

Articles
Where Are AFCI/GFCI Breakers Required
Modified: October 28, 2024
Learn about the importance of AFCI/GFCI breakers and where they are required in this informative article. Stay safe and compliant with electrical codes.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Electrical safety is of paramount importance in any building, whether it’s a residential, commercial, or industrial space. Protecting occupants from electrical hazards is a top priority, and one way to ensure this is by using AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) and GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) breakers.
AFCI and GFCI breakers are electrical devices that serve different purposes but share the common goal of preventing electrical accidents and fires. Understanding where and why these breakers are required can help ensure the safety of both individuals and the property in which they reside or work.
In this article, we will explore the function of AFCI and GFCI breakers, where they are required according to electrical code regulations, and the differences between the two.
Key Takeaways:
- AFCI breakers are crucial for preventing electrical fires in areas with combustible materials, such as bedrooms and living rooms. Their ability to detect arc faults and interrupt circuits enhances overall electrical safety.
- GFCI breakers protect against electrical shocks in moisture-prone areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Their rapid detection of ground faults reduces the risk of electrocution, making them essential for personal safety.
Read more: Where Are AFCI Breakers Required
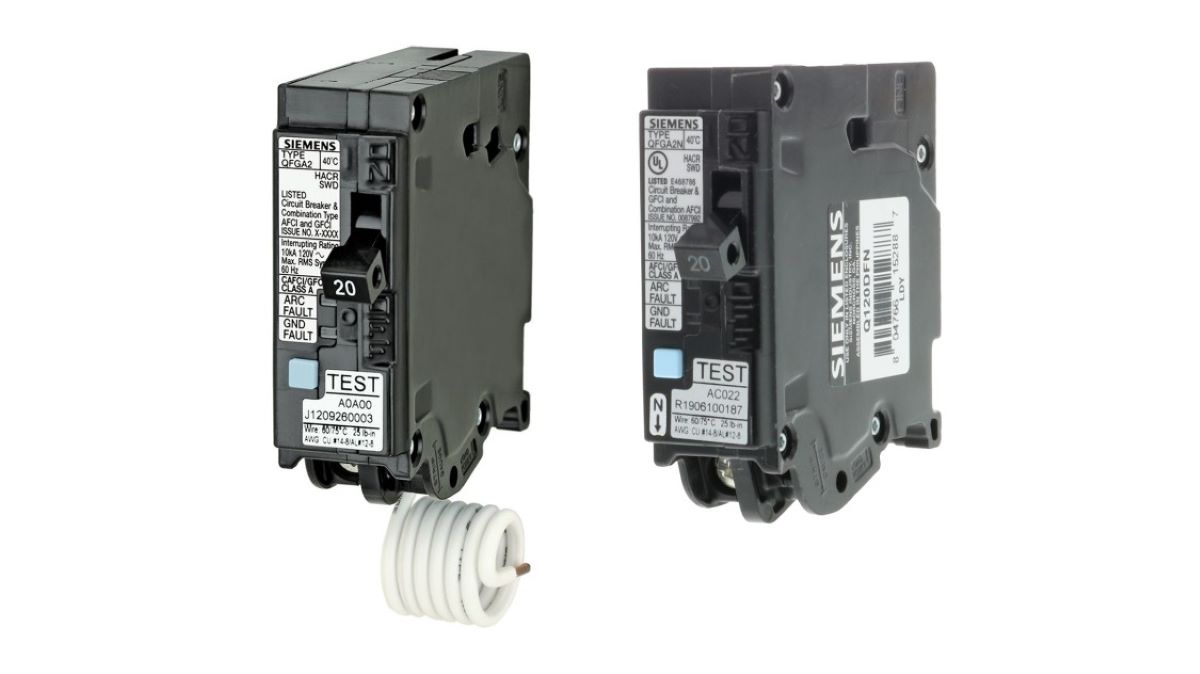
AFCI Breakers
An AFCI breaker, as mentioned earlier, stands for Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter. Its primary function is to detect and prevent arc faults from occurring in electrical circuits. Arc faults are created when there is an unintended electrical discharge, often caused by damaged or frayed wiring, loose connections, or damaged appliances.
An AFCI breaker is designed to quickly detect these arc faults and interrupt the circuit to prevent fires. It does so by continuously monitoring the electrical waveform and analyzing it for any abnormal arc patterns. When an arc fault is detected, the AFCI breaker trips, cutting off the power supply to the affected circuit, thus preventing further damage or potential fire hazards.
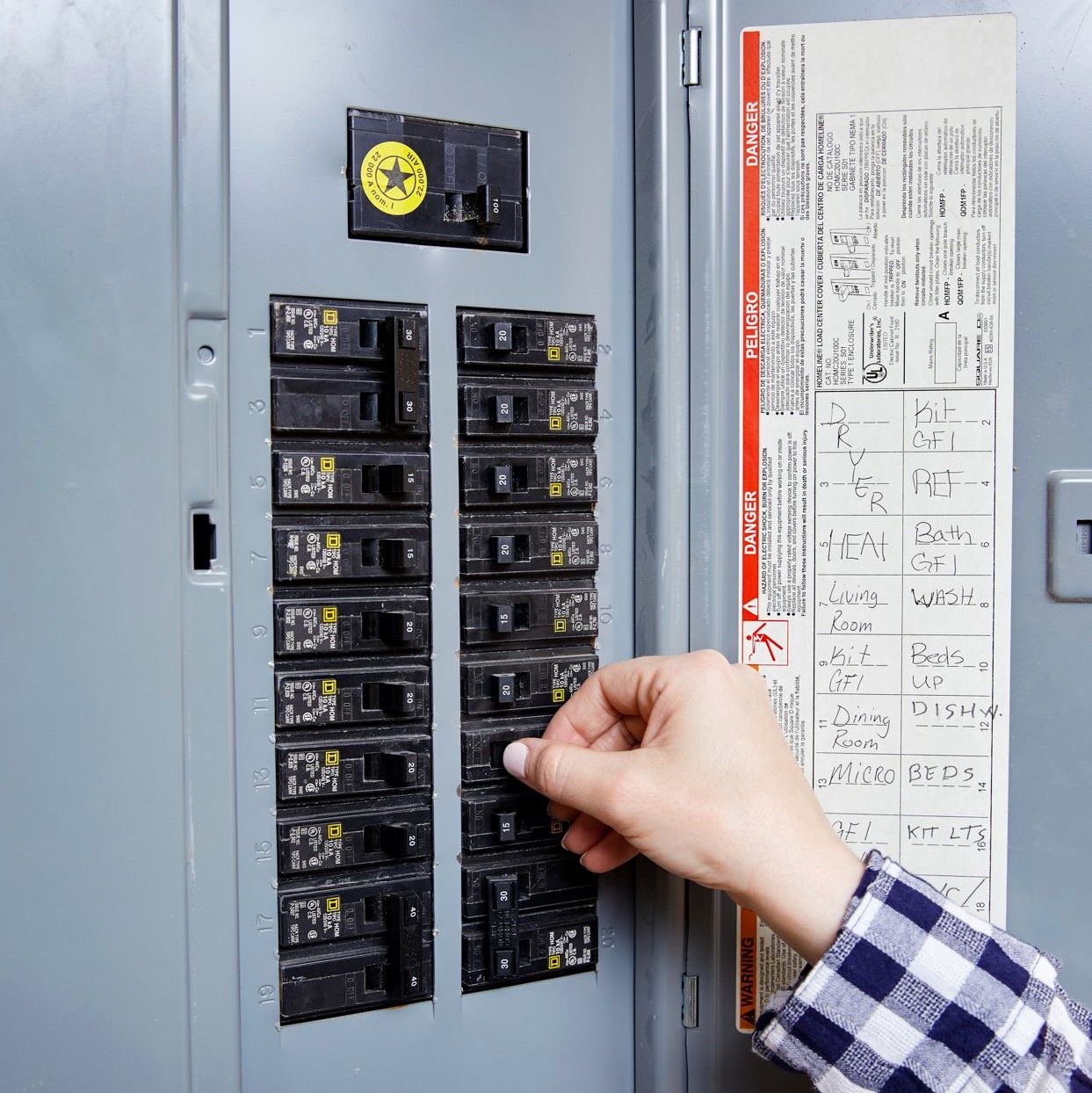
AFCI breakers are typically installed in bedrooms, living rooms, family rooms, and other areas where combustible materials, such as bedding, furniture, or curtains, are present. These breakers play a crucial role in reducing the risk of electrical fires, especially in older homes with outdated wiring systems that may be more prone to arc faults.
It is important to note that AFCI breakers have evolved over time. Initially, AFCI protection was provided by individual circuit breakers specifically designed for arc fault protection. However, more modern electrical panels now incorporate AFCI protection directly into the panel itself. This integration allows for more comprehensive protection throughout the entire electrical system of a building.
Purpose of AFCI Breakers
The primary purpose of AFCI breakers is to enhance electrical safety by detecting and preventing arc faults. Arc faults can occur due to various reasons, including damaged wiring, loose connections, or faulty appliances. These faults can generate intense heat and sparks, which can easily ignite flammable materials in the surrounding area, leading to a potential fire hazard.
AFCI breakers are designed to continuously monitor the electrical current flowing through a circuit. They are equipped with advanced technology that can differentiate between normal operating currents and abnormal arc patterns. When an arc fault is detected, the AFCI breaker rapidly interrupts the circuit, preventing the flow of electricity and eliminating the potential fire hazard.
By implementing AFCI breakers, the risk of electrical fires caused by arc faults is significantly reduced. This is especially crucial in residential areas where people may be asleep or unaware of potential electrical risks. Bedrooms, living rooms, and other areas with combustible materials are common locations for AFCI breaker installation to provide an extra layer of protection against fire hazards.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) has specific requirements for AFCI breakers in certain areas of a building. These requirements help ensure that AFCI protection is in place where it is most needed. By adhering to these regulations, building owners and occupants can have peace of mind knowing they are taking the necessary precautions to reduce the risk of electrical fires.
Overall, the purpose of AFCI breakers is to detect and mitigate the potential danger of arc faults. By interrupting the circuit in a timely manner, these breakers help prevent electrical fires and protect both lives and property.
Where AFCI Breakers are Required
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines on where AFCI breakers are required to be installed in residential buildings. These requirements are continually updated to improve electrical safety standards and reduce the risk of electrical fires caused by arc faults. While specific regulations may vary depending on local building codes, here are some common areas where AFCI breakers are typically required:
- Bedrooms: AFCI breakers are mandatory in bedrooms to protect against arc faults that can occur due to damaged or aging wiring, as well as electrical faults caused by portable electronic devices like chargers and bedside lamps.
- Living Rooms and Family Rooms: These areas often have a higher concentration of electrical devices and appliances. Installing AFCI breakers in these spaces ensures protection against arc faults that may be triggered by faulty wiring or damaged electrical cords.
- Dining Rooms: Although dining rooms may not have as many electrical devices as other areas of a house, they still require AFCI protection to safeguard against arc faults that can result from outdated or damaged wiring.
- Kitchens: Kitchens are considered high-risk areas due to the presence of water and the potential for electrical appliances and outlets to be exposed to moisture. AFCI breakers are required to prevent arc faults resulting from faulty or damaged electrical circuits in this area.
- Laundry Rooms: Similar to kitchens, laundry rooms have a higher risk of arc faults due to the combination of electrical appliances and water usage. Installing AFCI breakers in laundry rooms helps mitigate the risk of electrical fires caused by arc faults.
It is important to consult with local building codes and regulations to ensure compliance with the specific requirements for AFCI breakers in your area. Additionally, it is recommended to have a qualified electrician assess your electrical system and determine the appropriate locations for AFCI breaker installation.
By adhering to the NEC regulations and installing AFCI breakers in the required areas, homeowners can significantly reduce the risk of electrical fires caused by arc faults and provide a safer living environment for themselves and their families.
GFCI Breakers
GFCI stands for Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. Unlike AFCI breakers, which are primarily focused on detecting and preventing arc faults, GFCI breakers are designed to protect against ground faults. A ground fault occurs when an electrical current deviates from its intended path and flows through unintended conductive material, such as a person’s body or a conductive surface.
The purpose of GFCI breakers is to quickly detect these ground faults and interrupt the circuit, providing a high level of protection against electrical shocks and the risk of electrocution. They are specifically designed to monitor the difference in current between the hot wire and the neutral wire. If there is even a slight imbalance in current flow, which indicates a ground fault, the GFCI breaker immediately trips, cutting off the power supply and preventing further electrical hazards.
GFCI breakers are typically installed in areas where there is a higher risk of electrical shocks or moisture exposure. These include:
- Bathrooms: Water and electricity are a dangerous combination. GFCI breakers are required in bathrooms to protect against electrical shocks that may occur due to water contact with electrical devices, outlets, or faulty wiring.
- Kitchens: As another area prone to moisture and water exposure, kitchens require GFCI protection to prevent electric shocks and potential electrocution when using electrical appliances near sinks, countertops, or other wet areas.
- Garages and Outdoor Areas: GFCI breakers are necessary in areas where electrical outlets may come into contact with outdoor elements and moisture, such as in garages, outdoor kitchens, or patios.
- Swimming Pools and Hot Tubs: Due to the high risk of electrical accidents near water, GFCI breakers are indispensable for ensuring the safety of individuals using swimming pools, hot tubs, or any other water feature that involves electrical components.
- Basements and Crawlspaces: These areas often have exposed wiring and may be more susceptible to ground faults. Installing GFCI breakers in basements and crawlspaces provides an added layer of protection against electrical shocks.
It is crucial to consult with local building codes and regulations to determine the specific requirements for GFCI breaker installation in your area. Additionally, it is recommended to have a qualified electrician evaluate your electrical system and advise on the appropriate locations for GFCI breaker installation.
By utilizing GFCI breakers in the necessary areas, individuals can significantly enhance electrical safety and minimize the risk of electrical shocks and electrocution.
Afci/Gfci breakers are required in most areas of the home, including kitchens, bathrooms, garages, and outdoor outlets. Check local building codes for specific requirements.
Read more: Where Are Arc Fault Breakers Required?
Purpose of GFCI Breakers
The primary purpose of GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) breakers is to protect against electrical shocks and the risk of electrocution. GFCI breakers are specifically designed to detect ground faults, where electrical current deviates from its intended path and flows through unintended conductive material, like a person’s body or a damp surface.
Electrical shocks can occur when a person comes into contact with an energized conductor, potentially leading to severe injury or even death. GFCI breakers are designed to rapidly detect even minor imbalances in current flow, which are indicative of a ground fault. As soon as a ground fault is detected, the GFCI breaker trips and interrupts the circuit, cutting off the flow of electricity and preventing electrical shocks.
The primary purpose of GFCI breakers is to safeguard individuals from the hazards of electrical shocks. By promptly interrupting the circuit when a ground fault is detected, GFCI breakers significantly reduce the likelihood of electric shock injuries.
In addition to personal safety, GFCI breakers also protect against electrical fires that can result from ground faults. When current is diverted from its intended path, it can generate heat and potentially ignite nearby flammable materials. By tripping the circuit upon detecting a ground fault, GFCI breakers help prevent electrical fires and minimize property damage.
GFCI breakers are particularly essential in areas where there is a higher risk of electrical shocks, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas. These locations often involve water or moisture, making the risk of electrical accidents more significant.
Overall, the purpose of GFCI breakers is to provide a vital layer of protection against electrical shocks, electrocution, and potential fire hazards. By swiftly interrupting the circuit upon detecting a ground fault, GFCI breakers help enhance electrical safety, providing peace of mind for individuals and ensuring a safer environment for everyone.
Where GFCI Breakers are Required
The installation of GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) breakers is regulated by electrical codes to ensure the safety of individuals in specific areas of a building. These codes may vary depending on your location and local building regulations. However, here are some common locations where GFCI breakers are typically required:
- Bathrooms: GFCI breakers are mandatory in bathrooms due to the high risk of water contact with electrical devices and outlets. Water is a conductor of electricity, and accidents involving electrical shocks can occur if proper protection is not in place.
- Kitchens: Kitchens are another area where GFCI breakers are required, as it is common to have electrical appliances, sinks, and countertops in close proximity. The presence of water and dampness increases the risk of electrical shocks, making GFCI protection crucial.
- Outdoor Areas: GFCI breakers are necessary for electrical outlets located outdoors, such as in gardens, patios, or swimming pool areas. These areas are exposed to the elements and are more vulnerable to moisture, which can cause ground faults and potential electrical hazards.
- Garages and Workshops: Since garages and workshops often involve the use of power tools and other electrical equipment, they require GFCI breakers to protect against accidental electrical shocks or ground faults that may arise from faulty wiring or equipment.
- Laundry Rooms: Laundry rooms typically have water sources, such as washing machines and utility sinks, which can pose an electrical hazard. GFCI breakers should be installed in these areas to ensure safety during the use of electrical appliances.
- Basements: Basements may have exposed wiring, and potential ground faults can occur due to moist conditions or faulty electrical components. It is essential to have GFCI breakers installed in basements to minimize the risk of electrical shocks.
It is important to consult your local building codes and regulations to determine the precise requirements for GFCI breaker installation in your area. It is also recommended to have a qualified electrician assess your electrical system and advise on the appropriate locations for GFCI breakers based on the specific needs of your building.
By adhering to the necessary GFCI breaker requirements, you can ensure the safety of individuals and mitigate the risk of electrical shocks and potential electrocution in your home or workplace.
Comparison of AFCI and GFCI Breakers
AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) and GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) breakers are both critical components in enhancing electrical safety, but they serve different purposes and protect against different electrical hazards. Let’s compare AFCI and GFCI breakers to understand their differences:
Purpose:
AFCI Breakers: The primary purpose of AFCI breakers is to detect and prevent arc faults, which are unintentional electrical discharges that can lead to fires. They are designed to monitor the electrical waveform and interrupt the circuit when arc faults are detected.
GFCI Breakers: GFCI breakers, on the other hand, protect against ground faults, where an electrical current deviates from its intended path and flows through unintended conductive material. They are designed to rapidly detect ground faults and interrupt the circuit, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and potential electrocution.
Required Locations:
AFCI Breakers: AFCI breakers are typically required in areas where arc faults pose a significant fire hazard, such as bedrooms, living rooms, and dining rooms.
GFCI Breakers: GFCI breakers are required in areas where there is a higher risk of electrical shocks due to water or moisture exposure, including bathrooms, kitchens, outdoor areas, and garages.
Safety Benefits:
AFCI Breakers: AFCI breakers play a crucial role in reducing the risk of electrical fires caused by arc faults. By promptly detecting and interrupting the circuit, they help prevent potential fire hazards, especially in older homes with outdated wiring.
GFCI Breakers: GFCI breakers significantly enhance electrical safety by protecting against electrical shocks and the risk of electrocution. They are particularly important in areas where water and moisture are present, preventing accidents that can occur due to the exposure of individuals to live electrical currents.
Installation Requirements:
AFCI Breakers: AFCI breakers are typically installed within the electrical panel or at specific circuit locations, depending on the design of the electrical system. They may be integrated into the electrical panel itself or installed as individual breakers.
GFCI Breakers: GFCI breakers are installed at the electrical panel just like AFCI breakers. Additionally, GFCI receptacles are available for installation in individual outlets to provide localized protection.
Code Regulations:
AFCI Breakers: The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines on where AFCI breakers are required in residential buildings. These requirements are intended to enhance electrical safety by reducing the risk of electrical fires caused by arc faults.
GFCI Breakers: The NEC also outlines where GFCI breakers are required to protect against electrical shocks. Regulations focus on areas where water and moisture exposure increase the potential for electrical accidents.
It is important to consult with local building codes and regulations to ensure compliance with the specific requirements for AFCI and GFCI breaker installation in your area. Proper installation and adherence to electrical safety guidelines are essential to create a safer living or working environment.
Conclusion
Ensuring electrical safety is a top priority in any building, and AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) and GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) breakers play crucial roles in achieving this goal. While AFCI breakers focus on detecting and preventing arc faults to reduce the risk of electrical fires, GFCI breakers protect against ground faults and help prevent electrical shocks and potential electrocution.
AFCI breakers are typically required in areas where arc faults can pose a significant fire hazard, such as bedrooms, living rooms, and dining rooms. By monitoring the electrical waveform and quickly interrupting the circuit upon detecting an arc fault, AFCI breakers help enhance electrical safety and reduce the risk of fires, especially in homes with older wiring systems.
GFCI breakers are essential in areas where there is a higher risk of electrical shocks due to water or moisture exposure. Locations such as bathrooms, kitchens, outdoor areas, and garages require GFCI protection to minimize the risk of electrical accidents and potential electrocution. Swiftly tripping the circuit when a ground fault is detected, GFCI breakers significantly enhance personal safety and help prevent property damage resulting from electrical hazards.
Compliance with local building codes and regulations is crucial when determining the specific requirements for AFCI and GFCI breaker installation. Consulting with a qualified electrician is recommended to assess the electrical system and ensure the appropriate installation locations for these devices.
In conclusion, implementing AFCI and GFCI breakers in the necessary areas enhances electrical safety and reduces the risk of electrical fires, shocks, and potential electrocution. These breakers are essential components in protecting lives and property, offering individuals peace of mind that they are taking necessary precautions to mitigate electrical hazards. By incorporating AFCI and GFCI breakers in accordance with electrical codes, buildings can provide a safer environment for their occupants.
Frequently Asked Questions about Where Are AFCI/GFCI Breakers Required
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “Where Are AFCI/GFCI Breakers Required”