Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is A Blueprint, And Why Is It Important


Architecture & Design
What Is A Blueprint, And Why Is It Important
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover the significance of blueprints in architecture and design. Learn how blueprints provide vital guidelines and specifications for constructing structures, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
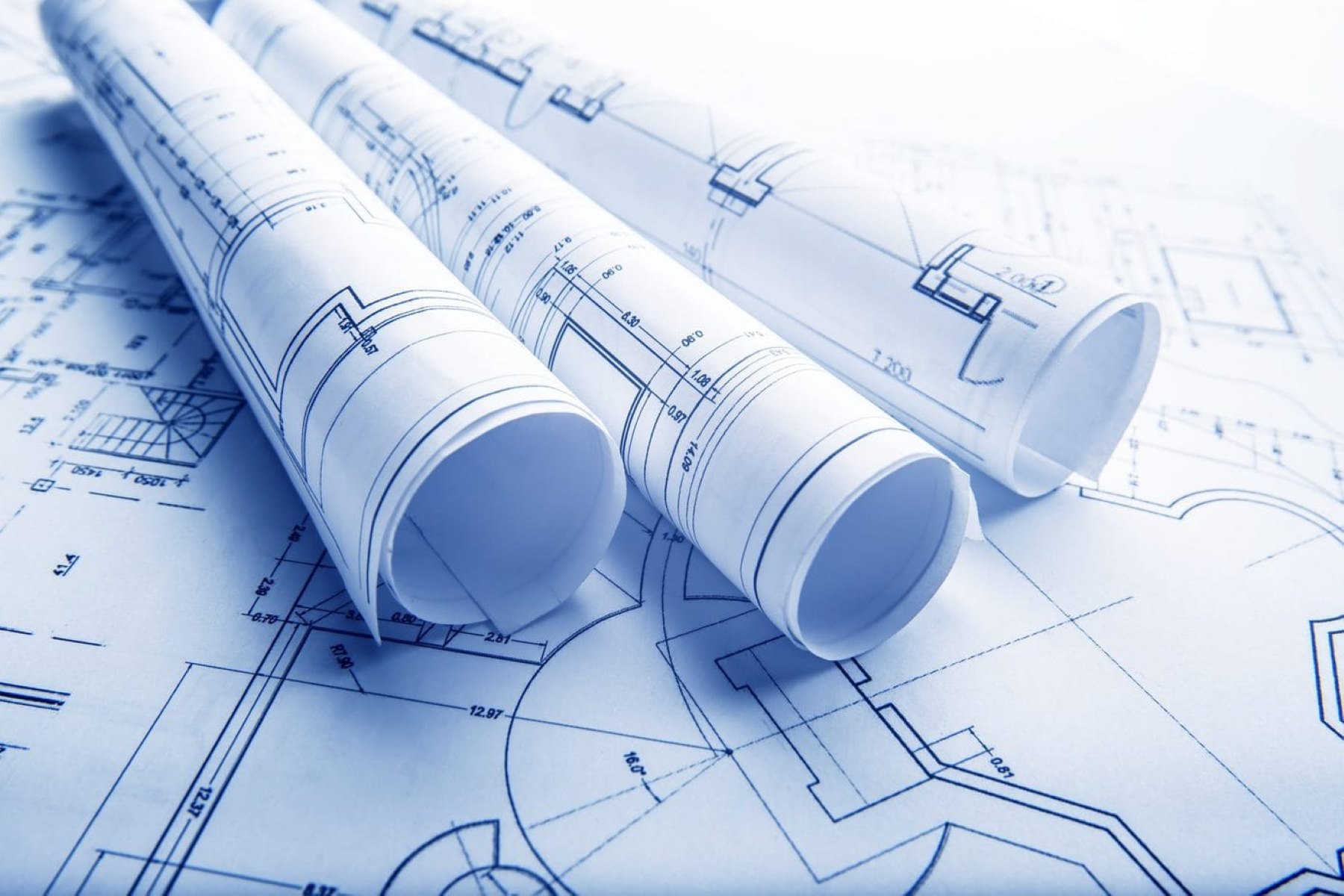
A blueprint is a detailed plan or design that serves as a guide for the construction, engineering, or manufacturing of a project. It provides a visual representation of the project’s requirements, dimensions, and specifications. A blueprint is an essential tool in the field of architecture and design, ensuring that projects are executed accurately and efficiently.
The term “blueprint” originated in the 19th century when architectural drawings were reproduced using a process called cyanotype, which resulted in a blue-tinted print. Although modern blueprints are now created using digital technology, the term “blueprint” has stuck as a common reference.
Blueprints play a crucial role in various industries, including construction, engineering, and manufacturing. They serve as a communication tool between architects, designers, engineers, and contractors, ensuring that all parties are on the same page regarding project specifications and requirements.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of blueprints, the benefits they offer, and their significance in different industries. Understanding the value of blueprints will shed light on the critical role they play in creating successful projects.
Key Takeaways:
- Blueprints are crucial in architecture, engineering, and manufacturing, providing visual representation, precise instructions, and fostering collaboration for successful project outcomes.
- Clear and detailed specifications in blueprints ensure accurate execution, compliance with regulations, and drive continuous improvement in construction, engineering, and manufacturing processes.
Read more: Why Is Blueprint Called Blueprint
Definition of a Blueprint
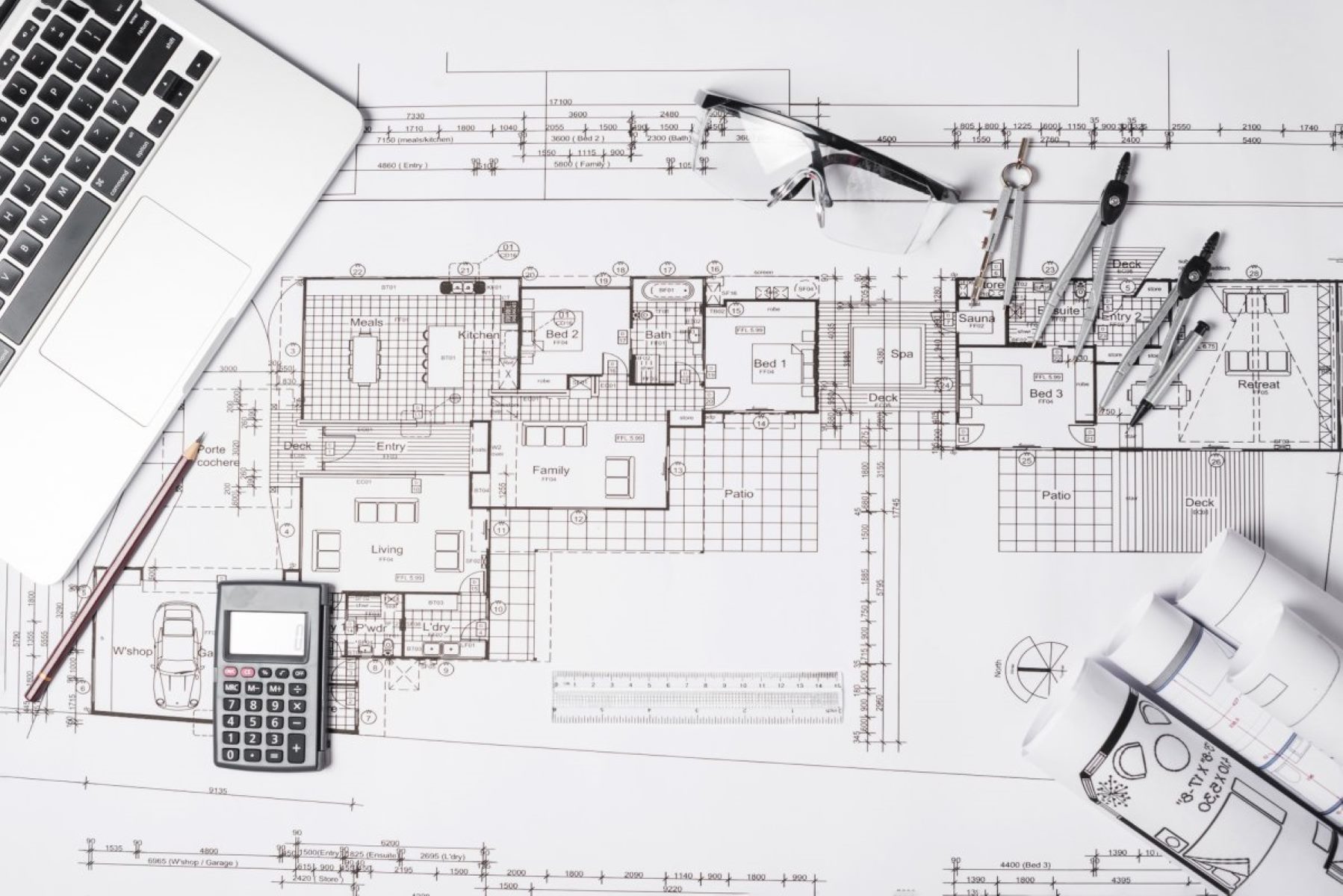
A blueprint is a detailed, scaled representation of a design or plan. It provides a comprehensive layout of a project, illustrating key elements, measurements, and specifications. Typically, blueprints are created by architects, engineers, or designers to showcase the intended structure or product before it is constructed or manufactured.
Blueprints can take various forms, including physical paper prints or digital files. However, regardless of the format, they all share the common characteristic of conveying a comprehensive visual representation of the project’s requirements.
At its core, a blueprint includes essential information such as floor plans, elevations, sections, and details. Floor plans illustrate the layout of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other structural elements. Elevations show the project from different perspectives, allowing a better understanding of the project’s appearance. Sections provide a cut-through view, revealing interior details and structural components. Details focus on specific elements, such as junctions, materials, or hardware, providing further clarity on implementation.
Furthermore, blueprints often incorporate annotations, dimensions, and symbols to help interpret the design. These annotations and symbols provide specific instructions relating to materials, construction techniques, and finishes required for the project. They serve as a universal language, ensuring clear communication and understanding among the project team.
Blueprints are typically created at the initial stages of a project and are subject to revisions throughout the design and construction process. As the project progresses, changes and adjustments may be necessary, and blueprints are updated accordingly to reflect these modifications.
In summary, a blueprint is a detailed plan or design that visually represents a project’s requirements and specifications. It serves as a crucial reference for architects, engineers, designers, and contractors, ensuring accurate execution and successful completion of the project.
Importance of a Blueprint
Blueprints play a pivotal role in various industries, providing a multitude of benefits and ensuring the success of projects. Let’s explore why blueprints are important:
- Clear Communication: Blueprints serve as a common language between architects, engineers, designers, and contractors. They provide a visual representation of the project’s requirements and specifications, eliminating confusion and miscommunication. With a blueprint, everyone involved in the project can understand the design intent and work towards a shared goal.
- Precise Planning and Execution: A blueprint allows for meticulous planning and execution. It provides accurate measurements, dimensions, and specifications, ensuring that all elements of the project are precisely implemented. With a blueprint as a guide, construction or manufacturing processes become more efficient and effective.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Blueprints enable proper resource allocation. By clearly depicting the project’s layout and requirements, blueprints help determine the necessary materials, equipment, and manpower. This leads to better cost estimation, preventing overstocking or understocking of resources, ultimately saving time and money.
- Minimized Errors and Rework: With a blueprint, potential errors and design flaws can be identified and rectified at an early stage. Through careful examination of the design, stakeholders can anticipate and address any potential issues before execution, reducing the need for costly rework or modifications later on in the project.
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Blueprints ensure compliance with building codes, regulations, and legal requirements. They provide a record of the project’s design that can be reviewed and approved by relevant authorities. This helps to ensure that the project meets safety standards and satisfies legal obligations.
- Collaboration and Decision-making: Blueprints facilitate collaboration and decision-making processes. Different stakeholders can study the design, provide feedback, and make informed decisions based on the visual representation and specifications. This fosters a collaborative environment, encouraging input from all team members to achieve optimal project outcomes.
In summary, blueprints are crucial for clear communication, precise planning, efficient resource allocation, error reduction, compliance, and collaborative decision-making. They are essential tools that contribute to the successful execution of projects in various industries.
Benefits of Using a Blueprint
Using a blueprint offers numerous advantages throughout the lifecycle of a project. Let’s explore the benefits of using a blueprint:
- Visual Representation: Blueprints provide a visual representation of the project’s design, allowing stakeholders to visualize the end result. This helps ensure that everyone involved has a clear understanding of the project’s scope, layout, and aesthetics.
- Accuracy and Precision: A blueprint offers precise measurements, dimensions, and specifications, ensuring accurate execution of the project. It eliminates guesswork in construction or manufacturing processes, leading to improved quality and adherence to design intent.
- Efficiency: With a blueprint as a guide, processes become more efficient and streamlined. Contractors and manufacturers can follow the blueprint to complete their tasks without unnecessary delays or mistakes. This results in timely project delivery and optimized resource utilization.
- Cost Savings: By using a blueprint during the planning stage, potential design flaws or errors can be identified and addressed early on. This minimizes the need for costly rework or modifications, ultimately saving both time and money.
- Improved Communication: Blueprints act as a universal language, facilitating clear and effective communication among project stakeholders. They ensure that everyone involved, from architects to contractors, is on the same page, reducing misunderstandings and discrepancies.
- Collaboration: Blueprints encourage collaboration among team members. Stakeholders can study the blueprint, provide feedback, and make informed decisions together. This promotes a collaborative environment where different perspectives can be considered, resulting in higher-quality outcomes.
- Documentation: Blueprints serve as crucial documentation throughout the project’s lifecycle. They provide a record of the project’s design, meeting legal requirements and facilitating future modifications, renovations, or repairs.
- Standardization: Blueprints follow industry standards and conventions, ensuring consistency and uniformity in design and construction practices. This helps ensure that projects meet regulatory guidelines and quality standards.
Overall, using a blueprint offers benefits such as visual representation, accuracy, efficiency, cost savings, improved communication, collaboration, documentation, and standardization. It is an indispensable tool that enhances project outcomes and ensures successful project completion.
Uses of Blueprints in Different Industries
Blueprints find invaluable applications in various industries, providing essential guidance and documentation. Let’s explore some of the common uses of blueprints:
Read more: Why Insulation Is Important
Construction Industry:
In the construction industry, blueprints play a central role in planning and executing building projects. Architects create blueprints that showcase the layout, dimensions, and specifications of the structure. Contractors and builders refer to these blueprints to understand the project requirements and carry out the construction process accurately. Blueprints help ensure that the structure is built according to the intended design, following safety standards and local building codes.
Engineering and Infrastructure Projects:
In engineering and infrastructure projects, blueprints are crucial for designing and constructing bridges, roads, tunnels, and other large-scale structures. Engineers and designers utilize blueprints to visualize the project’s layout, structural components, and electrical or mechanical systems. Blueprints guide the construction teams, facilitating the precise implementation of these complex projects.
Manufacturing Industry:
In the manufacturing industry, blueprints are used to design and manufacture products ranging from automobiles to electronic devices. The blueprints detail the product’s dimensions, material specifications, and assembly instructions. Manufacturers refer to these blueprints to ensure accurate production and adherence to quality standards. Blueprints help streamline the manufacturing process, resulting in consistent and reliable products.
Architectural Design:
Blueprints are essential in architectural design to illustrate the layout, floor plans, and elevations of buildings. Architects create blueprints that provide a visual representation of their design intent, enabling clients and other stakeholders to understand and provide feedback on the proposed structure. Blueprints help architects refine their designs and communicate important details to the construction team.
Read more: Why Are Pillows Important
Interior Design:
In the field of interior design, blueprints are used to plan and design room layouts, furniture placement, and other interior elements. Blueprints assist designers in visualizing the space and determining the ideal arrangement to maximize functionality and aesthetics. Interior designers work with blueprints alongside clients to create personalized and functional spaces.
Mechanical and Electrical Systems:
Blueprints are utilized to design and install mechanical and electrical systems in buildings and industrial facilities. These blueprints depict the layout of pipes, ducts, wiring, and equipment, ensuring efficient and safe installation. Contractors and technicians refer to these blueprints to ensure accurate system integration and functionality.
Overall, blueprints are indispensable tools in the construction, engineering, manufacturing, architecture, interior design, and mechanical/electrical industries. They provide a visual representation of plans, ensuring accurate execution and successful completion of projects.
Common Elements of a Blueprint
A blueprint contains a variety of elements that collectively provide a comprehensive representation of a project. These elements help communicate the design intent and ensure proper implementation. Let’s explore some of the common elements found in a blueprint:
Floor Plans:
Floor plans are a primary element of a blueprint that depict the layout of a building or space from a top-down view. They showcase the arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other structural elements. Floor plans provide a clear understanding of the spatial organization and flow of the project.
Read more: Why HVAC Is Important
Elevations:
Elevations are visual representations of the exterior or interior of the project from different perspectives. They show the project’s appearance and provide insights into the building’s façade, including the design of windows, doors, and other architectural features. Elevations help stakeholders envision the project’s aesthetics and make informed decisions about materials, finishes, and architectural details.
Sections:
Sections are cut-through views of the project, revealing interior details and the relationship between different levels or spaces. They allow stakeholders to understand the internal structure, materials, and dimensions of the project. Sections help identify potential construction challenges and ensure correct implementation.
Details:
Details in a blueprint focus on specific elements, such as junctions, building materials, hardware, or construction techniques. They provide in-depth information and instructions for accurately implementing these elements. Details are essential for ensuring consistency and quality in the execution of the project.
Annotations and Dimensions:
Annotations and dimensions are important elements that enhance the clarity and accuracy of a blueprint. Annotations provide additional information, clarifications, or specific instructions related to the design and construction process. Dimensions indicate the size and scale of objects, enabling precise measurements and ensuring correct proportions.
Read more: Why Plumbing Is Important
Symbols:
Blueprints often incorporate symbols to represent various elements such as electrical outlets, plumbing fixtures, or different types of materials. These symbols provide a standardized way of communicating specific features and facilitate clear interpretation of the design by professionals involved in the project.
In addition to these elements, blueprints may include a title block, which contains essential information such as the project’s name, owner, designer, and date. This information helps to identify and track the blueprint throughout the project’s lifecycle.
By combining these elements, blueprints provide a comprehensive visual representation of the project’s design and specifications. They enable effective communication, accurate execution, and successful project outcomes.
Importance of Clear and Detailed Specifications
Clear and detailed specifications serve as the backbone of any project, providing essential guidance and ensuring successful execution. Whether it’s a construction project, engineering design, or manufacturing process, having precise specifications is of utmost importance. Let’s explore the significance of clear and detailed specifications:
Preventing Ambiguity and Misinterpretation:
Clear specifications leave no room for misinterpretation or confusion. They provide explicit details about the project’s requirements, materials, dimensions, and quality standards. This helps all stakeholders involved in the project to have a common understanding, preventing ambiguity and minimizing the risk of errors or misunderstandings.
Accuracy in Execution:
Detailed specifications ensure that the project is executed accurately and in accordance with the desired outcome. By specifying precise measurements, materials, and procedures, specifications guide contractors, engineers, and manufacturers in implementing the project as intended. This helps prevent deviations from the original design and ensures consistent quality.
Read more: Why Are Gutters Important
Cost Estimation and Resource Allocation:
Clear specifications enable accurate cost estimation and effective resource allocation. With detailed specifications, project managers can determine the necessary materials, equipment, and labor required. This facilitates proper planning and prevents unnecessary expenses or delays due to inadequate resources.
Regulatory Compliance:
Clear specifications ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards. Specifications outline the necessary compliance parameters, such as safety regulations, building codes, or industry standards. By adhering to these specifications, projects can meet legal requirements and avoid potential legal disputes or penalties.
Quality Assurance:
Clear and detailed specifications contribute to quality assurance. They outline the desired quality standards, performance criteria, and tolerances for the project. This helps ensure that the final deliverable meets the expected level of quality and functionality, resulting in customer satisfaction and long-term project success.
Contractual Agreements:
Clear specifications are essential in contractual agreements. They serve as the basis for defining the scope of work, timelines, deliverables, and expectations. Well-defined specifications minimize the potential for disputes or disagreements between parties by providing a clear reference point for evaluating the project’s progress and completion.
In summary, clear and detailed specifications are crucial for preventing ambiguity, ensuring accuracy in execution, facilitating cost estimation and resource allocation, ensuring regulatory compliance, ensuring quality assurance, and establishing the basis for contractual agreements. They are fundamental in achieving successful project outcomes and satisfying the requirements and expectations of all stakeholders involved.
Read more: Why Is Woodworking Important
Role of Blueprints in Construction Projects
Blueprints are a vital component in the success of construction projects, serving as an essential tool for architects, engineers, contractors, and other project stakeholders. Let’s explore the key roles of blueprints in construction projects:
Design Visualization:
Blueprints provide a visual representation of the project’s design, enabling stakeholders to envision the end result. They showcase the layout, dimensions, and specifications of the structure, allowing decision-makers to assess and approve the design before construction begins. This visualization aids in understanding how different elements of the project will come together.
Planning and Coordination:
Blueprints form the foundation of project planning and coordination. They serve as a reference for scheduling activities, allocating resources, and coordinating different trades and teams involved in the construction process. Blueprint details help determine sequencing, dependencies, and phasing of work, ensuring smooth and efficient project execution.
Accuracy in Execution:
Blueprints provide precise measurements, dimensions, and specifications necessary for accurate execution. Contractors and builders rely on blueprints to understand the project’s requirements and translate them into physical form. From setting foundations to erecting walls, installing electrical systems to plumbing fixtures, the blueprint acts as a guide, ensuring that each aspect of the construction aligns with the intended design.
Read more: Why Organizing Is Important
Identification of Structural Components and Systems:
Blueprints highlight key structural components and systems of the building, such as beams, columns, walls, and foundation. They provide detailed information about load-bearing elements, allowing for proper engineering and construction. Blueprints also delineate the location of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, guiding the installation of essential building infrastructure.
Collaboration and Communication:
Blueprints facilitate collaboration and effective communication among project stakeholders. Architects, engineers, contractors, and subcontractors can refer to the blueprint to discuss design intent, technical specifications, and resolve any conflicts or discrepancies. This ensures that everyone involved is on the same page, fostering a collaborative environment for successful project completion.
Quality Assurance and Compliance:
Blueprints play an integral role in quality assurance and compliance with building codes and regulations. They serve as a reference to ensure that the construction adheres to safety standards and meets specific requirements. Inspectors and regulatory authorities can review the blueprint to assess compliance, assess the structural integrity of the building, and evaluate the quality of workmanship.
In summary, blueprints are essential in construction projects for design visualization, planning and coordination, accuracy in execution, identification of structural components and systems, collaboration and communication, as well as quality assurance and compliance. They serve as a crucial guide throughout the construction process, ensuring that the project is executed accurately and in line with the desired design and specifications.
Role of Blueprints in Engineering Design
Blueprints play a critical role in engineering design, serving as a fundamental tool for engineers to communicate their designs and ensure accurate implementation. Let’s explore the key roles of blueprints in engineering design:
Read more: Why Are Rugs Important
Visualization of Design Concepts:
Blueprints provide a visual representation of engineering design concepts, allowing engineers to communicate their ideas effectively. They illustrate the layout, dimensions, and specifications of intricate systems or components, helping clients and stakeholders understand the intended design before construction or manufacturing begins.
Precision and Accuracy:
Blueprints ensure precision and accuracy in engineering design. They provide precise measurements, technical specifications, and material requirements, enabling engineers to create designs that align with project objectives and meet client expectations. Detailed blueprints guide engineers in integrating complex systems and components, ensuring seamless functionality.
Coordination and Collaboration:
Blueprints facilitate coordination and collaboration among engineers and project stakeholders. They serve as a common reference point for discussions, enabling effective communication and ensuring everyone is aligned with the design intent. Engineers can use blueprints to share ideas, gather feedback, and incorporate necessary modifications to optimize project outcomes.
Technical Documentation:
Blueprints serve as crucial technical documentation in engineering design. They provide a comprehensive record of the design, including specifications, calculations, and drawings. These blueprints can be referred to in the future for maintenance, repairs, or modifications, ensuring the longevity and continued functionality of the engineered systems or components.
Read more: What Is Blueprint App
Implementation Guides:
Blueprints guide engineers during the implementation of engineering designs. They provide step-by-step instructions, detailing the assembly process, material selection, and manufacturing techniques required. Blueprints empower engineers to translate design concepts into physical products or systems accurately, minimizing errors and ensuring adherence to quality standards.
Compliance and Safety:
Blueprints help engineers ensure compliance with industry standards, regulations, and safety requirements. They include necessary labels, symbols, and annotations to highlight specific safety measures or regulatory considerations. Engineers rely on blueprints to incorporate appropriate design elements that ensure the safety and reliability of the engineered systems or components.
In summary, blueprints are essential in engineering design as they facilitate visualization of design concepts, ensure precision and accuracy, enhance coordination and collaboration, serve as technical documentation, guide implementation, and ensure compliance and safety. They enable engineers to effectively communicate their designs, leading to successful engineering projects and the creation of functional and reliable systems or components.
Role of Blueprints in Manufacturing
Blueprints play a crucial role in the manufacturing industry, providing essential guidance and documentation throughout the production process. Let’s explore the key roles of blueprints in manufacturing:
Design Communication:
Blueprints serve as a means of effectively communicating design specifications between product designers and manufacturers. They provide a visual representation of the product, detailing the dimensions, materials, tolerances, and assembly instructions. Blueprints ensure that all parties involved in the manufacturing process have a clear understanding of the design intent, enabling efficient production.
Precision and Accuracy:
Blueprints ensure precision and accuracy in manufacturing processes. They provide detailed measurements, specifications, and technical details necessary for precise fabrication and assembly of the product. Manufacturers refer to the blueprints to ensure the precise placement of components, accurate machining, and adherence to quality standards, resulting in consistent and reliable products.
Manufacturing Workflow:
Blueprints play a critical role in guiding the manufacturing workflow. They provide step-by-step instructions, detailing the manufacturing processes, materials, and tools required at each stage. Manufacturers can refer to the blueprints to understand the sequence of operations, minimizing errors and ensuring efficient production flow.
Quality Control and Assurance:
Blueprints are essential for quality control and assurance in manufacturing. They define the quality standards, inspection criteria, and test requirements for the manufactured products. Manufacturers can reference the blueprints throughout the production process to ensure that the finished products meet the specified design and functional requirements.
Tooling and Equipment:
Blueprints guide manufacturers in the design and fabrication of specialized tooling and equipment required for manufacturing processes. The blueprints detail the specifications for jigs, fixtures, molds, and other custom tools necessary for efficient and accurate production. Manufacturers rely on blueprints to ensure the compatibility of tooling with the product design.
Read more: Why BIM Is Important?
Documentation and Traceability:
Blueprints serve as critical documentation for manufactured products. They provide a record of the product’s design, including part numbers, specifications, and manufacturing processes. This documentation enables traceability, facilitating future repairs, modifications, or recalls. Manufacturers can refer to the blueprints as a reference for quality control, troubleshooting, or reproducing the product if needed.
Continuous Improvement:
Blueprints play a role in driving continuous improvement in manufacturing processes. By analyzing the blueprint and examining the production outcomes, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions. Blueprints provide a baseline for evaluating manufacturing efficiency, productivity, and quality, enabling refinement and optimization of the production processes.
Overall, blueprints are essential in the manufacturing industry for design communication, precision and accuracy, guiding the manufacturing workflow, quality control and assurance, tooling and equipment design, documentation and traceability, and driving continuous improvement. They ensure the successful production of high-quality products that meet the specified design requirements and deliver value to customers.
Conclusion
Blueprints are an indispensable tool in the fields of architecture, engineering, construction, and manufacturing. They serve as a visual representation of a project’s design, providing precise measurements, specifications, and instructions for accurate implementation. The importance of blueprints cannot be overstated, as they offer numerous benefits and play a crucial role throughout the lifecycle of a project.
Clear and detailed specifications in blueprints ensure effective communication, accurate execution, and successful project outcomes. They prevent ambiguity and misinterpretation, promote precision and accuracy, facilitate cost estimation and resource allocation, ensure compliance with regulations, and foster quality assurance and collaboration among project stakeholders.
In construction projects, blueprints empower architects, engineers, contractors, and regulators to plan, coordinate, and execute building projects with accuracy and efficiency. In engineering design, blueprints enable visualization, precision, collaboration, documentation, and compliance, ensuring the successful execution of complex systems or components. In manufacturing, blueprints guide communication, precision, workflow, quality control, tooling, documentation, and continuous improvement, ensuring the production of consistent and reliable products.
With their ability to convey design intent, provide technical details, and facilitate collaboration, blueprints have become a vital component of project success. They contribute to efficient planning, accurate execution, and adherence to quality standards. Moreover, blueprints serve as a valuable source of documentation for future reference, maintenance, and modifications.
As technology continues to advance, digital blueprints have become prevalent, enhancing accessibility, ease of sharing, and version control. However, the fundamental principles of clarity, precision, and communication remain paramount, regardless of the format.
In conclusion, blueprints are an essential tool in architecture, engineering, construction, and manufacturing industries. They empower project stakeholders with a clear vision, precise instructions, and effective collaboration, leading to successful project outcomes, accurate implementation, and satisfied clients. With their ability to convey design intent, ensure accuracy, and foster communication, blueprints continue to shape the way projects are planned, designed, and executed.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Blueprint, And Why Is It Important
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.



0 thoughts on “What Is A Blueprint, And Why Is It Important”