Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>What Is Safety Glass


Interior Design Trends
What Is Safety Glass
Published: February 3, 2024
Discover the latest interior design trends with safety glass, a stylish and practical choice for modern homes. Learn how safety glass enhances both aesthetics and security.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Safety glass is an essential component of modern architecture and interior design, offering a blend of functionality, aesthetics, and most importantly, protection. As the name suggests, safety glass is designed to minimize the risk of injury in the event of breakage, making it a crucial element in various structures and applications. From residential homes to commercial buildings, safety glass plays a pivotal role in ensuring the well-being of occupants while adding a touch of sophistication to the overall design.
The evolution of safety glass has revolutionized the way we perceive and utilize glass in our surroundings. Gone are the days when traditional glass posed significant hazards due to its propensity to shatter into sharp, dangerous shards upon impact. With safety glass, the inherent fragility of conventional glass is mitigated, offering a reliable solution that prioritizes safety without compromising on visual appeal.
In this comprehensive exploration of safety glass, we will delve into its definition, various types, functionality, applications, and the myriad benefits it brings to the table. By understanding the intricacies of safety glass, one can gain a deeper appreciation for its significance in contemporary design and construction. Let's embark on a journey to unravel the secrets behind this innovative material and discover the unparalleled advantages it offers in enhancing both safety and style.
Key Takeaways:
- Safety glass is a special type of glass that minimizes the risk of injury when it breaks. It comes in different types like tempered, laminated, and bullet-resistant, offering enhanced protection in various settings.
- Safety glass enhances safety, durability, and aesthetics in architecture, automotive, and interior design. It minimizes injury risks, deters vandalism, and complies with safety standards, making it an essential element in modern construction.
Read more: What Is A Home Safety Walkthrough
Definition of Safety Glass
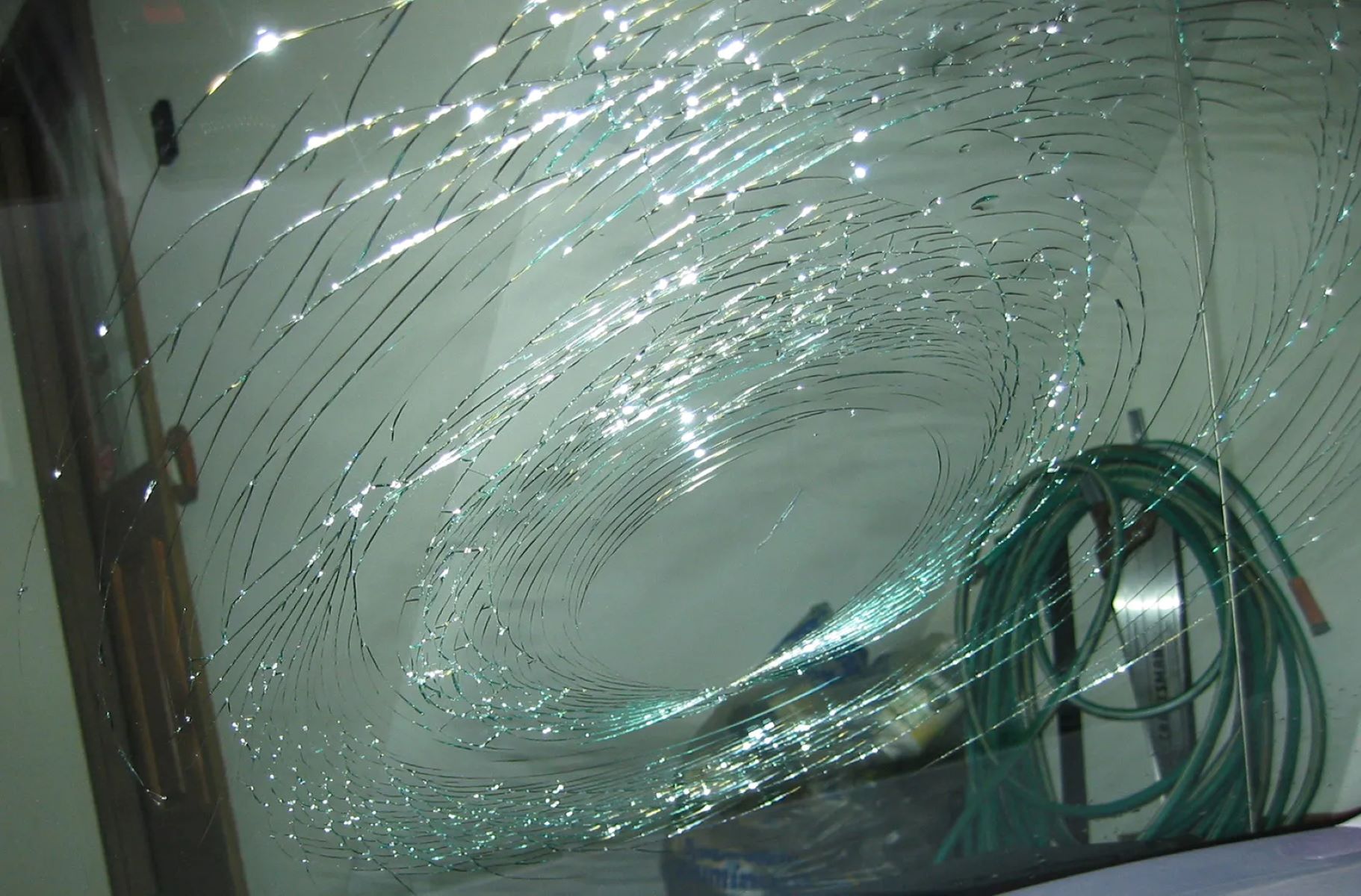
Safety glass is a specialized type of glass that is designed to minimize the risk of injury when it breaks. Unlike traditional annealed glass, which shatters into sharp, jagged pieces upon impact, safety glass is engineered to hold together when broken, reducing the likelihood of severe injuries caused by flying or falling glass shards. This unique characteristic is achieved through various manufacturing processes and the incorporation of specific materials, resulting in a durable and resilient glass product that offers enhanced protection.
The primary purpose of safety glass is to enhance safety in environments where glass breakage is a potential hazard. This includes but is not limited to, architectural applications such as windows, doors, skylights, and glass partitions, as well as automotive windshields, shower enclosures, and glass tabletops. By minimizing the risk of injury associated with glass breakage, safety glass contributes to creating secure and reliable spaces for occupants, thereby aligning with modern safety standards and regulations.
There are different standards and regulations governing the production and use of safety glass, ensuring that it meets specific criteria for impact resistance and structural integrity. These standards may vary depending on the intended application of the safety glass, with different requirements for architectural, automotive, or industrial use. Compliance with these standards is crucial to guarantee the effectiveness of safety glass in safeguarding individuals and property in the event of breakage.
In essence, safety glass represents a significant advancement in glass technology, offering a proactive approach to mitigating the potential dangers associated with glass breakage. By prioritizing safety without compromising on transparency or aesthetics, safety glass has become an indispensable element in modern design and construction, catering to the evolving needs of safety-conscious consumers and industry professionals alike.
Types of Safety Glass
Safety glass encompasses various types, each tailored to specific applications and performance requirements. Understanding the distinct characteristics of these types is essential for selecting the most suitable option based on the intended use and environmental factors. The following are the primary types of safety glass:
-
Tempered Glass: Also known as toughened glass, tempered glass is created through a process of controlled thermal or chemical treatments. This results in increased strength and resistance to impact. When tempered glass breaks, it fractures into small, granular pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing the risk of severe injuries. It is commonly used in architectural applications such as doors, windows, and shower enclosures, as well as in automotive and electronic devices.
-
Laminated Glass: Laminated glass is composed of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). This construction allows the glass to hold together when shattered, offering enhanced protection against forced entry, impact, and even sound transmission. Laminated glass is widely used in architectural settings, including skylights, canopies, and balustrades, as well as in automotive windshields.
-
Wire-Embedded Glass: This type of safety glass features a layer of wire mesh embedded within the glass pane. The wire mesh holds the glass together upon breakage, preventing it from disintegrating into hazardous fragments. While less common in modern applications, wire-embedded glass is still utilized in specific industrial and security contexts where added reinforcement is necessary.
-
Acrylic Glass: Also referred to as acrylic or plexiglass, this is a type of thermoplastic that offers exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity. While not technically glass, acrylic panels are often used as a safety glass alternative due to their shatter-resistant properties. Acrylic glass is prevalent in settings requiring lightweight, durable glazing, such as in public transportation vehicles, sports arenas, and protective barriers.
-
Bullet-Resistant Glass: Designed to withstand ballistic impact, bullet-resistant glass is engineered to provide protection against firearms and explosive threats. It is composed of multiple layers of glass and thermoplastic interlayers, offering varying levels of resistance based on specific threat levels. Commonly employed in high-security environments, such as banks, government buildings, and military vehicles, bullet-resistant glass exemplifies the pinnacle of safety glass technology.
Each type of safety glass offers distinct advantages and is tailored to address specific safety concerns, making it crucial to assess the unique requirements of each application when selecting the appropriate type of safety glass. By leveraging the diverse characteristics of these safety glass variants, designers, architects, and engineers can effectively enhance safety while elevating the aesthetic and functional aspects of their projects.
How Safety Glass Works
Safety glass operates on the principle of controlled fragmentation, ensuring that in the event of breakage, the glass remains intact and minimizes the risk of injury. The functionality of safety glass is achieved through its unique composition and manufacturing processes, which impart specific properties that differentiate it from traditional annealed glass.
Tempered Glass
Tempered glass is created through a process of rapid heating and cooling, resulting in increased surface compression and edge strength. This thermal tempering induces balanced internal stresses within the glass, enhancing its resistance to impact. When tempered glass is subjected to excessive force, it fractures into small, granular pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing the likelihood of severe injuries. This controlled fragmentation is a result of the internal stress distribution, which causes the glass to disintegrate into small, relatively harmless fragments upon breakage.
Read more: What Is A Home Safety Concern
Laminated Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). The interlayer serves as a cohesive element, holding the glass layers together when shattered. This prevents the glass from breaking into hazardous pieces, as the interlayer maintains the structural integrity of the glass panel. The cohesive nature of laminated glass ensures that even when broken, the glass remains in place, reducing the risk of injuries from flying or falling glass fragments.
Wire-Embedded Glass
Wire-embedded glass incorporates a layer of wire mesh within the glass pane, providing reinforcement and containment in the event of breakage. The wire mesh acts as a barrier, preventing the glass from disintegrating into sharp shards. This type of safety glass is particularly effective in containing glass fragments, minimizing the potential harm caused by broken glass.
Acrylic Glass
Acrylic glass, although not a traditional glass material, offers exceptional impact resistance and shatterproof properties. Its composition as a thermoplastic allows it to withstand significant force without shattering into hazardous fragments. In the event of breakage, acrylic glass tends to crack rather than shatter, reducing the risk of injury from sharp edges or flying debris.
Bullet-Resistant Glass
Bullet-resistant glass is engineered to withstand ballistic impact, offering protection against firearms and explosive threats. Its multi-layered construction, comprising glass and thermoplastic interlayers, is designed to absorb and dissipate the energy from ballistic impacts, preventing penetration and fragmentation. This specialized form of safety glass exemplifies the highest level of protection, ensuring the safety and security of occupants in high-risk environments.
In summary, the functionality of safety glass is rooted in its ability to resist breakage and minimize the risk of injury through controlled fragmentation and containment. Whether through thermal tempering, lamination, wire reinforcement, or specialized compositions, safety glass serves as a reliable safeguard, offering peace of mind and protection in diverse applications.
Read more: What Is The Westmead Home Safety Assessment
Applications of Safety Glass
Safety glass finds extensive applications across diverse industries and environments, owing to its unparalleled protective properties and versatility. From architectural marvels to everyday essentials, the utilization of safety glass has redefined safety standards and elevated the functionality and aesthetics of various structures and products.
Architectural Glazing
In the realm of architecture, safety glass is a cornerstone of modern glazing solutions. It is widely employed in the construction of windows, doors, skylights, and glass facades, where its impact resistance and safety features enhance the structural integrity of buildings while allowing natural light to permeate interior spaces. The use of laminated glass in balustrades and canopies further ensures the safety of occupants, offering protection against accidental falls and impact.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector extensively utilizes safety glass in the form of windshields, side windows, and rear windows. Tempered glass is commonly employed in side and rear windows, providing enhanced safety by minimizing the risk of injury in the event of breakage. Laminated glass, with its ability to hold together upon impact, is the material of choice for windshields, offering protection and structural support in the event of collisions.
Interior Design and Decor
In interior design, safety glass serves as a versatile and stylish material for various applications. From sleek glass partitions and shower enclosures to contemporary glass tabletops and shelving, safety glass adds a touch of sophistication while ensuring safety and durability. Its use in decorative elements such as glass railings and partitions contributes to open, light-filled interiors while maintaining a secure environment.
Read more: What Should Be In A Home Safety Kit
Public Spaces and Infrastructure
Public spaces and infrastructure benefit from the implementation of safety glass in numerous ways. Bus shelters, train stations, and airport terminals utilize safety glass for its resilience and safety features, providing protection against vandalism and ensuring the well-being of commuters. Additionally, safety glass is employed in public art installations, creating visually stunning yet secure exhibits that withstand environmental elements and human interaction.
Security and High-Risk Environments
In high-security environments, such as banks, government buildings, and military installations, the use of bullet-resistant glass is imperative. This specialized form of safety glass offers unparalleled protection against ballistic threats, safeguarding personnel and assets in critical settings. Furthermore, the incorporation of laminated glass in security doors and windows enhances the resistance to forced entry, reinforcing the security infrastructure of sensitive facilities.
Retail and Commercial Displays
The retail and commercial sectors leverage safety glass for product displays, showcases, and storefronts, where its durability and safety features enhance the presentation of merchandise while ensuring the security of valuable items. The use of tempered glass in display cases and shelving provides a secure and visually appealing platform for showcasing products, contributing to a safe and engaging shopping experience.
In essence, the applications of safety glass are as diverse as they are essential, permeating various aspects of modern life and design. Its seamless integration into architectural, automotive, interior, and security contexts underscores its pivotal role in enhancing safety, functionality, and visual appeal across a myriad of applications.
Benefits of Safety Glass
Safety glass offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond its primary function of enhancing safety. Its unique properties and versatile applications contribute to a range of advantages that resonate across diverse industries and environments.
Enhanced Safety and Injury Prevention
The foremost benefit of safety glass is its ability to minimize the risk of injury in the event of breakage. Unlike traditional glass, which poses a hazard due to sharp, jagged shards upon impact, safety glass remains intact or breaks into relatively harmless fragments, reducing the likelihood of severe injuries. This feature is particularly crucial in architectural settings, automotive applications, and public spaces, where the safety of occupants and users is paramount.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Safety glass exhibits exceptional resistance to impact, making it highly durable and resilient in various scenarios. Whether subjected to environmental forces, accidental collisions, or deliberate attempts at damage, safety glass maintains its structural integrity, offering long-term reliability and protection. This durability contributes to cost savings and reduced maintenance requirements, making safety glass a practical and sustainable choice for architectural and automotive applications.
Security and Vandalism Prevention
In addition to safeguarding against accidental breakage, safety glass serves as a deterrent to vandalism and forced entry. Laminated glass and bullet-resistant glass variants provide enhanced security measures, offering protection against intrusions and criminal activities. This benefit is particularly significant in high-risk environments, retail displays, and public infrastructure, where the integrity of glass installations is crucial to maintaining security and order.
Sound Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Certain types of safety glass, such as laminated glass, contribute to sound insulation and energy efficiency in architectural settings. By reducing external noise transmission and enhancing thermal insulation, safety glass creates a more comfortable and sustainable indoor environment. This benefit aligns with modern design principles focused on occupant well-being and environmental responsibility, making safety glass an integral component of energy-efficient and acoustically optimized structures.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Safety glass offers unparalleled design flexibility, allowing architects, designers, and engineers to explore innovative and visually striking applications. From expansive glass facades to intricate interior partitions, safety glass enables the creation of open, light-filled spaces while maintaining safety and security. Its transparency, clarity, and adaptability to various forms and finishes make safety glass a preferred choice for contemporary design and decor, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of architectural and interior elements.
Compliance with Safety Standards and Regulations
By utilizing safety glass, designers and builders can ensure compliance with industry-specific safety standards and regulations. This adherence to established guidelines not only reinforces the safety and reliability of structures and products but also instills confidence in occupants, users, and regulatory authorities. The assurance of meeting safety requirements underscores the value of safety glass as an indispensable component in modern construction and design practices.
In summary, the benefits of safety glass encompass a wide spectrum of advantages, ranging from fundamental safety enhancements to design versatility and regulatory compliance. Its multifaceted contributions to safety, security, sustainability, and aesthetics position safety glass as an indispensable material that continues to shape and elevate the built environment across global industries and applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, safety glass stands as a testament to human ingenuity and innovation, redefining the boundaries of glass technology and safety standards. From its inception to its widespread integration across diverse industries, safety glass has transcended conventional limitations, offering a harmonious blend of protection, functionality, and aesthetic appeal.
The evolution of safety glass has not only addressed inherent safety concerns associated with traditional glass but has also unlocked new possibilities in architectural design, automotive engineering, interior decor, and security infrastructure. Its ability to withstand impact, resist breakage, and enhance security has revolutionized the way we perceive and utilize glass in our surroundings, paving the way for safer, more sustainable built environments.
As safety regulations and design principles continue to prioritize occupant safety and well-being, the significance of safety glass in shaping modern structures and products cannot be overstated. Its role in mitigating injury risks, enhancing security, and contributing to energy-efficient, acoustically optimized spaces underscores its pivotal position in contemporary design and construction practices.
Looking ahead, the continued advancements in safety glass technology, coupled with its adaptability to evolving design trends and sustainability imperatives, are poised to further elevate its impact across global industries. The seamless integration of safety glass into architectural marvels, automotive innovations, public infrastructure, and interior spaces will continue to exemplify the convergence of safety, style, and performance.
In essence, safety glass serves as a testament to the unwavering commitment to safety and innovation, embodying the collective pursuit of creating secure, inspiring, and sustainable environments for generations to come. Its enduring legacy as a cornerstone of modern design and construction reaffirms its indispensable role in shaping the future of safety-conscious, visually captivating, and resilient built environments.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Safety Glass
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “What Is Safety Glass”