Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Does MDF Stand For In Construction


Building & Construction
What Does MDF Stand For In Construction
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover the meaning and significance of MDF in building construction. Learn how this versatile material is used and why it is a popular choice for many construction projects.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
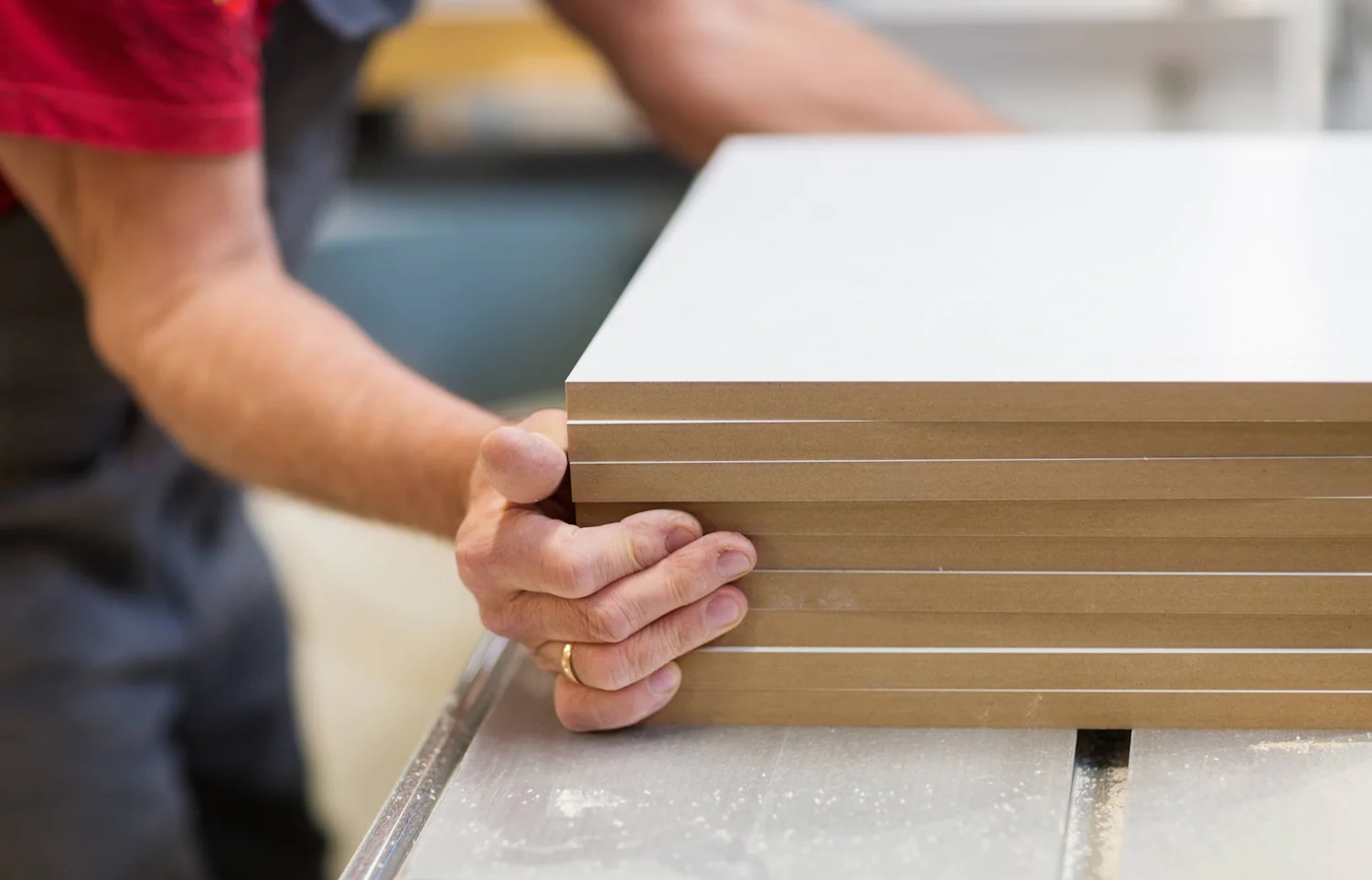
When it comes to construction materials, there are numerous options to choose from. One such material that is widely used in the construction industry is MDF. If you’ve ever come across the term MDF but were unsure of its meaning, this article is here to demystify it for you. MDF stands for Medium Density Fiberboard, and it has become a popular choice for various construction applications.
MDF is a type of engineered wood product that is made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into fibers and then combining them with a resin binder under high heat and pressure. The resulting boards have a smooth and uniform surface with no grain pattern, making them highly versatile for multiple construction uses.
In this article, we will explore the uses of MDF in construction, its advantages and disadvantages, common applications, and the maintenance and care required to ensure its longevity. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of what MDF is and why it is such a popular choice in the construction industry.
Key Takeaways:
- MDF, or Medium Density Fiberboard, is a versatile and cost-effective material widely used in construction for interior trim, cabinetry, furniture, and decorative elements due to its uniform density, stability, and ease of customization.
- While MDF offers advantages such as durability and environmental benefits, it is important to consider its limitations, including moisture sensitivity and limited load-bearing capacity. Proper maintenance and care are essential for maximizing its longevity in construction applications.
Read more: What Is MDF Construction Material
Definition of MDF
Medium Density Fiberboard, abbreviated as MDF, is a type of engineered wood product that is made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into fibers and then combining them with a resin binder under high heat and pressure. The resulting boards have a consistent density throughout, hence the name “Medium Density.” MDF boards are typically made from a mixture of wood fibers, resin, and wax, which are compressed to create a durable and versatile construction material.
MDF is different from other wood-based panels, like plywood or particleboard, in terms of its density. While particleboard is made from wood particles and plywood is made from thin layers of wood veneer, MDF is created by forming wood fibers into boards with a specific density range. This density range contributes to the strength, stability, and workability of MDF, making it a popular choice for various construction applications.
The density of MDF usually ranges from 600 kg/m³ (37 lb/ft³) to 800 kg/m³ (50 lb/ft³). Its uniform density and smooth surface make it an ideal substrate for laminating, veneering, or painting. Additionally, the absence of natural wood grain in MDF allows for precise cutting and shaping without the risk of splintering or chipping, making it a favored material for intricate designs and decorative elements.
MDF is available in a variety of thicknesses, typically ranging from 2mm to 25mm (0.08″ to 1″), which allows for flexibility in its application. It is also known for its exceptional dimensional stability, meaning it is less prone to expansion or contraction due to changes in temperature or humidity. This makes MDF a reliable choice for interior construction projects where consistency and durability are essential.
In summary, MDF is a type of engineered wood product that is created by compressing wood fibers with resin under high heat and pressure to form boards with a consistent density. Its uniform density, smooth surface, and dimensional stability make it a versatile material for a wide range of construction applications.
Uses of MDF in Construction
MDF has gained popularity in the construction industry due to its versatility and wide range of applications. Whether it’s for residential, commercial, or industrial projects, MDF finds its use in various construction elements. Let’s explore some of the key uses of MDF in construction:
- Interior Trim: MDF is a popular choice for interior trim due to its smooth surface and ability to hold paint and finishes exceptionally well. It is commonly used for baseboards, crown molding, door and window casings, and chair rails. MDF trim provides a clean and uniform appearance, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of interior spaces.
- Cabinetry and Furniture: MDF is widely used in the construction of cabinets, shelves, and furniture pieces. Its stability, durability, and the ability to hold screws and hardware securely make it an ideal material for such applications. MDF can be shaped, routed, and coated to achieve various designs, allowing for customization and creativity in furniture and cabinetry construction.
- Doors and Drawer Fronts: MDF is a popular choice for doors and drawer fronts due to its smooth surface and resistance to warping or splitting. They can be painted, stained, or covered with veneers to mimic the appearance of natural wood, providing a stylish and cost-effective alternative.
- Wall Paneling and Wainscoting: MDF panels are commonly used for wall paneling and wainscoting. The uniformity and rigidity of MDF make it easy to install and create visually appealing wall treatments. It can be painted or laminated with decorative surfaces to enhance the aesthetics of any interior space.
- Structural Elements: While MDF is not typically used for load-bearing applications, it can be used for non-structural elements such as shelving, partitions, and wall linings. Its stability and ability to hold its shape make it a suitable choice for creating sturdy and functional interior structures.
- Crafts and DIY Projects: MDF is a popular choice for crafts and DIY projects due to its versatility and ease of working with. It can be easily cut, shaped, and painted, making it an ideal material for creating decorative items, signs, and small-scale constructions.
These are just a few examples of the many uses of MDF in construction. Its versatility, stability, and ease of customization make it a highly sought-after material for various applications in the construction industry.
Advantages of MDF in Construction
MDF offers several advantages that make it a popular choice in the construction industry. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of using MDF in construction:
- Cost-Effective: MDF is generally more affordable compared to solid wood or other wood-based panels. This makes it a cost-effective option for construction projects, especially when large quantities of material are required.
- Uniform and Stable: MDF has a consistent density throughout the board, resulting in a uniform and stable material. Unlike natural wood, MDF is less prone to warping, expanding or contracting due to changes in temperature and humidity, ensuring dimensional stability in construction applications.
- Easy to Work With: MDF is relatively easy to cut, shape, and manipulate, making it a preferred choice for intricate designs and detailed construction elements. It can be routed, drilled, and molded with precision, allowing for customization and creativity in construction projects.
- Smooth Surface: MDF has a smooth and uniform surface, making it an excellent substrate for painting, veneering, or laminating. It holds paint and finishes exceptionally well, resulting in a professional and polished appearance in construction elements.
- Durable: MDF offers good overall durability and resistance to wear and tear. The homogeneous nature of MDF makes it less susceptible to cracking, splitting, or splintering, ensuring longevity in construction applications.
- Versatility: MDF is a versatile material that can be used for a wide range of construction elements. From trim and cabinetry to wall paneling and furniture, MDF can be adapted to suit various design and construction requirements.
- Environmental Benefits: MDF is an environmentally friendly choice as it is made from recycled wood fibers and does not contribute to deforestation. Additionally, MDF can be easily recycled at the end of its life cycle, reducing waste and promoting sustainability in the construction industry.
These advantages make MDF an attractive option for construction projects, offering cost-effectiveness, versatility, and durability, while also providing an aesthetically pleasing and environmentally conscious solution.
MDF stands for Medium Density Fiberboard. It is a versatile and cost-effective material commonly used in construction for cabinets, furniture, and molding. It is made from wood fibers and resin, providing a smooth and uniform surface for painting or veneering.
Disadvantages of MDF in Construction
While MDF offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider its potential disadvantages as well. Here are some of the key drawbacks of using MDF in construction:
- Moisture Sensitivity: MDF is highly susceptible to moisture damage. When exposed to moisture or high levels of humidity, MDF can swell, warp, or even disintegrate. Therefore, it is not recommended for use in areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms or outdoor applications.
- Not Suitable for Load-Bearing Applications: MDF is not structurally strong and is not designed for load-bearing applications. It is not recommended to use MDF for structural elements or areas that require significant weight-bearing capacity.
- Cannot Withstand Extreme Temperatures: MDF is sensitive to extreme temperature changes. Exposure to excessive heat or cold can cause MDF to expand or contract, leading to warping or cracking in extreme cases. Therefore, it is important to avoid exposing MDF to extreme temperature conditions.
- Limited Screw-Holding Capacity: While MDF can hold screws reasonably well, it does not have the same screw-holding capacity as solid wood. Over-tightening screws or using larger screws can result in the material splitting or losing its grip.
- Prone to Chip and Damage Edges: MDF has a dense and homogeneous structure, which can make it prone to chipping or damage along the edges if not properly handled or installed. Care should be taken during cutting and installation to prevent damage to the edges of MDF boards.
- Exposure to Formaldehyde: MDF is manufactured using adhesive resins that may contain formaldehyde. Although formaldehyde emissions from MDF have significantly reduced over the years due to improved manufacturing practices, it is still recommended to choose low-emission or formaldehyde-free MDF products for applications where indoor air quality is a concern.
- Less Natural Aesthetics: Unlike solid wood, MDF lacks the natural grain and texture that many people appreciate. While it can be painted or veneered to mimic the appearance of wood, it may not provide the same authentic feel or appeal.
Considering these disadvantages, it is crucial to assess the specific requirements of each construction project and determine whether MDF is the appropriate material choice. Attention to proper installation, maintenance, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines can help mitigate these disadvantages and ensure the longevity and performance of MDF in construction applications.
Read more: What Does PR Stand For In Construction
Common Applications of MDF in Construction
MDF is a versatile material that finds its application in various construction projects. From interior elements to decorative pieces, MDF offers a wide range of uses. Let’s explore some of the common applications of MDF in construction:
- Interior Trim: MDF is commonly used for interior trim, including baseboards, crown molding, door and window casings, and chair rails. Its smooth surface and ability to hold paint make it an ideal choice for adding a finishing touch to interior spaces.
- Cabinetry and Furniture: MDF is widely used in the construction of cabinets, shelves, and furniture pieces. Its stability, durability, and ability to hold hardware securely make it a preferred material for cabinetry and furniture construction.
- Doors and Drawer Fronts: MDF is often used for doors and drawer fronts. It can be painted, stained, or covered with veneer to achieve a desired look, providing a cost-effective alternative to solid wood doors and fronts.
- Wall Paneling and Wainscoting: MDF panels are commonly used for wall paneling and wainscoting. They can be painted, laminated, or covered with wallpaper to enhance the aesthetics of interior spaces.
- Shelving and Storage Units: MDF is an excellent choice for creating shelving and storage units. Its stability and ability to hold weight make it suitable for organizing spaces and maximizing storage options.
- Partitions and Room Dividers: MDF can be used to create partitions and room dividers in open floor plans. It provides privacy while allowing for customization in terms of design and finish.
- Display and Decorative Elements: MDF can be used to construct display units, decorative wall panels, and other decorative elements. Its versatility allows for intricate and creative designs to enhance the visual appeal of spaces.
- Crafts and DIY Projects: Due to its ease of cutting, shaping, and painting, MDF is popular for crafts and DIY projects. It can be used to create signs, small-scale constructions, and various decorative items.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of MDF in construction. With its flexibility, durability, and ability to be customized, MDF continues to be a favored choice for a wide range of construction projects.
Maintenance and Care of MDF in Construction
Proper maintenance and care are essential to ensure the longevity and performance of MDF in construction applications. By following a few simple guidelines, you can keep MDF in optimal condition. Here are some maintenance and care tips for MDF:
- Avoid Excessive Moisture: MDF is sensitive to moisture and should not be exposed to excessive humidity or direct contact with water. Use appropriate waterproofing materials in areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms or exterior applications. Clean up any spills promptly and avoid placing MDF in areas exposed to frequent moisture.
- Protect from Extreme Temperatures: MDF should be protected from extreme temperature conditions. Avoid placing it near heat sources or in areas with fluctuating temperatures. Extreme heat can cause MDF to warp or melt, while extreme cold can lead to cracking or splitting.
- Prevent Scratches and Dents: MDF has a smooth surface that can be prone to scratches and dents. Use protective pads or coasters under heavy objects to prevent indentations. Avoid dragging or sliding objects across MDF surfaces to minimize the risk of damage.
- Proper Cleaning: Regular cleaning is important to maintain the appearance of MDF. Use a soft, slightly damp cloth or sponge to wipe down the surfaces. Avoid abrasive cleaners or harsh chemicals that may damage the finish or cause discoloration. Dry the surface thoroughly to prevent moisture absorption.
- Avoid Excessive Weight: Although MDF is relatively strong, it is not designed for heavy loads. Avoid placing excessive weight on MDF shelves or surfaces to prevent sagging or structural damage. Distribute the weight evenly and consider adding support if needed.
- Protect from Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can cause fading or discoloration of MDF surfaces. Use curtains or blinds to minimize the exposure to UV rays. Consider finishing or sealing MDF with a protective coating to enhance its resistance to sunlight.
- Handling with Care: When handling MDF, be cautious not to drop or impact the edges or corners, as they can be prone to chipping or damage. Use appropriate lifting techniques and protective measures during transportation to prevent breakage.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: It is important to follow the guidelines provided by the manufacturer regarding installation, finishing, and maintenance of MDF. Different types of MDF may have specific recommendations and requirements, so be sure to consult the manufacturer’s instructions for optimal results.
By following these maintenance and care tips, you can extend the lifespan of MDF in construction applications and ensure its durability and aesthetics over time.
Conclusion
MDF, or Medium Density Fiberboard, has emerged as a versatile and popular choice in the construction industry. Its unique composition and characteristics make it ideal for a wide range of applications, from interior trim and cabinetry to decorative elements and crafts.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of MDF and its manufacturing process. We have discussed its advantages, such as cost-effectiveness, versatility, and ease of customization. We have also acknowledged its limitations, including moisture sensitivity and limited load-bearing capacity. Nevertheless, by following proper maintenance and care practices, MDF can continue to perform well in construction projects.
With its smooth surface, uniform density, and stability, MDF offers a level of consistency and aesthetic appeal that can enhance any construction project. Its ability to be painted, laminated, and shaped further expands the creative possibilities for designers and builders.
Despite the rise of alternative materials, MDF remains a popular choice due to its cost-effectiveness, environmental benefits, and ease of use. It provides a sustainable option as it is made from recycled wood fibers and is recyclable at the end of its life cycle.
As you embark on your next construction project, consider the different applications and advantages of MDF. From interior trim and cabinetry to decorative elements and crafts, MDF offers a durable and versatile solution that can meet your construction needs.
In conclusion, MDF continues to play a significant role in the construction industry, providing an affordable, customizable, and environmentally friendly option. By understanding its uses, advantages, disadvantages, and maintenance requirements, you can make informed decisions about incorporating MDF into your construction projects.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does MDF Stand For In Construction
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Does MDF Stand For In Construction”