Home>Home Appliances>Heating & Cooling>What Is A Hot Air Heating System


Heating & Cooling
What Is A Hot Air Heating System
Modified: February 18, 2024
Learn about the benefits of a hot air heating system for efficient heating and cooling. Find out how it works and if it's the right choice for your home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Hot air heating systems are a popular and efficient way to keep homes and businesses warm during the colder months. These systems work by heating air and then distributing it throughout a building to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Whether you're considering installing a hot air heating system or simply want to learn more about how they work, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of these heating systems.
Hot air heating systems have been a staple in the heating and cooling industry for many years, offering reliable and consistent warmth to countless properties. Understanding the mechanics, benefits, and drawbacks of these systems is crucial for making informed decisions about heating solutions. In the following sections, we will delve into the inner workings of hot air heating systems, the various types available, their advantages and disadvantages, as well as essential maintenance tips to ensure their longevity and efficiency.
As we explore the intricacies of hot air heating systems, you will gain valuable insights into their functionality, enabling you to make informed choices when it comes to heating your home or business. Whether you're a homeowner, a business owner, or simply someone interested in heating and cooling technologies, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to understand, maintain, and appreciate the benefits of hot air heating systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Hot air heating systems work by heating air in a furnace and distributing it through ducts, providing quick and even warmth. They can also improve air quality and offer energy-efficient heating options.
- Property owners should prioritize regular maintenance for hot air heating systems to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and cost savings. This includes professional inspections, filter replacement, duct cleaning, and addressing system issues promptly.
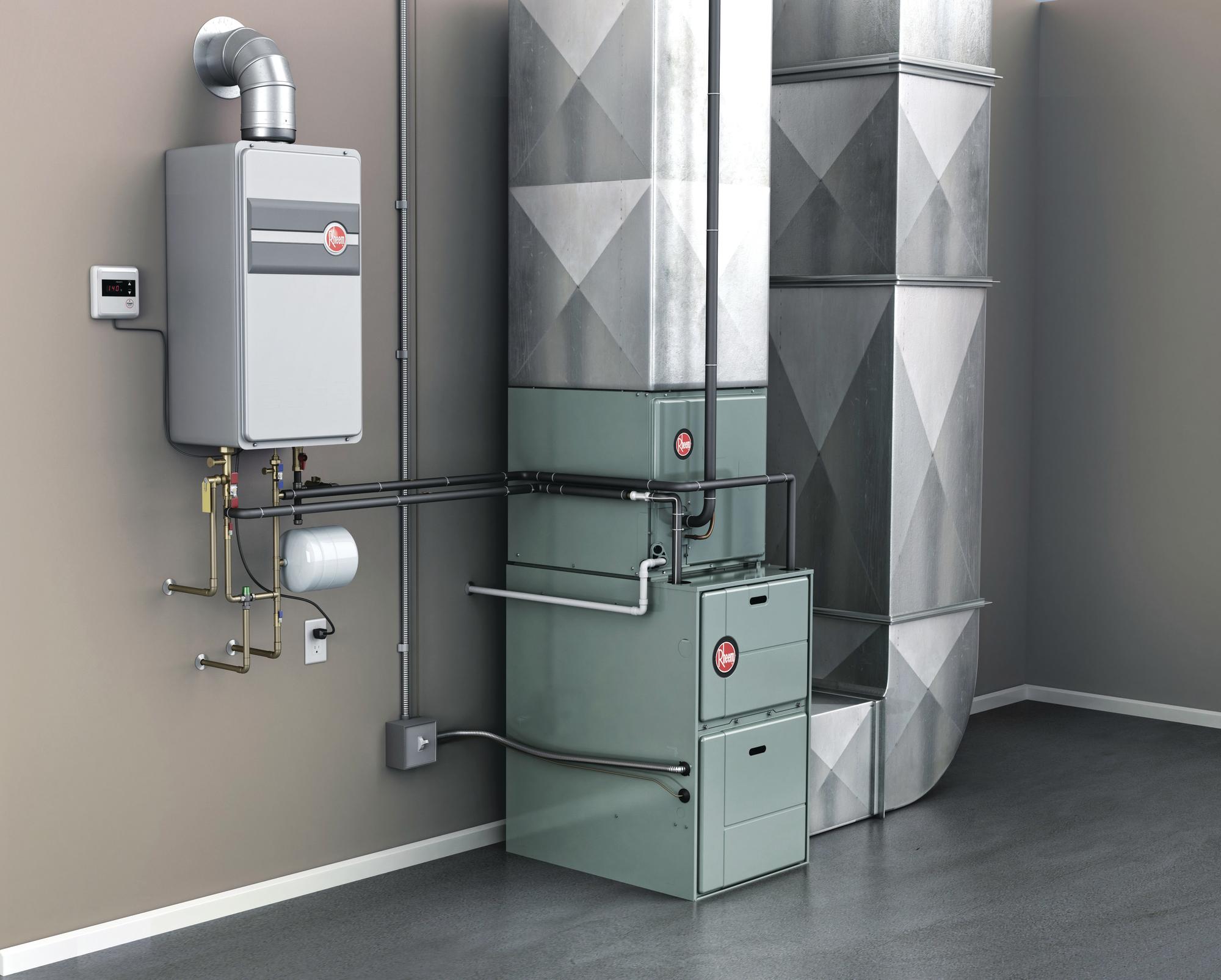
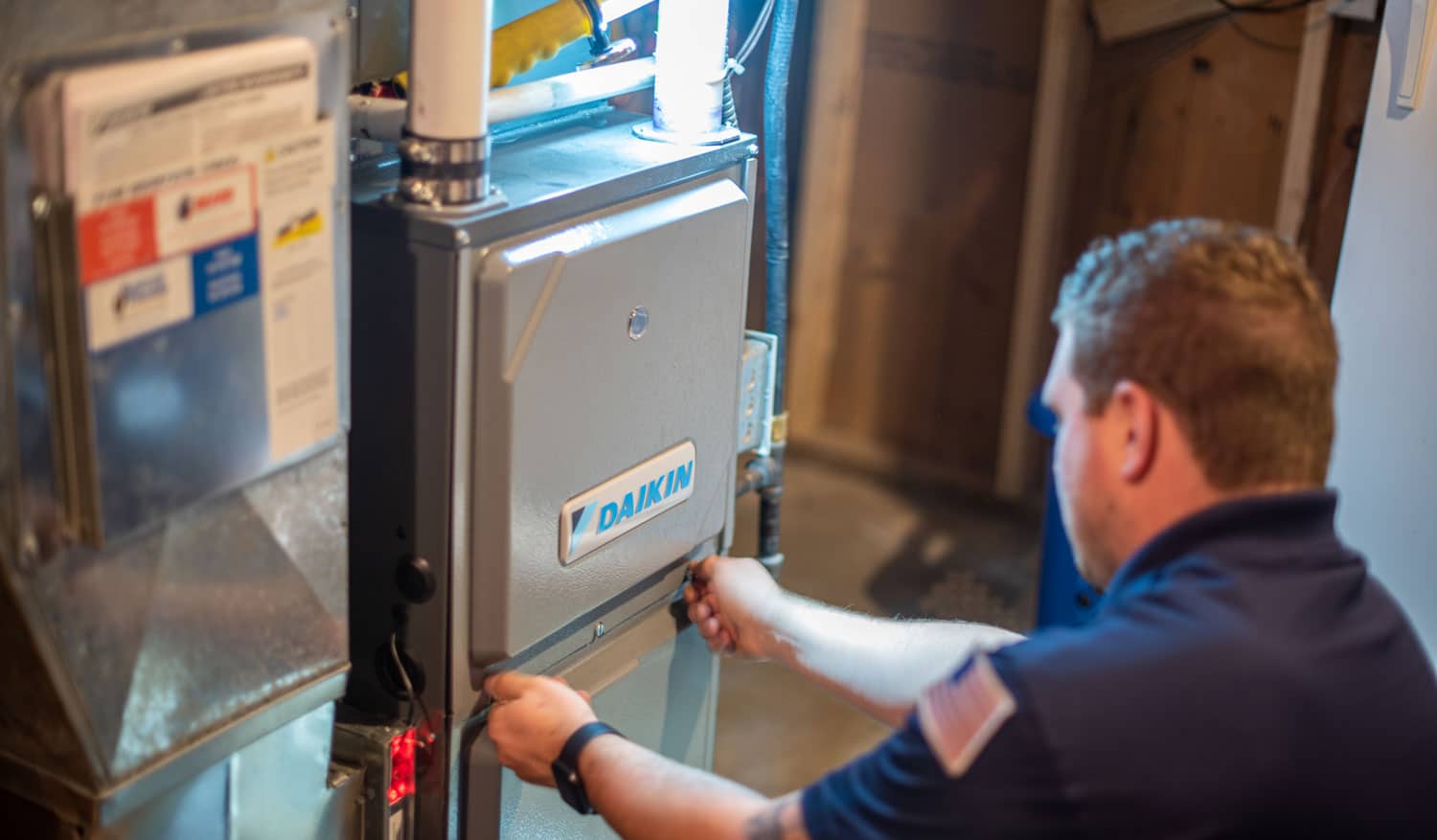
How Does a Hot Air Heating System Work?
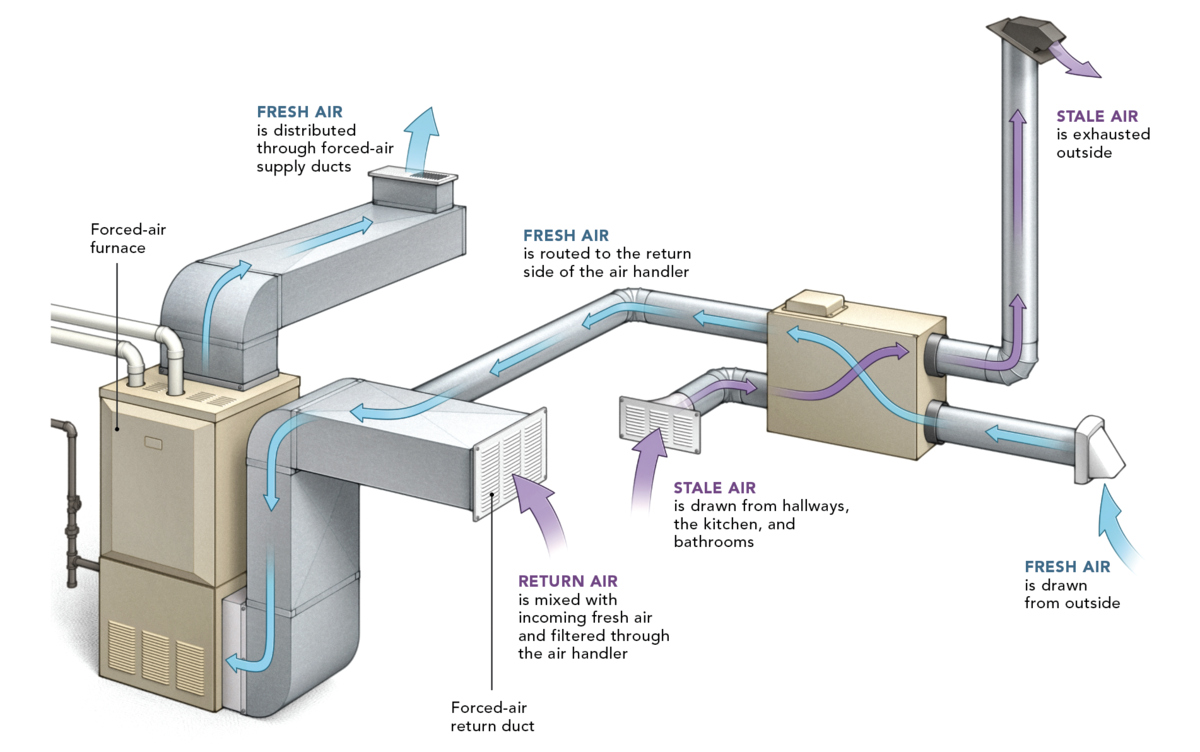
A hot air heating system operates by using a furnace to heat air, which is then distributed throughout a building via a network of ducts and vents. The process begins with the furnace igniting a fuel source, such as natural gas, propane, or oil, to generate heat. As the air inside the furnace heats up, a blower fan forces it through the ductwork, where it is then dispersed into various rooms through vents or registers.
The furnace's heat exchanger plays a critical role in the heating process. This component absorbs heat from the combustion of the fuel and transfers it to the air passing through the system. Once the air reaches the desired temperature, it is released into the living spaces, effectively raising the indoor temperature to the set thermostat level.
To maintain a comfortable environment, the thermostat continuously monitors the indoor temperature and signals the furnace to cycle on or off as needed. This ensures that the heating system operates efficiently and keeps the indoor climate consistent.
Hot air heating systems can also incorporate air filtration and humidification components. Air filters help remove dust, allergens, and other particles from the heated air, enhancing indoor air quality. Additionally, humidifiers can be integrated into the system to add moisture to the air, preventing dryness and improving overall comfort during the winter months.
In summary, a hot air heating system works by heating air in a furnace, distributing it through ductwork, and releasing it into living spaces to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. The integration of a thermostat, air filtration, and humidification components further enhances the system's functionality, ensuring a cozy and healthy indoor environment. Understanding the fundamental operation of hot air heating systems provides valuable insight into their effectiveness and the benefits they offer for residential and commercial heating needs.
Types of Hot Air Heating Systems
Hot air heating systems come in various types, each offering unique features and benefits to suit different heating needs. Understanding the different types of hot air heating systems is essential for selecting the most suitable option for residential or commercial spaces. Here are some common types of hot air heating systems:
-
Forced Air Systems: This type of hot air heating system utilizes a furnace to heat air, which is then distributed through ductwork using a blower fan. Forced air systems are popular for their ability to quickly and evenly distribute heated air throughout a building, providing consistent warmth. These systems are versatile and can accommodate air filtration and humidification components to enhance indoor air quality and comfort.
-
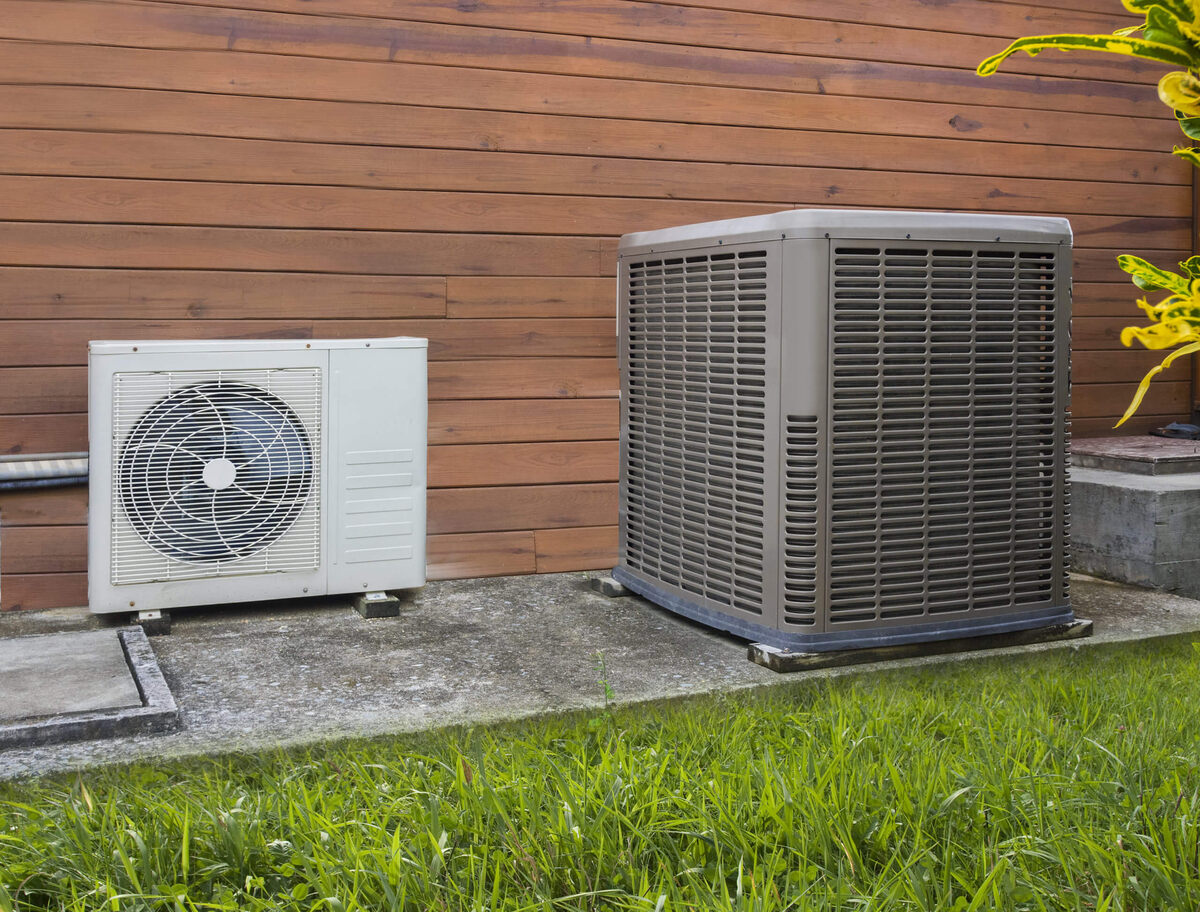
Heat Pumps: Heat pump systems are an energy-efficient option for heating and cooling spaces. They work by transferring heat between the indoor and outdoor environments, providing both heating and cooling capabilities. In heating mode, heat pumps extract heat from the outdoor air and transfer it indoors, offering an efficient way to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. Heat pump systems are known for their eco-friendly operation and cost-effective heating solutions.
-
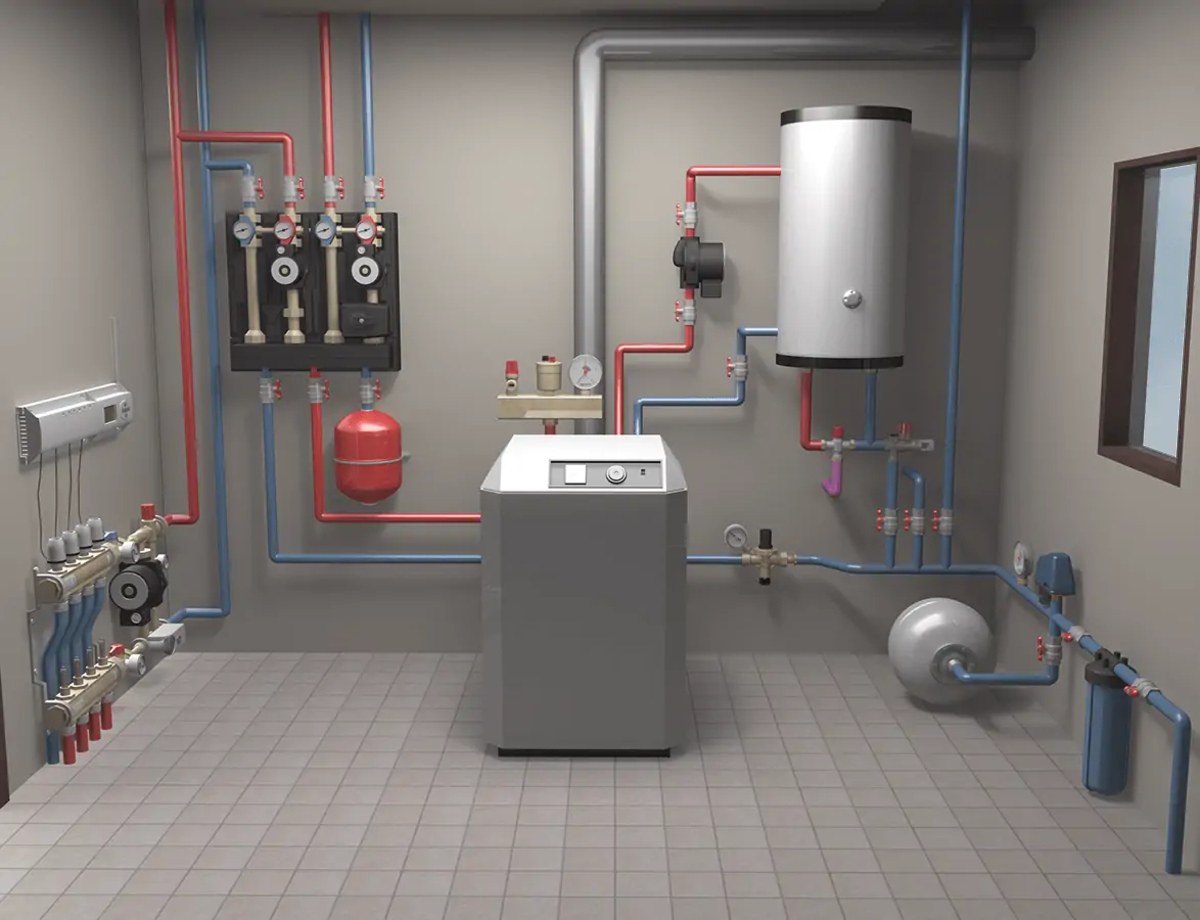
Hydronic Heating Systems: While not directly heating air, hydronic heating systems utilize hot water or steam to distribute heat throughout a building. These systems can incorporate radiant floor heating, baseboard heaters, or radiators to emit warmth into living spaces. Hydronic heating systems offer quiet and consistent heating, making them a popular choice for many homeowners.
-
Electric Furnaces: Electric hot air heating systems use electric resistance coils to generate heat, which is then distributed through ductwork. These systems are known for their simplicity and ease of installation, making them a convenient option for spaces where natural gas or other fuel sources may not be available. Electric furnaces are also considered a clean and efficient heating solution.
-
Geothermal Heat Pumps: Geothermal heat pump systems utilize the stable temperature of the earth to provide heating and cooling. By circulating a heat transfer fluid through underground pipes, these systems harness the earth's natural heat, offering a sustainable and energy-efficient heating solution. Geothermal heat pumps are known for their long-term cost savings and minimal environmental impact.
Understanding the different types of hot air heating systems allows homeowners and business owners to make informed decisions when selecting a heating solution. Each type offers distinct advantages and considerations, and choosing the most suitable system depends on factors such as energy efficiency, installation requirements, and overall heating needs. By exploring the various options available, individuals can identify the best hot air heating system to meet their specific requirements.
Advantages of Hot Air Heating Systems
Hot air heating systems offer a range of advantages that make them a popular choice for residential and commercial heating needs. Understanding these advantages provides valuable insight into the benefits of utilizing hot air heating systems to maintain comfortable indoor environments. Here are the key advantages of hot air heating systems:
-
Efficient Heating Distribution: Hot air heating systems utilize ductwork to distribute heated air evenly throughout a building. This results in consistent warmth in every room, ensuring a comfortable and cozy indoor environment. The efficient distribution of heat is particularly beneficial for larger properties, where maintaining uniform temperatures can be a challenge with other heating methods.
-
Quick Heating Response: Hot air heating systems provide rapid heating response, allowing spaces to reach the desired temperature quickly. This is especially advantageous during cold weather, as the system can promptly counteract the chill, providing immediate comfort to occupants. The ability to achieve rapid heating response enhances the overall convenience and functionality of hot air heating systems.
-
Integration with Air Filtration and Humidification: Many hot air heating systems can be integrated with air filtration and humidification components. This feature enhances indoor air quality by removing airborne particles and adding moisture to the air, creating a healthier and more comfortable living or working environment. The ability to improve air quality while maintaining optimal warmth is a significant advantage of hot air heating systems.
-
Compatibility with Thermostats and Zoning: Hot air heating systems can be easily integrated with programmable thermostats and zoning systems. This allows for precise temperature control in different areas of a building, optimizing energy efficiency and providing personalized comfort. The compatibility with advanced control systems enhances the flexibility and customization options for hot air heating systems.
-
Versatility and Energy Efficiency: Hot air heating systems offer versatility in terms of fuel sources, with options including natural gas, propane, oil, and electricity. This flexibility allows property owners to choose the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly fuel source for their heating needs. Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of energy-efficient hot air heating systems, reducing energy consumption and operating costs.
-
Cost-Effective Installation and Maintenance: Hot air heating systems are known for their relatively straightforward installation and maintenance requirements. This can result in cost savings for property owners, as the systems are designed for ease of installation and routine upkeep. The cost-effective nature of hot air heating systems makes them an attractive option for those seeking efficient and reliable heating solutions.
In summary, hot air heating systems offer efficient heating distribution, quick heating response, integration with air filtration and humidification, compatibility with advanced control systems, versatility in fuel sources, energy efficiency, and cost-effective installation and maintenance. These advantages collectively contribute to the appeal and practicality of hot air heating systems for both residential and commercial applications.
Disadvantages of Hot Air Heating Systems
While hot air heating systems offer numerous benefits, it is important to consider their potential drawbacks. Understanding the disadvantages of these systems provides a comprehensive view of their limitations and challenges. Here are the key disadvantages of hot air heating systems:
-
Air Quality Concerns: One of the primary drawbacks of hot air heating systems is the potential impact on indoor air quality. As the systems circulate air through ductwork, dust, allergens, and other particles can accumulate within the ducts and vents. Without proper maintenance and regular cleaning, these contaminants can be released into the indoor environment, potentially affecting the respiratory health of occupants.
-
Dry Air: Hot air heating systems can contribute to dry indoor air, especially during the winter months. As the systems heat and distribute air, moisture levels may decrease, leading to discomfort such as dry skin, throat irritation, and static electricity buildup. While some systems offer humidification options, addressing dry air concerns may require additional measures to maintain optimal indoor humidity levels.
-
Noise Levels: The operation of hot air heating systems, particularly the blower fans and ductwork, can generate noticeable noise within the living or working spaces. This can be a concern for individuals seeking a quieter indoor environment, especially during the system's cycling on and off periods. Noise reduction strategies may be necessary to mitigate the impact of operational sounds.
-
Uneven Heating: In some cases, hot air heating systems may result in uneven heating distribution throughout a building. Certain areas or rooms may experience variations in temperature, leading to potential discomfort for occupants. Addressing uneven heating may require adjustments to the system's ductwork, registers, or the implementation of zoning solutions to achieve consistent warmth in all areas.
-
Dependence on Ductwork: Hot air heating systems rely on ductwork to distribute heated air, and the condition of the ducts can significantly impact system performance. Issues such as leaks, blockages, or inadequate insulation within the ductwork can compromise the efficiency and effectiveness of the heating system. Ensuring proper duct maintenance and addressing any duct-related issues is essential for optimal system operation.
-
Initial Cost and Installation Considerations: The installation of a hot air heating system may involve significant upfront costs, especially if ductwork needs to be installed or modified. Additionally, properties without existing ductwork may require extensive retrofitting, adding to the overall installation expenses. Property owners should carefully assess the initial investment and installation requirements when considering hot air heating systems.
Understanding the potential disadvantages of hot air heating systems allows individuals to make informed decisions regarding their heating needs. While these drawbacks present considerations for system operation and maintenance, proactive measures and appropriate system design can help mitigate these challenges, ensuring a comfortable and efficient heating experience.
Maintenance and Care for Hot Air Heating Systems
Proper maintenance and care are essential for ensuring the optimal performance, longevity, and safety of hot air heating systems. By implementing regular maintenance practices and addressing potential issues promptly, property owners can maximize the efficiency of their heating systems while minimizing the risk of malfunctions and safety hazards. Here are key maintenance tasks and care considerations for hot air heating systems:
1. Professional Inspections:
Scheduling annual inspections by qualified HVAC professionals is crucial for assessing the overall condition of hot air heating systems. During these inspections, technicians can examine the furnace, ductwork, vents, and other system components to identify any potential issues, such as worn-out parts, leaks, or blockages. Professional inspections also include safety checks to ensure that the system operates securely and complies with industry standards.
2. Filter Replacement:
Regular filter replacement is a fundamental maintenance task for hot air heating systems. Air filters trap dust, debris, and airborne particles, preventing them from circulating through the system and into indoor spaces. Clogged filters can impede airflow and strain the system, leading to reduced efficiency and potential damage. Property owners should adhere to the manufacturer's recommendations for filter replacement intervals and use high-quality filters to maintain optimal indoor air quality.
3. Duct Cleaning:
Periodic duct cleaning is essential for removing accumulated dust, allergens, and contaminants from the ductwork. Professional duct cleaning services can eliminate debris that may hinder airflow and compromise indoor air quality. Clean ducts contribute to efficient heating distribution and help prevent the circulation of pollutants throughout the property.
Read more: What Is Emergency Heat On HVAC
4. Lubrication and Component Maintenance:
The moving parts of hot air heating systems, such as blower fan motors and bearings, may require regular lubrication to reduce friction and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, components such as belts, pulleys, and electrical connections should be inspected and maintained to prevent wear and tear. Property owners should follow manufacturer guidelines for lubrication and seek professional assistance for component maintenance when necessary.
5. Thermostat Calibration:
Calibrating and testing the thermostat is essential for accurate temperature control and efficient system operation. Property owners should verify that the thermostat accurately reflects the indoor temperature and that it cycles the heating system appropriately. Upgrading to programmable or smart thermostats can provide advanced control features and energy-saving benefits.
6. Addressing System Issues Promptly:
Promptly addressing any system malfunctions, unusual noises, or performance issues is crucial for preventing further damage and ensuring uninterrupted heating. Property owners should not overlook warning signs such as inconsistent heating, unusual odors, or increased energy consumption, and should seek professional assistance to diagnose and resolve these issues promptly.
By prioritizing regular maintenance and care for hot air heating systems, property owners can optimize the performance, efficiency, and longevity of their heating systems. Proactive maintenance not only enhances the comfort and safety of indoor environments but also contributes to cost savings by reducing energy consumption and minimizing the need for extensive repairs. With a commitment to proper maintenance and care, hot air heating systems can reliably provide warmth and comfort for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hot air heating systems offer a reliable and efficient means of maintaining comfortable indoor environments in residential and commercial settings. These systems operate by heating air in a furnace and distributing it through ductwork, providing rapid heating response and consistent warmth throughout the property. The integration of advanced control features, air filtration, and humidification options further enhances the functionality and comfort provided by hot air heating systems.
Understanding the various types of hot air heating systems, including forced air systems, heat pumps, hydronic heating systems, electric furnaces, and geothermal heat pumps, allows property owners to select the most suitable option based on their specific heating needs and preferences. Each type offers distinct advantages, such as energy efficiency, versatility in fuel sources, and compatibility with advanced control systems, providing flexibility and customization options for property owners.
While hot air heating systems offer numerous benefits, it is important to consider potential drawbacks, such as air quality concerns, dry air issues, and the dependence on ductwork for heating distribution. Proactive measures, including regular maintenance, filter replacement, duct cleaning, and addressing system issues promptly, are essential for mitigating these challenges and ensuring the optimal performance and safety of hot air heating systems.
By prioritizing proper maintenance and care, property owners can maximize the efficiency and longevity of their hot air heating systems, contributing to cost savings and a comfortable indoor environment. Professional inspections, lubrication of moving parts, thermostat calibration, and prompt resolution of system issues are integral to the ongoing care and maintenance of hot air heating systems.
In essence, hot air heating systems continue to be a popular choice for their efficient heating distribution, quick heating response, and compatibility with advanced control features. With a comprehensive understanding of their operation, types, advantages, and maintenance requirements, property owners can make informed decisions when selecting, utilizing, and maintaining hot air heating systems to meet their heating needs effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Hot Air Heating System
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is A Hot Air Heating System”