Home>Home Appliances>Heating & Cooling>Hydro Air Heating Air Bound: How To Bleed Air Both Way


Heating & Cooling
Hydro Air Heating Air Bound: How To Bleed Air Both Way
Published: February 16, 2024
Learn how to effectively bleed air from your hydro air heating system in both directions. Keep your heating and cooling system running smoothly with our expert tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Hydro air heating and cooling systems are a popular choice for many homeowners due to their efficiency and versatility. These systems utilize a combination of water and air to provide comfortable temperatures throughout the home, offering both heating and cooling capabilities. However, like any complex system, hydro air systems can encounter issues that require attention and maintenance.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of hydro air heating and cooling systems, exploring the common issues associated with air bound systems and providing practical solutions for bleeding air from both the heating and cooling components. Whether you're a homeowner with a hydro air system or a professional in the heating and cooling industry, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques needed to address air bound challenges effectively.
By understanding the inner workings of hydro air systems and learning how to identify and resolve air bound issues, you can ensure that your heating and cooling system operates at peak performance, providing optimal comfort and energy efficiency for your home. Let's embark on this journey to unravel the mysteries of hydro air heating and cooling, empowering you to conquer air bound challenges with confidence and expertise.
Key Takeaways:
- Don’t let trapped air ruin your home’s comfort! Learn to spot air bound issues like reduced heating or cooling, strange noises, and pressure changes. Regularly bleed air from your system for peak performance.
- Keep your hydro air system in top shape by bleeding air from both the heating and cooling components. This simple maintenance task ensures consistent comfort and efficient operation throughout the year.
Read more: What Is A Hydro Air Heating System
Understanding Hydro Air Heating Systems
Hydro air heating systems, also known as hydronic air handlers, are a versatile and efficient option for maintaining comfortable temperatures in residential and commercial spaces. These systems integrate the principles of both hydronic heating and forced air heating, utilizing a combination of water and air to distribute warmth throughout the building.
At the core of a hydro air heating system is a boiler, which heats water to a predetermined temperature. The heated water is then circulated through a network of pipes to various terminal units, such as air handlers or radiators, where heat is transferred to the surrounding air. This warm air is then distributed throughout the building via ductwork, providing consistent and even heating.
One of the key advantages of hydro air systems is their ability to seamlessly transition between heating and cooling functions. In addition to providing warmth during the colder months, these systems can be equipped with air conditioning components, allowing them to deliver cool air during the warmer seasons. This dual functionality makes hydro air systems a popular choice for regions with fluctuating climate patterns.
Furthermore, hydro air systems offer precise temperature control and zoning capabilities, enabling users to customize the heating and cooling levels in different areas of the building. This level of flexibility contributes to energy efficiency and personalized comfort, as occupants can adjust the temperature settings to suit their preferences.
In summary, hydro air heating systems represent a sophisticated fusion of hydronic heating and forced air technology, offering efficient and adaptable solutions for maintaining indoor comfort. By harnessing the power of water and air, these systems provide reliable heating and cooling performance, making them a compelling choice for modern residential and commercial applications.
Identifying Air Bound Issues
Identifying air bound issues in a hydro air heating and cooling system is crucial for maintaining its optimal functionality. Air bound, or air-locked, conditions can impede the proper circulation of water or air within the system, leading to reduced efficiency and potential damage if left unresolved. Recognizing the signs of air bound issues is the first step in addressing and rectifying these challenges.
Common Indicators of Air Bound Systems
-
Reduced Heating or Cooling Performance: When air becomes trapped within the system, it can hinder the flow of water or air, resulting in diminished heating or cooling output. Occupants may notice uneven temperatures or a decrease in overall comfort levels.
-
Unusual Noises: Air pockets within the system can cause gurgling, banging, or knocking sounds, particularly in the pipes or air handlers. These noises are indicative of air interference and should prompt further investigation.
-
Fluctuating Pressure Readings: For hydronic systems, fluctuating pressure readings on the boiler or pressure gauge may signal the presence of air within the water circulation system. Inconsistent pressure levels can indicate air blockages that need to be addressed.
-
Inefficient Air Bleeding: During routine maintenance or when attempting to bleed air from the system, if air continues to be present despite bleeding procedures, it is a strong indication of persistent air bound issues.
Visual Inspection
Inspecting the components of the system, such as the boiler, pipes, air handlers, and radiators, can reveal air bound symptoms. Look for air bubbles in the sight glass of the boiler, which indicate the presence of air in the water circulation. Additionally, visually inspecting the piping and terminal units for air pockets or irregularities can help identify potential air bound areas.
Read more: How To Bleed A Central Heating System
Monitoring System Behavior
Regularly monitoring the system's behavior and performance can provide valuable insights into potential air bound issues. Keep an eye on temperature differentials across various zones, as well as any fluctuations in pressure or flow rates. Anomalies in these parameters can serve as early indicators of air bound conditions within the system.
By recognizing these telltale signs and symptoms, homeowners and HVAC professionals can promptly address air bound issues, ensuring that the hydro air heating and cooling system operates at its full capacity, delivering consistent comfort and efficiency.
Bleeding Air from the Heating System
Bleeding air from a hydro air heating system is a critical maintenance task that helps to ensure the system's optimal performance and efficiency. Air trapped within the heating system can impede the circulation of hot water, leading to reduced heating capacity and potential damage to system components. By bleeding air from the heating system, homeowners and HVAC professionals can effectively address air bound issues and restore the system to its peak functionality.
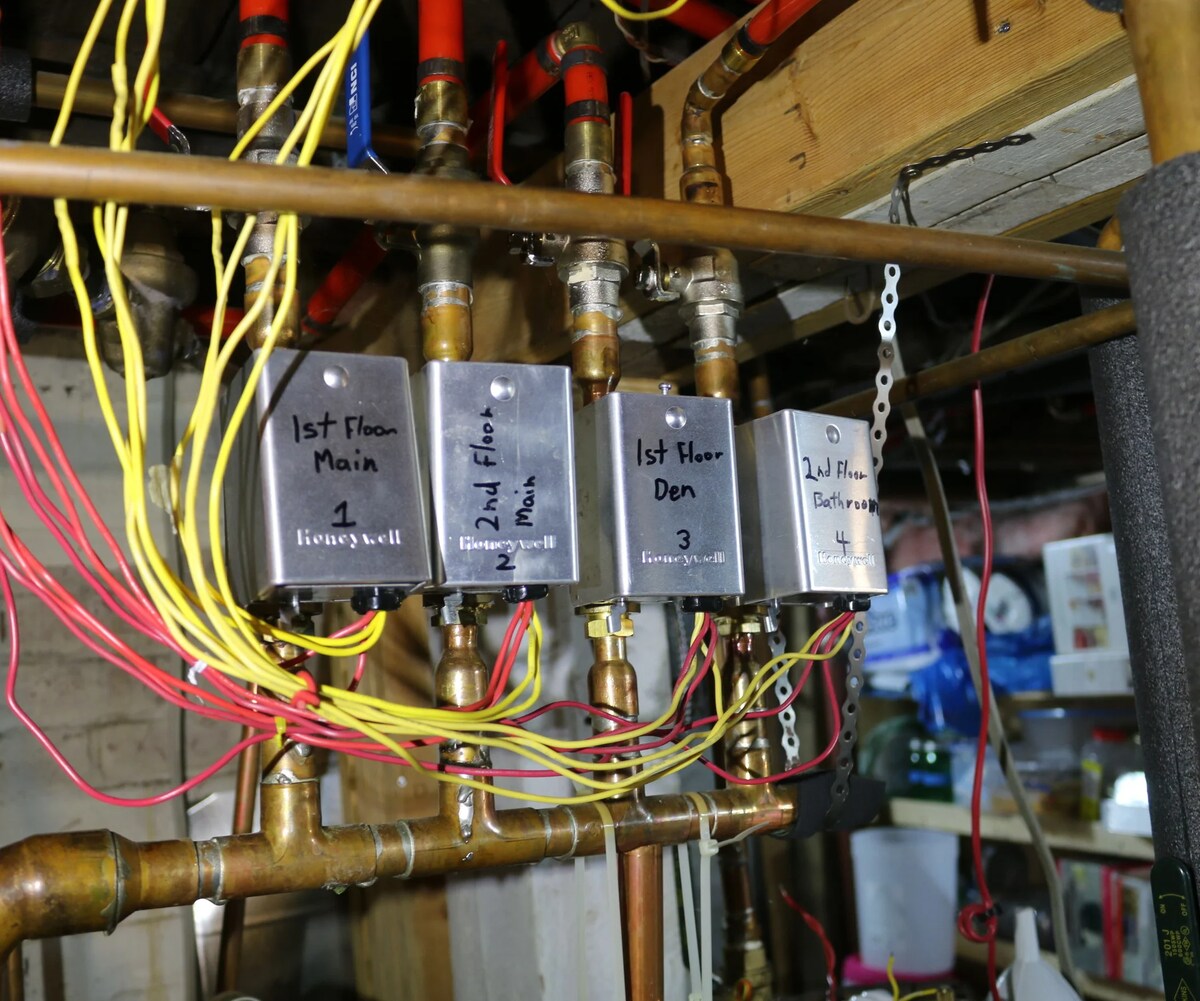
The process of bleeding air from the heating system involves purging trapped air from the water circulation network, allowing for smooth and uninterrupted flow. To begin, it is essential to locate the air bleed valves, which are typically found at high points in the system, such as near radiators or at the top of piping loops. These valves are designed to release air while retaining water within the system.
Before initiating the bleeding process, it is crucial to ensure that the heating system is turned off and allowed to cool down. This precaution prevents potential scalding from hot water and ensures a safe working environment. Once the system has cooled, the air bleed valves can be opened using a suitable tool, such as a flat-blade screwdriver or a specialized air vent key.
As the air bleed valves are opened, air trapped within the system will begin to escape, often accompanied by a hissing or gurgling sound. It is important to have a container or cloth ready to capture any water that may be released along with the air. As the air is purged, the valves should be carefully monitored until a steady stream of water flows out, indicating that the air has been successfully expelled.
After bleeding air from the heating system, the air bleed valves should be closed securely to prevent water leakage. It is advisable to check the system pressure and top up the water level if necessary, ensuring that the heating system operates within the recommended parameters.
Regularly bleeding air from the heating system is an essential maintenance practice that promotes the longevity and efficiency of the hydro air heating system. By addressing air bound issues proactively, homeowners can enjoy consistent and reliable heating performance, while minimizing the risk of potential damage to system components.
Bleeding Air from the Cooling System
Bleeding air from the cooling system of a hydro air heating and cooling system is a crucial maintenance task that contributes to the efficient operation of the system. Air trapped within the cooling components can impede the circulation of chilled water or refrigerant, leading to reduced cooling capacity and potential damage to system elements. By bleeding air from the cooling system, homeowners and HVAC professionals can effectively address air bound issues and restore the system to its peak functionality.
The process of bleeding air from the cooling system involves purging trapped air from the water or refrigerant circulation network, allowing for smooth and uninterrupted flow. To begin, it is essential to locate the air bleed valves or vents, which are typically positioned at high points in the cooling system, such as near air handlers or at the apex of piping loops. These valves are designed to release air while retaining the cooling medium within the system.
Before commencing the bleeding process, it is crucial to ensure that the cooling system is turned off to prevent any potential hazards. Once the system is safely powered down, the air bleed valves can be opened using an appropriate tool, such as a flat-blade screwdriver or a specialized air vent key.
As the air bleed valves are opened, air trapped within the system will begin to escape, often accompanied by a hissing or gurgling sound. It is important to have a container or cloth ready to capture any water or refrigerant that may be released along with the air. As the air is purged, the valves should be carefully monitored until a steady stream of water or refrigerant flows out, indicating that the air has been successfully expelled.
After bleeding air from the cooling system, the air bleed valves should be closed securely to prevent any leakage of the cooling medium. It is advisable to check the system pressure and ensure that the cooling system operates within the recommended parameters.
Regularly bleeding air from the cooling system is an essential maintenance practice that promotes the longevity and efficiency of the hydro air heating and cooling system. By addressing air bound issues proactively, homeowners can enjoy consistent and reliable cooling performance, while minimizing the risk of potential damage to system components.
To bleed air from a hydro air heating system, locate the bleed valve on the highest point of the system. Use a key or screwdriver to open the valve and release the trapped air. Repeat this process for all radiators and pipes in the system to ensure proper heating.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of hydro air heating and cooling systems is essential for homeowners and HVAC professionals alike. These versatile systems, which integrate the principles of hydronic heating and forced air technology, offer efficient and adaptable solutions for maintaining indoor comfort throughout the year. By harnessing the power of water and air, hydro air systems provide reliable heating and cooling performance, making them a compelling choice for modern residential and commercial applications.
Identifying air bound issues within a hydro air system is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality. Common indicators such as reduced heating or cooling performance, unusual noises, fluctuating pressure readings, and inefficient air bleeding serve as valuable cues for recognizing air bound conditions. Visual inspections and monitoring system behavior are essential in identifying potential air bound areas, allowing homeowners and HVAC professionals to promptly address these issues.
Bleeding air from the heating and cooling components of a hydro air system is a critical maintenance task that helps to ensure the system's optimal performance and efficiency. By purging trapped air from the water or refrigerant circulation network, the system can operate smoothly and deliver consistent comfort. Regularly bleeding air from both the heating and cooling components is an essential maintenance practice that promotes the longevity and efficiency of the hydro air system.
In essence, by understanding the inner workings of hydro air systems, recognizing air bound issues, and effectively bleeding air from the system, homeowners and HVAC professionals can ensure that their heating and cooling system operates at peak performance, providing optimal comfort and energy efficiency for the home or building. This comprehensive guide equips individuals with the knowledge and techniques needed to conquer air bound challenges with confidence and expertise, ultimately enhancing the overall functionality and longevity of hydro air heating and cooling systems.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hydro Air Heating Air Bound: How To Bleed Air Both Way
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “Hydro Air Heating Air Bound: How To Bleed Air Both Way”