Home>Furniture>Bedroom Furniture>How Long Does It Take For Bed Bug Eggs To Hatch


Bedroom Furniture
How Long Does It Take For Bed Bug Eggs To Hatch
Modified: October 28, 2024
Learn how long it takes for bed bug eggs to hatch in your bedroom furniture. Discover the timeline and take action to prevent an infestation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction:
Bed bugs are resilient pests that can cause a great deal of frustration and discomfort. These tiny insects, known scientifically as Cimex lectularius, have been a nuisance to humans for centuries. Infestations can result in itchy bites, sleepless nights, and a sense of unease in our own homes.
Understanding the life cycle of bed bugs is crucial in managing and eliminating these pests. Knowing when their eggs hatch can help individuals and pest control professionals develop effective strategies for eradication. In this article, we will explore the fascinating process of bed bug egg development and dive into the question: how long does it take for bed bug eggs to hatch?
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s briefly explore the life cycle of a bed bug. Bed bugs go through several stages of development, starting from eggs and progressing into nymphs and finally adult bugs. This life cycle, from egg to adult, is known as simple metamorphosis.
Understanding the bed bug life cycle is vital for effective pest control. By targeting different stages of development, such as eggs and nymphs, we can disrupt their reproductive cycle and reduce their numbers. However, to effectively combat bed bugs, we must first comprehend the intricate process of egg incubation and hatching.
Key Takeaways:
- Bed bug eggs typically hatch within 6 to 10 days, influenced by temperature, humidity, and blood meal availability. Understanding these factors aids in effective pest management and eradication.
- Signs of hatching bed bug eggs include empty eggshells, small nymphs, blood stains, increased activity, and continued bites. Prompt action and vigilance are crucial in managing infestations.
Read more: How Long Does It Take To Notice Bed Bugs
Bed Bug Life Cycle:
The life cycle of a bed bug consists of five stages: egg, nymph, and adult. Let’s explore each stage to gain a better understanding of how these pests develop.
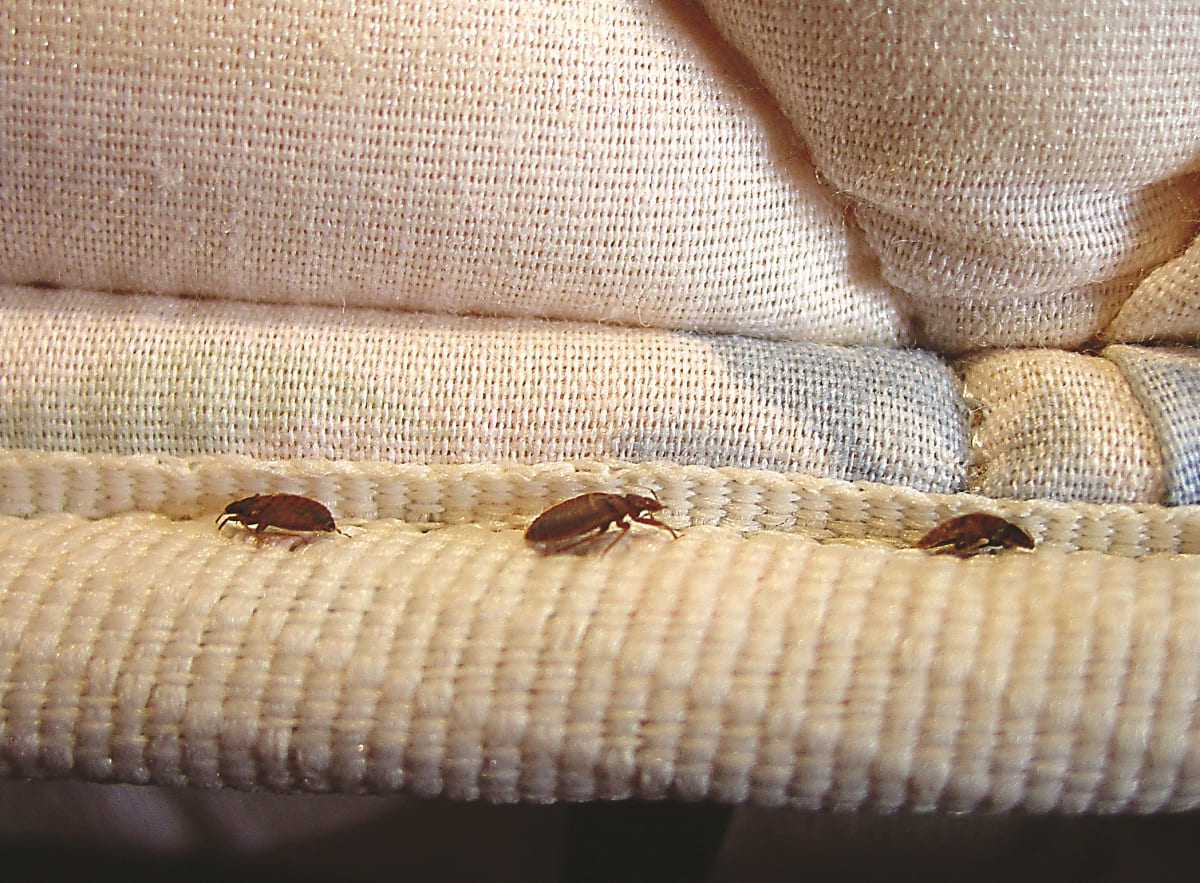
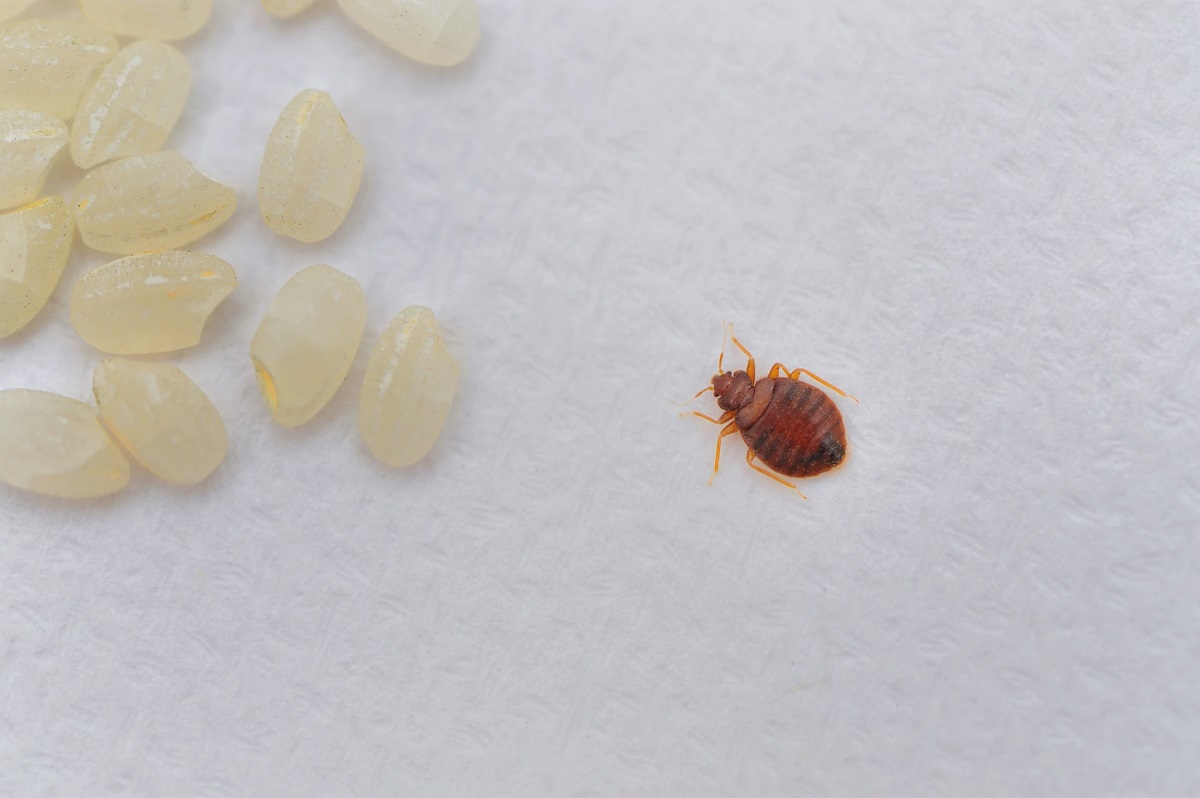
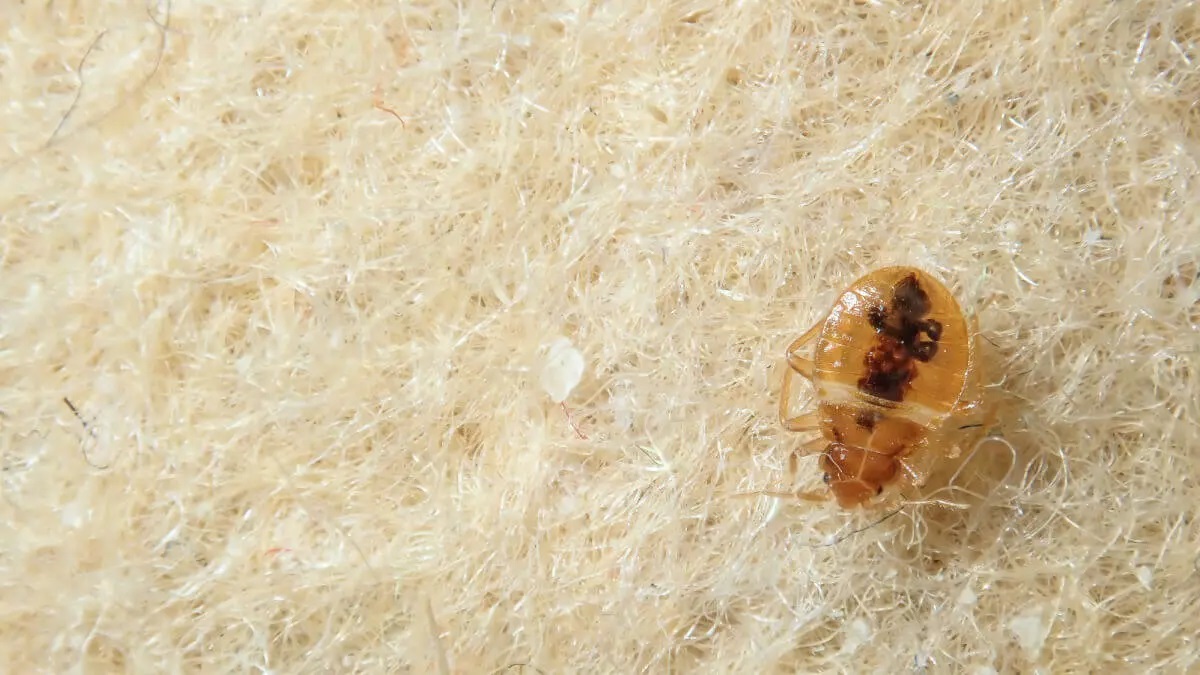
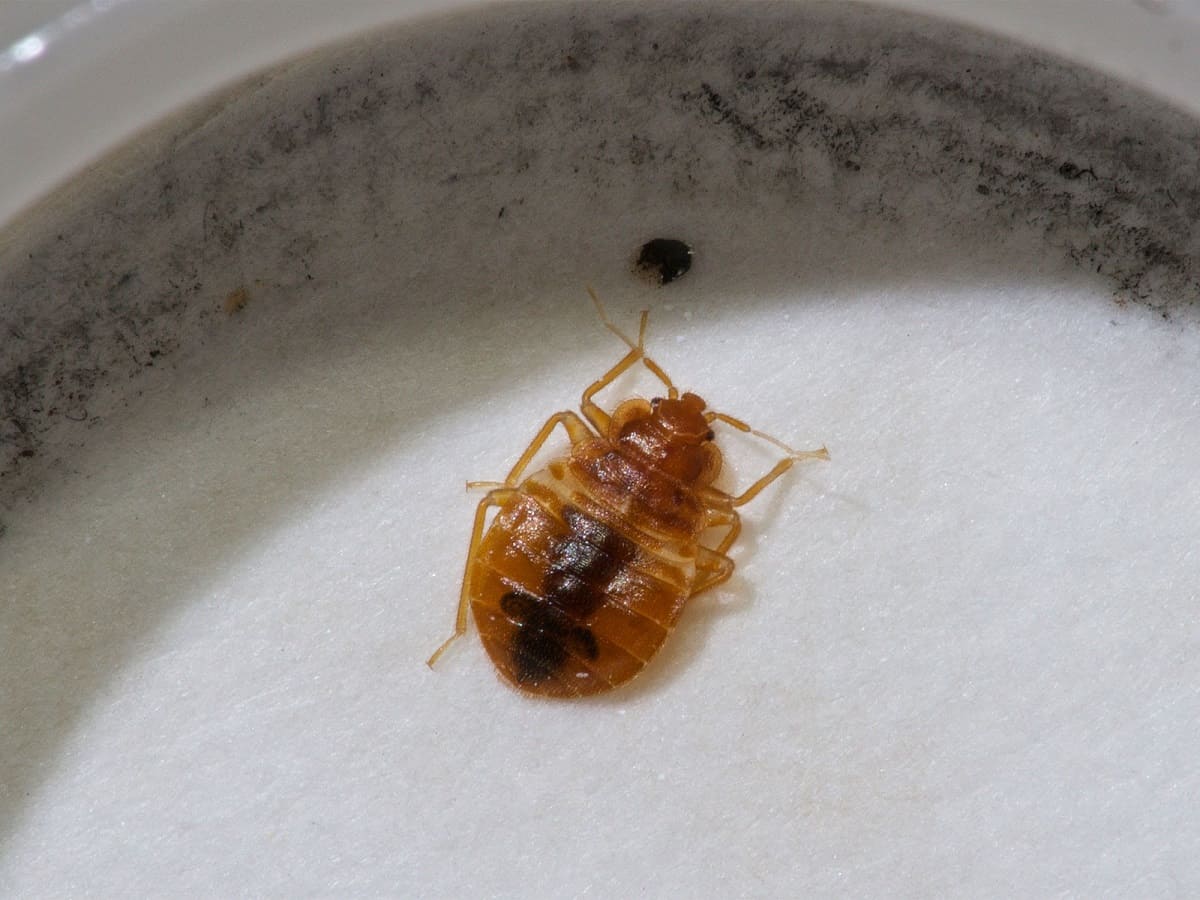
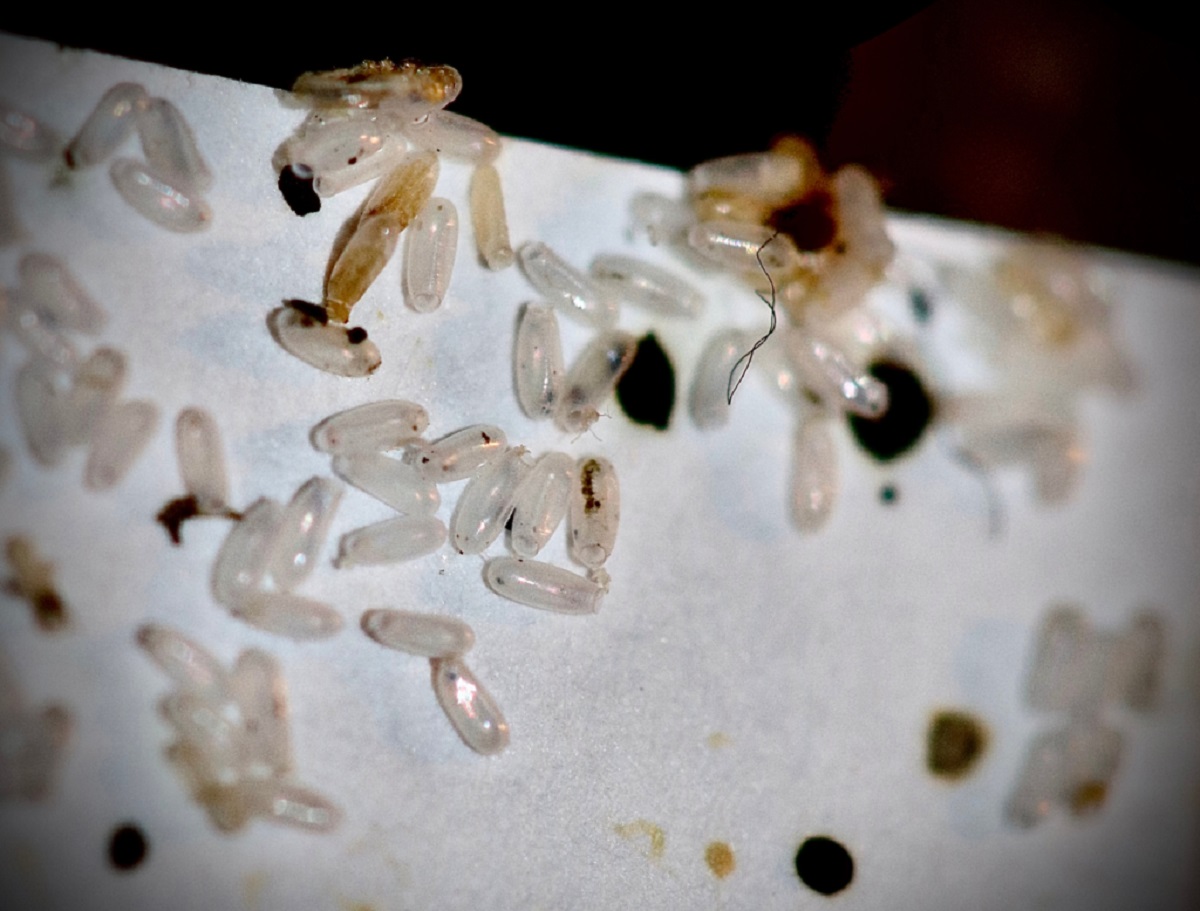
- Egg: The bed bug life cycle begins with an egg. After mating, female bed bugs lay tiny, translucent eggs in secluded areas, such as cracks and crevices, close to their feeding source. A female bed bug can lay up to 200 eggs in her lifetime. These eggs are roughly the size of a pinhead and are difficult to spot without magnification.
- Nymph: Once the eggs are laid, they go through a process called incubation. After about one to two weeks, nymphs hatch from the eggs. Nymphs resemble smaller versions of adult bed bugs but are lighter in color and lack wings. Like adult bed bugs, nymphs require regular blood meals to molt and reach the next stage of development.
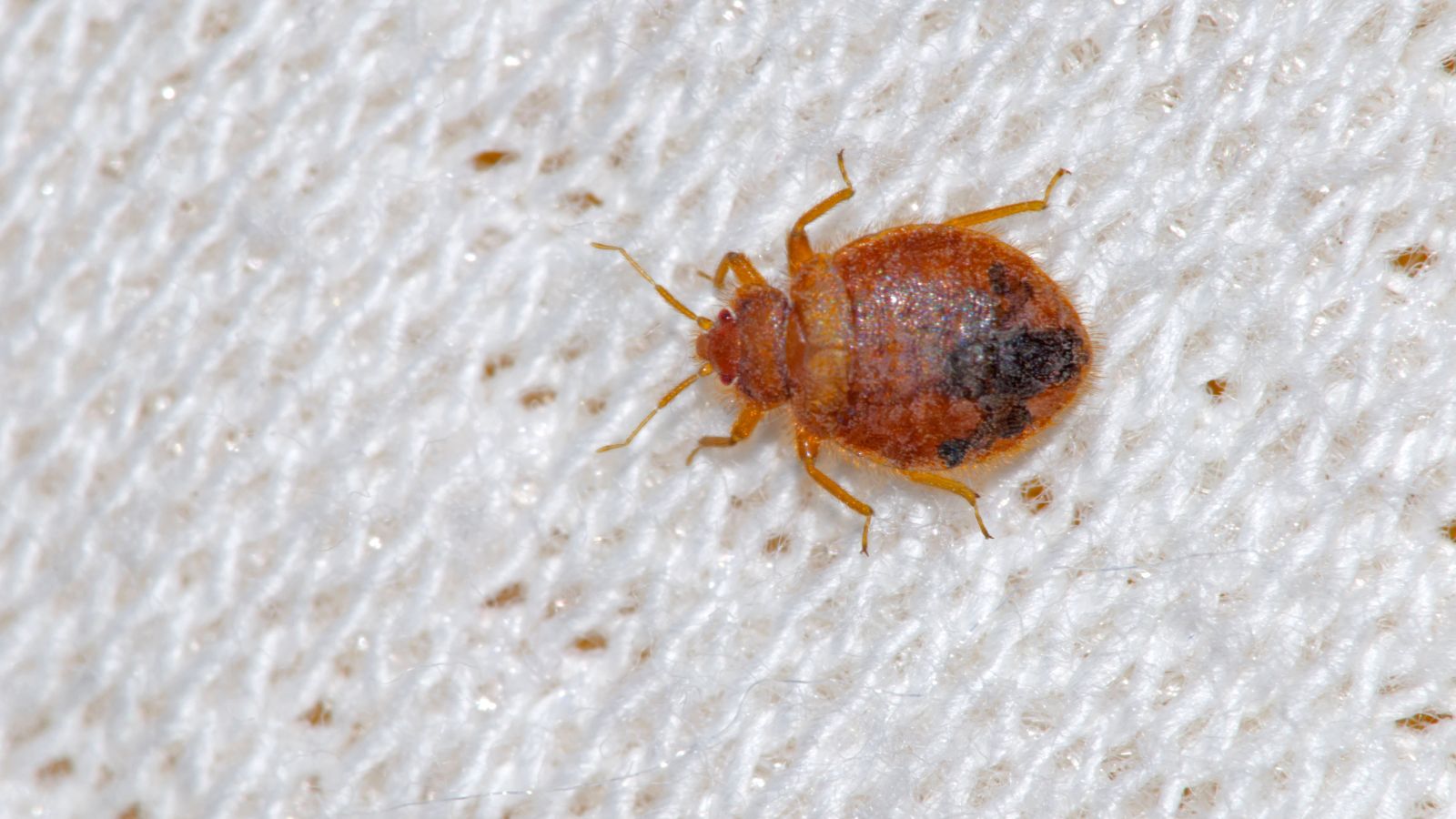
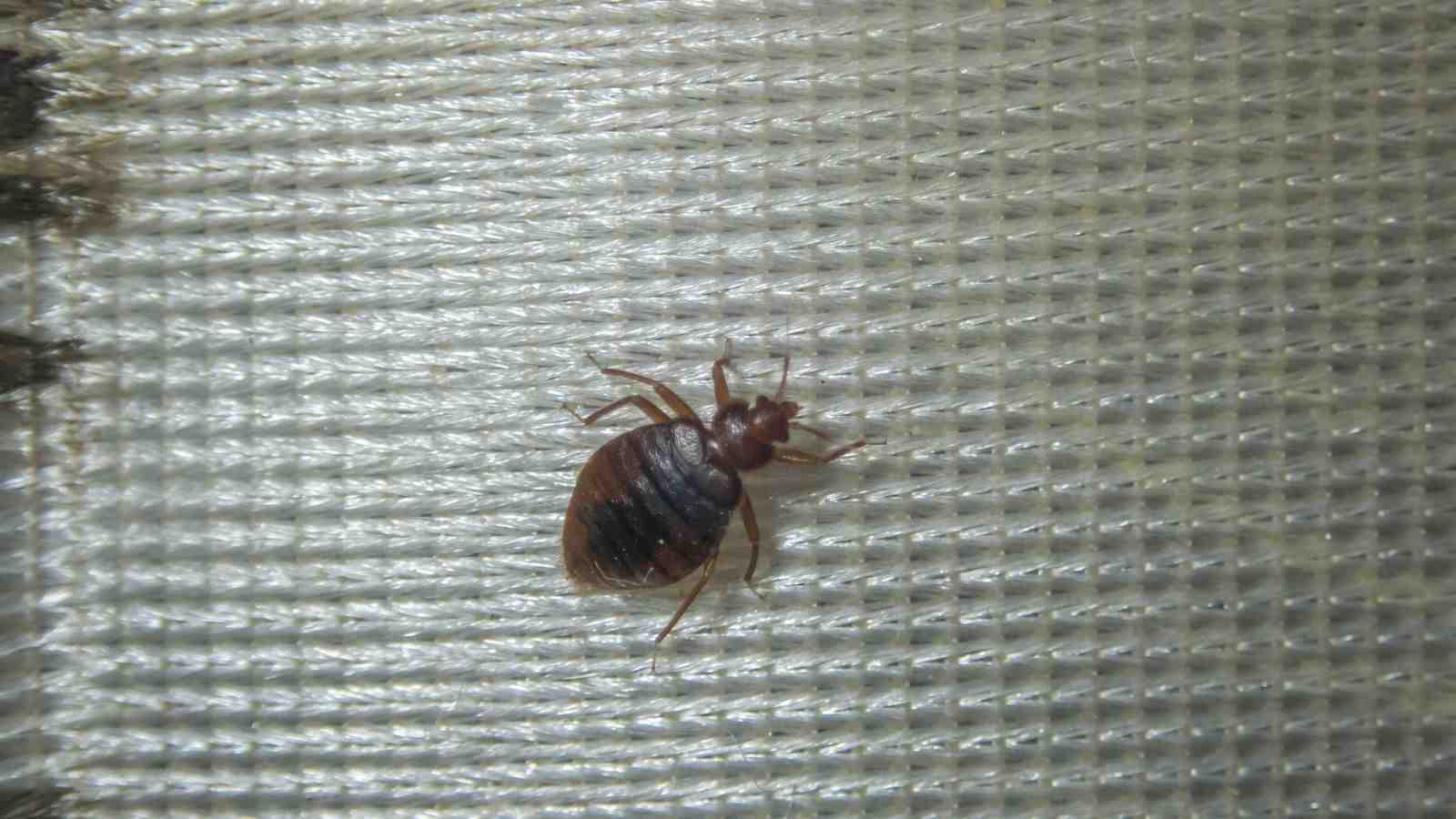
- Adult: Nymphs go through several molting stages, shedding their exoskeletons as they grow. After each molt, they become larger and darker in color. It takes five molts for a nymph to reach adulthood. Once mature, adult bed bugs are about the size of an apple seed, reddish-brown in color, and have distinct bodies with a flat, oval shape.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the bed bug life cycle, let’s focus on the crucial stage of egg development and hatching.
Bed Bug Egg Development:
Bed bug eggs are a crucial stage in their life cycle and play a significant role in their proliferation. Understanding the development process of these eggs is key to combatting infestations effectively.
After a female bed bug lays her eggs, they undergo a process known as incubation. This period is when the eggs develop and eventually hatch into nymphs. The duration of the incubation period can vary depending on several factors.
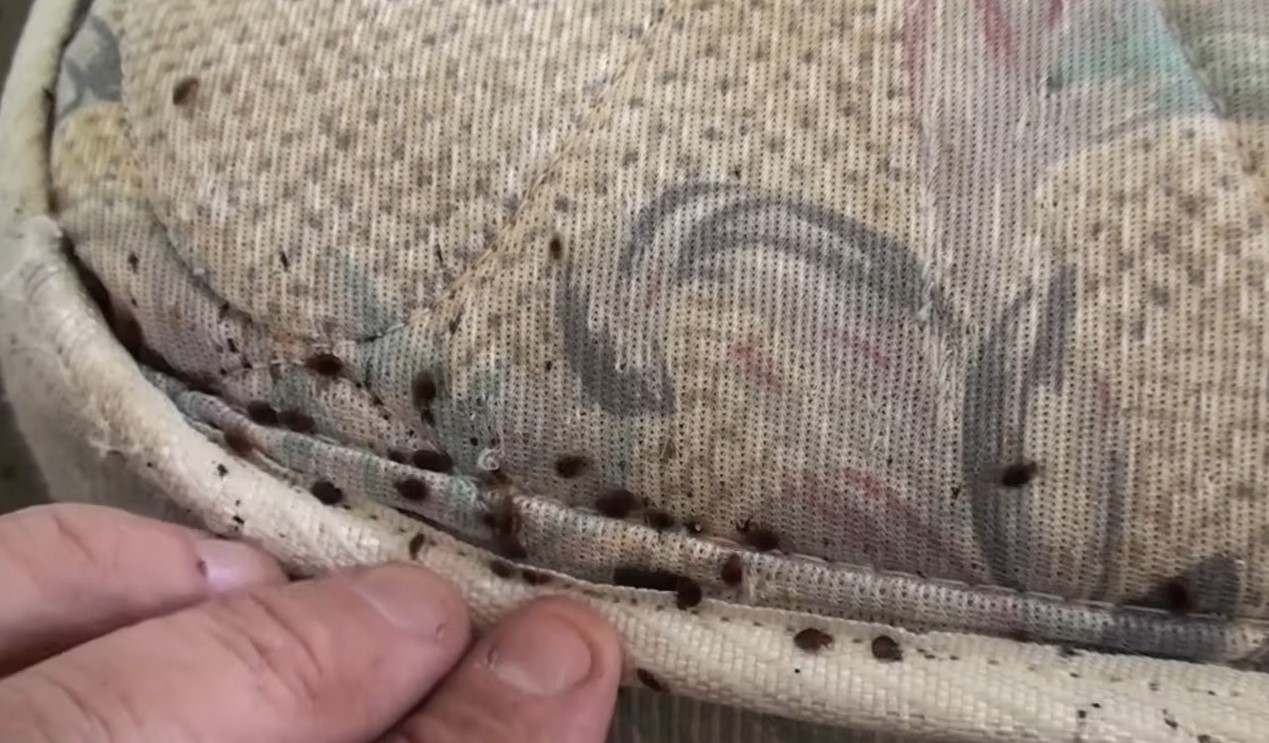
Bed bug eggs are tiny, approximately 1mm in size, and are usually laid in clusters. The female bed bug uses a sticky substance to attach the eggs to surfaces close to their harborage areas. Common locations for egg deposition include mattress seams, cracks in furniture, and wall voids.
The incubation period for bed bug eggs typically ranges from 6 to 10 days, but it can be influenced by several factors.
Temperature: Temperature plays a crucial role in the development of bed bug eggs. Ideally, bed bugs prefer a temperature of around 70°F to 80°F (21°C to 27°C). In warmer conditions, the eggs may hatch faster, while cooler temperatures can extend the incubation period.
Humidity: The humidity level also affects bed bug egg development. These pests thrive in moderate to high humidity environments, with an optimal range of 70% to 80% humidity. Higher humidity levels may expedite egg hatching, while low humidity can delay it.
Availability of Blood Meal: Bed bugs require a blood meal to develop and molt into the next stage. The presence of a readily available host can accelerate egg development and hatch time. Conversely, if a blood meal is scarce, the eggs may take longer to hatch.
Genetics: The genetics of bed bugs can influence the duration of the incubation period as well. Different populations of bed bugs may have variations in their development time, with some eggs hatching faster than others.
It is worth noting that bed bug eggs are resilient and can survive for several weeks even in unfavorable conditions. This survival mechanism allows them to withstand periods without a blood meal and survive the application of pesticides.
Now that we understand the factors that affect bed bug egg development, let’s explore the average time it takes for bed bug eggs to hatch.
Factors Affecting Egg Incubation Period:
The incubation period of bed bug eggs can vary based on several factors. Understanding these factors can help us predict and control the hatching time of bed bug eggs, facilitating more effective pest management strategies.
1. Temperature: Temperature is a critical factor influencing the incubation period of bed bug eggs. Higher temperatures accelerate egg development, while lower temperatures slow it down. The optimal temperature range for bed bug egg incubation is approximately 70°F to 80°F (21°C to 27°C).
2. Humidity: Bed bugs prefer moderate to high humidity environments. Elevated humidity levels can expedite egg hatching, while low humidity can delay it. The ideal humidity range for bed bug egg development is around 70% to 80%. A dry environment can prolong the incubation period.
3. Availability of Blood Meal: Bed bugs require a blood meal in order to develop and hatch. The presence of a readily available host can accelerate the incubation period, while a scarcity of blood meals can delay it. Without a blood meal, the eggs may take longer to hatch or may not hatch at all.
4. Genetics: The genetic makeup of bed bugs can also influence the duration of the incubation period. Different populations may have variations in their development time, affecting how quickly the eggs hatch.
5. Environmental Disturbances: Any disturbances that disrupt the normal conditions of the bed bug’s environment can affect the incubation period. These disturbances may include changes in temperature, humidity, or the availability of blood meals. Bed bugs can detect and respond to these changes, potentially altering the duration of egg incubation.
It’s important to note that bed bug eggs are resilient and can survive for several weeks, even in adverse conditions. They have developed a tolerance to survive without a blood meal and can withstand the application of certain pesticides. This adaptability makes bed bugs challenging to control and eradicate.
By understanding and manipulating these factors, individuals and pest management professionals can potentially expedite or delay the hatching of bed bug eggs. Utilizing this knowledge in conjunction with other pest management strategies can result in more successful and efficient eradication efforts.
Now that we have explored the factors that influence the incubation period, let’s move on to the average time it takes for bed bug eggs to hatch.
Bed bug eggs typically hatch in about 6 to 10 days, but this can vary depending on temperature and other environmental factors. Keep in mind that newly hatched bed bugs will need a blood meal before they can develop into adults.
Average Time for Bed Bug Eggs to Hatch:
The average time for bed bug eggs to hatch can vary depending on various factors, such as temperature, humidity, and the availability of a blood meal. Generally, bed bug eggs take around 6 to 10 days to hatch under optimal conditions.
Temperature plays a significant role in determining the hatching time of bed bug eggs. At temperatures around 70°F to 80°F (21°C to 27°C), bed bug eggs typically hatch within a week. However, cooler temperatures can extend the incubation period, while warmer temperatures can expedite it. In higher temperatures, the eggs may hatch in as little as four to five days, while in cooler temperatures, it may take up to two weeks for them to hatch.
Humidity also affects the hatching time of bed bug eggs. A moderate to high humidity level, ranging from 70% to 80%, is favored by bed bugs for their development. In environments with optimal humidity, the eggs are more likely to hatch within the usual 6 to 10-day timeframe. Conversely, lower humidity levels can delay the hatching process, potentially extending it by a few days or even longer.
The availability of a blood meal is another crucial factor. Bed bug eggs require a blood meal to develop and hatch into nymphs. If a suitable host is readily available, the eggs are more likely to hatch within the expected timeframe. However, if the supply of blood meals is limited, the eggs may take longer to hatch or may not hatch at all until a suitable host is found.
It’s important to note that these estimates represent the average hatching time for bed bug eggs. Individual circumstances, such as variations in temperature, humidity, and the availability of blood meals, can influence the actual hatching time. Additionally, genetic factors may lead to slight variations between bed bug populations, resulting in some eggs hatching slightly earlier or later than the average timeframe.
By understanding the average hatching time, individuals and pest control professionals can plan their treatment strategies accordingly. Monitoring the infested area and ensuring proper temperature and humidity levels can help maximize the effectiveness of eradication efforts.
Now that we know the average time it takes for bed bug eggs to hatch, let’s explore the signs that indicate the hatching of these eggs.
Read more: How Long Does It Take Bed Bugs To Die
Signs of Hatching Bed Bug Eggs:
Although bed bug eggs are quite small and often difficult to see with the naked eye, there are some signs that indicate the hatching of these eggs. By being aware of these signs, you can take prompt action to address a potential infestation.
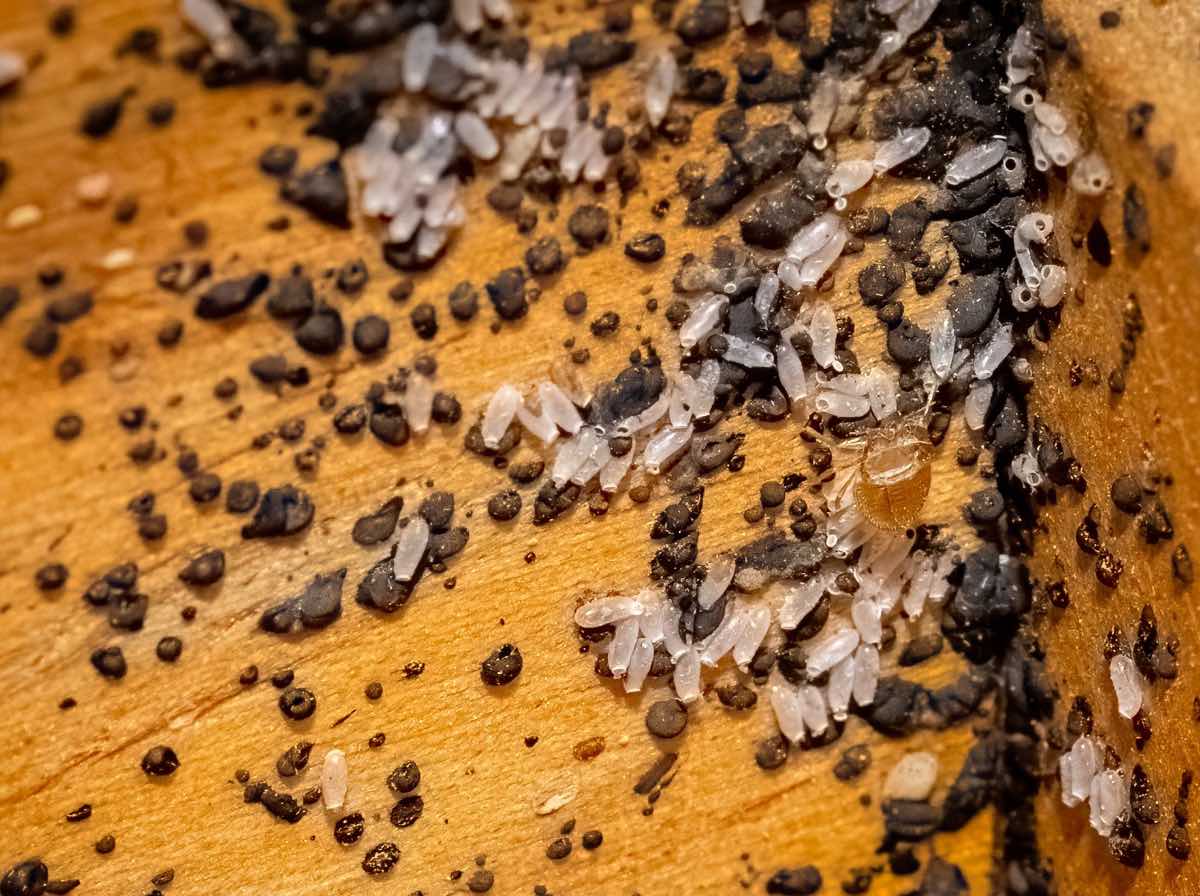
1. Empty Egg Shells: Once bed bug eggs hatch, the nymphs emerge from the eggs, leaving behind empty eggshells. These empty shells are translucent and resemble tiny, pale-colored skins. You may notice them on surfaces where the eggs were laid, such as mattress seams, furniture cracks, or along baseboards.
2. Small, Newly Hatched Nymphs: After hatching, the nymphs are extremely small and almost transparent. They will seek out a blood meal to feed and begin their development into adulthood. Nymphs go through several molting stages, gradually becoming darker in color and larger in size.
3. Blood Stains: As the newly hatched nymphs feed on a host, they may leave behind small blood stains on bedding or upholstery. These stains can appear as small reddish-brown spots or smears. Blood stains, along with the presence of bed bug fecal matter, are a clear indication of an infestation.
4. Increased Bed Bug Activity: Following the hatching of bed bug eggs, there is often an increase in bed bug activity. This may manifest as an increase in bites, sightings of adult bed bugs or nymphs, or the presence of their discarded exoskeletons. Increased activity indicates a growing infestation that requires immediate attention.
5. Continued Bites: If you continue to experience bites even after attempting treatment, there may be newly hatched nymphs in your living space. Bed bug nymphs require frequent blood meals to grow and molt into the next stage, so their presence is often accompanied by lingering bite marks.
Remember that detecting the signs of hatching bed bug eggs may be challenging, as they are often hidden in cracks and crevices. Regular inspections, along with professional assistance if needed, can help identify and address any bed bug activity before it escalates into a full-blown infestation.
By remaining vigilant and taking immediate action upon detecting signs of hatching eggs, you can effectively manage a bed bug infestation and prevent it from spreading to other areas of your home.
Now, let’s explore some preventive measures that can help keep your home free of bed bugs.
Preventing Bed Bug Infestations:
Prevention is key when it comes to dealing with bed bugs. By following some simple preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of a bed bug infestation in your home or prevent a re-infestation after successfully eliminating these pests. Here are some important steps to take:
1. Inspect Secondhand Items: When acquiring secondhand furniture, mattresses, or clothing, thoroughly inspect them for any signs of bed bugs. Check the seams, cracks, and crevices carefully. If possible, consider treating the items before bringing them into your home.
2. Be Cautious When Traveling: Bed bugs are excellent hitchhikers and can easily find their way into your luggage when you stay in infested accommodations. Inspect hotel rooms for signs of bed bugs before unpacking. Keep your luggage elevated and away from the bed. Wash and dry your clothes on high heat as soon as you return home.
3. Seal Cracks and Crevices: Reduce potential hiding spots for bed bugs by sealing cracks and crevices in your walls, baseboards, and furniture. Use caulk or sealant to seal any gaps where bed bugs could potentially hide.
4. Use Protective Covers: Encase mattresses, box springs, and pillows with bed bug-proof covers. These covers are designed to prevent bed bugs from infesting your bedding and make it easier to detect and eliminate any potential infestations.
5. Maintain Cleanliness: Regularly clean your home, paying special attention to areas where bed bugs may hide, such as mattress seams, furniture cracks, and baseboards. Vacuum thoroughly, and dispose of the vacuum bag in a sealed plastic bag outside your home. Wash and dry bedding and clothing on high heat to kill any bed bugs or eggs.
6. Education and Awareness: Stay informed about bed bug prevention techniques and early signs of infestations. Educate yourself and your family members about what bed bugs look like and how they spread. Early detection is crucial in preventing a minor infestation from turning into a major problem.
7. Professional Pest Control: If you suspect or confirm a bed bug infestation, it’s best to seek professional help. Pest control professionals have the knowledge and experience to effectively eliminate bed bugs and help prevent future infestations.
By implementing these preventive measures and staying vigilant, you can significantly reduce the risk of bed bug infestations in your home. Remember, early detection and immediate action are key to preventing these pests from taking over your living space.
Now that you are equipped with knowledge on preventing bed bug infestations, let’s sum up the key points.
Conclusion:
Bed bug infestations can be a source of frustration and discomfort, but by understanding the life cycle of bed bugs, particularly the development and hatching of their eggs, we can take effective steps to prevent and control these pests.
Bed bug eggs play a vital role in the proliferation of infestations. They are small, translucent, and usually laid in clusters in hidden areas. The incubation period for bed bug eggs typically ranges from 6 to 10 days, but it can vary depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, availability of a blood meal, and genetics.
To prevent bed bug infestations, it’s important to seal cracks and crevices, inspect secondhand items, and exercise caution when traveling. Regular cleaning, using protective covers on mattresses and pillows, and staying educated on bed bug prevention techniques are also key preventive measures. If you suspect or confirm an infestation, seeking professional pest control assistance is recommended for effective eradication.
By staying vigilant, detecting signs of hatching bed bug eggs, and taking immediate action, we can effectively manage bed bug infestations and protect our homes from these persistent pests.
Remember, prevention is always better than dealing with a full-blown infestation. By implementing these preventive measures and staying proactive, you can maintain a bed bug-free living environment.
We hope that this article has provided you with valuable insights into bed bug egg development, hatching timeframes, and preventive measures. With this knowledge, you are better equipped to protect your home and loved ones from the nuisance of bed bugs.
Stay informed, stay vigilant, and enjoy a peaceful and bed bug-free environment!
Now that you're equipped with knowledge on tackling bed bug eggs, why stop there? Dealing with pests is a continual battle. For those struggling with unwanted guests in their pantry, our next read offers expert advice on managing these nuisances effectively. Interested in maintaining a pest-free home year-round? Dive into our insightful guide on combating pantry moths, a must-read for any household.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Long Does It Take For Bed Bug Eggs To Hatch
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.