Home>Home Security and Surveillance>When Were Night Vision Cameras Invented

Home Security and Surveillance
When Were Night Vision Cameras Invented
Modified: October 29, 2024
Learn about the fascinating history of night vision cameras and their role in home security and surveillance. Discover when this innovative technology was first invented.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Home security and surveillance play a vital role in protecting our homes and loved ones. With advancements in technology, the range of options for home security has expanded significantly. One such advancement is the invention of night vision cameras, which have revolutionized the way we monitor and secure our properties.
Night vision cameras are designed to capture clear and detailed footage even in low-light or complete darkness. They have become an essential tool for both residential and commercial applications, offering enhanced security and peace of mind. In this article, we will explore the history of night vision cameras, from their early days to the cutting-edge technology available today.
Key Takeaways:
- Night vision cameras were invented in the early 20th century, during World War II, to help the military operate in low-light or no-light conditions, leading to significant advancements in home security and surveillance technology.
- Night vision cameras have evolved from bulky devices to compact and powerful tools, enhancing home security, wildlife observation, law enforcement, and outdoor activities. Ongoing advancements promise further improvements in image quality and detection range.
Read more: When Were Rugs Invented
The Early Days of Night Vision
The concept of night vision dates back centuries, with early attempts to enhance visibility in low-light conditions. In the 17th and 18th centuries, inventors experimented with various optical devices to amplify available light. However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that significant advancements were made in night vision technology.
One of the earliest breakthroughs came in the late 1920s when a Hungarian physicist named Kálmán Tihanyi invented an electronic television camera capable of capturing images in the dark. Tihanyi’s invention was based on the concept of detecting infrared radiation, which is invisible to the human eye but can be converted into visible light.
During the 1930s, several inventors and scientists further explored the potential of capturing images in darkness. However, these early night vision devices were bulky, expensive, and had limited capabilities.
The development of night vision technology gained momentum during World War II, driven by the need for improved military surveillance and reconnaissance capabilities. Military forces recognized the value of being able to operate in low-light or no-light conditions, particularly during nighttime operations.
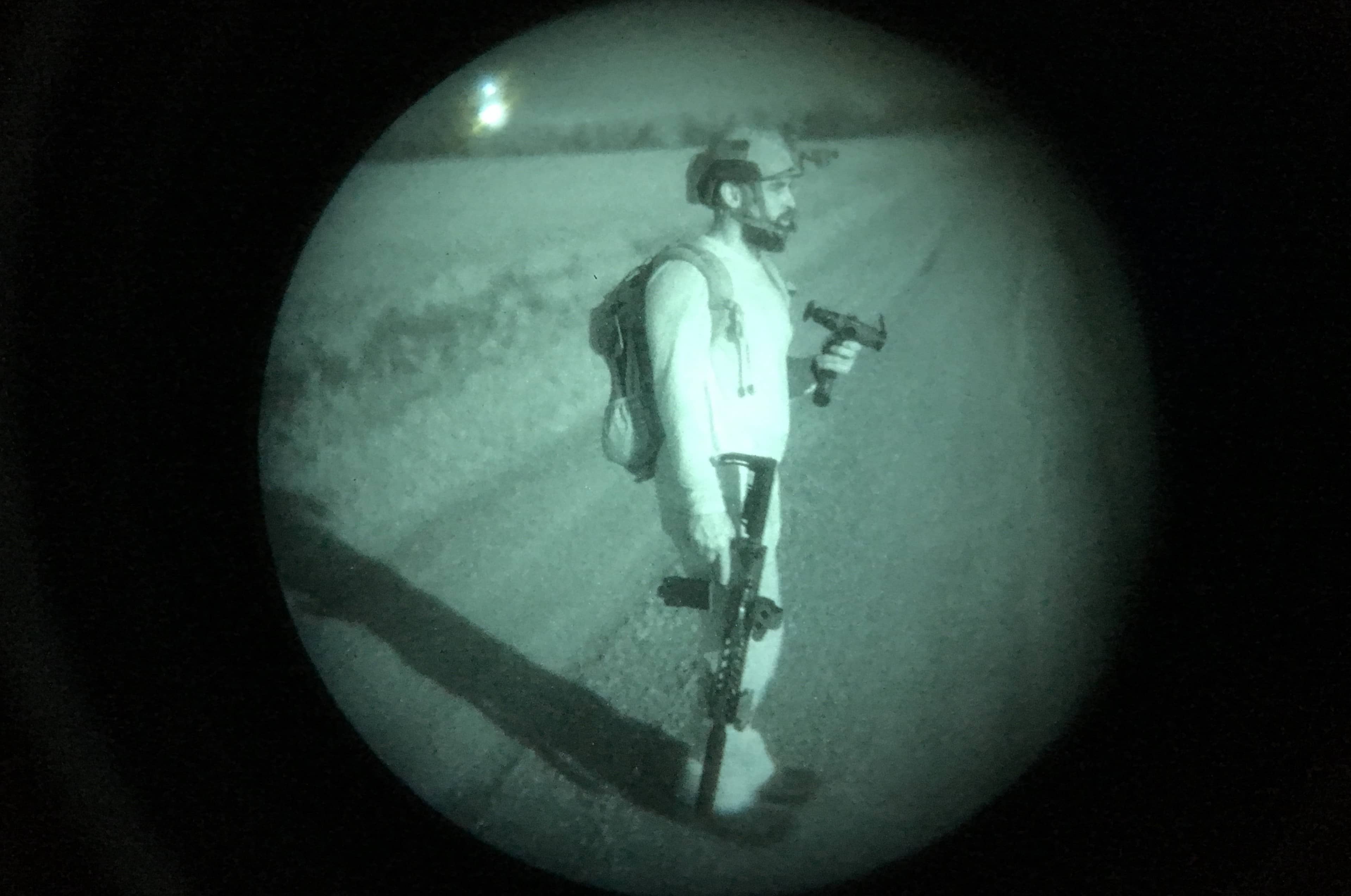
As the war escalated, research and development efforts led to the emergence of the first practical night vision devices. These devices used image intensification technology, which involved collecting available photons of light, amplifying them, and converting them into visible images.
It was during this time that the term “night vision” came into common usage. The United States military led the way in night vision research and produced the first generation of night vision devices, known as “Generation 0.”
Although these early devices were large and cumbersome, they represented a significant advancement in night vision technology. They were primarily used by the military for surveillance, target acquisition, and navigation purposes.
Over the following decades, night vision technology continued to evolve, leading to smaller, more efficient, and affordable devices. Let’s explore the different generations of night vision cameras and the advancements that have transformed the field.
World War II and the Development of Night Vision Cameras
World War II played a pivotal role in advancing night vision technology. The military recognized the critical need for reliable night vision equipment to gain a tactical advantage on the battleground. As a result, significant efforts were made to develop improved night vision cameras.
During this time, the United States military actively invested in research and development to enhance night vision capabilities. They established programs such as the National Defense Research Committee (NDRC) and the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), which focused on advancing technology for military purposes.
The first practical night vision devices, known as Generation 0, were developed during World War II. These early devices used an image intensification technology called photocathode tubes. These tubes converted photons of light into electrons, amplifying them through a process of electronic-coupling, and then reconverted them into visible images on a phosphor screen.
The US Army Signal Corps played a central role in developing night vision cameras for military use. They created the Signal Corps Engineering Laboratories, where scientists and engineers worked tirelessly to improve the performance and reliability of night vision devices.
One notable figure during this period was Dr. Vladimir Zworykin, a Russian-born American inventor. He made significant contributions to the development of night vision technology, focusing on improving image intensification devices. Zworykin’s work laid the groundwork for subsequent generations of night vision cameras.
By the end of World War II, night vision technology had become a critical asset for the military, allowing them to conduct covert operations and gather intelligence under the cover of darkness. The success and effectiveness of these devices sparked further research and development in the post-war years.
The advancements made during World War II set the stage for subsequent generations of night vision technology. The lessons learned from the early development of night vision cameras provided valuable insights that fueled further innovations in the field.
In the following sections, we will explore the different generations of night vision cameras and the significant technological breakthroughs that have shaped the landscape of home security and surveillance.
The First Generation Night Vision Cameras
The first generation of night vision cameras, also referred to as Generation 1 (Gen 1), emerged in the late 1960s and early 1970s. These cameras featured significant advancements compared to their predecessors, offering improved image quality and lower costs.
Gen 1 night vision cameras relied on passive image intensification technology, similar to the devices developed during World War II. These cameras used an image intensifier tube to amplify the available light and produce a visible image. The image intensifier tube consisted of three basic components: a photocathode, a microchannel plate, and a phosphor screen.
The photocathode in the image intensifier tube converted photons of light into electrons. These electrons were then accelerated and multiplied by the microchannel plate, which contained tiny channels that served as electron multipliers. The amplified electrons were then directed onto a phosphor screen, where they produced a visible image.
First-generation night vision cameras introduced significant improvements in terms of image clarity and light amplification. However, they still had limitations, including a noticeable level of image distortion, limited range, and susceptibility to blooming from bright light sources.
Despite these limitations, Gen 1 night vision cameras were widely adopted for military applications and gradually found their way into law enforcement and civilian use. These cameras provided an affordable and practical solution for nighttime surveillance, wildlife observation, and other low-light activities. They were a game-changer in the field of home security and surveillance.
Gen 1 night vision cameras were typically bulky and required a significant power source, such as batteries or an external power supply. They often featured separate infrared illuminators to enhance visibility in complete darkness, using infrared light that is invisible to the human eye.
The affordability and availability of Gen 1 night vision cameras made them accessible to a broader market, driving their popularity among outdoor enthusiasts, hunters, and homeowners looking to enhance their security measures. These cameras became an invaluable tool for night-time monitoring, allowing users to detect potential threats and capture clear footage in low-light conditions.
Stay tuned as we explore the advancements in night vision technology with the subsequent generations of night vision cameras. We will delve into the breakthroughs that have shaped the field and continue to improve home security and surveillance systems.
The first practical night vision device was invented in Germany in 1939, during World War II. It was called the “Vampir” and was used by the German military.
Advances in Night Vision Technology
Since the introduction of first-generation night vision cameras, significant advancements have been made in night vision technology. These advances have resulted in improved image quality, extended detection range, enhanced durability, and smaller form factors. Let’s explore some of the key advances that have shaped the landscape of night vision cameras.
Generation 2 (Gen 2)
Generation 2 night vision cameras, introduced in the 1980s, marked a significant improvement in image quality and low-light performance. These cameras featured a more advanced image intensifier tube and a microchannel plate with better electron amplification. This resulted in brighter and more detailed images, reduced distortion, and increased visibility in extremely low light conditions.
Generation 3 (Gen 3)
Generation 3 night vision cameras, which emerged in the 1990s, offered even greater performance enhancements compared to Gen 2. These cameras incorporated an improved photocathode material, resulting in higher signal-to-noise ratio and increased sensitivity. Gen 3 cameras also featured an ion barrier film, which extended the lifespan of the tube and reduced image degradation caused by ion burn.
In addition to the improved image quality, Gen 3 night vision cameras introduced autogating technology. This feature allowed the cameras to automatically adjust to varying light conditions, preventing damage and blooming caused by sudden exposure to bright light sources.
Generation 4 (Gen 4)
Generation 4 night vision cameras, also known as filmless or unfilmed Gen 3, represented another significant leap forward in night vision technology. These cameras eliminated the thin film that was previously applied to the microchannel plate, resulting in improved resolution, better light transmission, and reduced halo effects around intense light sources.
Gen 4 cameras offered enhanced image quality, particularly in extremely dark conditions, and were more durable and reliable compared to previous generations. However, they were primarily developed for military and law enforcement applications and are not as widely available to the general public.
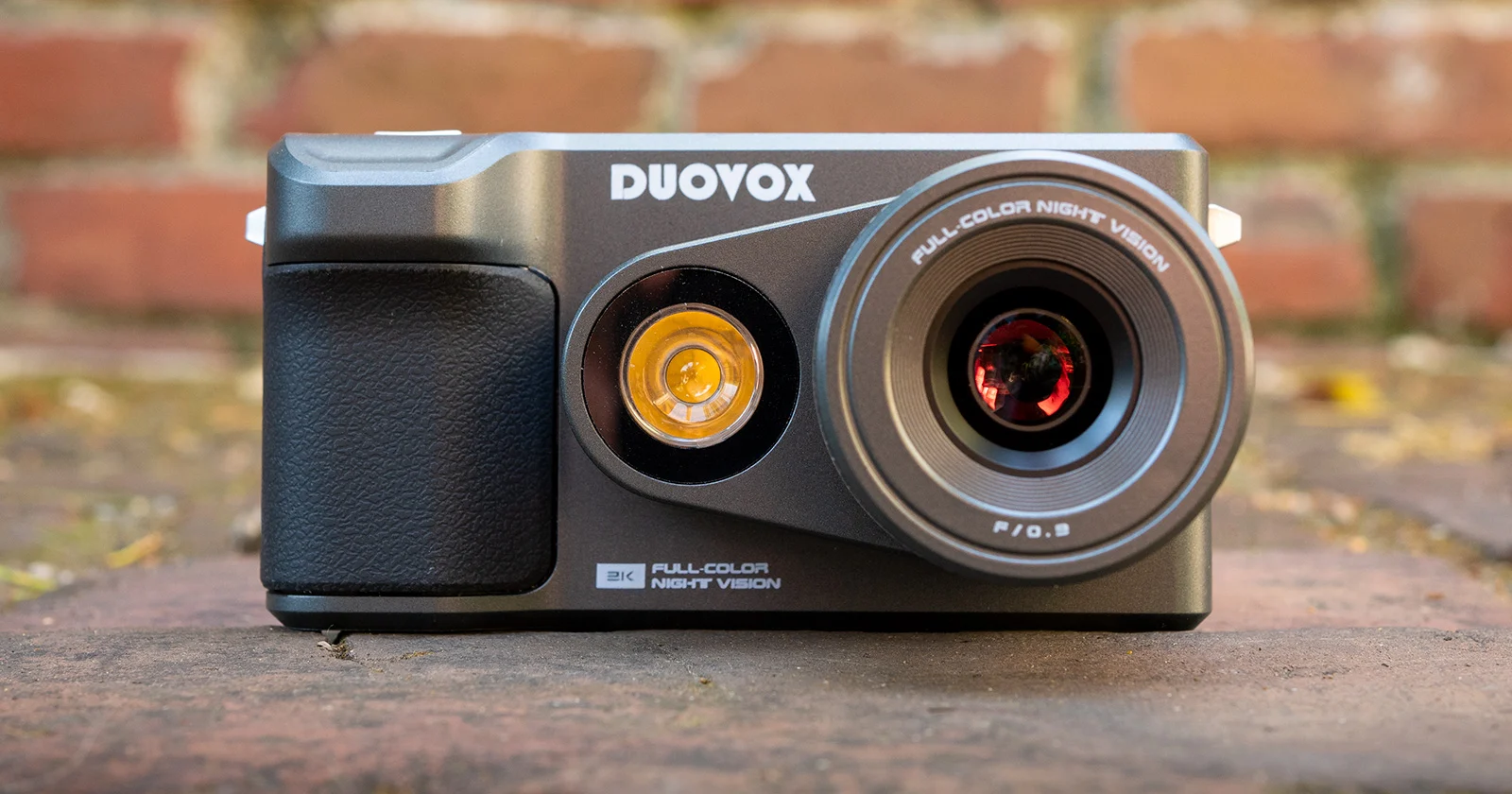
Digital Night Vision
In recent years, digital night vision technology has gained popularity. Digital night vision cameras use an image sensor and digital processing to capture and enhance images in low-light conditions. These cameras offer the advantage of being able to record and view footage directly on a built-in screen or transmit it wirelessly to a connected device.
Digital night vision cameras often incorporate additional features such as infrared illuminators, adjustable sensitivity settings, and the ability to capture still images or record videos. They are generally more compact and affordable than traditional image intensifier-based night vision cameras.
With ongoing advancements in night vision technology, we can expect to see further improvements in image quality, detection range, and overall performance. These advancements will continue to make night vision cameras more accessible and effective for various applications, including home security and surveillance.
Read more: When Were Gutters Invented
Current Applications of Night Vision Cameras
Night vision cameras have expanded beyond their military origins and are now widely used in various applications for both residential and commercial purposes. Let’s explore some of the current applications of night vision cameras and how they enhance security and surveillance.
Home Security
Night vision cameras have become an integral part of home security systems, providing homeowners with around-the-clock monitoring and protection. These cameras allow for the detection of intruders and the recording of clear video footage, even in total darkness. With the ability to view live feeds remotely through smartphones or computers, homeowners can always keep an eye on their property, ensuring peace of mind and prompt response to any suspicious activity.
Wildlife Observation
Night vision cameras have immensely benefited wildlife enthusiasts and researchers in monitoring and studying nocturnal animals. These cameras enable the observation of wildlife behavior, migration patterns, and even rare species that are only active during the night. By capturing high-resolution images and videos in natural habitats without disturbing the animals, night vision cameras provide valuable insights into the animal kingdom.
Law Enforcement and Surveillance
Night vision cameras continue to be instrumental in law enforcement activities and surveillance operations. They allow police and security agencies to monitor high-risk areas, detect criminal activities, and gather crucial evidence during nighttime operations. Night vision cameras enhance officer safety and improve situational awareness in low-light environments, enabling law enforcement personnel to respond effectively to potential threats.
Outdoor Activities
Night vision cameras have become popular among outdoor enthusiasts, such as hunters, hikers, and campers. These cameras provide them with a clear view of the surroundings when natural light is limited, ensuring safety and enabling better navigation in dark or unfamiliar terrains. Additionally, night vision cameras enhance the thrill of wildlife spotting and allow for capturing memorable moments in the great outdoors.
Industrial and Construction Sites
Night vision cameras play a crucial role in securing industrial and construction sites. These cameras help monitor the premises during non-working hours, detect unauthorized access, and prevent theft or vandalism. By capturing detailed footage even in low-light conditions, night vision cameras provide valuable evidence in case of any security breaches or accidents.
As night vision technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further expansion of its applications. New innovations, such as thermal imaging and augmented reality, are already being integrated into night vision cameras, opening up new possibilities in security, surveillance, and various other fields.
From protecting our homes to exploring the depths of nature, night vision cameras have become an essential tool for enhancing safety, improving situational awareness, and uncovering the mysteries of the night.
Conclusion
Night vision cameras have come a long way since their early days, evolving from large and bulky devices to compact and powerful tools for enhancing home security and surveillance. From their wartime origins to their current applications in various fields, night vision cameras have revolutionized the way we see in the dark.
The advancements in night vision technology, ranging from the first-generation devices to the latest digital cameras, have significantly improved image quality, detection range, and overall performance. This has made night vision cameras more accessible and effective for a wide range of applications.
Home security has been greatly enhanced with the incorporation of night vision cameras into residential surveillance systems. Homeowners can now monitor their properties 24/7, even in complete darkness, providing a sense of security and peace of mind. Night vision cameras have become an invaluable tool for deterring intruders, capturing clear footage, and facilitating prompt responses to any suspicious activity.
Night vision cameras have also found applications beyond home security. Wildlife enthusiasts, researchers, and law enforcement agencies benefit from the ability to observe and monitor nocturnal animals and conduct surveillance operations in low-light conditions. Outdoor enthusiasts, such as hunters and campers, rely on night vision cameras for better visibility and safety during their adventures.
The future of night vision technology is promising. Ongoing advancements are likely to further improve image quality, extend detection range, and introduce new features and capabilities. Innovations such as thermal imaging and augmented reality are expected to further enhance the functionality and versatility of night vision cameras.
In conclusion, night vision cameras have brought about a revolution in home security, wildlife observation, law enforcement, and various other fields. With their ability to provide clear and detailed images in low-light or complete darkness, night vision cameras have become an indispensable tool in our quest for enhanced security, surveillance, and exploration of the nocturnal realm.
Frequently Asked Questions about When Were Night Vision Cameras Invented
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














