

Articles
What Size Conduit For A 4-Gauge Wire
Modified: February 23, 2024
Discover the right size conduit for #4 wire with our informative articles. Get expert advice and guidance for your electrical installations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to electrical installations, it is crucial to ensure that everything is properly sized and fitted to comply with safety regulations and maintain optimum performance. One such aspect is choosing the correct conduit size for the wires you are using.
A conduit is a protective sleeve that houses electrical wires, providing insulation and reducing the risk of damage from external factors. It is essential to select the appropriate conduit size to accommodate the wire gauge and prevent any potential hazards.
In this article, we will delve into the topic of conduit sizing specifically for #4 wire, exploring the factors to consider, the importance of proper sizing, and the relevant specifications outlined in the National Electrical Code (NEC).
By understanding the intricacies of conduit sizing, you can ensure a safe and efficient electrical installation, whether it’s for residential, commercial, or industrial purposes.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper conduit sizing for #4 wire is crucial for safety, efficient installation, and optimal performance. Consider wire gauge, insulation, ambient temperature, and future expansion to ensure compliance with NEC guidelines.
- Consult NEC and local codes to determine the correct conduit size for #4 wire. Consider factors like wire gauge, insulation, and ambient temperature for safe and efficient electrical installations.
Read more: What Size Conduit For 4 6-Gauge Wires
Understanding Conduit Sizes
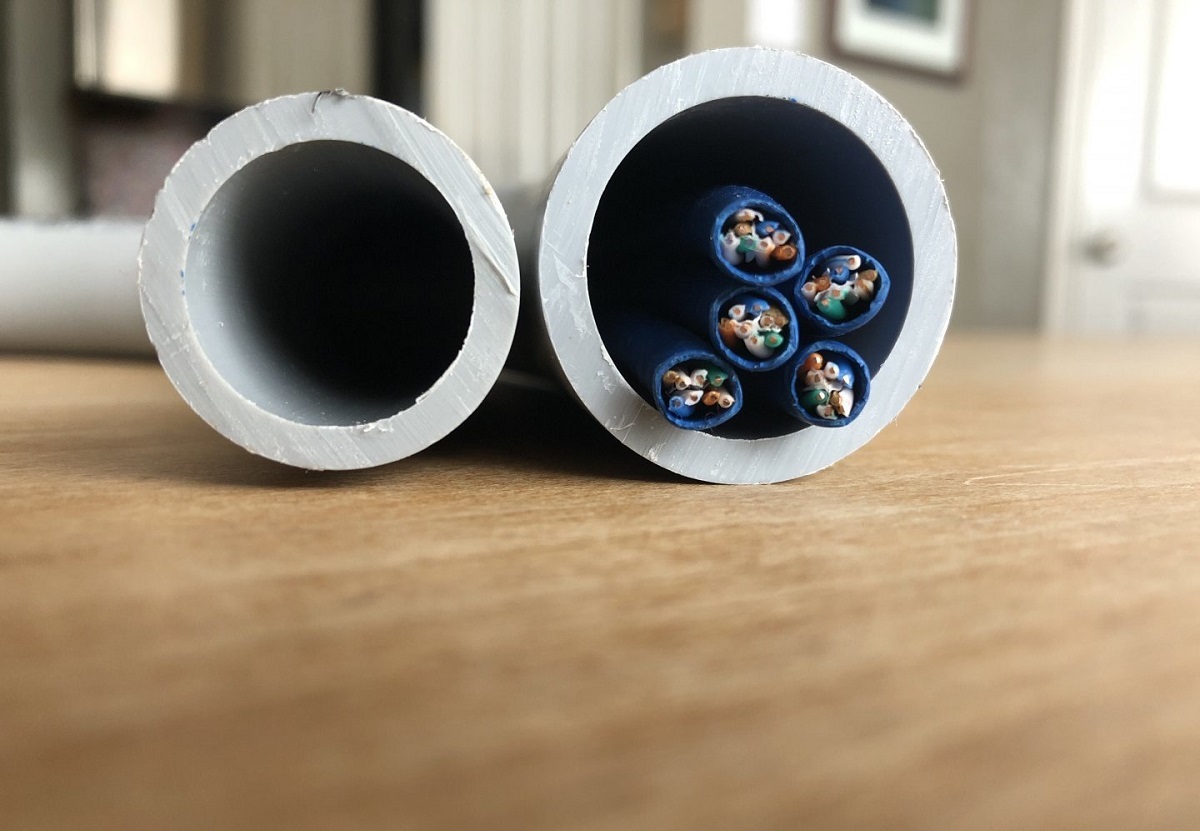
Conduit sizes are essential to accommodate the wires and cables that are being installed. They are measured by their inside diameter (ID) and are typically indicated in inches or millimeters. The size of the conduit determines the maximum number and size of wires that can fit inside it.
Conduit sizes range from 1/2 inch to 6 inches or even larger, depending on the specific application. It is important to note that the conduit size should always be larger than the size of the wires it will contain. This ensures that the wires can be easily pulled through the conduit during the installation process.
Conduit sizing can be a bit complicated as it involves specific calculations based on factors like the number and size of wires, the type of insulation, and the ambient temperature. It is crucial to consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local building codes to determine the appropriate conduit size for your specific installation.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the type of conduit being used. There are various types available, including PVC (polyvinyl chloride) conduit, rigid conduit, flexible conduit, and EMT (electrical metallic tubing). Each type has its own set of sizing requirements, so it is crucial to choose the right conduit type for your application.
Now that we have a basic understanding of conduit sizes, let’s explore the importance of selecting the proper conduit size for your #4 wire installation.
Importance of Proper Conduit Sizing
Proper conduit sizing is critical for a variety of reasons. Firstly, it ensures the safety of the electrical installation. Choosing a conduit that is too small for the wires can lead to overheating, insulation damage, and potentially dangerous electrical failures. On the other hand, selecting a conduit that is too large can lead to issues with wire alignment, which can compromise the performance and longevity of the electrical system.
Additionally, proper conduit sizing allows for easier installation and maintenance. When the conduit is sized correctly, it provides enough space for the wires to be easily pulled through during installation. This not only saves time and effort but also minimizes the risk of damaging the wires or the conduit itself. It also allows for future maintenance and upgrades, as there is enough room for additional wires to be added if necessary.
Choosing the right conduit size also aids in efficient cable management. By providing adequate space for the wires, you can neatly arrange and organize them within the conduit. This helps to minimize tangling, reduce the risk of interference between wires, and facilitate troubleshooting and repairs when needed.
Another factor to consider is the impact of conduit size on electrical performance. Using an appropriately sized conduit ensures that the wires have the necessary airflow for proper heat dissipation. This is especially important for larger wire gauges like #4, as they can generate more heat. Without adequate ventilation, the wires can overheat, leading to reduced conductivity and increased resistance, which can ultimately affect the overall efficiency and reliability of the electrical system.
Ultimately, proper conduit sizing is essential for the safety, ease of installation, maintenance, cable management, and overall performance of the electrical system. It ensures compliance with electrical codes and regulations, prevents potential hazards, and provides a reliable and efficient electrical infrastructure.
Factors to Consider
There are several factors that need to be taken into consideration when determining the appropriate conduit size for #4 wire. These factors include:
- Wire Gauge: The size of the wire is a crucial determining factor. Wire sizes are measured in gauge, with smaller numbers indicating thicker wires. For #4 wire, a larger conduit size is typically required.
- Number of Conductors: The number of conductors being installed in the conduit will affect the conduit size requirement. More conductors will require a larger conduit to provide enough space for easy installation and maintenance.
- Wire Insulation: The type of insulation used on the wires can impact the conduit size. Insulation can add thickness to the wire, requiring a larger conduit size to accommodate it.
- Ambient Temperature: The temperature of the environment where the conduit and wires are installed should be considered. Higher temperatures can affect the performance and durability of the wires, requiring additional space for heat dissipation.
- Bend Radius: The bend radius, or the minimum radius at which a wire can be safely bent, is another factor to consider. Wires need to maintain their integrity and avoid damage during installation, so the conduit must be large enough to accommodate the necessary bends.
- Future Expansion: It is important to consider any potential future expansions or additions to the electrical system. Leaving room for additional wires can help prevent the need for extensive rework in the future.
It is important to consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local building codes to ensure compliance with specific regulations and requirements for conduit sizing. These codes provide guidelines and formulas for calculating the appropriate conduit size based on the aforementioned factors.
By carefully considering these factors, you can determine the correct conduit size for your #4 wire installation, ensuring safety, functionality, and adherence to electrical standards and regulations.
When choosing the size of conduit for #4 wire, it is recommended to use a 1-inch conduit to allow for easy installation and future maintenance. This size will provide enough space for the wire and ensure proper protection.
National Electrical Code (NEC) Specifications
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is a set of standards and guidelines established by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) to ensure the safe installation of electrical systems. These specifications play a crucial role in determining the appropriate conduit size for various wire gauges, including #4 wire.
The NEC provides specific requirements for conduit sizing based on factors such as wire gauge, insulation type, and number of conductors. It also considers the ambient temperature, voltage drop limitations, and the specific application of the electrical system.
It is important to consult the NEC for the specific requirements and calculations necessary for conduit sizing. However, as a general guideline, the NEC recommends the following conduit fill percentages for different types of conduit:
- Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): Up to 40% conduit fill
- PVC Conduit: Up to 53% conduit fill for schedule 40 and up to 40% conduit fill for schedule 80
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): Up to 40% conduit fill
- Flexible Conduit: Depending on the specific type, the conduit fill percentage may vary. It is important to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for flexible conduit sizing.
Keep in mind that these percentages are the maximum fill capacity allowed by the NEC. It is always recommended to aim for a lower fill percentage to allow for ease of installation, cable management, and future expansions.
Furthermore, the NEC provides calculations and tables to determine the conduit size required for specific wire sizes and configurations. These calculations take into account factors such as wire gauge, insulation thickness, and the number of conductors within the conduit.
It is crucial to consult the most current edition of the NEC and comply with the specific requirements and calculations outlined within it. This ensures the proper sizing and safe installation of conduits for #4 wire and other wire gauges, promoting electrical system integrity and compliance with electrical standards.
Read more: What Size Conduit For 2-2-2-4 Wire
Conduit Size Recommendations for #4 Wire
When it comes to choosing the appropriate conduit size for #4 wire, several factors need to be considered, including the type of conduit, the number of conductors, and the specific application. However, as a general guideline, here are some conduit size recommendations for #4 wire:
- Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): For a single #4 wire, a 3/4-inch RMC may be sufficient. However, if multiple #4 wires are being installed, a larger conduit size, such as 1 inch or 1 1/4 inch, may be necessary to accommodate the additional conductors and provide adequate space for installation and maintenance.
- PVC Conduit: For a single #4 wire, a 1-inch PVC conduit is typically recommended. If multiple #4 wires are being installed, a larger conduit size, such as 1 1/4 inch or 1 1/2 inch, may be required to ensure proper spacing, ease of installation, and future expansion possibilities.
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): For a single #4 wire, a 1-inch EMT conduit is commonly used. If multiple #4 wires are being installed, a larger conduit size, such as 1 1/4 inch or 1 1/2 inch, may be necessary to provide sufficient space for the additional conductors.
- Flexible Conduit: The recommended conduit size for #4 wire in flexible conduit can vary depending on the type and manufacturer. It is important to consult the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines to determine the appropriate conduit size for your specific installation.
It is crucial to consider the specific requirements of the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local building codes when determining the correct conduit size for #4 wire. These codes may have additional guidelines or calculations that need to be followed to ensure compliance and the safe installation of electrical systems.
Additionally, it is always recommended to consult with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer to assess the specific requirements of your installation. They can provide expert guidance based on factors such as the distance of wire runs, voltage drop considerations, and any unique circumstances that may affect the conduit sizing.
By following these recommendations and complying with electrical codes and standards, you can ensure that the conduit size for your #4 wire installation is appropriate, allowing for a safe and efficient electrical system.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct conduit size for #4 wire is a crucial step in any electrical installation. Proper conduit sizing ensures the safety, functionality, and compliance of the electrical system. By understanding conduit sizes and considering factors such as wire gauge, insulation type, number of conductors, ambient temperature, bend radius, and future expansion, you can determine the appropriate conduit size for your specific installation.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines and specifications for conduit sizing, which should be consulted and followed to ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations. It is important to keep in mind the maximum conduit fill percentages recommended by the NEC for different types of conduit.
For #4 wire, conduit size recommendations vary depending on the type of conduit being used. Rigid metal conduit (RMC), PVC conduit, electrical metallic tubing (EMT), and flexible conduit each have their own sizing requirements. It is recommended to consult industry standards, manufacturer specifications, and the expertise of qualified electricians or electrical engineers to determine the appropriate conduit size for your specific installation.
Proper conduit sizing is crucial for safety, ease of installation, efficient cable management, and optimal electrical performance. It ensures that the wires are protected, heat is dissipated properly, and future expansions are accounted for. By following the appropriate conduit sizing guidelines, you can minimize potential hazards, prevent issues like overheating and insulation damage, and promote the longevity and reliability of your electrical system.
In conclusion, selecting the right conduit size for #4 wire requires careful consideration of various factors and adherence to electrical codes and standards. By taking the time to accurately determine the appropriate conduit size, you can ensure a safe and efficient electrical installation that meets the requirements of your specific application.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Size Conduit For A 4-Gauge Wire
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Size Conduit For A 4-Gauge Wire”