Home>Home Security and Surveillance>How Does A Security Camera Work


Home Security and Surveillance
How Does A Security Camera Work
Modified: March 6, 2024
Discover how home security and surveillance systems use advanced technology to capture and monitor activity, providing peace of mind for you and your loved ones.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of home security and surveillance. With the advancements in technology, protecting our homes and loved ones has become more essential than ever. A key component of any comprehensive home security system is the security camera. These devices play a crucial role in monitoring and recording activities both inside and outside our homes.
In this article, we will explore the inner workings of security cameras and how they function to provide us with peace of mind. We will dive into the various components that make up a security camera system and discuss their roles and functions. Whether you’re considering installing a security camera yourself or simply curious about how they operate, you’ve come to the right place.
So, let’s begin our journey and uncover the fascinating world of security cameras.
Key Takeaways:
- Security cameras are complex devices with components like lenses, image sensors, and processors working together to capture, process, and store video footage, providing peace of mind and enhancing security for homes and businesses.
- Understanding the benefits, applications, and challenges of security cameras is crucial for their effective use. They offer deterrence, evidence gathering, remote access, and peace of mind, but considerations like privacy, placement, and data security must be addressed for responsible and ethical usage.
Read more: How Does Alexa Work With Security Cameras
Components of a Security Camera
A security camera is an intricate device comprised of various components working together seamlessly to capture, process, transmit, and store video footage. Let’s take a closer look at the key components that make up a security camera system:
- Lens: The lens is responsible for capturing the visual information in the form of light. It focuses the light onto the image sensor and determines the field of view and the level of detail in the captured footage.
- Image Sensor: The image sensor converts the optical image from the lens into an electrical signal. Security cameras typically use either CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) or CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensors to capture high-quality images.
- Processor: The processor, also known as the DSP (Digital Signal Processor), takes the electrical signals from the image sensor and performs various functions such as color correction, noise reduction, and image enhancement.
- IR Cut Filter: Many security cameras are equipped with an IR cut filter that blocks infrared light during the day to capture color-accurate images. In low-light conditions, the filter automatically switches to allow infrared light, enabling the camera to capture images in black and white.
- Infrared LEDs: Infrared LEDs are used to provide illumination in low-light or complete darkness. These LEDs emit infrared light, which is invisible to the human eye but can be detected by the camera, allowing for clear night vision.
- Encoder: The encoder is responsible for converting the analog video signal into a digital format. It compresses the video to reduce the file size and bandwidth requirements for storage and transmission.
- Memory: Security cameras have internal memory or slots for external memory cards to store the captured video footage. The memory capacity varies depending on the camera model and can be expandable for extended storage.
- Network Interface: Most modern security cameras are equipped with a network interface, typically Ethernet or Wi-Fi, allowing for seamless connectivity to a network or the internet. This enables remote viewing and monitoring from a computer or mobile device.
- Power Supply: Security cameras require a power source to operate. They can be powered by traditional electrical outlets or through Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology, which transmits power and data through a single Ethernet cable.
These components work together to capture, process, and transmit video footage in a way that ensures the utmost security and surveillance capabilities. Now that we have a clear understanding of the key components, let’s delve into the intricacies of image capture in security cameras.
Image Capture
Image capture is a fundamental process in security cameras, as it determines the quality and clarity of the recorded video footage. The lens and image sensor play critical roles in capturing the visual information accurately and efficiently:
Lens: The lens of a security camera focuses the light onto the image sensor. It determines the field of view, which is the area that the camera can capture, and the level of detail in the captured footage. Different lenses offer varying focal lengths, such as wide-angle, zoom, or fixed, allowing users to choose the appropriate lens based on their specific surveillance needs. The lens quality, including factors like aperture size, focal length, and lens material, greatly affects the overall image quality.
Image Sensor: The image sensor is a crucial component responsible for converting the optical image from the lens into an electrical signal. There are two primary types of image sensors used in security cameras: CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor).
CCD sensors are known for their excellent image quality, low noise levels, and better performance in low light conditions. They have traditionally been the preferred choice for high-end security cameras. However, they tend to consume more power compared to CMOS sensors and may be more expensive.
CMOS sensors, on the other hand, offer advantages such as lower power consumption, faster readout speeds, and cost-effectiveness. While they may not match the image quality of CCD sensors in some scenarios, advancements in CMOS technology have significantly narrowed the performance gap.
Once the lens focuses the light onto the image sensor, the sensor converts the visual information into an electrical signal, which is then processed and transmitted for storage and monitoring purposes. The efficiency of the image capture process is crucial in ensuring that the security camera delivers clear and detailed footage.
Next, let’s explore the process of video processing in security cameras, where the electrical signals from the image sensor are transformed into a digital video format for storage and transmission.
Video Processing
Video processing is a vital step in the functionality of security cameras, as it involves transforming the electrical signals captured by the image sensor into a digital video format. This process is necessary to enhance the quality of the footage and enable efficient storage and transmission:
Color Correction: Once the electrical signals are received from the image sensor, video processing algorithms adjust the color levels to ensure accurate representation. This color correction process helps to compensate for any lighting variations or color anomalies, resulting in more realistic and vibrant video footage.
Noise Reduction: Noise refers to unwanted artifacts in the video signal, such as graininess or distortion. Video processing algorithms employ various techniques to reduce noise and improve the overall quality of the footage. These techniques include spatial filtering, temporal filtering, and algorithms that analyze neighboring pixels to identify and remove noise patterns.
Image Enhancement: Video processing algorithms can enhance the captured video footage by sharpening the image, adjusting the contrast, and improving the overall visual clarity. These enhancements help to improve the visibility of objects, even in challenging lighting conditions.
Frame Rate Conversion: The frame rate of a video determines how many frames are displayed per second. Video processing can involve frame rate conversion, where the captured footage is adjusted to match the desired frame rate. This is particularly useful when integrating security cameras into existing surveillance systems or when optimizing bandwidth usage for remote viewing.
Overall, the video processing stage in security cameras plays a pivotal role in enhancing the quality and clarity of the footage. By applying algorithms to correct colors, reduce noise, enhance details, and adjust frame rates, security cameras can deliver superior video performance for effective monitoring and surveillance.
Now that we understand how video processing enhances the captured footage, let’s explore the critical process of compression and storage, which allows for efficient storage of large amounts of video data.
Compression and Storage
Compression and storage are crucial components in the functionality of security cameras as they allow for efficient storage and management of large amounts of video data. Let’s delve into these processes:
Compression: Video footage captured by security cameras can be quite large in size. Compression techniques are employed to reduce the file size without compromising the quality of the footage. There are two main types of video compression: lossless compression and lossy compression.
Lossless compression algorithms reduce the file size without sacrificing any image quality. This type of compression is commonly used when storing critical or forensic footage that requires the utmost accuracy and detail. However, lossless compression typically results in larger file sizes compared to lossy compression techniques.
Lossy compression, on the other hand, achieves greater file size reduction but may introduce some loss of image quality. This is the most common type of compression used in security cameras, as the visual details that can be lost are often negligible for surveillance purposes. Lossy compression algorithms, such as H.264 and H.265, are widely adopted due to their high compression ratios and ability to maintain acceptable video quality.
Storage: Once the video footage has been compressed, it needs to be stored for future reference or playback. Security cameras utilize various storage options, including:
- Internal Memory: Some security cameras have built-in memory to store video footage. The capacity of the internal memory can vary, ranging from a few gigabytes to several terabytes.
- External Storage: Security cameras often have slots for external storage devices, such as SD cards or hard drives. These external storage options provide additional capacity and flexibility.
- Network-Attached Storage (NAS): Security cameras can also be configured to store footage directly to a network-attached storage device. NAS allows for centralized storage and easy retrieval of video data.
- Cloud Storage: With the increasing popularity of cloud-based services, many security cameras offer the option of storing footage in the cloud. This provides off-site backup and accessibility from any location with an internet connection.
It is important to consider the storage capacity required for your surveillance needs. Factors such as the number of cameras, the desired retention period for video footage, and the resolution and frame rate of the recordings all impact the storage requirements.
Now that we understand how compression and storage work in security cameras, let’s move on to the crucial process of transmission and communication, which enables real-time monitoring and remote access to the surveillance footage.
Read more: How Does Blink Security Camera Work
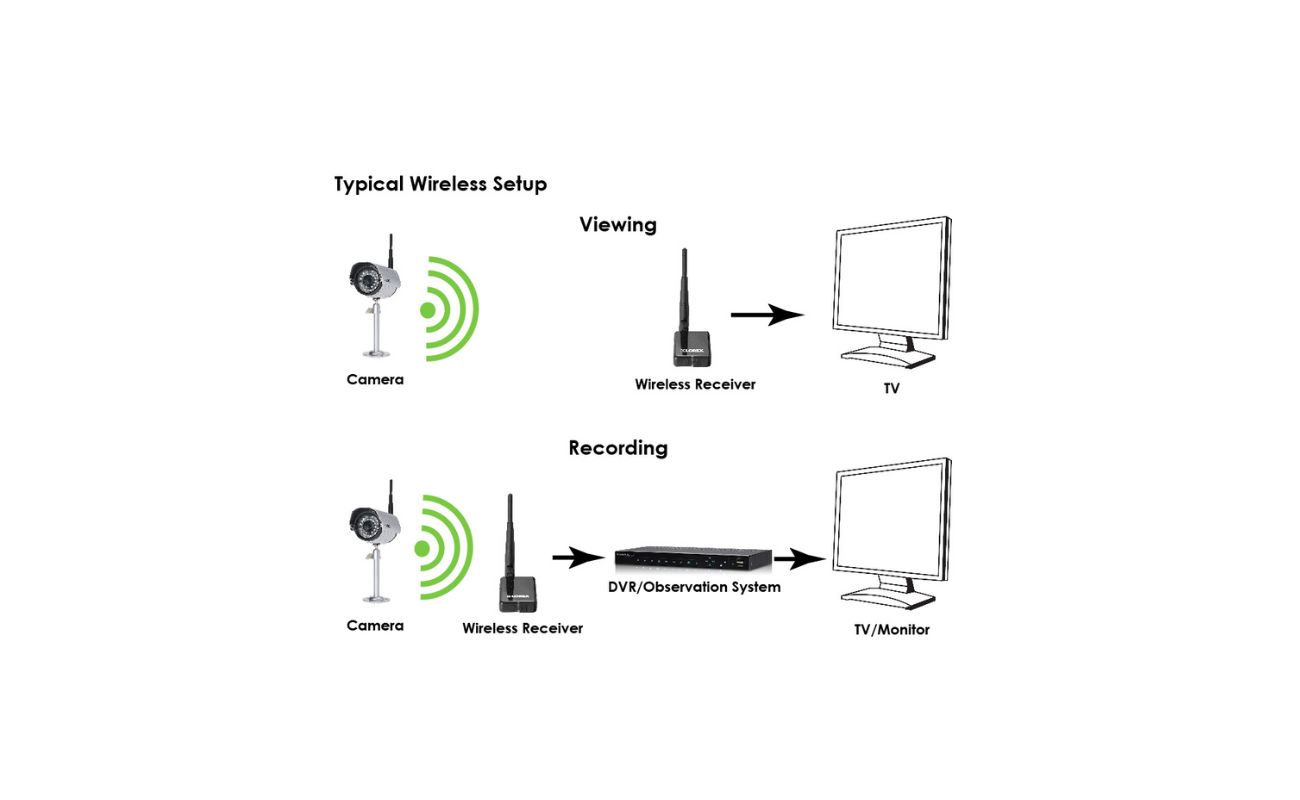
Transmission and Communication
Transmission and communication play a vital role in security camera systems, enabling real-time monitoring and remote access to surveillance footage. Let’s explore the key aspects of transmission and communication:
Transmission Protocols: Security cameras utilize various protocols to transmit video data over a network. The most commonly used protocol is TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), which ensures reliable and error-free data transmission. Other protocols such as UDP (User Datagram Protocol) may be used for real-time video streaming where a slight delay is acceptable.
Video Streaming: Video streaming allows for live monitoring of surveillance footage over a network or the internet. Security cameras can stream video in real-time, enabling users to view the footage remotely using a computer or mobile device. Streaming protocols like RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol) or HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) are commonly used to facilitate smooth video playback.
Network Connectivity: Security cameras can be connected to networks through Ethernet cables or wirelessly using Wi-Fi. Ethernet connections provide a stable and reliable connection, while Wi-Fi offers flexibility in camera placement. It is important to ensure a secure and robust network connection to prevent unauthorized access to the surveillance system.
Mobile Connectivity: Many security cameras offer mobile connectivity, allowing users to access the footage on their smartphones or tablets. Mobile apps provided by the camera manufacturer or third-party applications enable convenient remote monitoring and control of the cameras.
Push Notifications: Push notifications are a valuable feature of security camera systems. When the camera detects motion or triggers an alarm, it can send instant notifications to the user’s mobile device. This allows for immediate awareness of any potential security issues, even when the user is not actively monitoring the footage.
Video Management Software: Security camera systems often come with dedicated video management software. This software allows users to organize, playback, and manage the recorded video footage effectively. It may also provide advanced features such as motion detection, event logging, and video analytics for enhanced surveillance capabilities.
These elements of transmission and communication enable efficient access to real-time and recorded video footage, empowering users to monitor their properties remotely and respond swiftly to any suspicious activities or security breaches.
Now that we have covered transmission and communication, let’s discuss the critical aspects of power and connectivity in security camera systems.
A security camera works by capturing video footage and transmitting it to a recording device or monitor. It uses sensors to detect motion and light to capture clear images, providing a visual record of activity in the area it covers.
Power and Connectivity
In order for security cameras to function effectively, they require a reliable power source and connectivity options to ensure seamless operation and communication. Here are the key aspects of power and connectivity in security camera systems:
Power Sources: Security cameras can be powered through various methods, including:
- Electrical Outlets: Many security cameras can be plugged into traditional electrical outlets. This provides a consistent power source and eliminates the need for battery replacements.
- Battery Power: Some security cameras are battery-powered, allowing for flexible placement and mobility. Battery-powered cameras are a suitable option for areas without accessible power outlets or for temporary surveillance needs.
- Solar Power: Solar-powered security cameras utilize solar panels to convert sunlight into electrical energy, making them an eco-friendly and sustainable option. These cameras are ideal for areas with sufficient sunlight and where running electrical wires may be challenging.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE): Security cameras equipped with Power over Ethernet technology can receive both power and data through a single Ethernet cable. This simplifies the installation process and reduces the need for additional power sources near the camera’s location.
Connectivity Options: Connectivity is crucial for security cameras to communicate and transmit data. Here are the main connectivity options:
- Ethernet: Ethernet connectivity is widely used to connect security cameras to a local network or network video recorder (NVR). It provides a stable and reliable connection for data transmission.
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi connectivity allows for wireless communication, eliminating the need for physical Ethernet cables. Wi-Fi-enabled cameras offer flexibility in terms of placement and ease of installation.
- Cellular: In remote areas or locations without access to traditional wired networks, security cameras can utilize cellular connectivity. This allows for real-time monitoring and remote access to footage using cellular data networks.
It is essential to ensure a stable and secure power supply and connectivity for uninterrupted operation and effective surveillance. Depending on the specific needs and limitations of your security camera system, choosing the appropriate power source and connectivity option is crucial.
Now that we have covered power and connectivity, let’s move on to discussing the installation and setup process for security cameras.
Installation and Setup
The installation and setup process of security cameras is a crucial step in ensuring their optimal performance and effectiveness in providing reliable surveillance. Here’s a guide to help you with the installation and setup process:
- Determine Camera Placement: Before installing the cameras, carefully assess your property’s layout and identify key areas that require surveillance coverage. Consider factors such as entrances, blind spots, and high-value assets when determining the placement of your cameras.
- Mounting the Cameras: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to mount the cameras securely. Whether you’re mounting them on walls, ceilings, or poles, ensure that they are placed at the right height and angle to capture the desired field of view.
- Power Connection: Connect the cameras to a reliable power source. Depending on the power option chosen, either plug the camera into an electrical outlet, connect it to a battery, or utilize Power over Ethernet (PoE) for both power and data transmission.
- Network Connection: If your security camera system requires network connectivity, connect the cameras to your local network or Wi-Fi according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that the network connection is secure and properly configured for remote access if desired.
- Evaluate and Adjust Camera Settings: Once the cameras are installed and connected, access their settings through the manufacturer’s software or a web interface. Configure various camera settings including resolution, frame rate, motion detection, and privacy masking to align with your specific surveillance needs.
- Video Management Software: Install and set up the video management software provided by the security camera manufacturer. This software allows you to manage and monitor the cameras, view recorded footage, and configure additional features such as motion alerts and scheduled recording.
- Testing and Fine-Tuning: After the installation and setup, thoroughly test each camera to ensure they are capturing the desired field of view and producing high-quality footage. Make any necessary adjustments to camera angles, image settings, or placement if required.
- Remote Access: If remote access to your security cameras is desired, configure the necessary network settings and install mobile apps or remote viewing software. This will allow you to monitor and access the camera footage from anywhere using your smartphone, tablet, or computer.
It is important to consult the manufacturer’s documentation and follow their guidelines throughout the installation and setup process to ensure proper functionality and maximize the capabilities of your security camera system.
Now that we’ve covered the installation and setup process, let’s explore the different types of security cameras available in the market.
Types of Security Cameras
Security cameras come in various types, each designed to cater to specific surveillance needs and environments. Let’s explore the most common types of security cameras available:
- Indoor Cameras: Indoor cameras are designed for surveillance within indoor areas such as homes, offices, and retail stores. These cameras are usually compact, discreet, and blend seamlessly into the indoor environment.
- Outdoor Cameras: Outdoor cameras are built to withstand harsh weather conditions and provide surveillance coverage for the exterior of buildings, driveways, yards, and other outdoor areas. They are typically weatherproof and come equipped with features like infrared night vision and motion detection.
- Dome Cameras: Dome cameras are named after their dome-shaped housing. Their discreet design and wide-angle lenses make them ideal for surveillance in large areas like shopping malls, parking lots, and public spaces. Dome cameras are also difficult to tamper with due to their vandal-resistant features.
- Bullet Cameras: Bullet cameras are long and cylindrical, resembling a bullet in shape. They are commonly used for outdoor surveillance due to their weatherproof design and ability to capture distant objects with their adjustable lenses. Bullet cameras are visible and can act as a deterrent to potential intruders.
- PTZ Cameras: PTZ stands for Pan-Tilt-Zoom, and these cameras offer a high level of flexibility and control for monitoring large areas. PTZ cameras can pan (rotate horizontally), tilt (move vertically), and zoom in on objects of interest. They can be operated manually or set to automatically track motion.
- Wireless Cameras: Wireless cameras utilize Wi-Fi technology for data transmission, eliminating the need for physical Ethernet cables. They are easy to install and provide flexibility in camera placement. However, they may be susceptible to signal interference and have limited range compared to wired cameras.
- IP Cameras: IP (Internet Protocol) cameras are digital cameras that transmit video footage over an IP network or the internet. They offer high-resolution video, remote access capabilities, and advanced features such as motion detection and event-triggered alerts. IP cameras can be wired or wireless and are compatible with various software and video management systems.
- Thermal Cameras: Thermal cameras, also known as infrared cameras, detect heat signatures instead of visible light. They are effective in low-light and no-light environments and can detect objects even in complete darkness. These cameras are commonly used for perimeter security, detecting intruders, and monitoring temperature changes.
Each type of security camera offers unique features and advantages, catering to different surveillance requirements. It is essential to assess your specific needs and the environment to choose the right type of camera for your surveillance system.
Now that we have covered the types of security cameras available, let’s explore the benefits and applications of using such systems.
Benefits and Applications
Security cameras offer numerous benefits and find applications in a wide range of scenarios, providing enhanced safety, protection, and peace of mind. Here are some of the key benefits and applications of security camera systems:
Deterrence: One of the primary benefits of security cameras is their deterrent effect. Visible cameras act as a powerful deterrent to potential intruders and criminals, reducing the likelihood of theft, vandalism, and other criminal activities. The presence of security cameras can significantly increase the security of homes, businesses, and public spaces.
Surveillance and Monitoring: Security cameras allow for continuous surveillance and monitoring of both indoor and outdoor areas. They can capture and record activities in real-time, providing evidence in the event of an incident or criminal activity. Live monitoring of camera feeds enables immediate response to suspicious activities and can help prevent crimes before they occur.
Evidence Gathering: Security cameras serve as valuable tools in gathering evidence for investigations and legal proceedings. Recorded footage can be used to identify suspects, validate claims, and provide evidence in court. High-resolution cameras capture clear and detailed images, enhancing the reliability and value of the evidence.
Remote Access and Monitoring: Many security camera systems offer remote access and monitoring capabilities. With the use of mobile apps or computer software, users can view live camera feeds, playback recorded footage, and receive notifications on their smartphones, tablets, or computers from anywhere in the world. This provides flexibility and allows for real-time monitoring and response to security events even when physically away from the premises.
Peace of Mind: Security cameras provide peace of mind to homeowners, business owners, and individuals by offering a sense of security and control. Knowing that your property and loved ones are under surveillance can alleviate anxiety and provide a sense of comfort and reassurance, especially in times of increased security concerns.
Traffic and Parking Management: Security cameras find applications in traffic and parking management. They help monitor and analyze traffic patterns, detect violations such as speeding or running red lights, and provide documentation for traffic incidents. In parking lots and garages, cameras help monitor vehicles, deter theft or vandalism, and ensure compliance with parking regulations.
Workplace Safety and Productivity: Security cameras contribute to workplace safety and productivity by monitoring employee activities and maintaining a safe working environment. They can help prevent and investigate workplace accidents, deter theft or unauthorized access, and monitor employee productivity and adherence to protocols.
Remote Property Monitoring: For vacation homes, rental properties, or premises that remain unoccupied for extended periods, security cameras enable remote monitoring and protection of the property. Owners can keep an eye on their property, receive alerts in case of suspicious activities, and take immediate action when required.
These are just a few examples of the benefits and applications of security camera systems. The versatility and capabilities of security cameras make them an essential component of comprehensive security solutions in various settings.
Now, let’s discuss some of the challenges and considerations to keep in mind when using security camera systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While security camera systems offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind when using them. Understanding these challenges can help you make informed decisions regarding their implementation and usage. Here are some key challenges and considerations:
Privacy Concerns: Security cameras can raise privacy concerns, especially in public spaces or areas where individuals may have a reasonable expectation of privacy, such as bathrooms or changing rooms. It is important to adhere to local privacy laws and regulations and inform individuals when they are being recorded to respect their privacy rights.
Camera Placement and Coverage: Proper camera placement is crucial to achieving optimal coverage and effectively monitoring the desired areas. Consider factors such as blind spots, lighting conditions, and potential obstructions when determining camera placement. Conducting a thorough site survey and consulting professionals can help ensure comprehensive coverage and minimize gaps in surveillance.
Data Security: Security camera systems collect and store vast amounts of sensitive data. It is essential to implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect this data from unauthorized access or breaches. This includes securing the network, using strong passwords, keeping software up to date, and encrypting stored and transmitted data.
System Reliability and Maintenance: Security camera systems require proper maintenance to ensure their reliability and longevity. Regular monitoring, cleaning of camera lenses, and firmware updates are essential to maintain optimal performance. Backup power sources and redundant storage options should also be considered to mitigate the risk of system failures or data loss.
Cost and Scalability: Implementing a security camera system can involve significant upfront costs, including the cameras, installation, storage devices, and network infrastructure. It is important to consider the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs when planning the implementation. Additionally, scalability should be considered, as the system may need to expand or adapt to evolving security requirements in the future.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: It is crucial to understand and adhere to local laws, regulations, and industry standards related to the use of security cameras. This includes issues such as privacy laws, data retention policies, and rules governing the use of video surveillance in specific locations or industries. Consulting legal professionals can help ensure compliance and mitigate legal risks.
Interoperability and Integration: If integrating security cameras with an existing security system or video management software, compatibility and interoperability should be considered. Ensure that the cameras and software are compatible and able to integrate seamlessly to streamline operations and access a comprehensive security infrastructure.
By addressing these challenges and considering these factors, you can maximize the benefits of your security camera system while navigating potential pitfalls responsibly and ethically.
Now, let’s conclude our discussion on security cameras.
Conclusion
Security cameras have become an integral part of modern home security and surveillance systems. Through their advanced technology and functionality, they provide invaluable benefits and peace of mind to homeowners, businesses, and public spaces alike. By understanding the components, features, and considerations associated with security cameras, you can make informed decisions when implementing and utilizing these systems.
We explored the key components of security cameras, including the lens, image sensor, processor, and storage capabilities. We also discussed their role in image capture, video processing, compression, and storage. Additionally, we explored the importance of transmission and communication for real-time monitoring and remote access.
We delved into the various types of security cameras, such as indoor, outdoor, dome, bullet, PTZ, wireless, IP, and thermal cameras. Each type has its own unique features and applications, allowing for tailored surveillance solutions depending on specific needs.
The benefits of security cameras are vast and include deterrence, surveillance, evidence gathering, remote access, and peace of mind. They find applications in various settings, such as residential properties, businesses, traffic management, and workplace safety.
However, challenges and considerations exist, such as privacy concerns, proper camera placement, data security, and legal compliance. By addressing these challenges and considering factors like cost, scalability, and interoperability, you can ensure the efficient and ethical use of security camera systems.
In conclusion, security cameras offer a powerful tool for enhancing security, deterring crime, and monitoring activities. With the advancements in technology, security cameras have become more accessible, versatile, and user-friendly than ever before. By understanding their operation, benefits, applications, and potential challenges, you can harness the power of security cameras to protect your property, loved ones, and valuable assets.
Remember, selecting the right security camera system and deploying it effectively requires careful planning, research, and consultation with professionals. With the proper implementation and ongoing maintenance, security cameras can be a valuable asset in creating a safe and secure environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does A Security Camera Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.