Home>Home Appliances>Heating & Cooling>How To Design An Efficient Hot Air Heating System


Heating & Cooling
How To Design An Efficient Hot Air Heating System
Modified: February 17, 2024
Learn how to design an efficient hot air heating system for optimal heating and cooling. Discover expert tips and techniques for heating and cooling systems.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Hot air heating systems are a popular and efficient way to keep indoor spaces warm and comfortable. Whether it's a residential home, commercial building, or industrial facility, a well-designed hot air heating system can provide consistent warmth while minimizing energy consumption. Understanding the principles and components of hot air heating systems is essential for designing an effective and efficient heating solution.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of hot air heating systems, exploring the fundamental principles, key components, and best practices for designing an optimal heating system. By gaining insights into the various aspects of hot air heating, you will be equipped with the knowledge to create a heating system that not only meets your specific needs but also contributes to energy efficiency and cost savings.
Let's embark on a journey to unravel the inner workings of hot air heating systems, from understanding the basics to selecting the right components, designing efficient ductwork, and ensuring energy efficiency. Whether you are a homeowner, HVAC professional, or building manager, this guide will empower you to make informed decisions and design a hot air heating system that delivers exceptional performance and comfort.
Key Takeaways:
- Efficient hot air heating systems rely on components like furnaces, thermostats, and ductwork to distribute warmth effectively while minimizing energy consumption. Understanding these elements is crucial for creating a comfortable and cost-effective indoor environment.
- Designing an efficient hot air heating system involves careful consideration of factors such as heating load, energy sources, thermostat options, ductwork layout, and maintenance. By selecting the right components and implementing energy-efficient practices, individuals can create a sustainable and comfortable heating solution.
Read more: What Is A Hot Air Heating System
Understanding the Basics of Hot Air Heating Systems
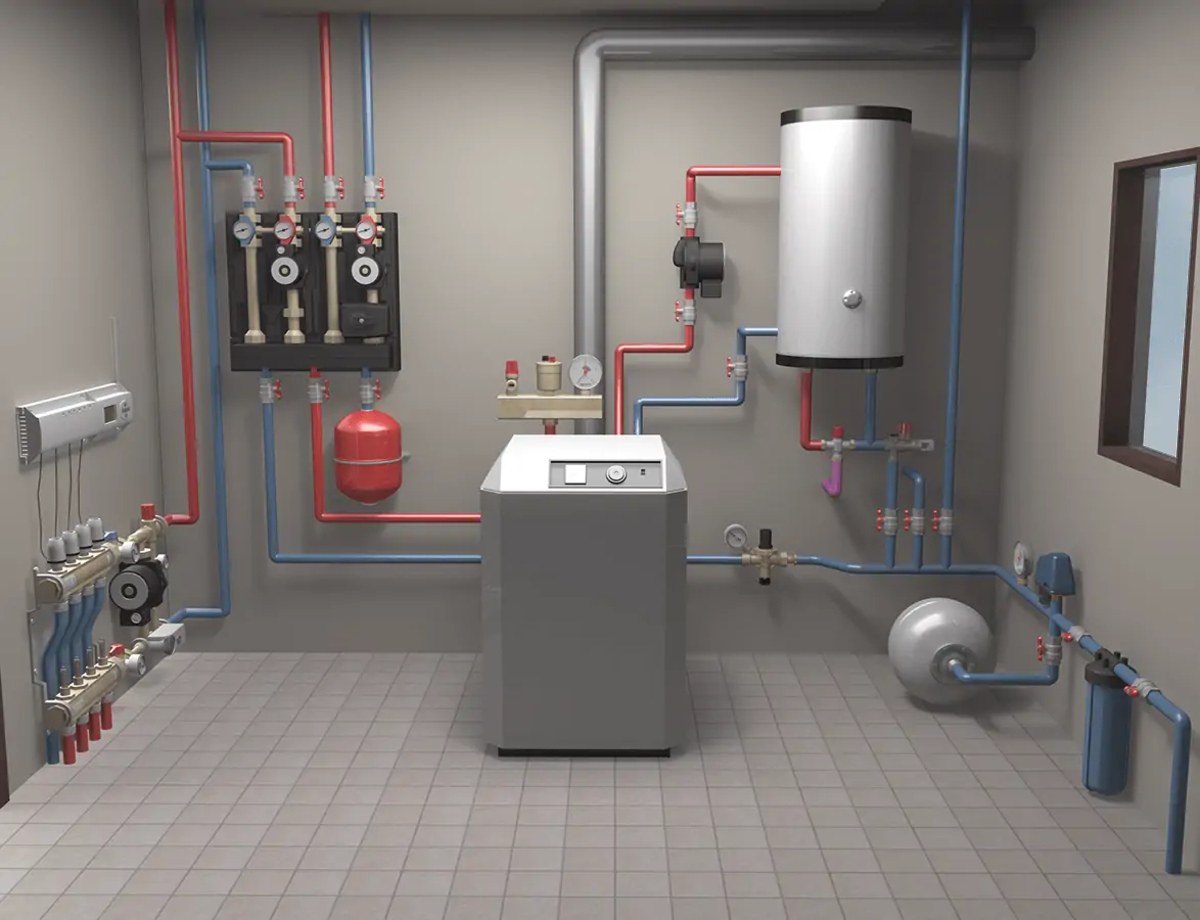
Hot air heating systems, also known as forced air heating systems, operate by distributing heated air through a network of ducts to provide warmth to indoor spaces. These systems are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings due to their efficiency and versatility. Understanding the fundamental principles of hot air heating is crucial for designing and maintaining an effective heating system.
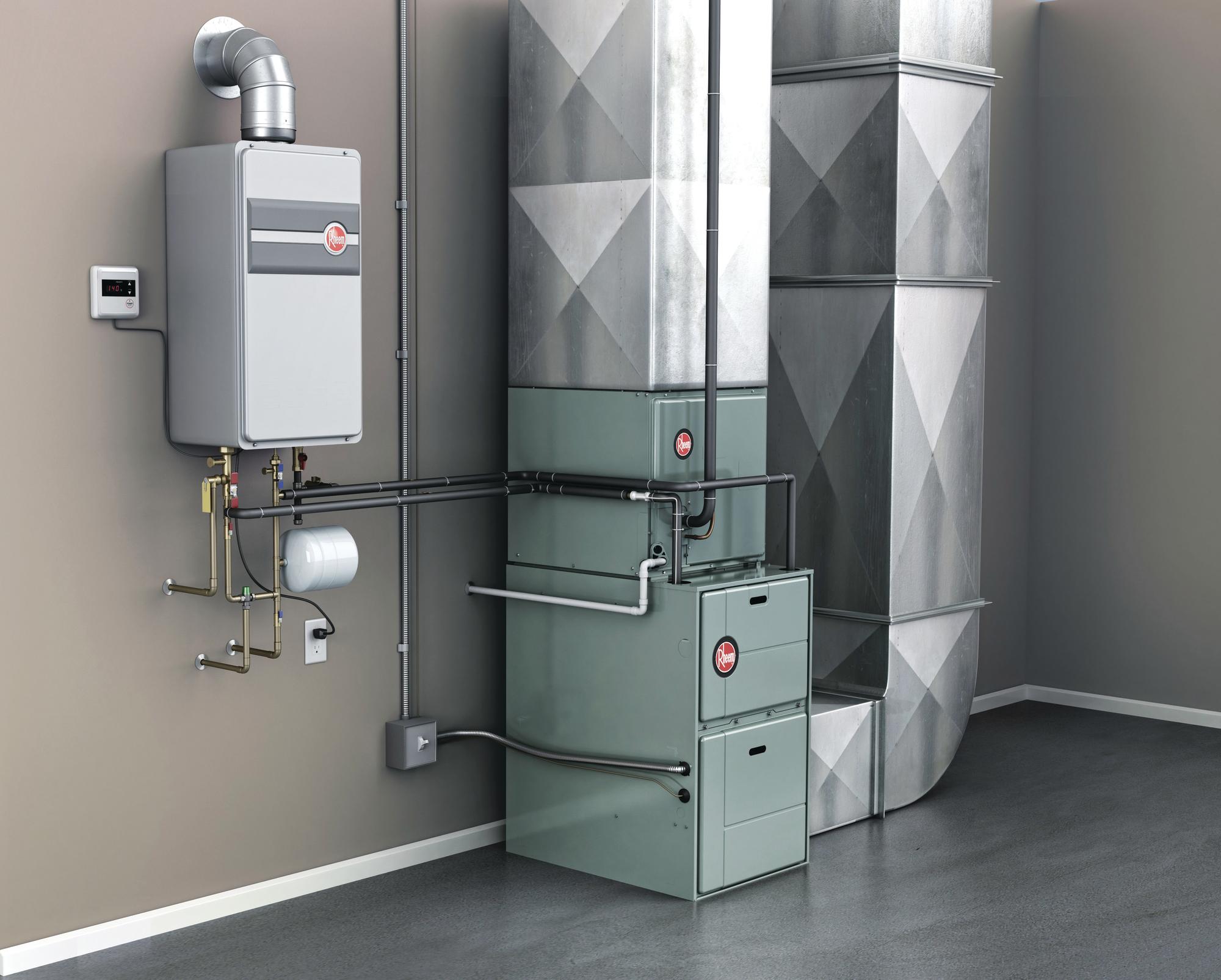
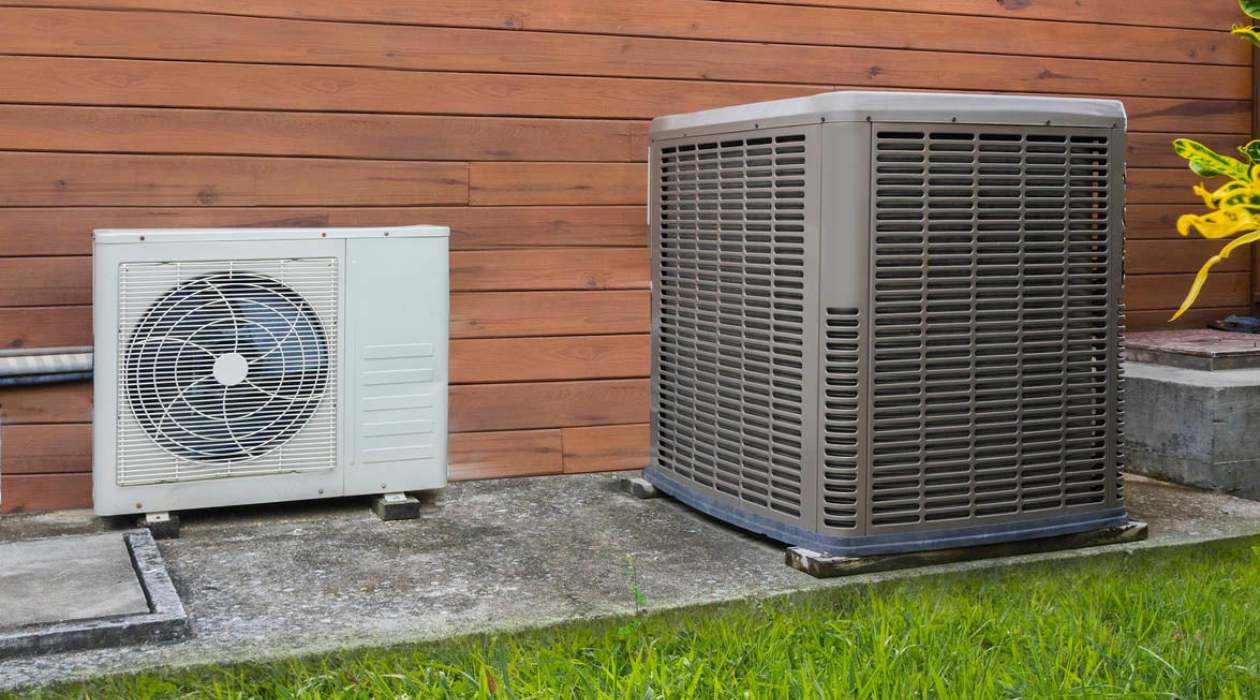
At the core of a hot air heating system is the furnace, which serves as the heat source. The furnace can be powered by natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity, and it generates heat through combustion or electrical resistance. Once the air is heated, it is propelled through the ductwork by a blower fan, distributing the warmth to different areas of the building.
Thermostats play a pivotal role in hot air heating systems, allowing users to regulate the temperature by signaling the furnace to activate or deactivate based on the desired settings. This level of control enables precise temperature management, contributing to comfort and energy efficiency.
The ductwork, comprising a network of interconnected channels, carries the heated air from the furnace to various rooms or zones within the building. Properly designed ductwork ensures even distribution of heat, minimizing temperature variations and optimizing comfort levels throughout the space.
Air filters are integral components of hot air heating systems, as they help maintain indoor air quality by capturing dust, debris, and other airborne particles. Regularly replacing or cleaning the filters is essential to ensure efficient airflow and prevent the buildup of contaminants within the system.
In addition to these key components, hot air heating systems may incorporate advanced features such as zoning controls, which allow for independent temperature regulation in different areas, and humidifiers or dehumidifiers to manage indoor humidity levels.
Understanding the basics of hot air heating systems provides a solid foundation for designing, operating, and maintaining these systems. By grasping the interplay of components and the principles of heat distribution, individuals can make informed decisions to optimize the performance and efficiency of their heating systems.
Factors to Consider When Designing a Hot Air Heating System
When embarking on the design of a hot air heating system, several crucial factors must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and comfort. By addressing these key elements during the design phase, individuals can create a heating system that aligns with their specific needs and delivers reliable warmth throughout the intended space.
-
Heating Load Calculation: Accurately determining the heating load of the building is fundamental to designing an effective hot air heating system. Factors such as the building's size, insulation, windows, and local climate must be taken into account to calculate the heat loss and gain, enabling the selection of an appropriately sized furnace and ductwork capacity.
-
Energy Source: The choice of energy source for the furnace, whether it be natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity, significantly impacts the system's efficiency and operating costs. Evaluating the availability, cost, and environmental impact of different energy sources is essential in making an informed decision that aligns with sustainability and budgetary considerations.
-
Thermostat and Control Options: Selecting the right thermostat and control options is crucial for achieving precise temperature management and energy savings. Programmable thermostats, smart thermostats, and zoning controls offer varying levels of functionality, allowing users to tailor the heating system's operation to their lifestyle and occupancy patterns.
-
Ductwork Design and Layout: The design and layout of the ductwork play a pivotal role in ensuring efficient heat distribution and airflow. Factors such as duct size, insulation, layout, and the location of supply and return vents must be meticulously planned to minimize air resistance, temperature differentials, and energy losses.
-
Air Quality Considerations: Integrating air filtration and purification systems into the heating system is essential for maintaining indoor air quality. High-efficiency air filters, UV air purifiers, and ventilation systems contribute to a healthier indoor environment by capturing and eliminating airborne contaminants.
-
Maintenance and Serviceability: Designing the heating system with accessibility and serviceability in mind simplifies maintenance tasks and prolongs the system's lifespan. Easy access to components such as filters, dampers, and the blower motor facilitates regular upkeep, ensuring the system operates at peak efficiency.
-
Future Expansion and Upgrades: Anticipating future needs and potential system upgrades is prudent when designing a hot air heating system. Allowing for scalability and compatibility with advanced technologies enables seamless integration of additional features or enhancements as requirements evolve.
By carefully considering these factors during the design phase, individuals can create a hot air heating system that not only meets their immediate heating needs but also aligns with long-term efficiency, comfort, and sustainability goals. Each element plays a critical role in shaping the overall performance and functionality of the heating system, making informed decisions at the design stage paramount to its success.
Selecting the Right Components for Your Hot Air Heating System
The process of selecting the right components for a hot air heating system is a critical step that significantly influences the system's performance, efficiency, and longevity. Each component, from the furnace to the ductwork and controls, plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal heat distribution and comfort within the indoor space. By carefully evaluating and choosing the appropriate components, individuals can design a heating system that meets their specific needs while maximizing energy efficiency.
Furnace Selection
The furnace serves as the heart of the hot air heating system, providing the heat source that warms the air distributed throughout the building. When selecting a furnace, factors such as fuel type, efficiency ratings, and heating capacity must be considered. Whether powered by natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity, the furnace should be sized to match the heating load of the building, ensuring it can deliver the necessary warmth without unnecessary energy consumption.
Read more: What Is An Air Handler In HVAC
Thermostat and Control Options
Choosing the right thermostat and control options is essential for achieving precise temperature management and energy savings. Programmable thermostats allow users to schedule temperature adjustments based on occupancy patterns, while smart thermostats offer advanced features such as remote access and adaptive learning capabilities. Zoning controls enable independent temperature regulation in different areas, optimizing comfort and reducing energy waste.
Ductwork and Ventilation Components
The design and layout of the ductwork are crucial for efficient heat distribution and airflow. Selecting appropriately sized ducts, optimizing the layout to minimize air resistance, and ensuring proper insulation are essential considerations. Additionally, the placement of supply and return vents should be strategically planned to facilitate even heat distribution and airflow throughout the building.
Air Filtration and Purification Systems
Integrating high-efficiency air filters, UV air purifiers, and ventilation systems into the heating system contributes to maintaining a healthy indoor environment. Advanced filtration systems capture and eliminate airborne contaminants, improving indoor air quality and promoting a comfortable and safe living or working environment.
Consideration of Energy Source and Efficiency
The choice of energy source for the furnace, whether it be natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity, impacts the system's efficiency and operating costs. Evaluating the availability, cost, and environmental impact of different energy sources is crucial in making an informed decision that aligns with sustainability and budgetary considerations.
By meticulously selecting the right components for a hot air heating system, individuals can create a reliable and efficient heating solution that meets their specific requirements while promoting energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Each component contributes to the overall functionality and performance of the system, making informed choices paramount to its success.
Designing the Ductwork for Optimal Airflow
The design and layout of the ductwork in a hot air heating system are critical factors that directly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of heat distribution throughout the building. Properly designed ductwork ensures optimal airflow, minimizes energy losses, and contributes to consistent comfort levels in every area of the space.
When designing the ductwork for a hot air heating system, several key considerations come into play. The size and layout of the ducts, the placement of supply and return vents, and the use of appropriate insulation all play pivotal roles in achieving optimal airflow and heat distribution.
One of the fundamental aspects of ductwork design is ensuring that the ducts are sized appropriately to accommodate the airflow required to meet the heating demands of each area within the building. Undersized ducts can lead to increased air resistance and reduced airflow, resulting in uneven heating and potential strain on the heating system. Conversely, oversized ducts may lead to decreased air velocity, impacting the system's ability to deliver warmth effectively. Therefore, meticulous calculations and considerations are essential to determine the correct duct sizes for different zones and rooms.
In addition to duct sizing, the layout of the ductwork should be strategically planned to minimize bends, turns, and obstructions that can impede airflow. Smooth, straight duct runs with minimal obstructions promote efficient airflow, reducing pressure drops and energy losses. Properly designed duct layouts also contribute to balanced air distribution, ensuring that each area receives an adequate amount of heated air without significant temperature differentials.
The placement of supply and return vents is another crucial aspect of ductwork design. Supply vents should be strategically located to deliver heated air effectively to each room, while return vents should be positioned to facilitate the circulation of air back to the heating system for reheating. Strategic placement of vents contributes to even heat distribution and balanced airflow, enhancing comfort and energy efficiency.
Furthermore, the use of appropriate insulation within the ductwork is essential for minimizing heat loss and maintaining the temperature of the heated air as it travels through the system. Well-insulated ducts prevent thermal energy from dissipating into unconditioned spaces, ensuring that the heated air reaches its intended destinations at the desired temperatures.
By meticulously designing the ductwork for optimal airflow, individuals can ensure that their hot air heating system operates at peak efficiency, delivering consistent warmth and comfort throughout the building. Thoughtful consideration of duct sizing, layout, vent placement, and insulation contributes to the overall effectiveness and performance of the heating system, enhancing its functionality and energy efficiency.
Ensuring Energy Efficiency in Your Hot Air Heating System
Energy efficiency is a paramount consideration when designing and operating a hot air heating system. By implementing strategies to maximize energy efficiency, individuals can reduce operating costs, minimize environmental impact, and enhance the overall sustainability of their heating system. Several key practices and technologies contribute to ensuring energy efficiency in hot air heating systems.
Proper maintenance and regular servicing are essential for optimizing the energy efficiency of a hot air heating system. Routine inspections, cleaning of components, and timely replacement of air filters are crucial to ensure that the system operates at peak efficiency. A well-maintained system experiences reduced energy consumption and performs optimally, contributing to long-term energy savings.
The integration of advanced thermostat technologies, such as programmable thermostats and smart thermostats, enables precise temperature control and automated adjustments based on occupancy patterns. By scheduling temperature setbacks during periods of reduced activity, these thermostats minimize energy usage without compromising comfort, resulting in significant energy savings over time.
Zoning controls offer a tailored approach to energy efficiency by allowing independent temperature regulation in different areas or zones of the building. This capability enables users to direct heated air only to occupied spaces, avoiding unnecessary heating of unoccupied areas. By selectively controlling heating output, zoning systems reduce energy waste and enhance overall efficiency.
The use of high-efficiency furnaces equipped with advanced combustion and heat exchanger technologies significantly improves the energy performance of hot air heating systems. Modern furnaces boast higher Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) ratings, indicating their ability to convert a greater proportion of fuel into usable heat. Upgrading to a high-efficiency furnace can result in substantial energy savings and reduced environmental impact.
Proper insulation of ductwork and the building envelope is instrumental in minimizing heat loss and optimizing energy efficiency. Well-insulated ducts prevent thermal energy from dissipating as heated air travels through the system, ensuring that the warmth reaches its intended destinations without unnecessary energy losses. Additionally, adequate insulation in walls, ceilings, and floors helps maintain indoor temperatures, reducing the workload on the heating system.
The integration of energy recovery ventilation (ERV) or heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems enhances energy efficiency by capturing and transferring heat from outgoing air to incoming fresh air. These systems mitigate heat loss during ventilation, improving indoor air quality while minimizing the energy required to maintain comfortable temperatures.
By incorporating these energy-efficient practices and technologies, individuals can design and operate hot air heating systems that deliver exceptional performance while minimizing energy consumption. The collective impact of these strategies not only reduces operational costs but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious approach to indoor heating.
Consider using a high-efficiency furnace or heat pump for your hot air heating system. These systems can help reduce energy consumption and lower heating costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the design and implementation of an efficient hot air heating system require a comprehensive understanding of the system's components, principles, and best practices. By delving into the intricacies of hot air heating systems, individuals can make informed decisions that optimize performance, energy efficiency, and indoor comfort.
Understanding the basics of hot air heating systems, including the role of the furnace, thermostat, ductwork, and air filtration, provides a solid foundation for designing a reliable heating solution. By grasping the interplay of these components and their impact on heat distribution, individuals can create a system that meets their specific needs while promoting energy efficiency.
When designing a hot air heating system, careful consideration of factors such as heating load calculation, energy source selection, thermostat options, ductwork design, air quality considerations, maintenance, and future expansion is paramount. Each of these elements plays a critical role in shaping the overall performance and functionality of the heating system, making informed decisions at the design stage crucial to its success.
Selecting the right components, including the furnace, thermostat, ductwork, ventilation components, and air filtration systems, is pivotal in ensuring optimal heat distribution and energy efficiency. By meticulously evaluating and choosing the appropriate components, individuals can design a heating system that aligns with their specific needs while maximizing energy efficiency.
The design of the ductwork is a critical factor that directly impacts the efficiency and effectiveness of heat distribution throughout the building. Properly designed ductwork ensures optimal airflow, minimizes energy losses, and contributes to consistent comfort levels in every area of the space.
Energy efficiency is a paramount consideration when designing and operating a hot air heating system. By implementing strategies such as proper maintenance, advanced thermostat technologies, zoning controls, high-efficiency furnaces, insulation, and energy recovery ventilation systems, individuals can reduce operating costs, minimize environmental impact, and enhance the overall sustainability of their heating system.
In essence, the design of an efficient hot air heating system is a multifaceted endeavor that requires careful planning, informed decision-making, and a commitment to energy efficiency. By integrating the principles and best practices outlined in this guide, individuals can create a heating system that not only delivers exceptional performance and comfort but also contributes to long-term energy savings and environmental responsibility.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Design An Efficient Hot Air Heating System
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How To Design An Efficient Hot Air Heating System”