Home>Furniture>Bedroom Furniture>How Many Eggs Do Bed Bugs Lay


Bedroom Furniture
How Many Eggs Do Bed Bugs Lay
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover how many eggs bed bugs lay and their impact on your bedroom furniture. Learn effective strategies to prevent and eliminate bed bug infestations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the fascinating world of bed bug egg-laying behaviors. Bed bugs are not only notorious for their biting tendencies but also for their ability to reproduce rapidly and infest homes and establishments in no time. Understanding their egg-laying habits is crucial in addressing and preventing infestations, making it an essential topic for anyone dealing with these persistent pests.
Bed bugs are small, flat, wingless insects that feed on the blood of animals and humans. They have been a nuisance for centuries, and despite advances in pest control methods, their populations continue to thrive in many parts of the world. One of the key reasons behind their success is their exceptional breeding capabilities.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of bed bug egg-laying behavior and explore various factors that affect the number of eggs they produce. We will also discuss the implications of their prolific egg production and highlight the importance of targeting eggs in controlling bed bug infestations. So, let’s get started by taking a closer look at the bed bug life cycle.
Key Takeaways:
- Bed bugs can lay up to 5 eggs per day, with a single female producing anywhere from 200 to 500 eggs in her lifetime. Their resilience and rapid reproduction make early detection and intervention crucial for effective control.
- Factors such as age, nutrition, and environmental conditions influence bed bug egg production. Targeted strategies, including thorough inspection, vacuuming, heat treatment, and professional pest control, are essential for disrupting their reproductive cycle and preventing infestations.
Read more: What Kills Bed Bugs And Their Eggs
Understanding the Bed Bug Life Cycle
Before we dive into the specifics of bed bug egg-laying behavior, let’s first gain a basic understanding of their life cycle. Like all insects, bed bugs go through a process called metamorphosis, which consists of distinct life stages: egg, nymph, and adult.
The life cycle of a bed bug typically takes about 6 to 10 weeks, but it can vary depending on various factors such as temperature and food availability. Female bed bugs can lay hundreds of eggs in their lifetime, making their reproductive abilities a critical factor in the rapid spread of infestations.
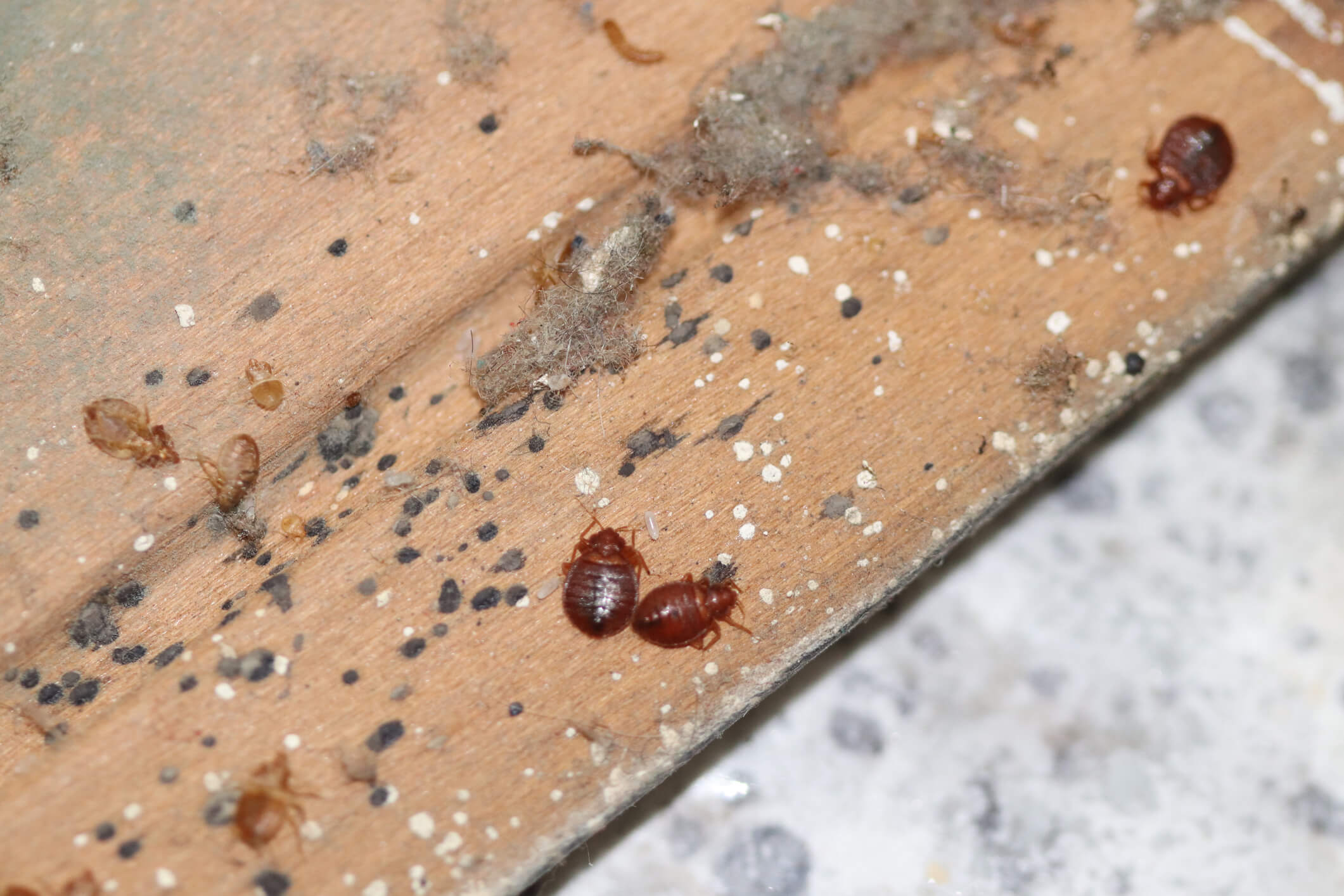
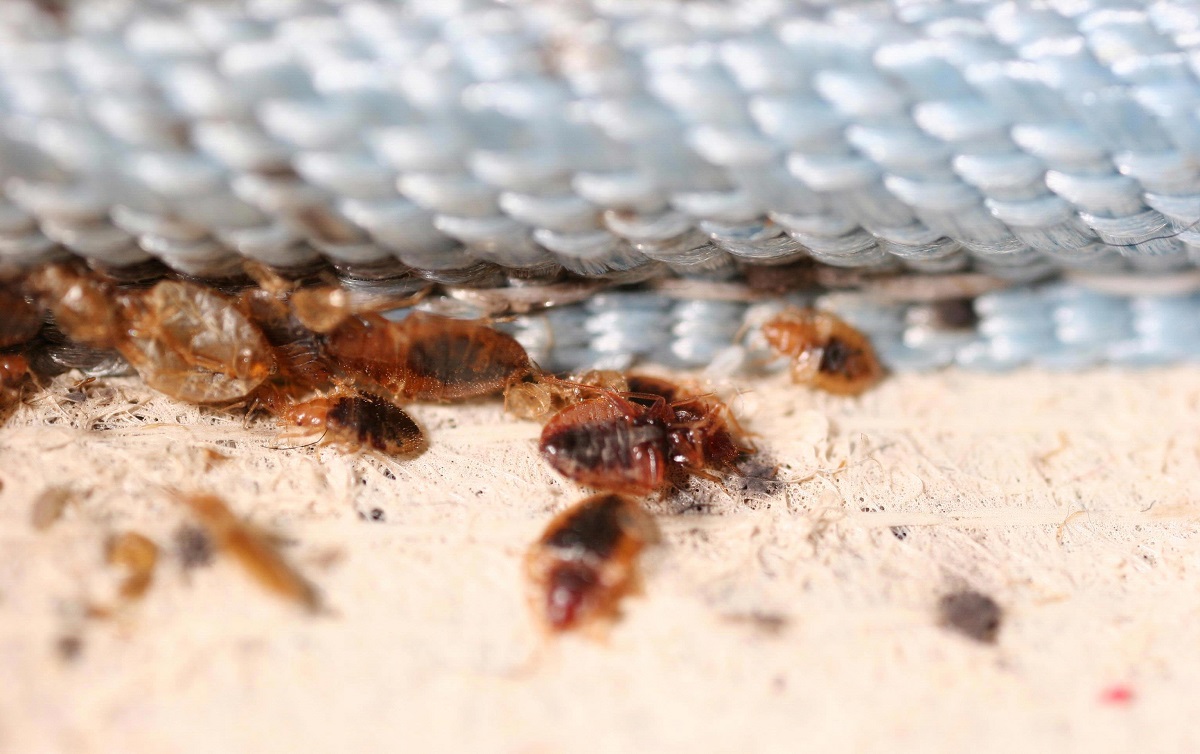
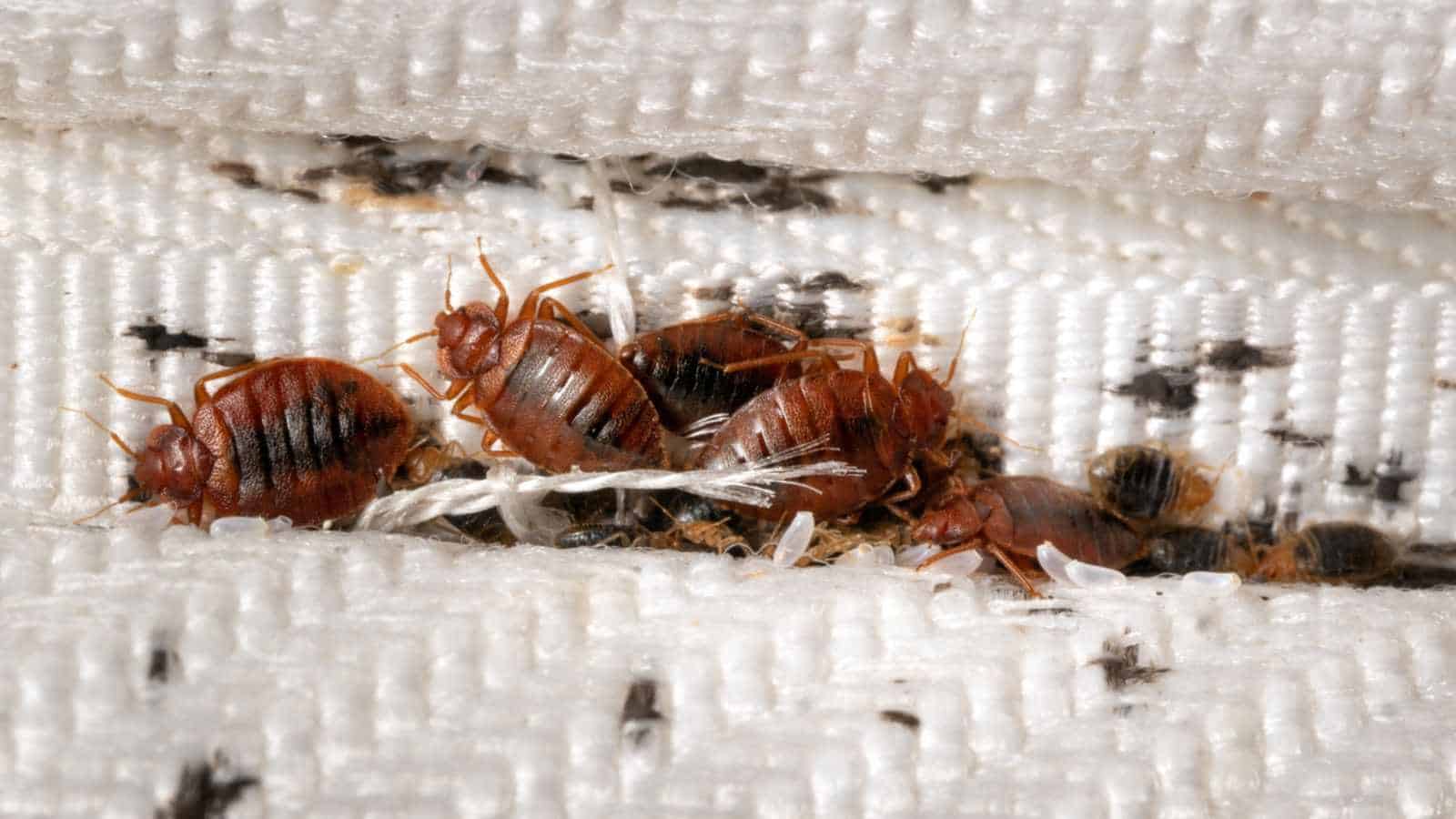
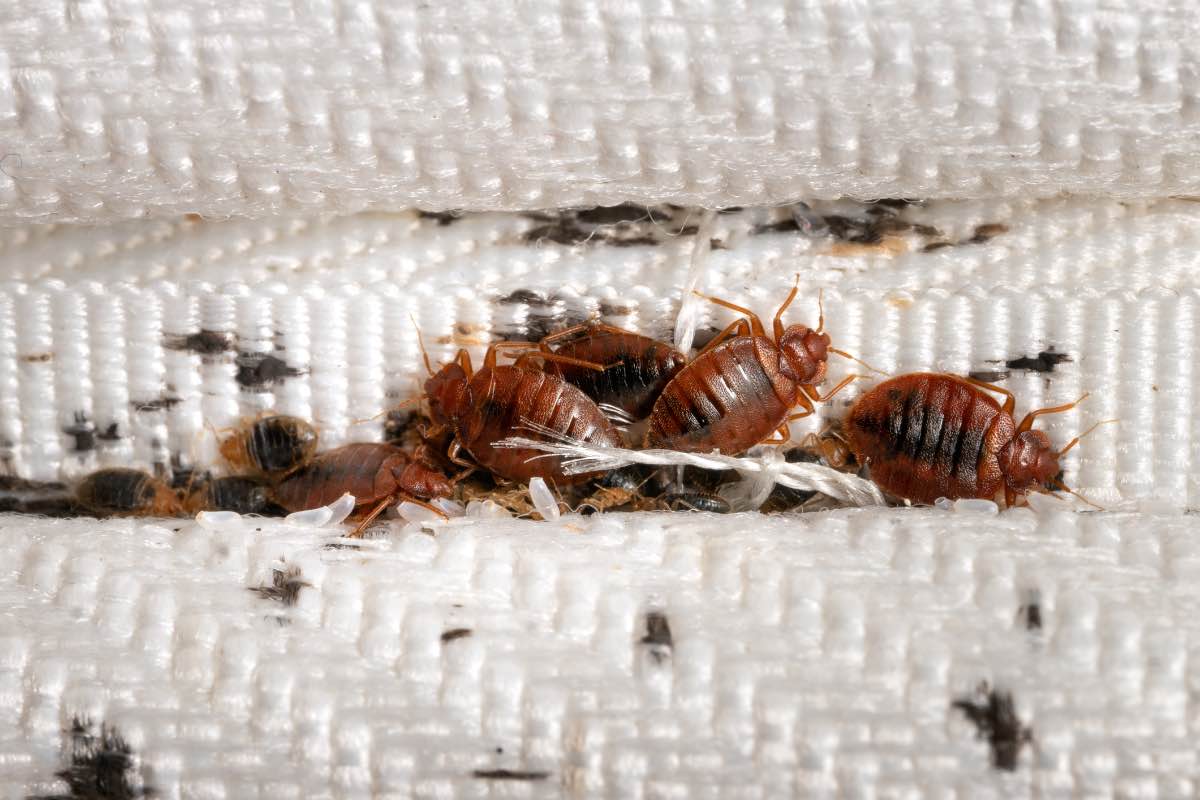
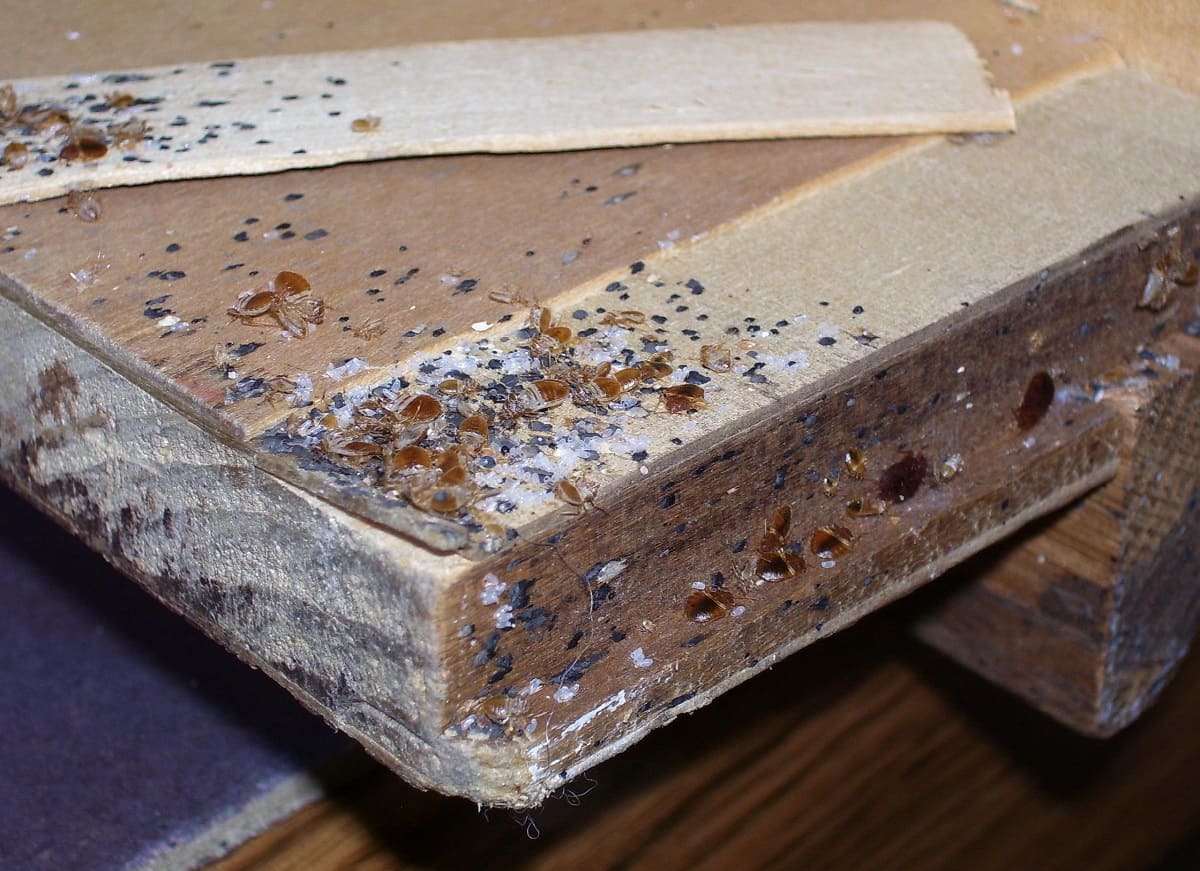
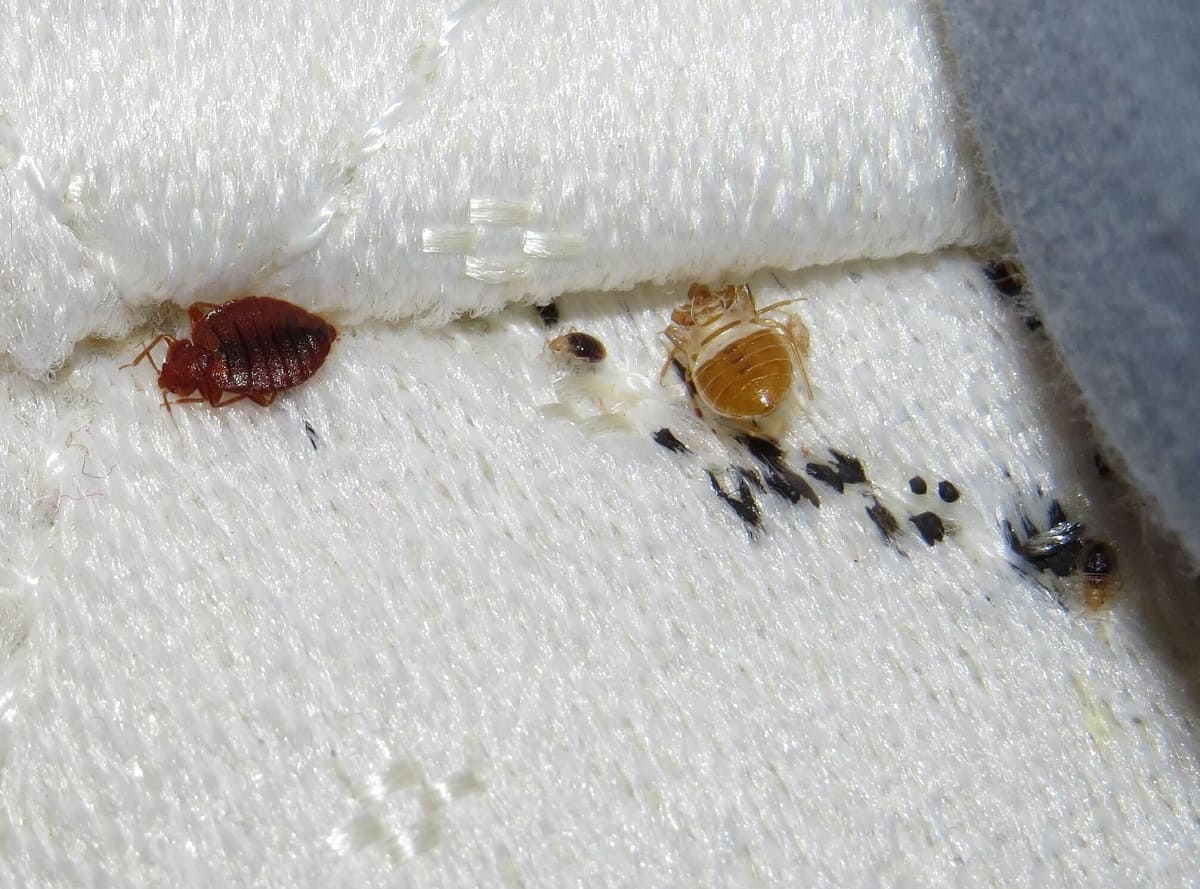
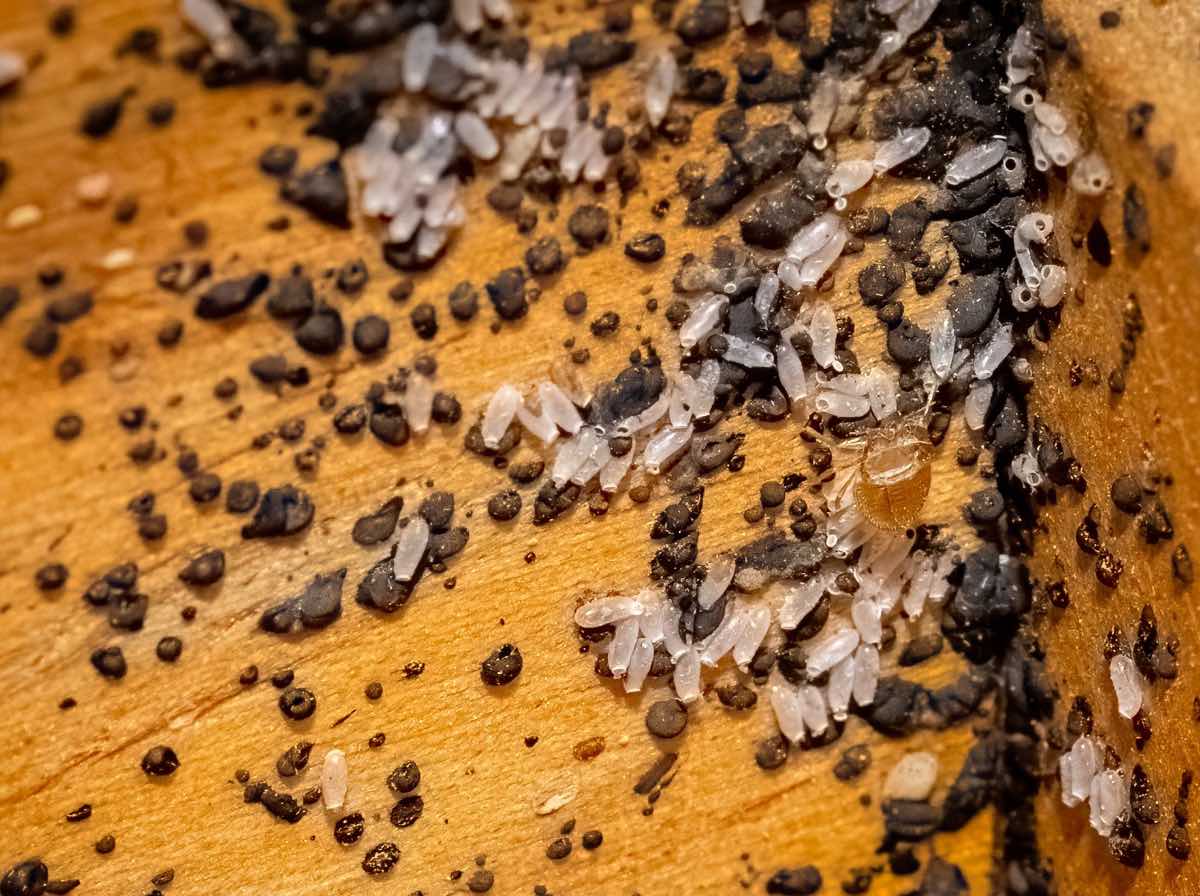
Bed bug eggs are tiny, white, and oval-shaped, with a length of about 1mm. These eggs are usually laid in clusters, and each female can lay up to 5 eggs per day. The eggs are usually cemented to hidden surfaces or cracks and crevices near their feeding areas, making them difficult to detect and eliminate.
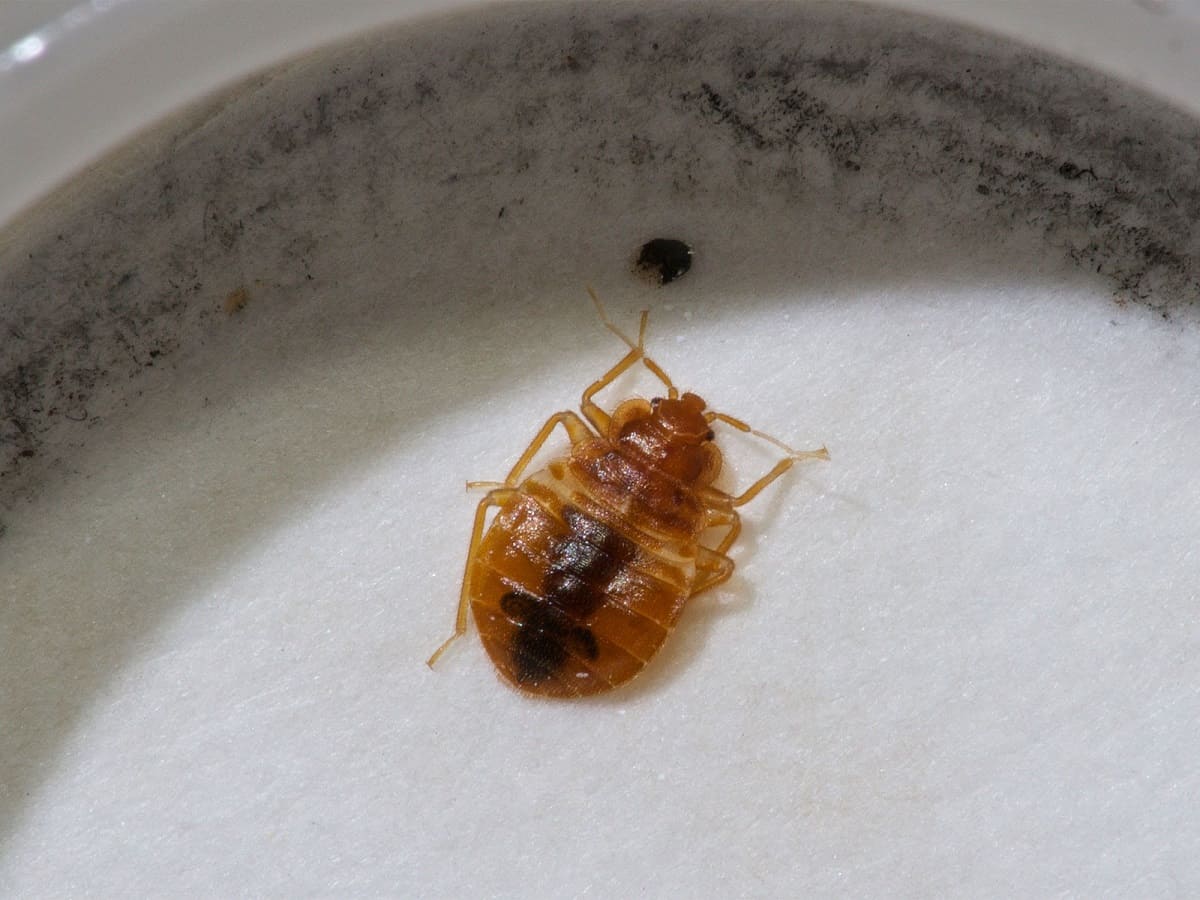
Once the eggs hatch, they enter the nymph stage, which is characterized by the absence of wings and a translucent appearance. Nymphs resemble smaller versions of adult bed bugs and go through several molting stages before reaching adulthood. During each nymph stage, they require a blood meal to progress to the next stage.
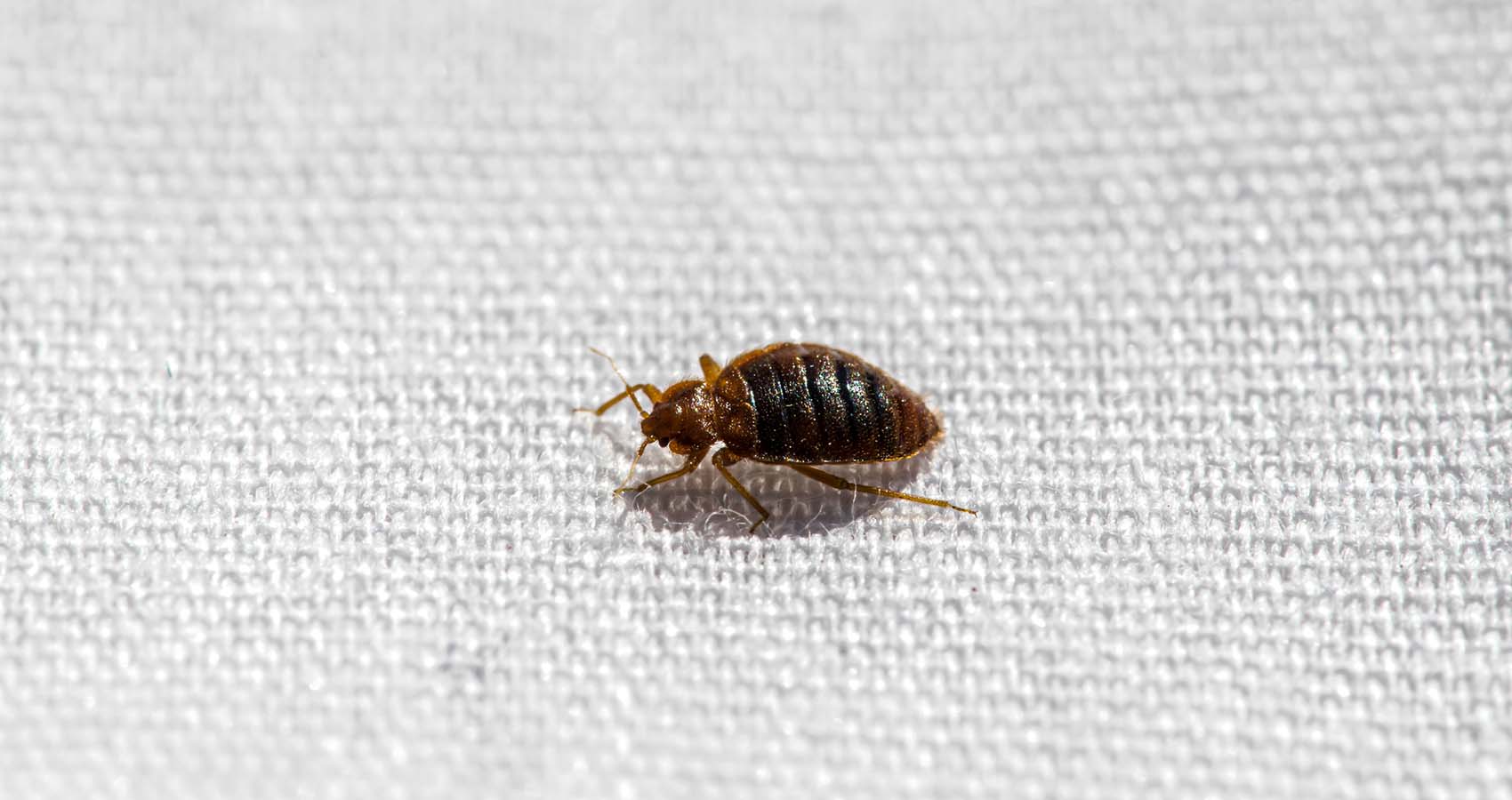
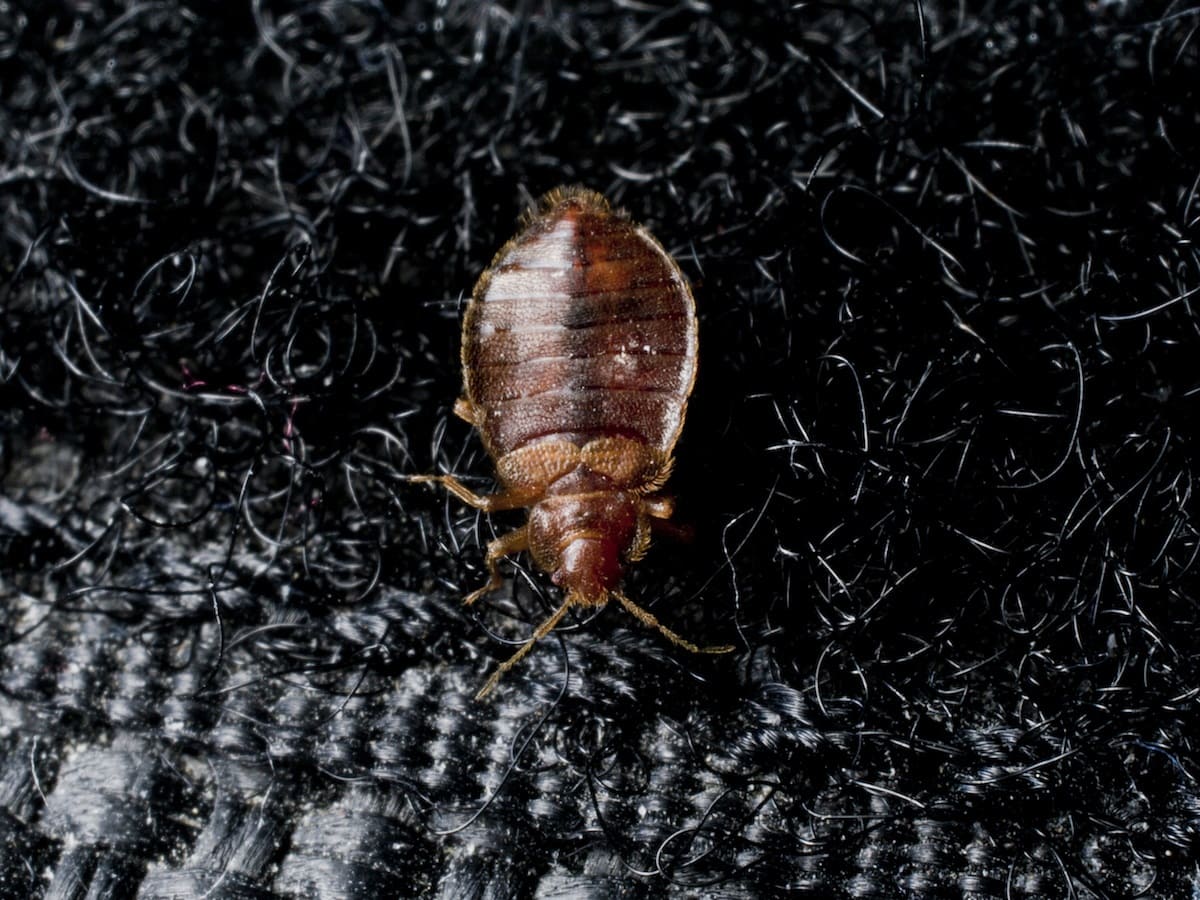
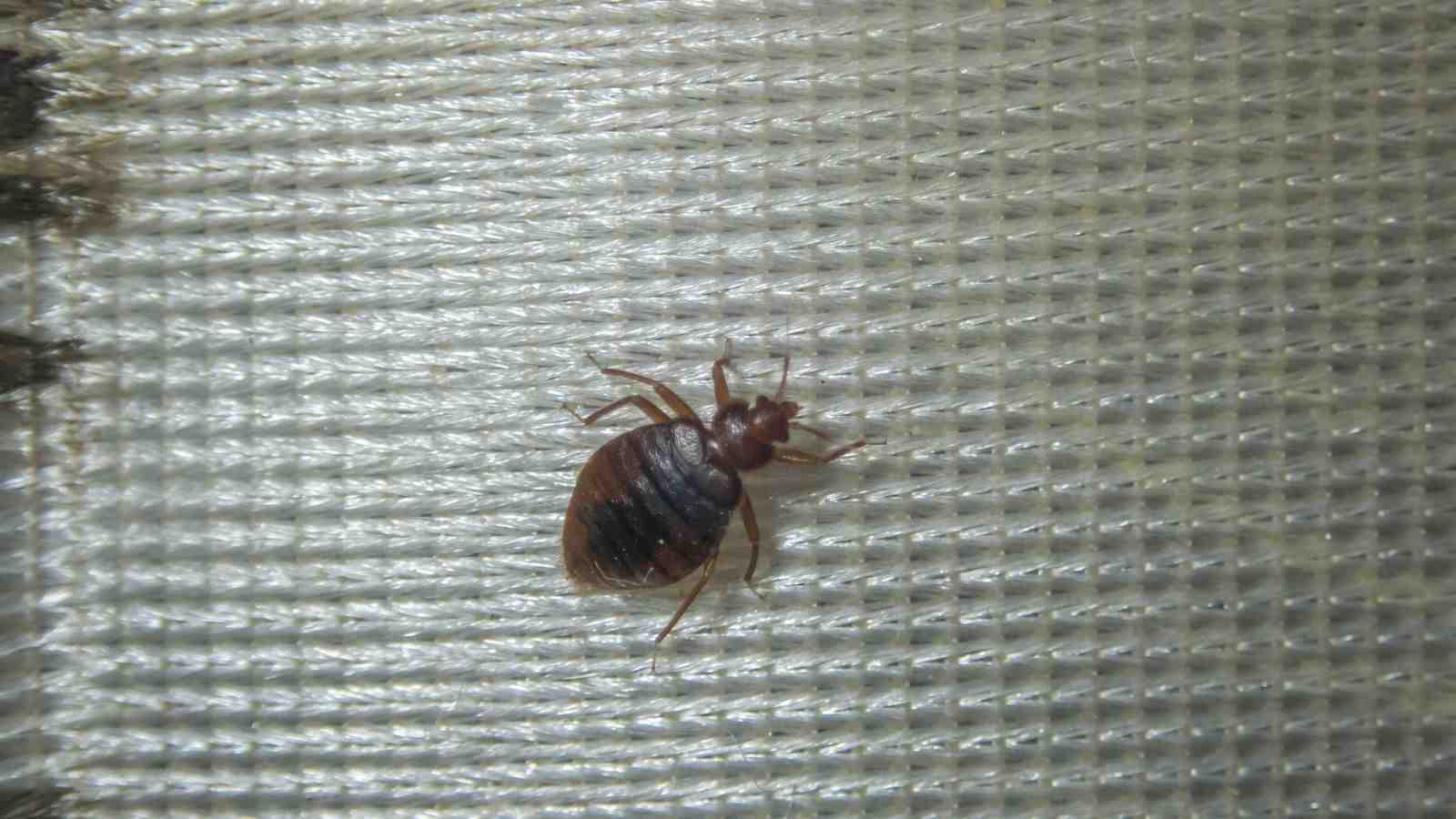
After going through five nymph stages, bed bugs finally reach adulthood. Adult bed bugs are reddish-brown in color, approximately the size of an apple seed, and have a distinct flattened oval shape. They have well-developed wings, although they do not fly. Adult bed bugs require regular blood meals to reproduce and continue the cycle.
Understanding the bed bug life cycle is crucial for effective pest management. By targeting their eggs and nymphs, it’s possible to suppress their population growth and ultimately eliminate an infestation. Now, let’s move on to explore the fascinating world of bed bug egg-laying behavior.
The Egg-Laying Behavior of Bed Bugs
The process of bed bug egg-laying is a fascinating and strategic behavior that ensures the survival and proliferation of their species. Understanding their egg-laying habits can provide valuable insights for effective pest control strategies.
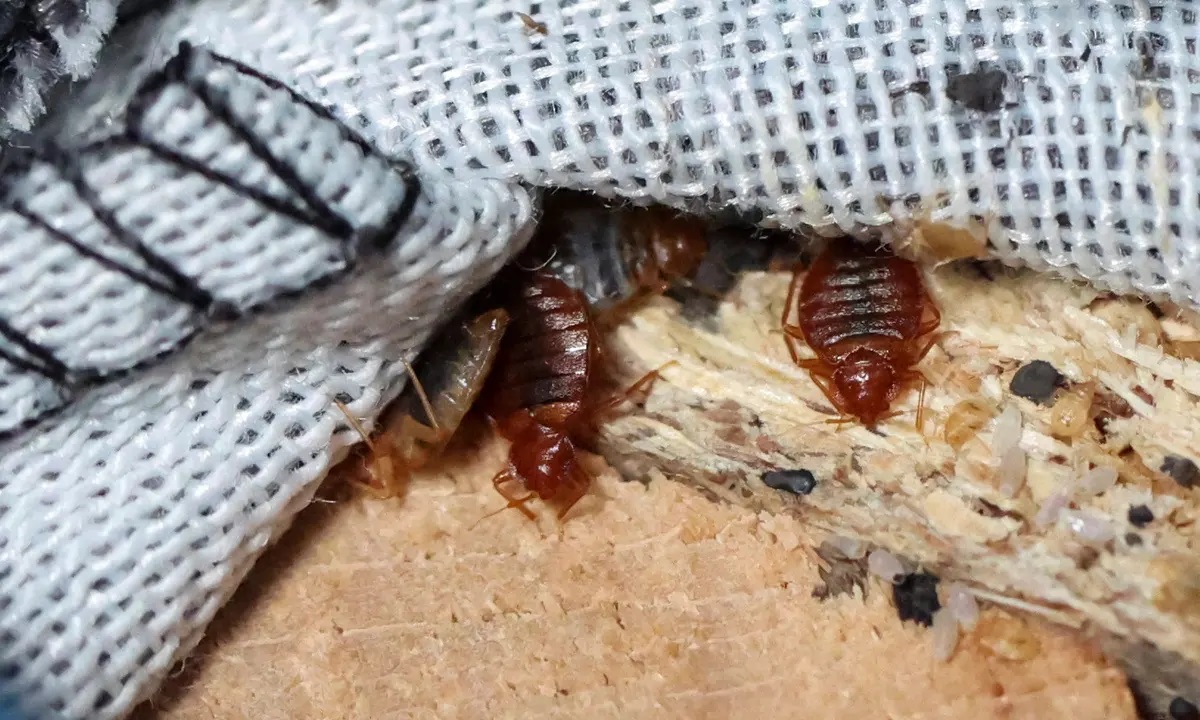
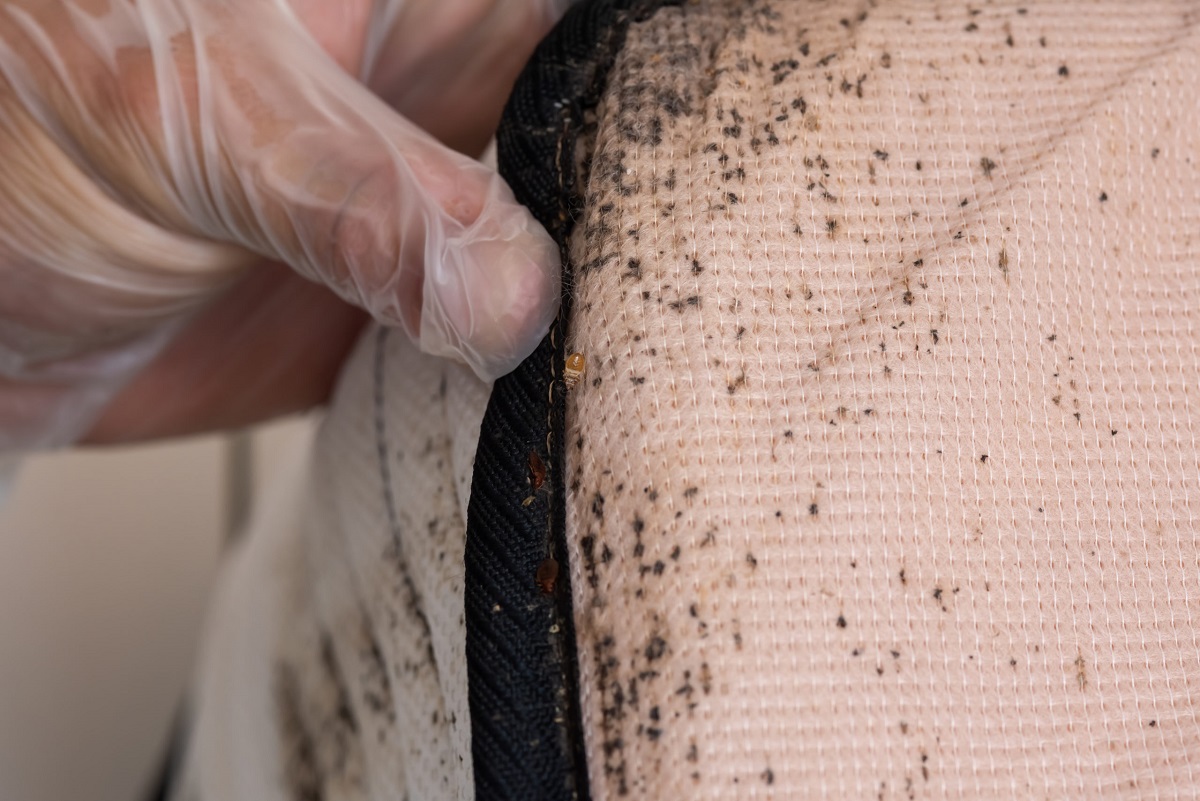
Female bed bugs are responsible for laying eggs, and they do so after a blood meal. Once they are engorged with blood, they will seek out a suitable location to deposit their eggs. Bed bugs have a preference for dark, secluded areas that offer protection and a nearby food source. Common egg-laying sites include cracks and crevices in walls, furniture seams, mattress seams, and behind baseboards.
Bed bug eggs are laid individually or in small clusters and are usually attached to surfaces using a sticky substance produced by the female. This adhesive material secures the eggs in place, preventing them from being easily dislodged. The eggs are typically laid in areas close to where bed bugs typically feed, ensuring easy access to a blood meal for the emerging nymphs.
The time it takes for bed bug eggs to hatch varies depending on environmental conditions such as temperature. On average, it takes around 6 to 10 days for the eggs to hatch. However, in cooler temperatures, the hatching process may be delayed. This adaptability allows bed bugs to survive and reproduce in a wide range of climates.
It’s important to note that bed bug eggs are resistant to many commonly used insecticides. They have a thick outer shell that protects the developing nymph inside. This resilience makes the elimination of bed bug infestations challenging, as simply targeting adult bed bugs may not be sufficient to eradicate the problem. Effective pest control strategies must include measures to eradicate eggs and nymphs.
Now that we have a better understanding of the egg-laying behavior of bed bugs, let’s explore some of the factors that can influence the number of eggs they produce.
Factors Affecting the Number of Eggs
Several factors can influence the number of eggs laid by bed bugs. Understanding these factors is crucial in developing effective strategies to control their population and prevent infestations.
1. Age and Maturity: Female bed bugs become sexually mature after feeding on blood. The older and more mature the female, the higher the likelihood of her laying eggs. Generally, adult females are more prolific egg layers than younger ones.
2. Nutrition and Feeding: The availability of a blood meal is essential for bed bugs to reproduce. The frequency and quality of their blood meals directly impact their ability to lay eggs. Well-fed bed bugs have higher reproductive potential compared to those with limited access to a blood source.
3. Temperature and Environmental Conditions: Bed bugs are incredibly adaptable and can survive in a variety of temperatures. However, warmer temperatures (around 70°F to 80°F) are optimal for their breeding and egg-laying activities. Higher temperatures accelerate their reproductive cycle and increase the number of eggs laid.
4. Stress and Disturbances: Bed bugs are sensitive to disturbances in their environment. Excessive disturbance, such as frequent cleaning or treating infested areas, can disrupt their egg-laying behavior. Bed bugs may delay or reduce egg production in response to perceived threats.
5. Population Density: The density of bed bug populations can influence their egg-laying behavior. In areas with high population densities, competition for limited resources may affect their reproductive potential. Lower population densities, on the other hand, may result in higher egg production per individual.
By considering these factors, pest control professionals can develop targeted strategies to address bed bug infestations more effectively. It’s important to remember that a multi-pronged approach that targets both adults and eggs is crucial for long-term success.
Now that we understand the factors that affect egg production, let’s explore the average number of eggs bed bugs can lay.
A female bed bug can lay 1-5 eggs per day and up to 500 eggs in her lifetime. Regular inspection and early intervention can help prevent a bed bug infestation from getting out of control.
Average Egg Production of Bed Bugs
The average number of eggs laid by a bed bug female can vary depending on various factors, including age, nutrition, and environmental conditions. While individual egg production can differ, bed bugs are still prolific egg layers, contributing to their rapid population growth and the resilience of infestations.
A single female bed bug can lay anywhere between 200 to 500 eggs throughout her lifetime. However, it’s essential to note that this number can be influenced by several factors, including the availability of blood meals and the overall health and maturity of the female.
The rate of egg production also depends on the feeding habits of the female. A well-fed female bed bug is more likely to lay more eggs compared to one that has limited access to blood meals. Studies have shown that females fed on a regular basis can lay up to five eggs per day, resulting in a higher overall egg production compared to those with infrequent feeding opportunities.
Additionally, the overall lifespan of a female bed bug can impact the total number of eggs she produces. Female bed bugs can live for several months to a year, allowing them to lay eggs over an extended period. This prolonged reproductive period contributes to the significant number of eggs produced by a single female during her lifetime.
In a conducive environment, where temperature and other environmental conditions are favorable, bed bugs can complete their reproductive cycle in as little as 6 to 10 weeks. This rapid life cycle, combined with the high number of eggs produced, makes bed bug infestations challenging to eliminate without proper intervention.
The high egg production rate of bed bugs highlights the importance of early detection and prompt action in controlling infestations. It’s crucial to address bed bug problems early on to prevent a small population from rapidly growing into a large and challenging infestation.
Now that we have explored the average egg production of bed bugs, let’s discuss the implications of their prolific egg-laying behavior.
Implications of Bed Bug Egg Production
The prolific egg production of bed bugs has significant implications for homeowners, pest control professionals, and the general public. Understanding these implications is crucial for effective bed bug management and prevention strategies.
1. Rapid Population Growth: Bed bugs reproduce at an alarming rate due to their ability to lay hundreds of eggs during their lifetime. This rapid reproduction allows infestations to grow quickly and spread to multiple areas within a short period. Without swift intervention, a small infestation can escalate into a severe problem.
2. Resilience and Persistence: The presence of bed bug eggs makes infestations more difficult to eradicate. As eggs are highly resistant to many insecticides, they can hatch and replenish the population even after treatment. Failure to address the eggs allows the infestation to rebound, leading to repeated outbreaks and frustrations for homeowners and pest control professionals.
3. Increased Discomfort and Health Risks: The high egg production of bed bugs means an increased number of biting insects in the vicinity. Bed bug bites can cause itching, swelling, and sleep disturbances, leading to physical discomfort and emotional distress. Moreover, bed bugs have been associated with allergic reactions and can potentially transmit diseases, although the latter is relatively rare.
4. Financial Burden: Dealing with a bed bug infestation can be costly. The need for repeated treatments, the potential loss of infested items, and the expenses involved in preventative measures can all add up. Additionally, the economic impact on the hospitality industry and other businesses can be substantial if infestations are not addressed promptly.
5. Psychological Impact: Bed bug infestations can take a toll on the mental well-being of individuals and families affected. The constant fear and anxiety associated with bed bugs can lead to sleep disturbances, stress, and a decreased quality of life. The psychological impact should not be underestimated when addressing the implications of bed bug egg production.
Given these implications, it is crucial to implement proactive measures to prevent bed bug infestations, including regular inspections, proper hygiene practices, and early intervention. Additionally, targeted treatments that address both adult bed bugs and their eggs are essential for successful eradication.
Now that we understand the implications of bed bug egg production, let’s explore strategies for controlling infestations by targeting their eggs.
Controlling Bed Bug Infestations through Targeting Eggs
Effective control of bed bug infestations requires a comprehensive approach that targets both adult bed bugs and their eggs. While adult bed bugs are more visible and easily eliminated, their eggs pose a significant challenge due to their resilience. By focusing on eradicating eggs, we can disrupt the reproductive cycle of bed bugs and successfully manage infestations.
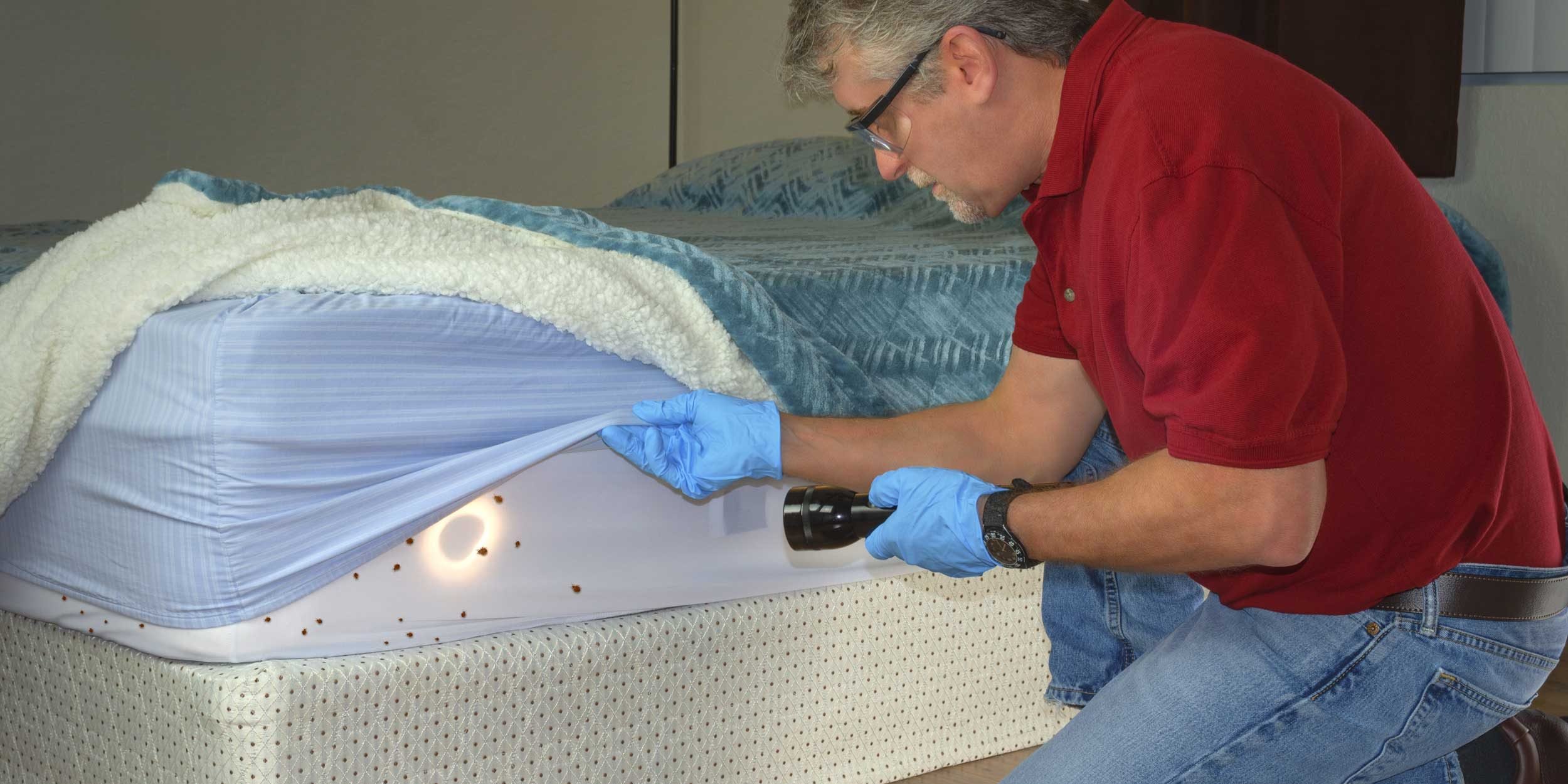
1. Thorough Inspection: Conduct a thorough inspection of the infested area to locate bed bug eggs. Pay close attention to bedding, furniture seams, cracks, and crevices where eggs are often laid. Utilize a flashlight and magnifying glass to aid in identification, as bed bug eggs are small and can be difficult to see with the naked eye.
2. Vacuuming: Vacuuming is an effective method to physically remove bed bug eggs from surfaces. Use a brush attachment to dislodge eggs and vacuum them up. Ensure proper disposal of the vacuum bag or empty it into a sealed plastic bag to prevent reinfestation.
3. Heat Treatment: Bed bug eggs are sensitive to high temperatures. By exposing infested items to heat above 120°F, such as through the use of hot dryers or steam cleaners, you can effectively kill bed bug eggs. This method is particularly useful for treating bedding, clothing, and other washable items.
4. Chemical Treatments: While bed bug eggs are often resistant to many insecticides, some products are labeled specifically for targeting eggs. These insecticides are designed to penetrate the egg shell and kill the developing nymph inside. Follow the instructions carefully when using chemical treatments and consider seeking professional assistance for optimal results.
5. Encasement: Encasing mattresses, box springs, and pillows in bed bug-proof encasements can prevent bed bugs from accessing these areas and laying eggs. The encasements should be durable, breathable, and specifically designed to keep bed bugs out. Regularly inspect the encasements for any signs of tears or holes.
6. Professional Pest Control: If you are dealing with a severe or persistent bed bug infestation, it is advisable to consult a professional pest control company. They have the expertise, equipment, and knowledge to effectively target eggs and develop customized treatment plans based on the extent of the infestation.
By implementing a combination of these strategies, targeted specifically at eliminating bed bug eggs, you can improve the effectiveness of your pest control efforts and reduce the chances of reinfestation. Consistency and persistence are key when dealing with bed bugs, as their reproductive abilities make them resilient adversaries.
Now that we have explored strategies for targeting bed bug eggs, let’s conclude our comprehensive guide on bed bug egg-laying behaviors.
Conclusion
Bed bugs are notorious for their ability to reproduce rapidly and infest homes and establishments, causing discomfort and frustration for countless individuals. Understanding their egg-laying behaviors and implementing effective control strategies is crucial in managing and preventing infestations.
We have explored the fascinating world of bed bug egg-laying behavior, delving into the factors that affect the number of eggs produced. Factors such as age, nutrition, temperature, and population density all play a role in determining the reproductive potential of these pests.
The average egg production of a female bed bug can range from 200 to 500 eggs during her lifetime. These eggs, protected by a resilient outer shell, give rise to a new generation of bed bugs, contributing to the survival and persistence of infestations. The implications of their prolific egg-laying behavior include rapid population growth, resilience, increased discomfort and health risks, financial burden, and psychological impact.
To effectively control bed bug infestations, it is crucial to target their eggs. Strategies such as thorough inspection, vacuuming, heat treatment, chemical treatments, encasement, and professional pest control all contribute to disrupting the reproductive cycle of bed bugs and preventing their spread.
Remember, early detection and intervention are key in managing bed bug infestations. Regular inspections and quick action can prevent small infestations from escalating into larger, more difficult-to-treat problems.
By combining knowledge of bed bug egg-laying behaviors with a holistic and targeted approach to pest control, we can effectively tackle these persistent pests and create safe and comfortable living environments.
Thank you for taking the time to explore the intriguing world of bed bug egg-laying behaviors. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights and practical strategies for managing and preventing bed bug infestations.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Many Eggs Do Bed Bugs Lay
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.