Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is The Design Of A Colonial House?


Architecture & Design
What Is The Design Of A Colonial House?
Modified: January 6, 2024
Discover the intricate architecture design of colonial houses and explore their unique features, from symmetrical facades to grand porches and ornate detailing. Uncover the elegance and charm of these historic homes.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Colonial architecture refers to the architectural style prevalent during the Colonial period, usually spanning from the early 17th century to the mid-19th century. It is a style that originated in European countries, particularly England, and was brought to the American colonies by settlers. With its symmetrical design, exquisite craftsmanship, and influence from various European cultures, colonial architecture has become an enduring and beloved style in the United States.
Throughout history, architecture has played a significant role in reflecting the values, aspirations, and lifestyles of a particular era. Colonial architecture is no exception, as it reflects the social and historical context of the time. From the early settlements in New England to the grand plantations in the Southern colonies, colonial houses have a distinct charm and elegance.
This article aims to delve into the design of colonial houses, exploring their history, characteristics, regional variations, and influences. We will also touch upon the contemporary interpretations of colonial architecture and how it has evolved over the years.
Key Takeaways:
- Colonial architecture in America reflects diverse European influences, from English symmetry to Spanish courtyards. Regional variations emerged, showcasing adaptability to local climates and resources, shaping the timeless charm of colonial houses.
- Contemporary colonial house designs blend historical elegance with modern amenities, preserving the architectural legacy while adapting to the needs of today’s homeowners. The harmonious balance between past and present captivates architects and homeowners alike.
Read more: What Is Porch In House
History of Colonial Architecture
The history of colonial architecture in America begins with the arrival of European settlers in the early 17th century. The English, Dutch, Spanish, and French were among the prominent European colonizers who influenced the architectural styles of the time.
English colonists brought with them the Renaissance and Elizabethan architectural styles. The rectangular shape and symmetrical design of English manor houses served as the foundation for the development of colonial houses in America. The use of wood as a primary building material was a practical choice due to its abundance in the New World.
The Dutch, with their influence in New York and New Jersey, introduced elements of their architecture, such as gambrel roofs and stepped gables. These unique features added a touch of Dutch charm to colonial houses, setting them apart from their English counterparts.
The Spanish colonizers left their mark primarily in the Southern colonies, such as Florida and Texas, with the introduction of Spanish colonial architecture. Characterized by thick-walled structures, arched doorways, and courtyards, these homes showcased the influence of Moorish, Spanish, and Mediterranean styles.
The French colonists, mainly settled in Louisiana, brought their distinct style, known as French colonial architecture. With its steep roofs, wrap-around galleries, and intricate ironwork, French colonial houses were a combination of French and Caribbean influences.
As the colonies grew, regional variations began to emerge, influenced by the local climate, available building materials, and cultural influences. Each region developed its own unique architectural identity, resulting in a diverse range of colonial house designs.
The colonial period saw architectural evolution and adaptation as settlers incorporated elements from their native countries and adapted them to suit the local conditions. This blend of influences laid the foundation for the distinctive design characteristics found in colonial architecture today.
Characteristics of Colonial Houses
Colonial houses are known for their distinctive features and design elements. These characteristics contribute to their timeless appeal and create a sense of elegance and symmetry. Let’s explore the key aspects that define colonial house design.
- Building Materials: Colonial houses were primarily constructed using locally available materials, which varied depending on the region. In New England, where forests were abundant, timber was the main building material. On the other hand, bricks were commonly used in the Mid-Atlantic colonies. Stone and stucco were also utilized in certain areas.
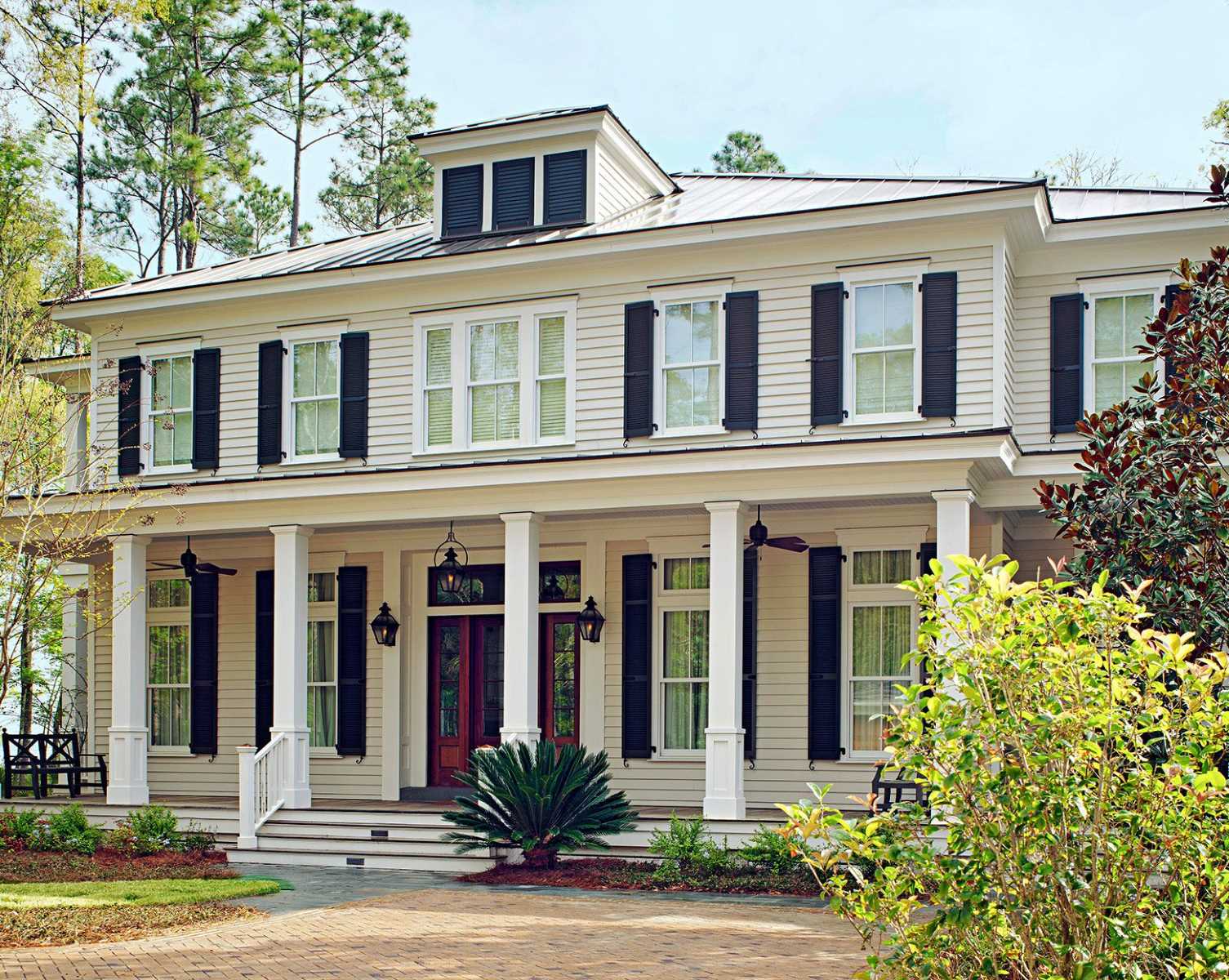
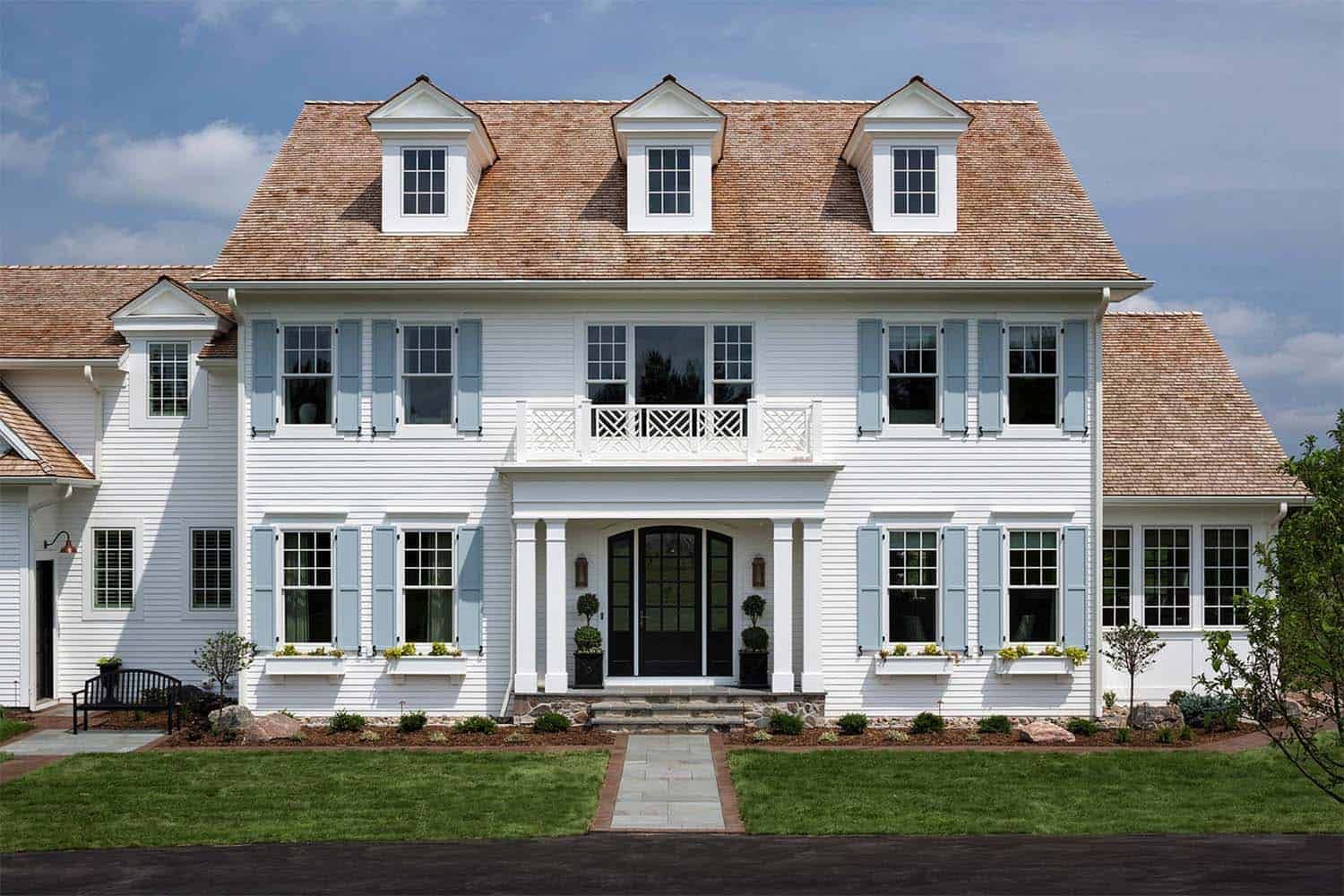
- Symmetrical Design: Symmetry is a hallmark of colonial architecture, reflecting the influence of classical architectural principles. Colonial houses typically feature a central entrance with an equal number of windows on either side. This symmetrical layout creates a balanced and harmonious facade.
- Roof Styles: Colonial houses exhibit a variety of roof styles depending on the region and the aesthetic preferences of the time. The most common roof styles include gable roofs, hip roofs, and gambrel roofs. Gable roofs feature two sloping sides that meet at a central ridge, while hip roofs have slopes on all four sides. Gambrel roofs, with their double slopes on each side, are often associated with Dutch colonial houses.
- Exterior Features: Colonial houses are characterized by their simple yet elegant exteriors. The facade often includes features such as dormer windows, chimneys, columns, and shutters. These elements add visual interest and create a sense of authenticity.
- Interior Layout: Colonial houses typically have a practical and efficient interior layout. The first floor includes common areas such as the living room, dining room, and kitchen, while the upper floors consist of bedrooms and additional living spaces. Central hallways are common, providing access to various rooms, and staircases are often centrally located.
These characteristics define the essence of colonial house design and contribute to their timeless beauty. Despite the variations and adaptations that emerged over time, these foundational elements remain integral to colonial architecture.
Types of Colonial Architecture
Colonial architecture encompasses various styles that emerged during the colonial period in America. These styles exhibit unique characteristics and reflect the diverse cultural influences of the colonizing nations. Let’s explore some of the prominent types of colonial architecture:
- Cape Cod: The Cape Cod style originated in New England and is known for its simplicity and practicality. These houses are typically one or two stories high, with a symmetrical design and a steep, sloping roof. The exteriors are often clad in clapboard or shingles, and the front entrance is centrally located. Cape Cod houses are characterized by their cozy and compact interiors.
- Georgian: The Georgian style, influenced by the architectural trends of 18th-century England, exudes elegance and grandeur. These houses are typically two or three stories high, with a symmetrical facade, evenly spaced windows, and a central entrance adorned with a decorative pediment. The exteriors are commonly made of brick or stone, and the interiors feature spacious rooms, elaborate moldings, and formal layouts.
- Dutch Colonial: Dutch colonial houses, prevalent in the Mid-Atlantic region, reflect the influence of Dutch settlers. These houses feature a distinctive gambrel roof with curved eaves, giving them a unique appearance. The exteriors are often clad in shingles or stone, and the entrance is typically located off to the side. Dutch colonial houses are known for their cozy interiors and efficient use of space.
- Spanish Colonial: Spanish colonial houses, found predominantly in the Southern colonies, showcase a blend of Spanish and Mediterranean influences. These houses have thick stucco walls, arched doorways, and red-tiled roofs. Courtyards and wrought iron embellishments are common, adding a touch of elegance. The interiors often feature open spaces and an emphasis on natural ventilation.
- French Colonial: French colonial architecture can be seen in areas like Louisiana, influenced by French and Caribbean styles. These houses often have steep roofs, wrap-around galleries, and ornate ironwork. The exteriors are typically made of brick or stucco, and the interiors boast spacious layouts with high ceilings and elaborate detailing.
These various types of colonial architecture highlight the rich diversity of design that emerged during the colonial period. Each style has its own unique charm, combining elements from different cultures to create distinctive and captivating homes.
When designing a colonial house, consider using symmetrical facades, a central front door, and evenly spaced windows. Incorporate traditional features such as columns, gable roofs, and decorative moldings for an authentic colonial look.
Regional Variations in Colonial Design
As the American colonies developed, regional variations in colonial architecture emerged, influenced by factors such as climate, available resources, and cultural preferences. Let’s explore the distinct characteristics of colonial design in different regions:
- New England: In New England, where harsh winters and abundant forests prevailed, colonial houses were designed to withstand the demanding climate. These houses often featured steep roofs to shed snow and sturdy frames made of timber. The exteriors were typically clad in shingles, and the interiors focused on functionality and practicality. Central chimney stacks provided heat to multiple rooms, while wrap-around porches offered protection from the elements.
- Mid-Atlantic: The Mid-Atlantic colonies, including New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, saw a diverse mix of architectural influences. Dutch settlers in this region introduced their unique style, characterized by stepped gables and the use of brick. This Dutch influence blended with English and Georgian styles, resulting in houses with symmetrical designs, brick or stone exteriors, and decorative details. The interiors often showcased rich woodwork and elaborate moldings.
- Southern Colonies: The Southern colonies, such as Virginia and South Carolina, experienced a warmer climate and a different set of influences. Plantation homes, grand in scale and elegance, were a prominent feature of the Southern architectural landscape. These houses often featured grand entrances, spacious layouts, and expansive gardens. The exteriors were typically made of brick or stucco, and the interiors boasted high ceilings, large windows, and intricate detailing.
These regional variations in colonial design highlight the adaptability and ingenuity of early settlers as they constructed homes suitable for their specific environments. Understanding these regional differences provides valuable insight into the history and development of colonial architecture in America.
Read more: How To Add A Porch To Your House
Influences on Colonial House Design
The design of colonial houses in America was shaped by various influences brought by the European colonizers. These influences, including architectural styles and cultural traditions, left a lasting impact on the development of colonial house design. Let’s explore some of the key influences:
- English Style: The English settlers in America brought with them the architectural styles prevalent in England during the colonial period. The simple yet elegant designs of English manor houses served as a foundation for colonial house design. The symmetrical layout, steep roofs, and central hallways found in English architecture influenced the overall structure of colonial houses.
- Dutch Influence: The Dutch settlers, particularly in the Mid-Atlantic region, introduced unique design elements to colonial architecture. The Dutch colonial style, with its distinctive gambrel roofs and stepped gables, added a touch of charm and individuality to colonial houses. Dutch influence was also evident in the use of brick as a primary building material in this region.
- Spanish Influence: The Spanish colonizers, particularly in the Southern colonies and areas like Florida and Texas, had a significant impact on colonial house design. Spanish colonial architecture, with its thick stucco walls, arched doorways, and red-tiled roofs, contributed to the distinctive look of colonial houses in these regions. Courtyards and wrought iron embellishments were also common features influenced by Spanish design traditions.
- French Influence: French colonial architecture had an impact on colonial house design, particularly in Louisiana and parts of the Caribbean. French influence brought steep roofs, wrap-around galleries, and intricate ironwork to colonial houses. The use of brick or stucco exteriors and spacious interiors with high ceilings reflected the elegance and flair of French design.
These various influences from England, the Netherlands, Spain, and France contributed to the rich diversity and aesthetics of colonial house design. The blending of these styles and cultural traditions shaped the unique and captivating architectural heritage found in colonial architecture across America.
Contemporary Colonial House Designs
While colonial architecture is deeply rooted in history, there is also room for contemporary interpretations of this timeless style. Modern architects and homeowners often incorporate elements of colonial design into their homes, blending the charm of the past with the convenience and innovation of the present. Let’s explore two aspects of contemporary colonial house designs:
- Modern Interpretations: Contemporary colonial house designs often pay homage to the traditional elements of colonial architecture while infusing modern aesthetics. Architects and designers may incorporate symmetrical facades, gabled roofs, and classic architectural details into the overall design. However, they also add modern touches, such as larger windows for increased natural light, open floor plans for a more spacious feel, and minimalist interior finishes that reflect current design trends. This blending of old and new creates a harmonious balance between historical charm and contemporary living.
- Advancements in Materials and Technology: The use of advanced materials and technology has greatly influenced contemporary colonial house design. Modern construction techniques allow for better insulation, energy efficiency, and durability. While traditional colonial houses were primarily built using timber, brick, or stone, contemporary designs may incorporate materials like concrete, steel, and glass, adding a modern twist to the classic aesthetic. Additionally, technological advancements have improved the structural integrity and functionality of colonial houses, enabling homeowners to enjoy the conveniences of modern living within a colonial-inspired setting.
Contemporary colonial house designs have successfully bridged the gap between the past and the present, offering homeowners the opportunity to live in a home that combines historical charm with modern amenities. These designs allow for the preservation of the colonial architectural legacy while adapting to the needs and preferences of today’s homeowners.
Conclusion
Colonial architecture stands as a testament to the rich history and cultural influences that shaped the early American colonies. From the simple charm of Cape Cod houses to the grandeur of Georgian and plantation homes, the design of colonial houses carries a sense of timeless elegance that continues to captivate homeowners and architects to this day.
Throughout the colonial period, various influences from England, the Netherlands, Spain, and France contributed to the diverse and distinctive features of colonial house design. The use of local materials, symmetrical layouts, and specific roof styles became synonymous with the architectural style of the time.
Regional variations further enriched colonial architecture, with different climates, available resources, and cultural preferences contributing to unique design elements. Whether it’s the practicality of New England houses, the blend of Dutch and English styles in the Mid-Atlantic region, or the Spanish and French influences in the Southern colonies, each region showcased its own architectural identity.
While colonial architecture continues to honor tradition, contemporary colonial house designs offer a modern interpretation of this timeless style. Architects and homeowners bring together the classic elements of colonial design with modern aesthetics and advancements in materials and technology. The result is a harmonious blend of historical charm and contemporary living.
Colonial architecture holds a significant place in American architectural heritage. Its enduring appeal, with its symmetrical facades, distinctive roof styles, and attention to detail, continues to inspire architects and homeowners alike. Whether living in a historically accurate reproduction or a modern interpretation, experiencing the charm and elegance of a colonial house is a window into the past and a connection to the cultural foundations of the United States.
As we appreciate and preserve the beauty of colonial architecture, we embrace not only the architectural forms but also the stories and history embedded within these structures. Colonial houses serve as reminders of our shared heritage and stand as iconic symbols of a bygone era—a living testament to the settlers who shaped the nation.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Design Of A Colonial House?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is The Design Of A Colonial House?”