Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Is M1 Zoning

Planning & Engineering
What Is M1 Zoning
Modified: October 20, 2024
Discover what M1 zoning is and how it relates to planning and engineering. Explore the regulations and guidelines for industrial land use.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
M1 zoning, or Manufacturing District zoning, is a land use classification system used by cities and municipalities to designate areas specifically for industrial and manufacturing activities. It plays a crucial role in urban planning and development by ensuring that industrial operations are located in appropriate areas, away from residential and commercial zones.
M1 zoning regulations define the permissible uses, building requirements, and restrictions for properties located within these designated zones. This type of zoning helps to maintain a balance between economic growth and the welfare of local communities by creating distinct areas where industries can thrive while minimizing potential conflicts with other land uses.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of M1 zoning, shedding light on its definition, purpose, permitted uses, restrictions, benefits, and challenges. By examining examples of M1 zoning regulations in different cities, we can gain insights into how this type of zoning is implemented and its impact on urban areas.
Key Takeaways:
- M1 zoning plays a vital role in urban planning by designating specific areas for industrial activities, promoting economic growth, and protecting the environment and public safety.
- While M1 zoning supports industrial development, it also poses challenges such as potential conflicts with residential areas, environmental considerations, and infrastructure demands. Effective management and community involvement are crucial for sustainable coexistence.
Read more: What Is A-1 Zoning
Definition of M1 Zoning
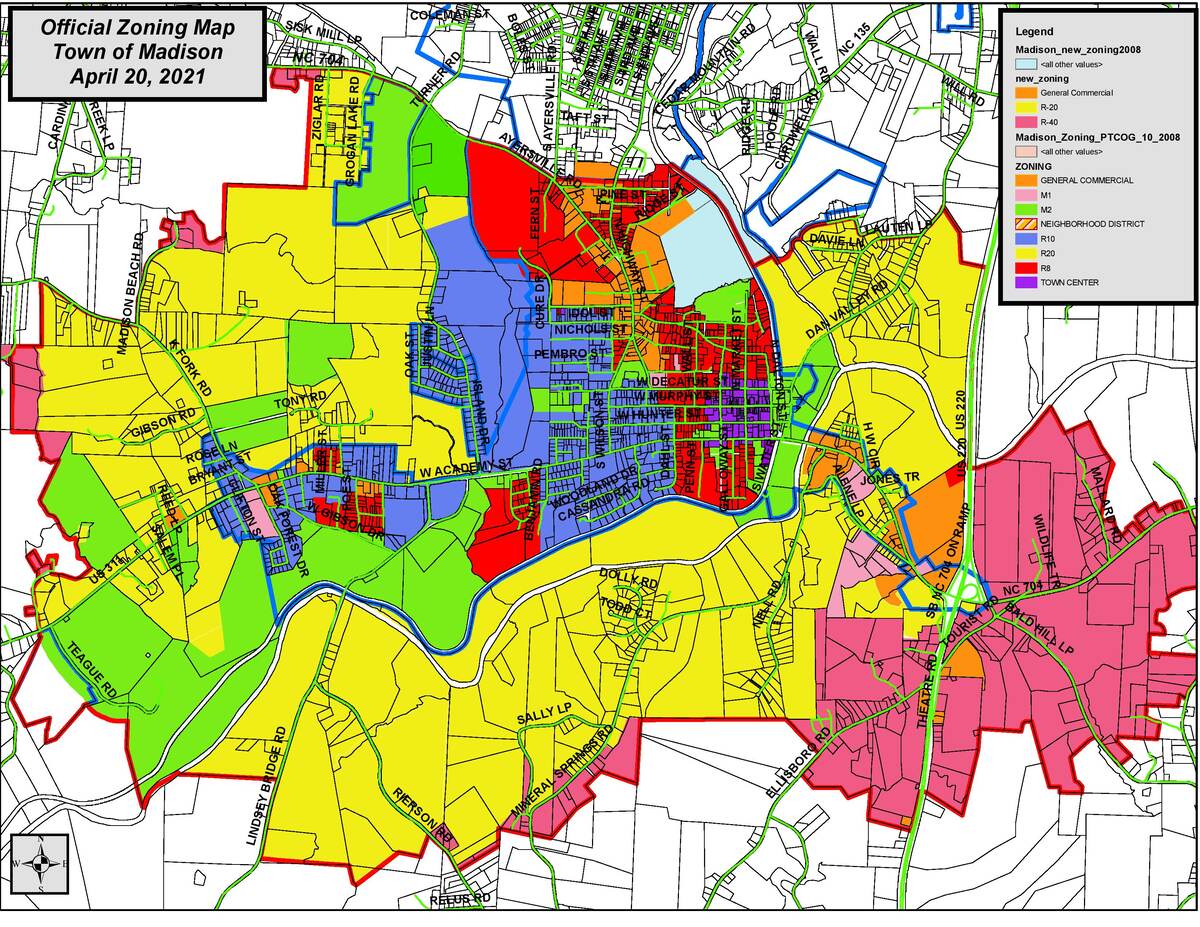
M1 zoning, also known as Manufacturing District zoning, is a classification system used by local governments to regulate land use in specific areas designated for industrial and manufacturing purposes. This zoning category is typically included in a city’s overall zoning ordinance and is part of the broader land use planning strategy.
Under M1 zoning, certain land uses, building regulations, and restrictions are established to create dedicated areas for industrial activities. These zones are typically located away from residential and commercial areas due to the potential noise, pollution, and heavy traffic associated with manufacturing operations.
The specific regulations and guidelines for M1 zoning can vary from city to city, but some common characteristics include:
- Permitted Uses: M1 zoning allows for a range of activities typically associated with manufacturing, including factories, warehouses, assembly plants, research and development facilities, and industrial storage facilities.
- Building Requirements: M1 zones often have specific building requirements, such as minimum setbacks, maximum building heights, and environmental considerations to mitigate potential impacts on surrounding areas.
- Infrastructure and Utilities: M1 zoning may require the provision of adequate infrastructure and utilities to support industrial operations, such as access to transportation networks, water, electricity, and sewer systems.
- Environmental Regulations: M1 zoning may include regulations aimed at protecting the environment, such as waste management and emissions control measures, to minimize the impact of industrial activities on air and water quality.
M1 zoning is crucial for urban planning as it ensures that industrial activities are concentrated in appropriate areas and separated from residential and commercial areas. This separation helps to maintain a balanced and sustainable urban environment by minimizing potential conflicts and promoting the overall well-being of communities.
Purpose of M1 Zoning
The primary purpose of M1 zoning is to designate specific areas within a city for industrial and manufacturing activities. This zoning classification serves several important purposes:
- Land Use Management: M1 zoning helps local governments efficiently manage the allocation of land for industrial purposes. By designating specific areas for manufacturing activities, city planners can ensure that industrial operations are concentrated in appropriate zones that have the necessary infrastructure and utilities to support them.
- Environmental Protection: M1 zoning plays a crucial role in protecting the environment and maintaining the quality of life in nearby residential and commercial areas. By separating industrial activities from other land uses, such as housing or shopping districts, potential impacts like noise, air pollution, and heavy traffic can be minimized.
- Economic Development: M1 zoning supports economic growth and job creation by providing dedicated spaces for manufacturing and industrial operations. Concentrating industrial activities in specific areas not only facilitates infrastructure planning but also encourages investment and business development in those zones.
- Public Safety: M1 zoning helps ensure public safety by keeping industrial activities separate from residential areas. This separation reduces the risk of accidents, such as fires or chemical spills, that could jeopardize the well-being of nearby communities.
- Community Planning: M1 zoning contributes to the overall planning and development of a city. By strategically locating industrial zones, urban planners can create a balanced and harmonious urban environment that takes into account the needs and concerns of all stakeholders.
Overall, the purpose of M1 zoning is to strike a balance between promoting industrial growth and protecting the well-being of communities. By clearly defining areas where industrial activities are permitted, M1 zoning helps ensure that industries can thrive while minimizing conflicts with other land uses and safeguarding the environment and public safety.
Permitted Uses in M1 Zones
M1 zones, or Manufacturing District zones, allow for a wide range of industrial and manufacturing activities. These zones are specifically designated for businesses that require heavy machinery, large-scale production, or specialized facilities. The permitted uses in M1 zones can vary depending on local regulations, but generally include the following:
- Manufacturing Facilities: M1 zones are intended to accommodate various types of manufacturing facilities, such as factories, assembly plants, production plants, and processing plants. These facilities engage in activities such as textile production, metalworking, food processing, and chemical manufacturing.
- Warehouses and Distribution Centers: M1 zones often permit the construction and operation of warehouses and distribution centers. These facilities serve as storage and distribution hubs for goods produced within the M1 zone or brought in from external sources.
- Research and Development Facilities: Many M1 zones allow for the development of research and development (R&D) facilities. These facilities are crucial for advancing innovation and technology in various sectors, providing a space for scientific research, product development, and experimentation.
- Industrial Storage Facilities: M1 zoning typically permits the establishment of industrial storage facilities, such as storage yards or silos. These facilities are used for storing raw materials, finished products, or equipment required for industrial operations.
- Heavy Industrial Uses: Some M1 zones may allow for heavy industrial activities, such as foundries, steel mills, power plants, and chemical refineries. These uses involve intensive processes and often require specialized infrastructure and environmental safeguards.
- Industrial Parks: M1 zones can also incorporate industrial parks, which are planned developments that provide a mix of industrial facilities and services. These parks aim to promote collaboration, efficiency, and economic growth by clustering related industries in a shared space.
It is important to note that the specific permitted uses in M1 zones can vary from city to city and may be subject to additional regulations and restrictions. Local authorities design zoning regulations to align with the unique needs and characteristics of their communities while still ensuring compatibility with neighboring land uses.
By allowing for a diverse range of economically productive activities, M1 zoning supports industrial growth, creates employment opportunities, and contributes to the overall vitality of a city’s economy.
Restrictions and Limitations in M1 Zones
While M1 zoning allows for a wide range of industrial and manufacturing activities, there are also restrictions and limitations in place to ensure that these activities are conducted in a responsible and sustainable manner. These restrictions are designed to protect the surrounding environment, maintain public safety, and prevent potential conflicts with neighboring land uses. Here are some common restrictions and limitations in M1 zones:
- Setback Requirements: M1 zoning often imposes setback requirements, specifying the minimum distance between industrial buildings and property lines or adjacent residential or commercial areas. This ensures that there is sufficient space between different land uses, reducing the potential for conflicts and allowing for proper access and circulation.
- Height Restrictions: Limits on building heights are often prescribed in M1 zoning regulations to prevent the visual impact of tall industrial structures and to preserve the character and skyline of the surrounding area.
- Noise and Emissions Controls: M1 zoning typically includes regulations for noise and emissions control to minimize the impact of industrial activities on neighboring properties and the environment. This may involve requirements to install soundproofing measures, use low-noise equipment, or implement emission reduction technologies.
- Environmental Protection: Regulations related to environmental protection are commonly enforced in M1 zones. These regulations may cover matters such as waste management, hazardous material storage and handling, stormwater runoff controls, and compliance with air and water quality standards.
- Traffic Management: M1 zoning often requires businesses in these zones to comply with traffic management regulations. These regulations may include provisions for truck routes, loading and unloading areas, and parking spaces to ensure the efficient and safe movement of vehicles within the zone.
- Limited Residential and Commercial Uses: M1 zones generally restrict or prohibit the establishment of residential and commercial uses within the zoning area. This helps prevent conflicts between industrial activities and non-compatible land uses, such as housing or retail establishments.
It is important for businesses and property owners within M1 zones to familiarize themselves with these restrictions and limitations. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures the well-being of neighboring communities but also helps businesses operate in a sustainable and responsible manner.
In addition, it is worth noting that specific restrictions and limitations may vary from city to city. Local zoning ordinances are tailored to meet the unique needs and characteristics of each community, while ensuring a balance between industrial growth and the surrounding environment.
M1 zoning is typically designated for light industrial use, allowing for activities such as manufacturing, warehousing, and some commercial uses. Be sure to check local zoning regulations for specific allowable uses and restrictions.
Benefits and Advantages of M1 Zoning
M1 zoning, or Manufacturing District zoning, offers a range of benefits and advantages for both the community and businesses operating within these designated areas. Here are some of the key benefits of M1 zoning:
- Optimal Land Use Allocation: M1 zoning ensures the efficient allocation of land for industrial and manufacturing activities. By designating specific areas for these uses, cities can avoid the haphazard development of industries and promote the orderly growth of their industrial sectors.
- Economic Growth and Job Creation: M1 zoning supports economic growth by providing a conducive environment for businesses in the manufacturing sector. Concentrating industrial activities in specific areas allows for economies of scale, encourages investment and business development, and stimulates job creation, contributing to local economic prosperity.
- Environmental Protection: By segregating industrial activities from residential and commercial areas, M1 zoning helps protect the environment. It enables the implementation of regulations and standards to mitigate the impact of industrial operations on air and water quality, noise pollution, and waste management. This promotes sustainable development and protects the well-being of neighboring communities.
- Infrastructure Planning: M1 zoning provides a framework for effective infrastructure planning. By designating specific areas for industrial activities, cities can anticipate and cater to the infrastructure needs of these zones, including transportation networks, utility services, and other necessary facilities. This ensures efficient and reliable support for manufacturing operations.
- Increased Public Safety: M1 zoning helps ensure public safety by keeping industrial activities segregated from residential areas. This reduces the risk of accidents, such as fires, explosions, or harmful emissions, which could endanger the well-being of nearby residents. This separation also provides better control over potential industrial hazards.
- Promotion of Innovation and Collaboration: M1 zones can serve as hubs for research and development and foster innovation and collaboration within the manufacturing sector. By clustering related industries and R&D facilities in close proximity, M1 zoning encourages knowledge exchange, partnerships, and the development of new technologies, which can enhance the competitiveness of local industries.
M1 zoning offers numerous advantages for cities, businesses, and communities. By creating designated areas for manufacturing activities, M1 zoning supports economic growth, protects the environment, promotes public safety, and stimulates innovation. By adhering to the regulations and guidelines of M1 zoning, businesses can operate in a responsible and sustainable manner, contributing to the overall well-being and prosperity of the local community.
Challenges and Concerns with M1 Zoning
While M1 zoning brings various benefits, there are also challenges and concerns associated with this type of land use classification. It is important to address and mitigate these challenges to ensure that the implementation of M1 zoning is effective and beneficial for all stakeholders. Here are some common challenges and concerns:
- Conflicts with Residential and Commercial Areas: One of the primary challenges with M1 zoning is the potential for conflicts with nearby residential and commercial areas. While efforts are made to separate industrial zones from other land uses, there may still be concerns regarding noise, pollution, traffic congestion, and visual impacts that could impact the quality of life and property values of neighboring communities.
- Environmental Considerations: Although M1 zoning includes environmental regulations, there may still be concerns related to pollution and environmental impacts. Industrial activities, particularly heavy industrial ones, can generate potential hazards, emissions, and waste that need to be carefully managed to safeguard the environment and public health.
- Infrastructure Demands: Concentrating industrial activities in specific areas can place demands on infrastructure and utilities, including transportation networks, water and sewer systems, and electricity supply. Ensuring that adequate infrastructure is in place to support the needs of businesses within M1 zones is essential to avoid strain on existing systems and maintain the efficient operation of industrial activities.
- Land Availability and Cost: The availability of suitable land for M1 zoning can sometimes be limited, especially in densely populated areas. The cost of acquiring and developing land for industrial use can be high, potentially posing a barrier for businesses looking to establish or expand their operations in these zones.
- Community Engagement and Participation: The implementation of M1 zoning should involve meaningful community engagement and participation to address concerns and ensure that the zoning aligns with the needs and aspirations of the local residents. Open dialogue and collaboration with stakeholders can help build understanding, trust, and support for industrial activities within M1 zones.
- Adaptability to Changing Industries: Another concern with M1 zoning is its adaptability to changing industries and technologies. As industries evolve and new technologies emerge, the zoning regulations may need to be flexible enough to accommodate these changes while still maintaining the intended separation of industrial activities from other land uses.
Addressing these challenges and concerns requires careful planning, ongoing monitoring, and adaptive management. Local authorities and stakeholders should work together to find a balance between promoting industrial growth, protecting the environment, and ensuring the well-being of communities living in and around M1 zones.
By addressing these challenges head-on and implementing effective strategies, M1 zoning can be a valuable tool to facilitate responsible and sustainable industrial development while mitigating potential negative impacts on neighboring communities and the environment.
Examples of M1 Zoning Regulations in Different Cities
M1 zoning regulations can vary from city to city based on local needs, land availability, and economic priorities. Here are a few diverse examples of M1 zoning regulations in different cities:
- Chicago, Illinois: In the city of Chicago, M1 zoning allows for a wide range of industrial uses, such as manufacturing, storage, distribution, and wholesale trade. However, certain restrictions are in place to protect residential areas and ensure compatibility with the surrounding community. For example, M1 zoning requires a buffer distance between industrial uses and residential zoning, and limits the height and intensity of certain land uses.
- Tokyo, Japan: In Tokyo, M1 zoning is part of a broader zoning classification called Industrial Use Zone. These zones are designated to promote diverse industrial activities and support the city’s manufacturing sector. M1 zoning in Tokyo specifies permitted uses for factories, warehouses, and research facilities, while also incorporating specific regulations for noise control, building height limitations, and environmental protection.
- Los Angeles, California: The city of Los Angeles has M1 zoning classifications that allow for a wide range of industrial activities, including manufacturing, processing, and distribution. Los Angeles also includes specific provisions for environmentally sensitive industries, such as waste management and recycling facilities, to ensure the proper handling and disposal of materials. Additionally, Los Angeles’ zoning regulations encourage the use of sustainable building practices and energy-efficient technologies.
- Sydney, Australia: In Sydney, M1 zoning falls under the general Industrial zoning category. M1 zones are intended primarily for light and medium industrial uses, focusing on manufacturing, warehousing, assembling, and logistics operations. Sydney’s zoning regulations also account for noise and environmental impacts and require adherence to specific design guidelines to minimize the potential effects on nearby residential areas.
- Berlin, Germany: In Berlin, M1 zoning is part of a larger zoning framework known as Specialized Commercial and Industrial Areas. M1 zones permit manufacturing, storage, and craft-related activities. Berlin’s M1 zoning regulations emphasize the integration of sustainable practices, energy efficiency, and renewable energy sources in industrial development. The city also promotes mixed-use development within M1 zones to create a dynamic and vibrant urban environment.
These examples provide a glimpse into how different cities approach M1 zoning with various considerations and priorities. The specific regulations and guidelines in each city reflect the unique characteristics and needs of the local community, while aiming to balance the growth of industrial activities with environmental protection, community well-being, and sustainable development.
It is important to note that these examples are just a small representation of the diverse approaches to M1 zoning worldwide, and each city will have its own specific regulations tailored to its context and goals.
Conclusion
M1 zoning, or Manufacturing District zoning, plays a critical role in urban planning and development by designating specific areas for industrial and manufacturing activities. Through its regulations and guidelines, M1 zoning ensures a balance between economic growth, environmental protection, public safety, and community well-being.
M1 zoning provides several benefits, including optimal land use allocation, economic growth, environmental protection, infrastructure planning, increased public safety, and promotion of innovation. By designating specific areas for industrial activities, M1 zoning helps cities efficiently manage industrial growth, attract investment, and create employment opportunities.
However, M1 zoning also has its challenges and concerns. Conflicts with residential and commercial areas, environmental considerations, infrastructure demands, land availability and cost, community engagement, and adaptability to changing industries are some of the key challenges associated with this type of zoning. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, community involvement, and adaptive management to ensure a sustainable and harmonious coexistence between industrial activities and neighboring land uses.
Examples of M1 zoning regulations in different cities highlight the diverse approaches to industrial zoning based on local priorities, land availability, and community needs. Each city adapts M1 zoning regulations to its unique context, striving to strike a balance between supporting industrial growth, protecting the environment, and fostering community well-being.
In conclusion, M1 zoning serves as a crucial tool for responsible and sustainable industrial development. By effectively implementing and managing M1 zoning, cities can create designated areas where industrial activities can thrive, while safeguarding the environment, maintaining public safety, and promoting the overall prosperity and quality of life for their communities.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is M1 Zoning
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “What Is M1 Zoning”