Home>Furniture>Kitchen Furniture>How Does An Induction Cooktop Work


Kitchen Furniture
How Does An Induction Cooktop Work
Modified: August 30, 2024
Discover how an induction cooktop works in this informative article. Learn about the technology behind induction cooking and its benefits.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
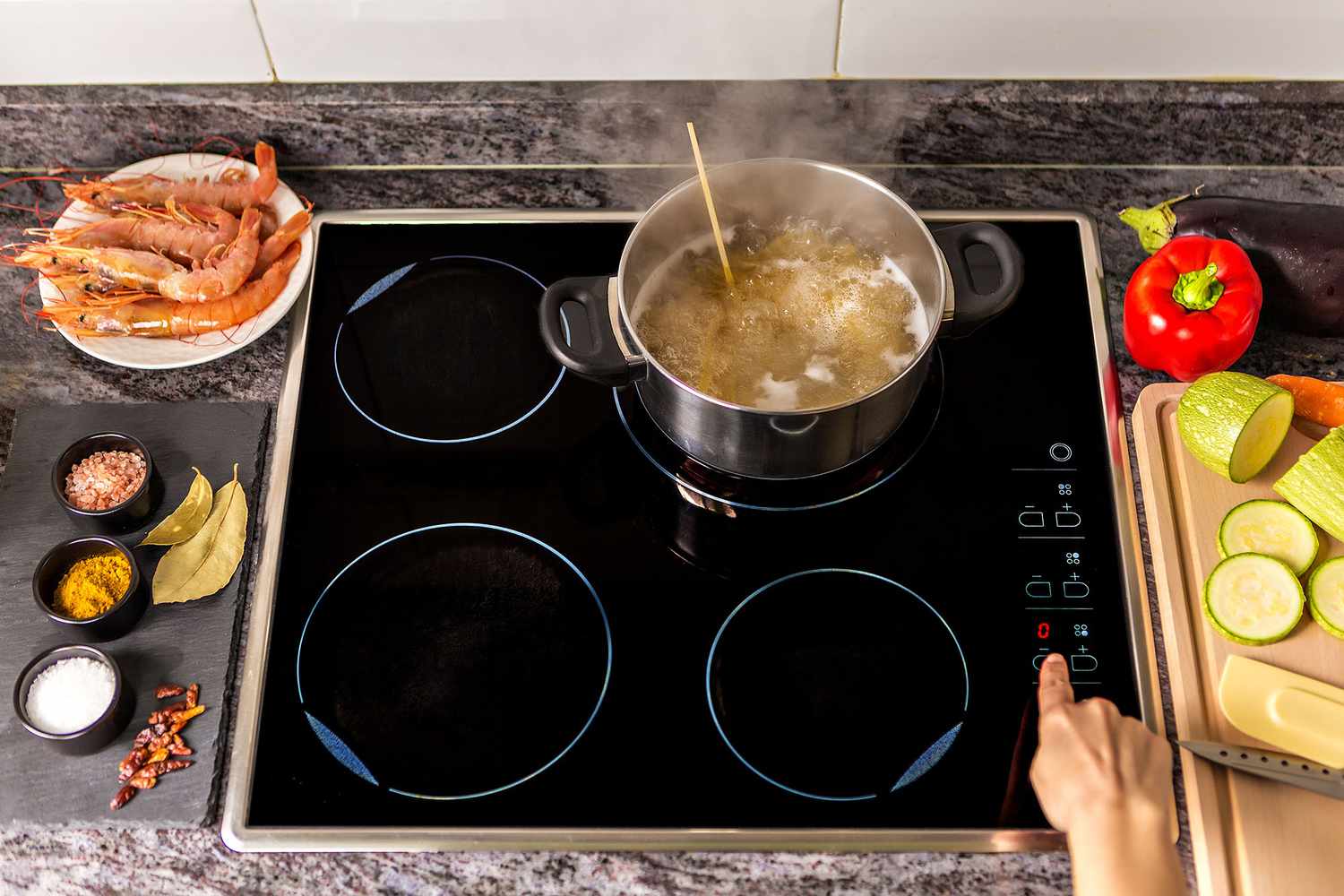
Induction cooktops have revolutionized the way we cook, offering a faster, more efficient, and safer alternative to traditional gas or electric cooktops. With their sleek design and advanced technology, these cooktops have become increasingly popular in modern kitchens. But how do induction cooktops work?
In this article, we will explore the basic principles behind induction cooking, the components of an induction cooktop, and the advantages and disadvantages of using this innovative cooking method.
Induction cooking relies on the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate heat. Unlike gas or electric cooktops that rely on the direct transfer of heat, induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly. This results in faster cooking times, precise temperature control, and improved energy efficiency.
So, let’s delve into the fascinating world of induction cooking and discover the inner workings of these impressive appliances.
Key Takeaways:
- Induction cooktops use electromagnetic induction to heat cookware directly, offering faster cooking times, precise temperature control, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional gas or electric cooktops.
- Induction cooktops prioritize safety with features like automatic shut-off, child safety locks, and cookware detection, making them a secure and efficient cooking option for modern kitchens.
Read more: How Does Nuwave Cooktop Work
Basic principles of induction cooking
Induction cooking operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which was first discovered by Michael Faraday in the early 19th century. This phenomenon involves the generation of an electrical current in a conductor when it is exposed to a changing magnetic field.
In the case of induction cooktops, the conductor is a coil of copper wire located beneath the ceramic surface. When an electric current passes through this coil, it creates a magnetic field. The cookware used on the induction cooktop must have a magnetic property, such as iron or stainless steel, in order to interact with the magnetic field.
When the magnetic cookware is placed on the induction cooktop, the magnetic field generated by the coil induces an electric current in the cookware. This electrical current creates resistance, which in turn generates heat. This heat is then transferred to the food within the cookware, cooking it evenly and efficiently.
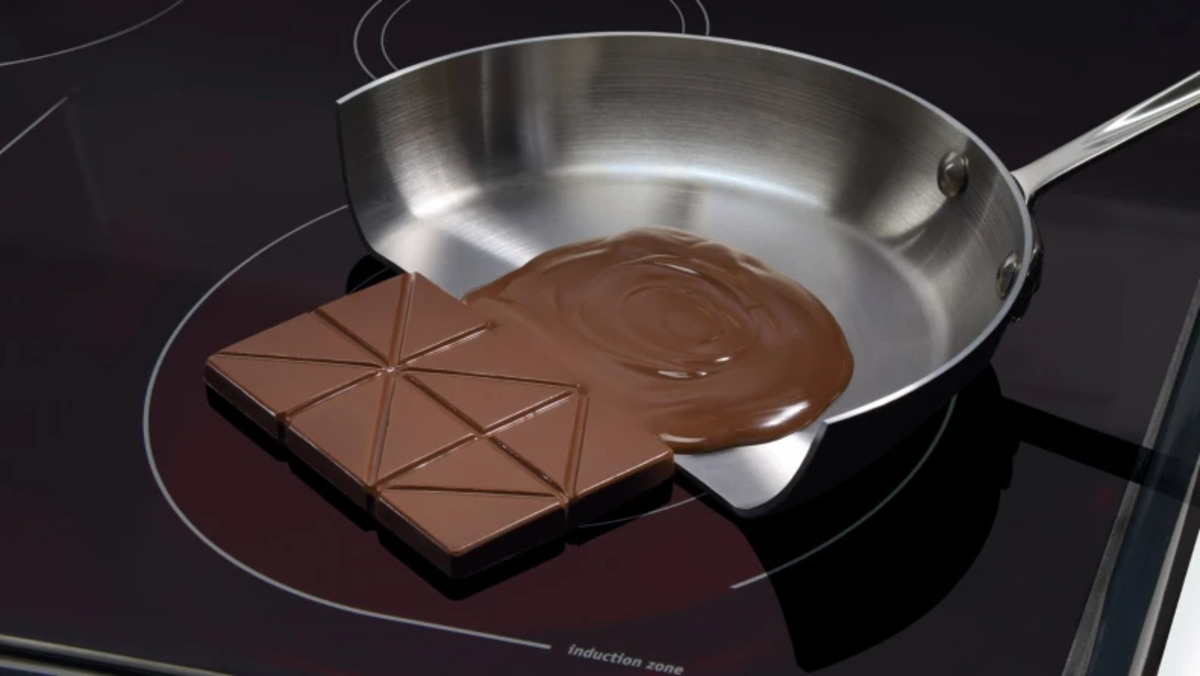
It’s important to note that the cookware itself does not get hot during induction cooking. Instead, the heat is produced directly in the cookware, allowing for precise temperature control and faster cooking times.
Another crucial aspect of induction cooking is the reliance on a high-frequency alternating current (AC) power supply. The rapidly changing magnetic field created by the AC current is what enables the efficient transfer of heat to the cookware. The frequency of the AC power supply is typically in the range of 20 to 100 kilohertz, which ensures optimal performance and reduces energy loss.
Overall, the basic principles of induction cooking involve the interaction of a magnetic field with magnetic cookware, resulting in the generation of an electric current and the subsequent production of heat. This innovative cooking method provides numerous benefits, which we will explore in more detail in the following sections.
Components of an induction cooktop
An induction cooktop consists of several key components that work together to generate heat and provide a seamless cooking experience. These components include:
- Induction coils: These coils are made of copper and are responsible for generating the electromagnetic field that heats the cookware. The number and arrangement of the coils vary depending on the size and design of the cooktop.
- Ceramic glass surface: The ceramic glass surface provides a sleek and durable platform for cooking. It is designed to withstand high temperatures and is easy to clean. The surface is also equipped with touch controls that allow users to adjust temperature settings and cooking modes.
- Control panel: The control panel is located on the surface of the cooktop and includes buttons, knobs, or touch controls for selecting temperature levels, cooking modes, and other settings. This panel also displays relevant information such as cooking time and power levels.
- Sensors: Induction cooktops are equipped with sensors that can detect the presence of cookware and adjust heat output accordingly. These sensors ensure that the cooking surface remains inactive when no cookware is detected, preventing accidental burns.
- Power supply: The power supply provides the necessary electrical current to the induction coils. It converts the incoming AC power from the mains into the high-frequency AC power needed for induction cooking.
In addition to these primary components, some induction cooktops may also have additional features or accessories. These can include built-in timers, child safety locks, power boost functions for quick heating, and specialized cooking zones for specific cookware sizes. Some cooktops may also include a bridge function, which allows two cooking zones to be combined to accommodate larger cookware or cooking surfaces.
It’s important to note that not all induction cooktops are the same, and different manufacturers may use slightly different designs and components. However, the overall functionality and principles behind induction cooking remain consistent across different models and brands.
Electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction is at the heart of how induction cooktops work. It is a phenomenon discovered by Michael Faraday in the 19th century and has since become the foundation for numerous technological advancements, including induction cooking.
The concept of electromagnetic induction involves the generation of an electric current in a conductor when it is exposed to a changing magnetic field. In the case of induction cooktops, the conductor is a coil of copper wire located beneath the ceramic surface.
When an electric current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field around it. This magnetic field is constantly changing and oscillating due to the alternating current (AC) passing through the coil. When a magnetic cookware, such as iron or stainless steel, is placed on the cooktop, it interacts with this changing magnetic field.
This interaction induces an electric current in the cookware, following Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. The electric current circulates within the cookware, creating resistance and generating heat due to the Joule effect. The heat produced by the electric current is then transferred to the food in the cookware, allowing for efficient and precise cooking.
It’s important to note that only magnetic cookware can be used on induction cooktops because non-magnetic materials, such as aluminum or copper, do not interact with the magnetic field and therefore cannot generate heat through induction.
The ability of the induction cooktop to rapidly generate heat through electromagnetic induction is what sets it apart from traditional gas or electric cooktops. Induction cooking offers several advantages, such as faster heating times, precise temperature control, and better energy efficiency.
By harnessing the power of electromagnetic induction, induction cooktops have revolutionized the way we cook, providing a safer, faster, and more efficient cooking experience.
How induction cooktops generate heat
Induction cooktops generate heat through the process of electromagnetic induction. This innovative technology allows for precise and efficient cooking by heating the cookware directly rather than relying on a traditional heat transfer method.
When a magnetic cookware, such as iron or stainless steel, is placed on the ceramic surface of an induction cooktop, the magnetic field generated by the coil beneath the surface induces an electric current in the cookware. This electric current creates resistance within the cookware, generating heat.
The heat produced by the electric current is then transferred to the food within the cookware, resulting in cooking or heating. Unlike gas or electric cooktops, where the heat is generated externally and transferred to the cookware, induction cooktops heat the cookware directly, offering greater control and efficiency.
The efficiency of induction cooktops is due to the fact that heat is generated only in the cookware itself. The ceramic surface of the cooktop remains relatively cool to the touch, reducing the risk of burns and making it easier to clean.
One key advantage of induction cooktops is their incredibly fast heating time. Because the heat is generated directly in the cookware, there is no need to preheat the cooktop or wait for the heat to transfer to the cookware. The heat is instantly produced once the cookware is placed on the cooktop, allowing for immediate cooking.
Another remarkable aspect of induction cooktops is their precise temperature control. Unlike traditional cooktops that rely on gas flames or electric heating elements, induction cooktops can adjust the heat output almost instantly. This fine-tuned temperature control ensures that dishes can be cooked at the exact desired temperature, resulting in better cooking results.
Furthermore, induction cooktops offer excellent energy efficiency. Because the heat is generated directly in the cookware, there is minimal energy loss compared to traditional cooktops. The energy is effectively utilized in heating the cookware and the food, reducing overall energy consumption.
Overall, induction cooktops generate heat through electromagnetic induction, providing fast and precise cooking while being energy-efficient and safe to use.
Read more: How To Install Induction Cooktop
Induction vs Traditional Gas or Electric Cooktops
When it comes to choosing a cooktop for your kitchen, there are several options available, including induction, gas, and electric cooktops. Each type of cooktop has its own advantages and considerations. Let’s compare induction cooktops with traditional gas or electric cooktops to understand their key differences.
1. Heating speed: Induction cooktops are known for their fast heating speed. With induction, the heat is generated directly in the cookware, resulting in quicker cooking times. Gas and electric cooktops, on the other hand, take some time to heat up before reaching the desired temperature.
2. Temperature control: Induction cooktops offer precise temperature control. They can quickly respond to changes in heat settings, allowing for more accurate and delicate cooking. Gas cooktops also offer immediate and precise heat control, while electric cooktops may have a slight delay in adjusting the heat levels.
3. Energy efficiency: Induction cooktops are more energy-efficient compared to gas or electric cooktops. As heat is generated directly in the cookware, there is minimal energy loss. Gas cooktops can be less efficient due to heat loss through flame and convection, while electric cooktops may have some energy loss during heat transfer.
4. Safety: Induction cooktops are considered safer than gas or electric cooktops. Since the surface of the induction cooktop doesn’t get hot, there is a lower risk of burns or accidents. Gas cooktops have open flames and electric cooktops retain residual heat even after being turned off, making them potentially hazardous.
5. Cookware compatibility: Induction cooktops require magnetic cookware for the induction process to work. Non-magnetic materials like aluminum or copper won’t heat up. Gas and electric cooktops, on the other hand, can accommodate a wider range of cookware materials.
6. Maintenance and cleaning: Induction cooktops are relatively easy to clean as the surface remains cool and spills don’t get baked on. Gas cooktops can be more challenging to clean due to burner grates and gas ports. Electric cooktops have smooth surfaces but may require more effort to remove stubborn stains.
7. Installation: Induction cooktops typically require professional installation due to electrical and ventilation requirements. Gas cooktops require a gas line and professional installation as well. Electric cooktops can be easier to install if the electrical connections are already in place.
Ultimately, the choice between induction and traditional gas or electric cooktops depends on individual preferences, cooking needs, and kitchen setup. Induction cooktops offer speed, precision, energy efficiency, and safety advantages, while gas and electric cooktops provide versatility and ease of installation. Consider your cooking style, budget, and kitchen requirements to make an informed decision.
When using an induction cooktop, make sure to use cookware with a magnetic bottom, such as cast iron or stainless steel, for optimal heating efficiency. Non-magnetic cookware will not work on an induction cooktop.
Advantages of Induction Cooking
Induction cooking offers numerous advantages that have made it a popular choice for modern kitchens. From its speed and efficiency to its safety features, here are the key advantages of induction cooking:
1. Speed: One of the most significant advantages of induction cooking is its speed. Induction cooktops heat up much faster than gas or electric cooktops because the heat is generated directly in the cookware. This means you can start cooking almost immediately, saving valuable time in the kitchen.
2. Precise temperature control: Induction cooktops provide precise temperature control, allowing you to adjust heat levels with great accuracy. This is especially beneficial for delicate tasks like simmering or melting chocolate, where even a slight variation in temperature can make a significant difference in the outcome.
3. Energy efficiency: Induction cooking is highly energy efficient. Since the heat is generated directly in the cookware, there is minimal heat loss. This translates to reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills. Additionally, the induction cooktop only uses electricity when cookware is placed on it, further enhancing its energy efficiency.
4. Safety: Induction cooktops are considered one of the safest cooking options. The ceramic surface remains relatively cool to the touch, reducing the risk of burns. Additionally, induction cooktops have built-in safety features such as automatic shut-off when no cookware is detected or when the cookware is removed from the surface.
5. Easy to clean: Cleaning an induction cooktop is a breeze. The smooth ceramic surface is easy to wipe clean, and spills do not get baked onto the surface since it does not get as hot as gas or electric cooktops. This makes maintenance and upkeep hassle-free.
6. Sleek and modern design: Induction cooktops offer a sleek and modern aesthetic that can enhance the overall appearance of your kitchen. With their smooth surfaces and often frameless design, they can seamlessly blend with any kitchen décor, adding a touch of sophistication.
7. Even heat distribution: Induction cooktops provide even heat distribution across the entire cooking surface. This ensures that your food is cooked evenly without any hot spots. Whether you’re using a small or large pan, the heat is evenly distributed for consistent cooking results.
Overall, induction cooking offers speed, precision, energy efficiency, safety, easy maintenance, and an attractive design. These advantages have made induction cooktops a popular choice for home cooks and professional chefs alike, providing a superior cooking experience in terms of both functionality and aesthetics.
Disadvantages of Induction Cooking
While induction cooking offers numerous advantages, there are a few considerations and potential disadvantages to keep in mind:
1. Cookware compatibility: Induction cooktops require magnetic cookware for the induction process to work. Non-magnetic materials like aluminum, copper, or glass will not heat up. This may require some users to invest in new cookware specifically designed for induction cooking.
2. Initial cost: Induction cooktops tend to have a higher initial cost compared to traditional gas or electric cooktops. The advanced technology and materials used in induction cooktops contribute to this higher price point. However, it is important to consider the long-term energy savings and benefits that induction cooking provides.
3. Installation requirements: Induction cooktops may require professional installation. They often have specific electrical and ventilation requirements that need to be met for safe and efficient operation. This can add to the overall cost of installing an induction cooktop.
4. Noise level: Some users may notice a slight humming sound or vibration when using an induction cooktop. This is a normal byproduct of the induction process and is generally not disruptive. However, if you are sensitive to noise, it may be something to consider.
5. Power supply limitations: Induction cooktops require a dedicated power supply. Depending on the model and the power requirements, it may not be possible to install an induction cooktop in certain homes without significant electrical upgrades. It is essential to ensure that your kitchen’s electrical system can support the power needs of an induction cooktop.
6. Learning curve: Induction cooking may have a learning curve for those transitioning from gas or electric cooktops. The immediate and precise temperature control may take some time to get used to, especially for those accustomed to the gradual heat adjustment of gas cooktops. However, with a little practice, users can quickly adapt to the nuances of induction cooking.
Despite these potential disadvantages, induction cooking remains an excellent option for fast, efficient, and precise cooking. It’s important to weigh the pros and cons based on your individual needs, budget, and kitchen setup before deciding if an induction cooktop is the right choice for you.
Safety Features of Induction Cooktops
Induction cooktops are designed with several built-in safety features to ensure a secure cooking experience. These features not only help prevent accidents but also provide peace of mind to users. Here are some of the common safety features found in induction cooktops:
1. Automatic shut-off: Many induction cooktops are equipped with an automatic shut-off feature. This feature activates when there is no cookware detected on the cooking surface or when the cookware is removed. It helps prevent the cooktop from functioning without proper cookware, reducing the risk of accidental burns or overheating.
2. Child safety lock: Induction cooktops often come with a child safety lock feature. This feature allows you to lock the control panel, preventing unintended use or changes in cooking settings. It is particularly useful in households with young children to prevent accidents or tampering.
3. Pan detection: Induction cooktops are equipped with sensors that detect the presence of compatible cookware on the cooking surface. If the cookware is removed or if an incompatible material is placed on the cooktop, the induction process is automatically paused or disabled. This safety feature helps prevent accidental burns from touching hot surfaces.
4. Overheat protection: Induction cooktops have overheat protection mechanisms in place. If the cooktop reaches a temperature that exceeds safe operating limits, the heat output is automatically reduced or discontinued. This protects the cooktop from damage and prevents potential hazards.
5. Residual heat indicators: Induction cooktops often include residual heat indicators to alert users when the cooking surface is still hot after use. These indicators provide a visual reminder of the hot surface and help prevent accidental burns. It is essential to avoid placing any objects or touching the surface until the residual heat indicator turns off.
6. Overflow detection: Some induction cooktops have an overflow detection feature that senses spills or liquid overflow on the cooking surface. When a spill occurs, the cooktop automatically shuts off or reduces the heat output to prevent damage and minimize the risk of electrical or fire hazards.
7. Temperature limiters: Induction cooktops may have temperature limiters that prevent the cookware from exceeding a certain temperature. This helps avoid overheating, burning food, or damaging the cookware. The temperature limiters provide an additional layer of safety and control during cooking.
While induction cooktops offer several safety features, it is still crucial to follow proper cooking precautions. Always handle cookware with oven mitts or pot holders, and keep flammable materials away from the cooking surface. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the specific safety features and guidelines provided by the manufacturer of your induction cooktop.
Overall, the safety features incorporated into induction cooktops contribute to a secure cooking environment, providing users with confidence and peace of mind while enjoying the benefits of this innovative cooking technology.
Tips for Using an Induction Cooktop
Induction cooktops offer a unique and efficient way of cooking. To make the most of your induction cooking experience, consider these tips:
1. Use compatible cookware: Induction cooktops require cookware with a magnetic bottom, typically made of materials like cast iron or stainless steel. Ensure your cookware is induction-compatible by checking for the induction symbol or conducting a simple magnet test.
2. Center the cookware: For optimal heating, center the cookware on the induction cooking zone. This will ensure maximum contact with the induction coils and promote efficient heat transfer.
3. Adjust heat settings gradually: Induction cooktops respond quickly to changes in heat settings. It’s recommended to adjust heat levels gradually to prevent sudden temperature changes that could lead to food burning or overheating.
4. Preheat when necessary: While induction cooktops heat up quickly, some cooking techniques may benefit from preheating the cookware. For tasks like searing or stir-frying, preheat the pan on a higher heat setting before lowering it to the desired cooking temperature.
5. Take advantage of boost features: Many induction cooktops have a boost function that increases the heat output temporarily. This feature can be useful for rapid boiling, bringing large pots of water to a boil quickly, or for searing meats at high temperatures.
6. Keep the cooktop clean: Maintaining a clean cooking surface is important for optimal performance. Regularly clean the induction cooktop using non-abrasive cleaners to remove any residue or spills. Wipe spills immediately to prevent them from hardening on the surface.
7. Avoid sliding cookware: Refrain from sliding or dragging cookware across the induction cooktop, as this can scratch the surface. Lift and place cookware gently to prevent any damage.
8. Use cookware with flat bottoms: To maximize heat transfer, make sure your cookware has a flat, smooth bottom that makes full contact with the cooking zone. Uneven or warped bottoms can lead to uneven heat distribution.
9. Don’t forget residual heat: Induction cooktops retain residual heat after cooking. Take note of the residual heat indicators to avoid accidental burns when removing cookware or placing objects on the surface.
10. Experiment and practice: Induction cooking may require some adjustment if you are accustomed to gas or electric cooktops. Take the time to experiment with different heat settings and cooking techniques to uncover the full potential of your induction cooktop.
By following these tips, you can make the most of your induction cooktop, enjoying its speedy heat-up, precise temperature control, and energy efficiency. With a little practice, you will be able to achieve outstanding cooking results and fully appreciate the benefits of induction cooking in your kitchen.
Conclusion
Induction cooking has revolutionized the way we cook, offering a fast, efficient, and safe alternative to traditional gas or electric cooktops. By harnessing the power of electromagnetic induction, induction cooktops provide precise temperature control, rapid heating, and energy efficiency, making them a popular choice for modern kitchens.
We have explored the basic principles behind induction cooking, understanding how electromagnetic fields generate heat directly in the cookware. The components of an induction cooktop, such as the induction coils and ceramic glass surface, work together to provide an exceptional cooking experience.
The advantages of induction cooking are evident. The speed at which induction cooktops heat up allows for quick and efficient cooking. The precise temperature control ensures that dishes are cooked to perfection, while the energy efficiency of induction cooking reduces overall energy consumption.
Induction cooktops also prioritize safety with features like automatic shut-off, child safety locks, and cookware detection. Users can confidently cook without the risk of burns or accidents, and the easy-to-clean surfaces of induction cooktops make maintenance a breeze.
While there may be a few considerations, such as cookware compatibility or initial cost, the benefits of induction cooking outweigh the potential drawbacks. With proper cookware and a little adjustment, users can fully enjoy the advantages of induction cooking.
As technology continues to advance, induction cooktops are becoming more widespread, enhancing kitchens with their sleek design and superior functionality. Whether you are a professional chef or a home cook, incorporating an induction cooktop into your kitchen offers an exceptional cooking experience like no other.
In conclusion, induction cooking provides a transformative and efficient way of cooking, offering speed, precision, energy efficiency, and safety. As more individuals become aware of its benefits, induction cooktops are undoubtedly reshaping the future of culinary experiences in households around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does An Induction Cooktop Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Does An Induction Cooktop Work”