suited for your gardening needs. Let’s explore these differences in more detail.
Key Takeaways:
- Choose garden soil for outdoor beds and potting soil for containers. Each type has unique compositions and uses, providing optimal conditions for different gardening scenarios and plant types.
- Garden soil offers a natural foundation, while potting soil provides controlled conditions for potted plants. Understanding their differences is key to successful gardening in various settings.
Read more: How To Store Potting Soil
Composition
When it comes to composition, garden soil and potting soil differ in terms of their ingredients and physical structure.<
Garden soil is often a mix of mineral particles, such as sand, silt, and clay, along with organic matter such as decomposed plants and animal material. It is typically heavier in texture and may contain rocks, roots, and other debris. This natural soil composition provides a solid foundation for outdoor plants to establish their root systems and thrive.
Potting soil, on the other hand, is designed to be lightweight and well-draining, allowing excess water to escape easily. It is typically a blend of organic materials like peat moss, coconut coir, compost, and perlite or vermiculite. The organic matter helps retain moisture and nutrients while promoting healthy root growth, while the added perlite or vermiculite improves aeration and drainage.
Additionally, potting soil often contains fertilizer or slow-release nutrients to provide plants with the necessary nourishment for their growth. These ingredients are carefully balanced to ensure plants have access to the right amount of nutrients over time.
In summary, garden soil has a more varied and dense composition, while potting soil is specifically engineered to be lightweight, well-draining, and nutrient-rich.
Nutrient Content
The nutrient content in garden soil and potting soil can vary significantly. This is primarily due to the fact that garden soil relies on natural nutrient cycles, while potting soil is often supplemented with fertilizers and organic matter to ensure optimal plant growth.
Garden soil typically contains a diverse range of nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and trace minerals. These nutrients are derived from the decomposition of organic matter, such as leaves, plant debris, and animal waste, as well as from mineral sources in the soil. However, the nutrient content of garden soil can vary depending on factors such as the soil’s location, previous plant growth, and overall soil fertility.
On the other hand, potting soil is specifically designed to provide plants with the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. It often contains added fertilizers, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, known as NPK fertilizers, in balanced ratios. These nutrients are readily available to plants and help support their development. In addition to the NPK fertilizers, potting soil may also include micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc, which are essential for overall plant health.
It’s worth noting that while potting soil may have a higher nutrient content initially, these nutrients can deplete over time as plants absorb them. Therefore, it’s important to regularly fertilize potted plants to replenish these nutrients and ensure continued healthy growth.
In summary, garden soil relies on natural nutrient reserves in the soil, while potting soil is specifically formulated with added fertilizers to provide plants with essential nutrients.
Drainage and Water Retention
One of the key differences between garden soil and potting soil is their drainage and water retention capabilities. The ability of soil to effectively drain excess water while retaining enough moisture for plant roots is crucial for the health of plants.
Garden soil, being part of the natural landscape, varies in its drainage properties. Some garden soils may have excellent drainage, especially if they have sandy or loamy textures, allowing water to flow freely and preventing waterlogging. However, other garden soils, such as those with high clay content, may have poor drainage, leading to water accumulation and potentially causing root rot or other problems for plants.
Potting soil, on the other hand, is specifically formulated to have optimal drainage and water retention properties. It typically contains materials such as perlite, vermiculite, or pumice, which help improve aeration and drainage. These materials create air pockets in the soil mixture and allow excess water to drain freely from the plant’s root zone. At the same time, potting soil also includes organic matter like peat moss or coconut coir, which help retain moisture for plants to access during dry periods.
The combination of good drainage and water retention in potting soil ensures that plants in containers receive adequate moisture without becoming waterlogged. This is particularly important as overwatering can lead to root rot and inhibit plant growth.
In summary, while garden soil can vary in its drainage abilities, potting soil is specifically formulated to have excellent drainage and water retention properties, providing the ideal environment for potted plants.
Garden soil is meant for outdoor use and may contain pests or diseases, while potting soil is sterilized and designed for container plants. Always use the appropriate soil for your gardening needs.
pH Level
The pH level of soil refers to its acidity or alkalinity and plays a crucial role in the availability of nutrients to plants. Different types of plants have varying pH requirements, and understanding the pH level of soil is essential for ensuring optimal plant growth.
Garden soil can have a wide range of pH levels, as it is influenced by various factors such as the parent material, organic matter content, and environmental conditions. Typically, garden soil has a neutral to slightly acidic pH level, ranging from 6 to 7.5. However, some regions may have naturally acidic or alkaline soil, which may require amendments to adjust the pH for specific plant needs.
Potting soil, on the other hand, can be adjusted to meet the specific pH requirements of different plants. This is achieved by incorporating pH-adjusting materials during the manufacturing process. For example, adding lime can help raise the pH if the soil is too acidic, while adding sulfur can lower the pH if the soil is too alkaline. This flexibility allows gardeners to create the ideal pH conditions for their potted plants.
It’s important to note that certain plants have specific pH preferences. For example, acid-loving plants like blueberries prefer acidic soil conditions, while some vegetables and flowers thrive in slightly alkaline soil. By understanding the pH requirements of your plants, you can choose the appropriate type of soil to provide the optimal pH environment for their growth.
In summary, while garden soil can have varying pH levels, potting soil offers the advantage of being customizable to meet the specific pH requirements of different plants, providing an ideal growing medium for a diverse range of species.
Sterilization
Sterilization of soil refers to the process of eliminating harmful pathogens, insects, weed seeds, and other organisms that can pose risks to plant health. While garden soil is typically not sterilized, potting soil often undergoes sterilization to ensure a clean and disease-free environment for potted plants.
Garden soil is considered to contain a wide range of microorganisms, some beneficial and some potentially harmful. These microorganisms contribute to the natural ecosystem of the garden and play a role in nutrient cycling and soil health. While some gardeners may choose to sterilize garden soil prior to planting, it is generally not a common practice since it can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms and beneficial soil life.
On the other hand, potting soil is commonly sterilized to prevent the introduction and spread of diseases, pests, and weed seeds in potted plants. Sterilization processes can include heat treatment, such as pasteurization or steam sterilization, or chemical treatment using fungicides or other methods. These sterilization techniques help eliminate pathogens, weed seeds, and harmful insects that may be present in the organic materials used in potting soil. By sterilizing the potting soil, gardeners can reduce the risk of plant diseases and ensure a healthier growing environment for their potted plants.
However, it’s important to note that sterilization may also kill beneficial soil microorganisms, reducing the natural fertility and health of the soil. Therefore, some potting soil manufacturers may incorporate beneficial microbes back into the sterilized soil to promote a healthy soil ecosystem.
In summary, while garden soil is generally not sterilized due to its natural microbiome, potting soil undergoes sterilization to eliminate harmful pathogens, insect pests, and weed seeds, ensuring a clean and disease-free growing medium for potted plants.
Uses
Garden soil and potting soil serve different purposes and are used in different gardening scenarios. Understanding their specific uses is important for achieving optimal plant growth and overall garden success.
Garden soil is primarily used for outdoor gardening in traditional garden beds, raised beds, or when amending existing soil. It provides a solid foundation for plants to establish their root systems and grow in the natural ground. Garden soil is well-suited for growing a variety of plants, including vegetables, fruits, flowers, and shrubs. It contains the necessary nutrients and organic matter to support plant growth, and its composition can be improved by incorporating amendments such as compost or organic fertilizers. Gardeners often rely on garden soil for larger-scale gardening projects and long-term plantings.
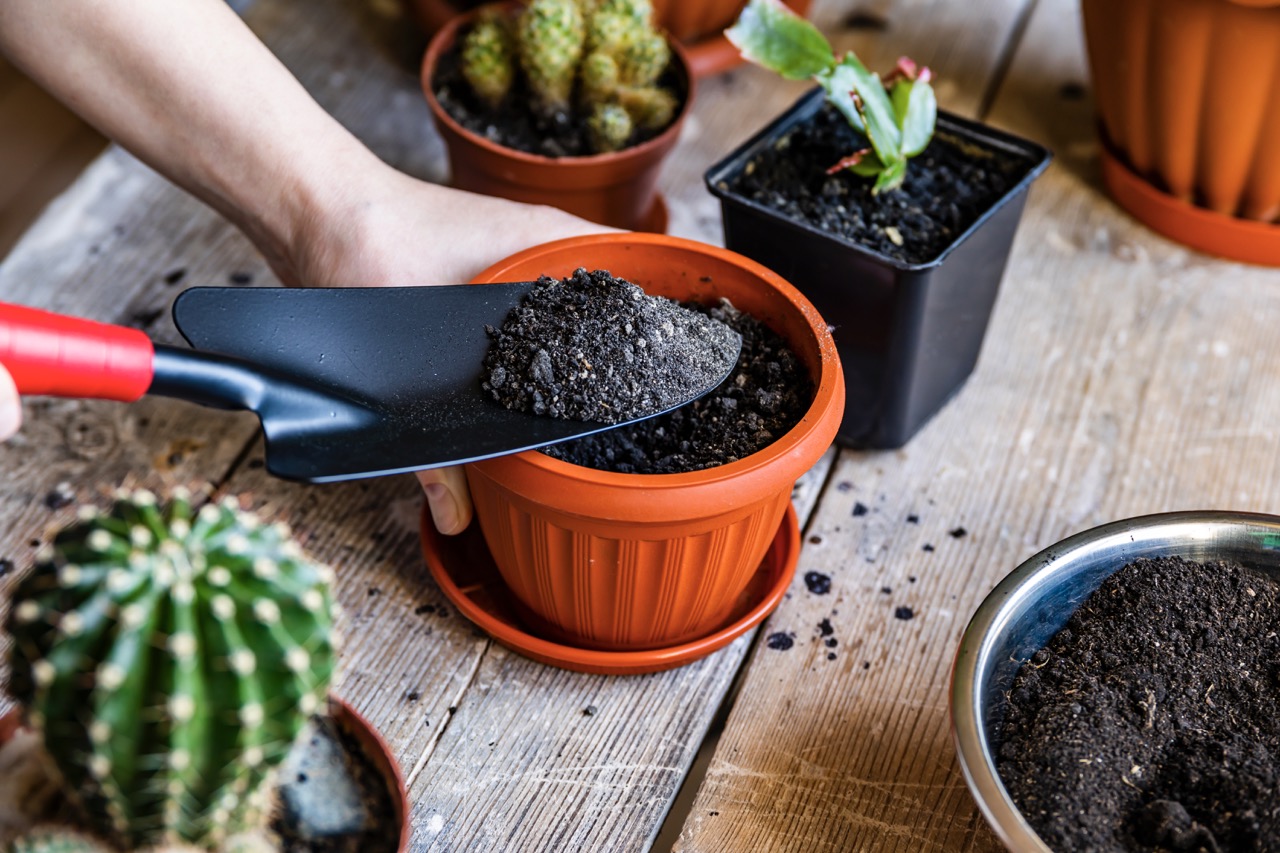
Potting soil, on the other hand, is specifically formulated for container gardening. It is lightweight, well-draining, and promotes healthy root growth in confined spaces. Potting soil is used in various containers such as pots, window boxes, hanging baskets, and planters. It provides the necessary nutrients, proper drainage, and moisture retention for potted plants. Potting soil is ideal for indoor plants, patio gardening, balcony gardening, and any situation where plants are grown in containers. Its versatility and customizable nature make it a popular choice for gardeners who want to have more control over the specific growing conditions of their potted plants.
It’s important to note that while garden soil is not recommended for use in containers due to its heavier composition and potential for poor drainage, potting soil can be used in garden beds as well. In some cases, gardeners may choose to incorporate potting soil into their garden beds to improve the soil structure and enhance drainage, particularly for areas with heavy clay soil.
In summary, garden soil is primarily used for outdoor gardening in traditional garden beds, while potting soil is specifically formulated for container gardening. Each serves its own unique purpose and provides optimal conditions for different gardening scenarios and plant types.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between garden soil and potting soil is essential for successful gardening. While both types of soil have their own unique characteristics, compositions, and uses, they play distinct roles in different gardening scenarios.
Garden soil, also known as topsoil or native soil, is the natural soil found in outdoor garden beds. It is typically a mixture of mineral particles, organic matter, water, and air. Garden soil provides a solid foundation for plants to establish their root systems and grow in the ground. It is well-suited for outdoor gardening and can be supplemented with organic amendments to improve its fertility and nutrient content.
Potting soil, also referred to as potting mix or container soil, is specifically formulated for potted plants. It is typically a blend of organic matter, such as peat moss or coconut coir, along with additives to provide optimal growing conditions. Potting soil is lightweight, well-draining, and enriched with nutrients to support healthy root growth in containers. It offers more control over the growing environment and is used for indoor plants, patio gardening, balcony gardening, and other situations where plants are grown in containers.
While garden soil and potting soil differ in composition, nutrient content, drainage, pH level, sterilization, and usage, both play important roles in gardening. Garden soil provides the foundation for outdoor plantings, while potting soil creates the ideal conditions for potted plants to thrive.
Understanding the characteristics of each soil type allows gardeners to select the appropriate soil for specific gardening needs. It is important to consider factors such as the type of plants being grown, the desired moisture retention and drainage, and the pH requirements of the plants.
By choosing the right soil for the right purpose, gardeners can create healthy and productive gardens, whether they are planting in the ground or in containers. So whether you’re tending to a beautiful backyard garden or nurturing a collection of vibrant potted plants, understanding the differences between garden soil and potting soil is key to achieving gardening success.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Difference Between Garden Soil And Potting Soil
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is The Difference Between Garden Soil And Potting Soil”