Home>Home Appliances>Heating & Cooling>How To Control Air Flow Forced Air Heating System


Heating & Cooling
How To Control Air Flow Forced Air Heating System
Published: February 16, 2024
Learn how to control air flow in your forced air heating system for optimal heating and cooling. Discover effective tips and techniques to improve air circulation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Forced air heating systems are a common feature in many homes and commercial buildings, providing efficient and effective heating during colder months. These systems work by distributing heated air through a network of ducts and vents, ensuring that every corner of the space is warmed evenly. While forced air heating systems offer numerous benefits, such as quick heating and the ability to incorporate air conditioning, controlling the air flow within these systems is crucial for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of forced air heating systems, explore the significance of controlling air flow, and provide valuable tips for effectively managing air flow in these systems. Whether you are a homeowner looking to maximize the comfort of your living space or a facility manager aiming to enhance energy efficiency, understanding and implementing strategies to control air flow in forced air heating systems is essential.
Let's embark on a journey to unravel the nuances of air flow control in forced air heating systems, empowering you to make informed decisions and optimize the performance of your heating system.
Key Takeaways:
- Controlling air flow in forced air heating systems is crucial for even warmth, lower energy costs, and better air quality. Regular maintenance, adjusting vents, and using zoning systems are key strategies.
- To optimize your heating system, clean ducts, balance vents, and invest in programmable thermostats. These simple steps can enhance comfort, save energy, and create a sustainable indoor environment.
Understanding Forced Air Heating Systems
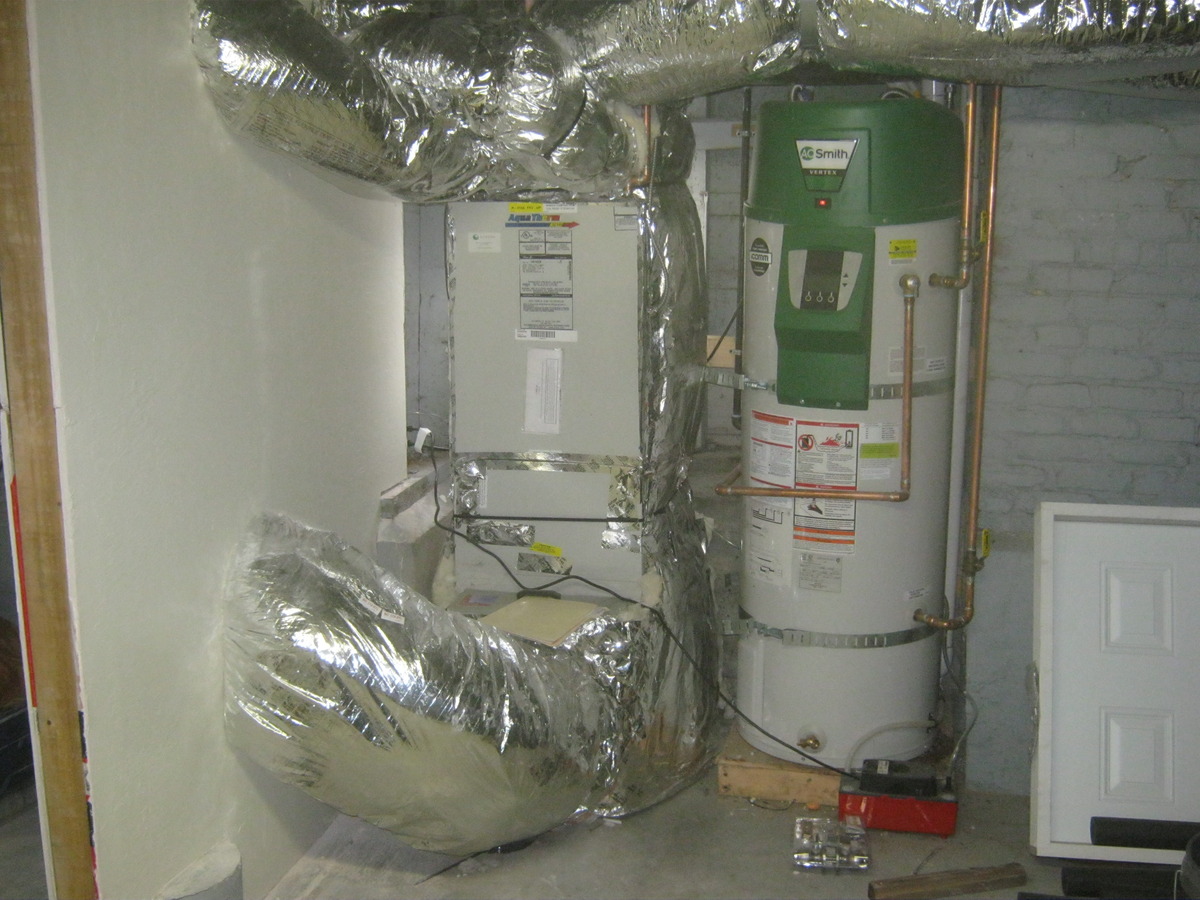
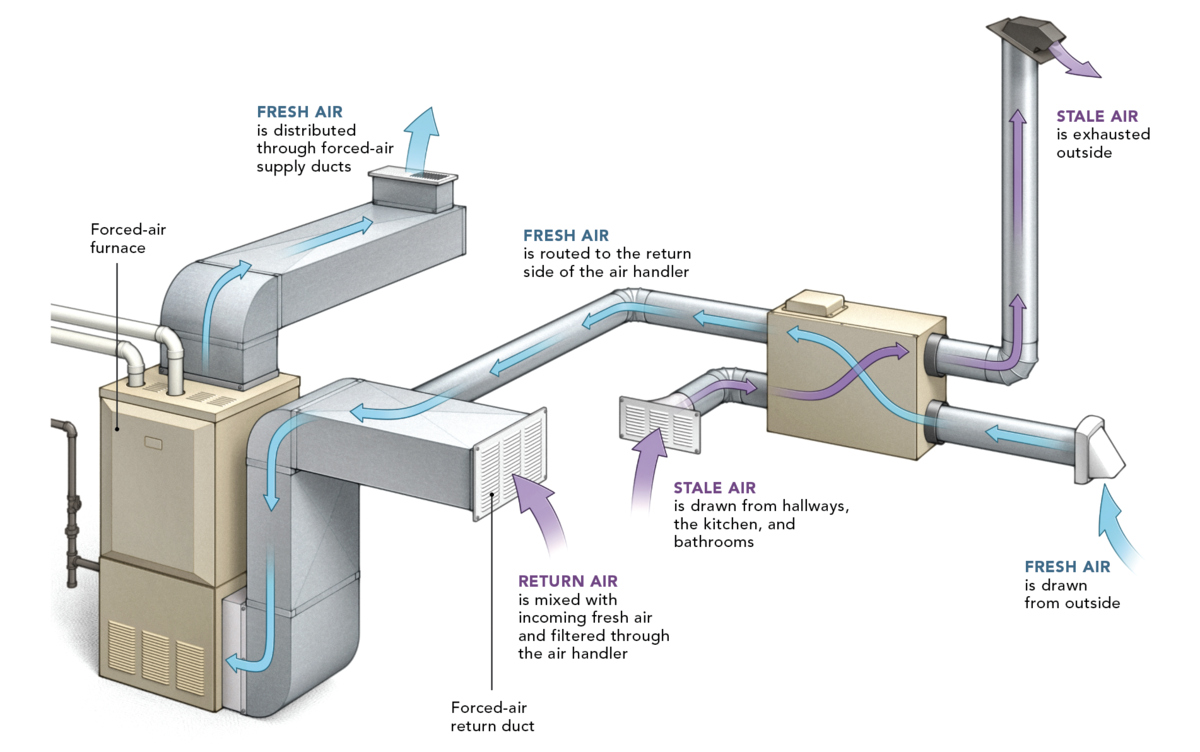
Forced air heating systems, also known as central heating systems, are a popular choice for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures in residential and commercial settings. These systems operate by heating air within a furnace or heat exchanger and then distributing the warmed air throughout the building via a network of ducts and vents. The process begins with the combustion of fuel, such as natural gas or propane, or the activation of electric heating elements to generate heat. Once the air is heated, a blower fan propels it through the ductwork, delivering warmth to every room.
One of the key components of a forced air heating system is the thermostat, which serves as the control center for regulating temperature. When the indoor temperature falls below the set point, the thermostat signals the heating system to activate, initiating the heating cycle. As the warm air circulates, it gradually raises the temperature until the desired level is reached, at which point the thermostat signals the system to cease heating.
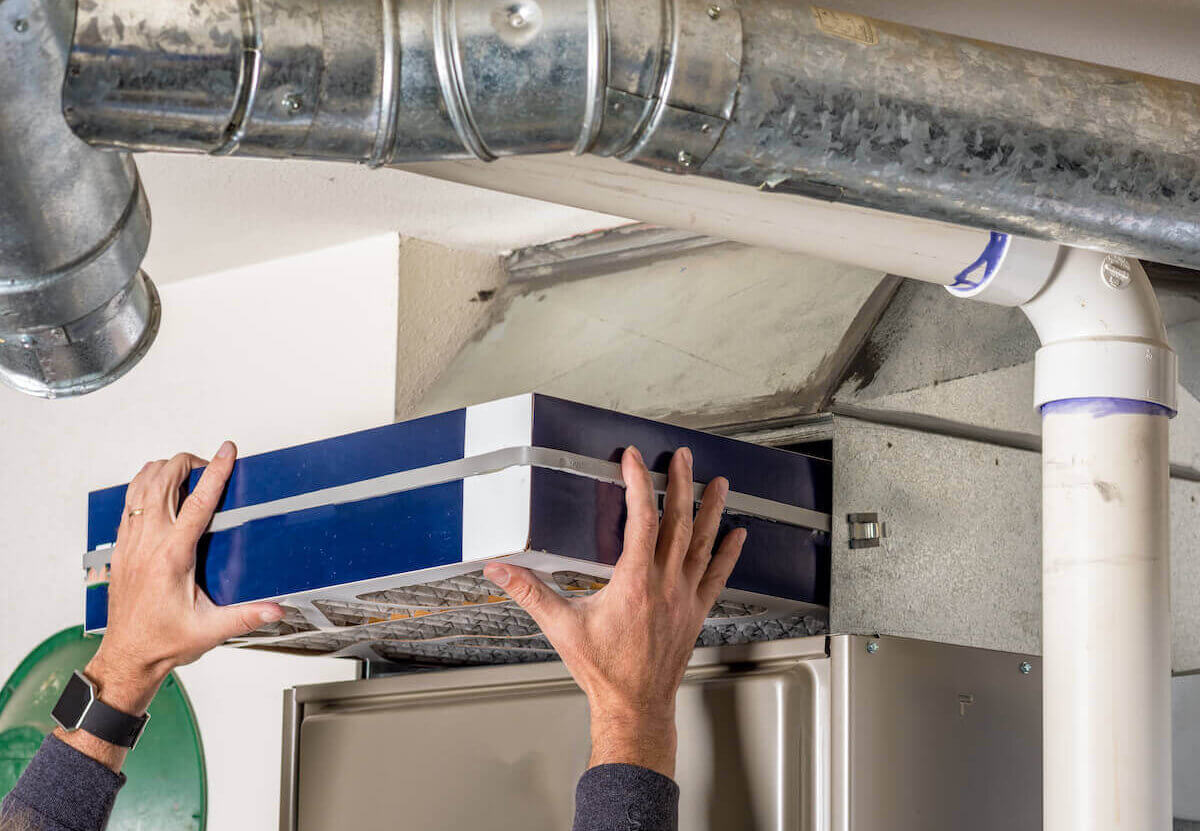
These systems can also be equipped with air filters and humidifiers to enhance indoor air quality and comfort. Air filters capture dust, allergens, and other particles, preventing them from circulating through the ducts and entering living spaces. Humidifiers, on the other hand, add moisture to the air, addressing issues related to dryness and improving overall comfort.
Forced air heating systems offer versatility, as they can be integrated with air conditioning units to provide year-round climate control. By utilizing the same ductwork, these systems efficiently distribute both heated and cooled air, offering a comprehensive solution for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment.
Understanding the fundamental operation and components of forced air heating systems is essential for effectively managing and optimizing their performance. By gaining insight into how these systems function, individuals can make informed decisions regarding maintenance, upgrades, and air flow control, ultimately ensuring a comfortable and energy-efficient living or working environment.
Importance of Controlling Air Flow
Controlling air flow within a forced air heating system is paramount for several reasons, each contributing to the overall efficiency, comfort, and functionality of the system. Proper air flow management not only ensures consistent and uniform heating throughout the living or working space but also plays a significant role in optimizing energy usage and reducing operational costs.
One of the primary reasons for controlling air flow is to maintain balanced temperatures across different areas within the building. Without adequate control, certain rooms may become excessively warm while others remain chilly, leading to discomfort and the need for constant thermostat adjustments. By regulating air flow, the heated air can be evenly distributed, eliminating temperature differentials and creating a more comfortable environment for occupants.
Furthermore, effective air flow control contributes to energy efficiency. When air flow is unregulated, the heating system may work harder to compensate for uneven distribution, leading to unnecessary energy consumption. This not only impacts utility bills but also places additional strain on the heating equipment, potentially shortening its lifespan. By managing air flow, the system can operate more efficiently, utilizing energy resources judiciously and reducing overall heating costs.
Controlling air flow also enables individuals to address indoor air quality concerns. Properly managed air flow helps in the circulation of fresh air and the removal of airborne pollutants, allergens, and odors. Additionally, it facilitates the distribution of humidity, ensuring that indoor air remains at an optimal moisture level for comfort and health.
Moreover, air flow control allows for the effective utilization of zoning systems, where different areas of the building can be heated or cooled independently. This level of control not only enhances comfort by catering to specific temperature preferences in different zones but also contributes to energy savings by avoiding unnecessary heating or cooling of unoccupied spaces.
In summary, the importance of controlling air flow in forced air heating systems cannot be overstated. From maintaining uniform temperatures and improving energy efficiency to enhancing indoor air quality and enabling zoning capabilities, effective air flow management is integral to the overall performance and comfort provided by these heating systems. By understanding and implementing strategies to control air flow, individuals can optimize their heating systems, reduce operational costs, and create a more pleasant and sustainable indoor environment.
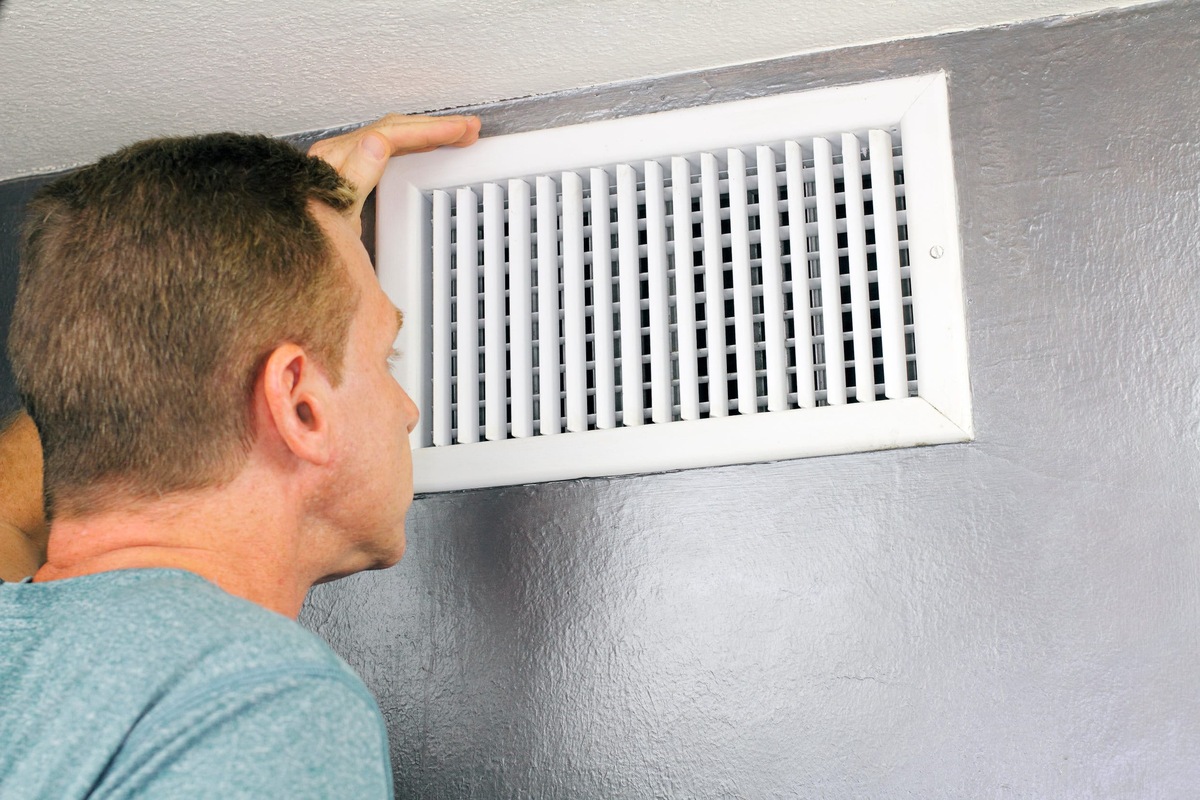
To control air flow in a forced air heating system, adjust the vents in each room to direct the air where you want it. Closing vents in unused rooms can help redirect more heat to the rooms you use most.
Tips for Controlling Air Flow in Forced Air Heating Systems
-
Regularly Clean and Maintain Air Ducts and Vents: Over time, dust, debris, and other particles can accumulate within the ductwork and vents, obstructing air flow and diminishing the system's efficiency. Regular inspection and cleaning of these components are essential to ensure unimpeded air circulation. By removing any obstructions and maintaining clean ducts and vents, the system can distribute heated air effectively, promoting consistent warmth throughout the building.
-
Adjust and Balance Air Vents: The proper adjustment and balancing of air vents play a crucial role in controlling air flow. By adjusting the vents in different rooms, occupants can regulate the amount of heated air entering each space, thereby achieving balanced temperatures throughout the building. This practice also allows for the customization of heating preferences based on individual room requirements, contributing to enhanced comfort and energy efficiency.
-
Utilize Zoning Systems: Implementing zoning systems enables precise control over the distribution of heated air within the building. By dividing the space into distinct zones and installing separate thermostats for each zone, occupants can independently regulate the temperature in different areas. This not only facilitates personalized comfort but also minimizes energy wastage by heating only the occupied zones, leading to potential cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
-
Invest in Programmable Thermostats: Programmable thermostats offer advanced functionality for managing air flow and temperature settings. These devices allow users to schedule specific temperature adjustments based on daily or weekly routines, ensuring optimal comfort while conserving energy when heating is not required. By programming the thermostat to lower the temperature during periods of absence or at night, individuals can effectively control air flow and reduce heating expenses.
-
Consider the Use of Dampers: Dampers are adjustable plates installed within the ductwork to regulate air flow to specific zones or rooms. By strategically adjusting these dampers, individuals can redirect air flow as needed, directing more heated air to areas requiring additional warmth and reducing it in spaces where less heating is necessary. This level of control contributes to balanced temperatures and efficient energy utilization.
-
Regularly Replace Air Filters: Clean air filters are essential for maintaining unobstructed air flow and preserving indoor air quality. Clogged or dirty filters can impede the movement of heated air, leading to reduced system efficiency and potential damage. Regularly replacing air filters, as recommended by the manufacturer, ensures proper air flow and contributes to the longevity and performance of the forced air heating system.
-
Seek Professional Maintenance and Inspection: Engaging the services of HVAC professionals for routine maintenance and inspection is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance of forced air heating systems. These experts can conduct thorough assessments, identify potential air flow issues, and provide necessary adjustments or repairs to enhance the system's efficiency and air flow control.
By implementing these tips for controlling air flow in forced air heating systems, individuals can optimize the performance, energy efficiency, and comfort provided by their heating systems, ultimately creating a more pleasant and sustainable indoor environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the effective control of air flow within forced air heating systems is essential for maintaining comfortable indoor environments, optimizing energy usage, and ensuring the overall efficiency of these heating systems. By understanding the fundamental operation of forced air heating systems and recognizing the significance of air flow control, individuals can implement strategies to enhance performance and comfort while minimizing operational costs.
Throughout this guide, we have explored the intricate workings of forced air heating systems, shedding light on the process of heating air, distributing it through ductwork, and regulating indoor temperatures via thermostats. This understanding serves as a foundation for comprehending the importance of managing air flow within these systems, as it directly impacts temperature consistency, energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and zoning capabilities.
The tips provided for controlling air flow offer practical and actionable guidance for homeowners, facility managers, and individuals responsible for the maintenance of forced air heating systems. From regular cleaning and maintenance of air ducts and vents to the utilization of zoning systems and programmable thermostats, these strategies empower individuals to optimize air flow, enhance comfort, and reduce energy consumption.
By embracing these recommendations and incorporating them into their heating system management practices, individuals can experience the benefits of balanced temperatures, improved indoor air quality, and potential cost savings. Furthermore, the implementation of these air flow control strategies contributes to the sustainable operation of forced air heating systems, aligning with the growing emphasis on energy conservation and environmental responsibility.
In essence, the effective control of air flow in forced air heating systems is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses temperature regulation, energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and personalized comfort. By prioritizing air flow management and leveraging the insights and tips provided in this guide, individuals can elevate the performance and functionality of their heating systems, creating welcoming and sustainable indoor environments for occupants.
As we conclude this exploration of air flow control in forced air heating systems, it is evident that a proactive approach to managing air flow not only enhances the functionality of these systems but also contributes to a more comfortable, efficient, and environmentally conscious living and working environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Control Air Flow Forced Air Heating System
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.















0 thoughts on “How To Control Air Flow Forced Air Heating System”