Home>Technology>Home Office Tech>How Does A Car Charging Station Work


Home Office Tech
How Does A Car Charging Station Work
Modified: March 1, 2024
Learn how a home office tech, such as a car charging station, works to power electric vehicles. Understand the process and benefits of this innovative technology.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the future of transportation! As the world transitions towards sustainable energy solutions, electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. However, the widespread adoption of EVs hinges on the availability of efficient charging infrastructure, and this is where car charging stations play a pivotal role.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the inner workings of car charging stations, exploring their components, working principles, and the various types available. Additionally, we will highlight the numerous benefits associated with utilizing these stations, shedding light on the positive impact they have on the environment and our daily lives.
So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on an electrifying journey to uncover the intricacies of car charging stations and their significance in the realm of sustainable transportation.
Key Takeaways:
- Car charging stations are like gas stations for electric cars, providing the electricity needed to power up the vehicle’s battery. They have different types and offer benefits like cost savings and environmental impact.
- Charging stations work by managing the flow of electricity to the vehicle, ensuring safe and efficient charging. They contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable transportation ecosystem and promote energy independence.
Read more: How Does A Tesla Charging Station Work
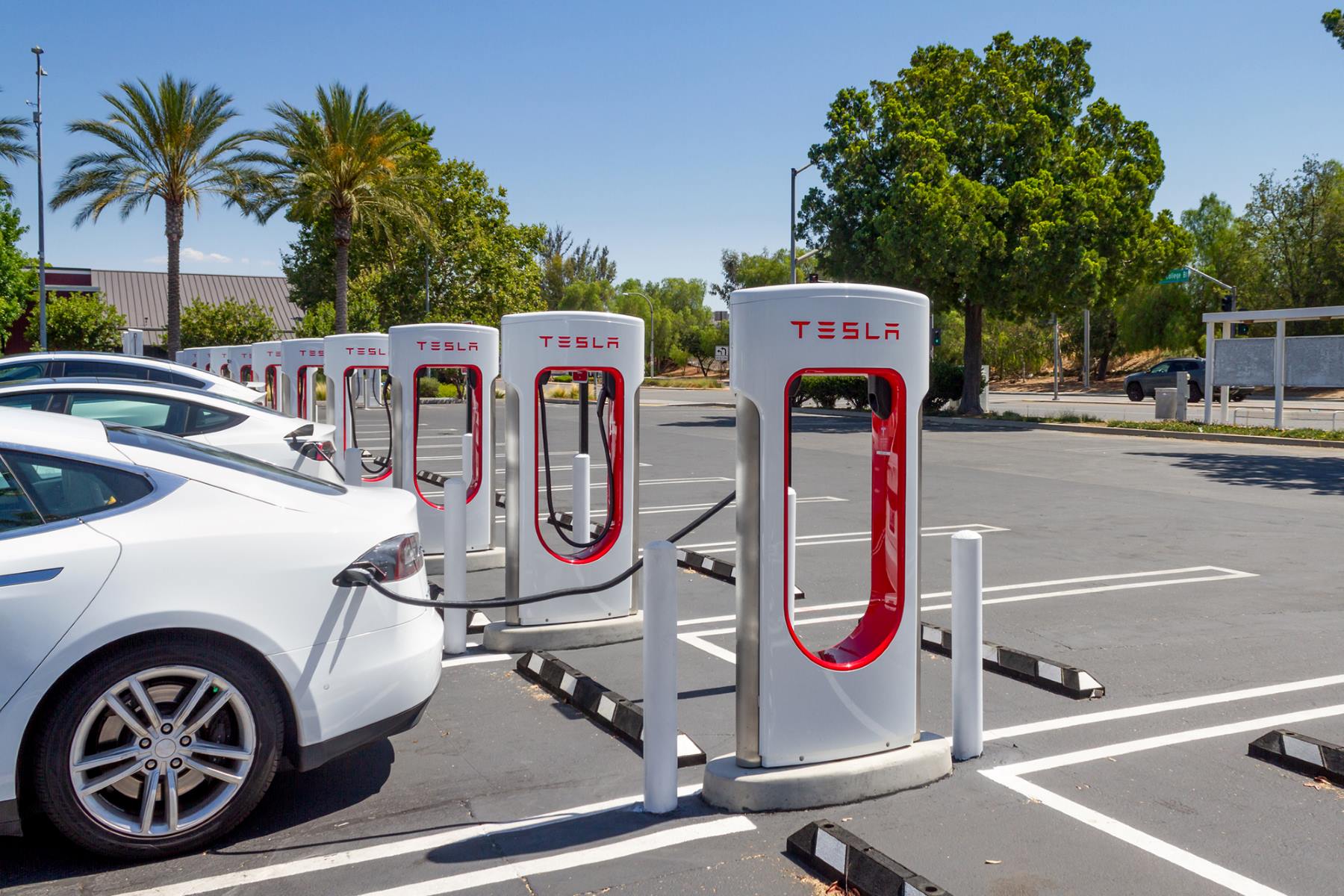
Components of a Car Charging Station
Car charging stations, also known as electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), consist of several key components that work together to facilitate the charging process. Understanding these components is crucial for gaining insight into the functionality and infrastructure of these stations.
Here are the primary components of a car charging station:
- Power Source: The power source, typically the electrical grid, provides the electricity required to charge the vehicle’s battery. It is essential for the power source to deliver a consistent and reliable supply of electricity to ensure efficient charging.
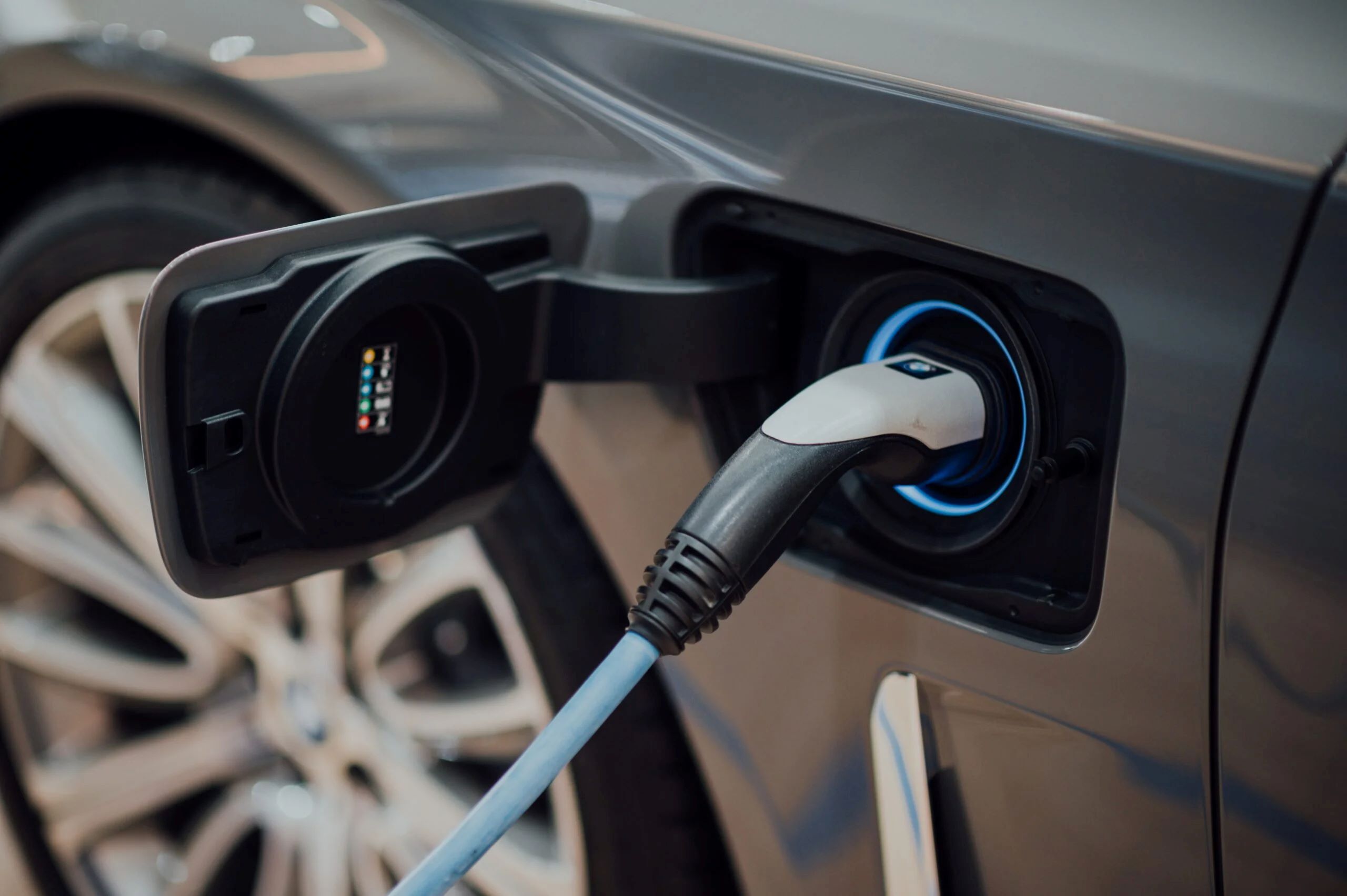
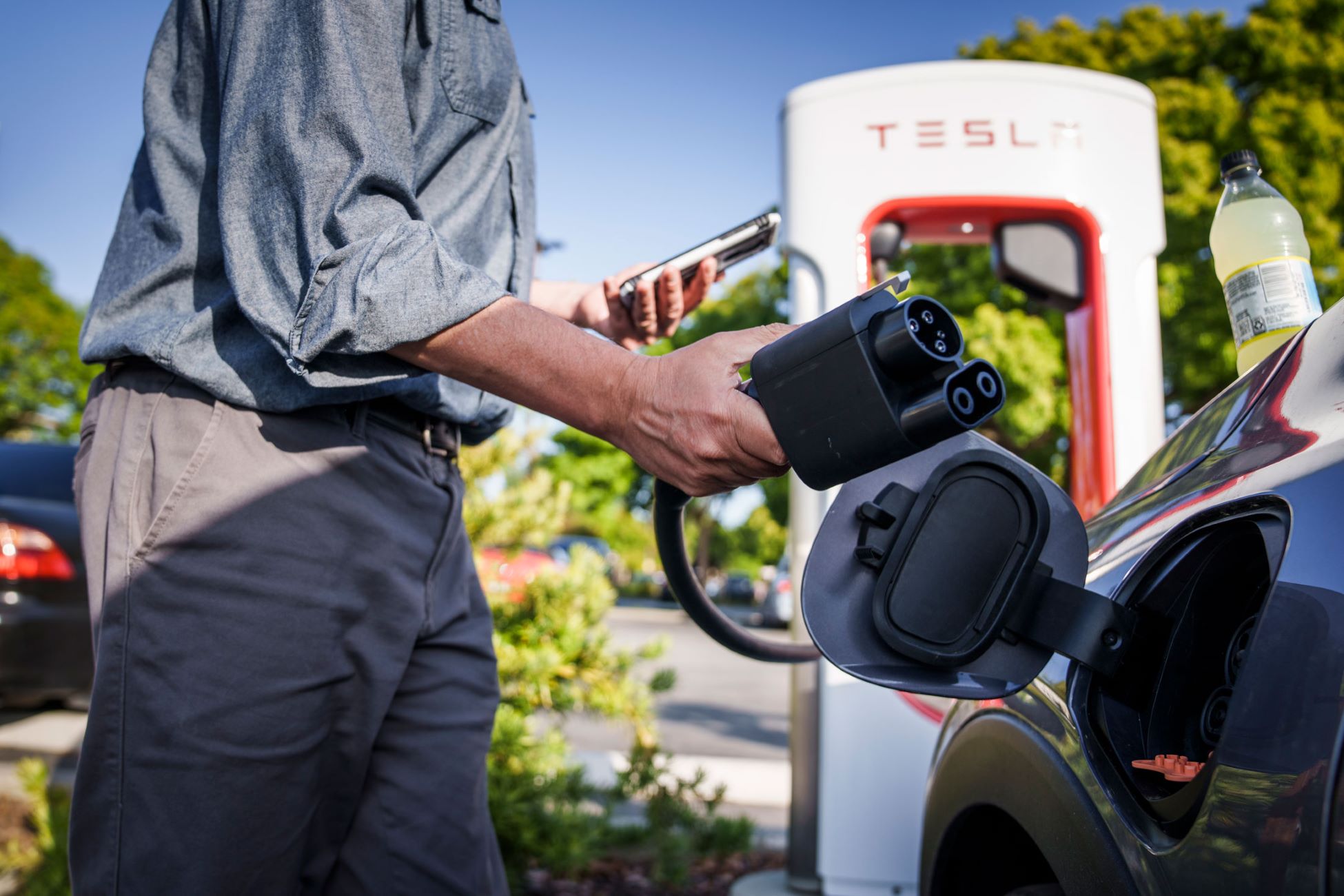
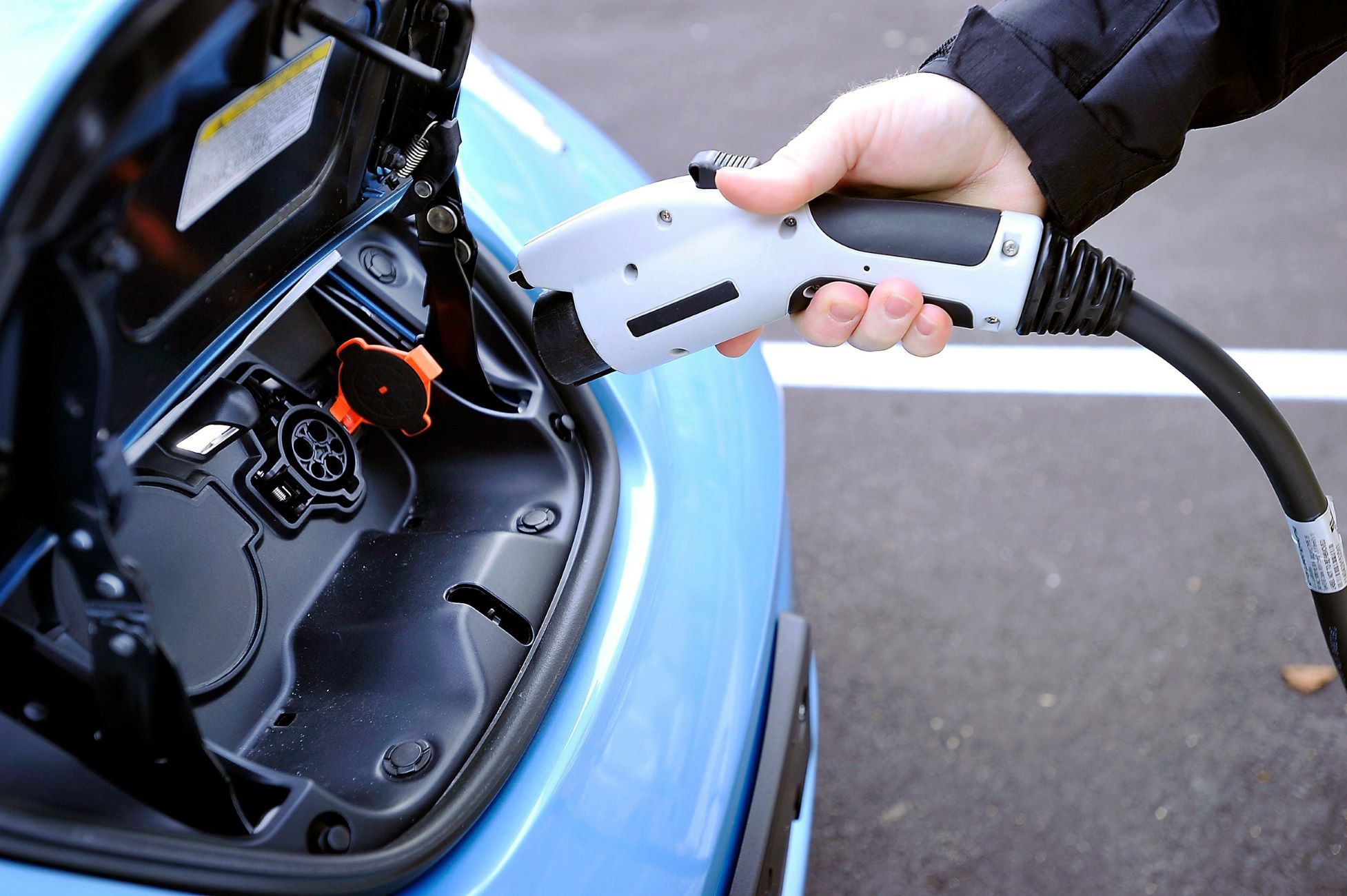
- Charging Cable: The charging cable serves as the physical link between the charging station and the vehicle. It transfers electricity from the station to the vehicle’s onboard charger, initiating the charging process. High-quality, durable cables are essential for safe and effective charging.
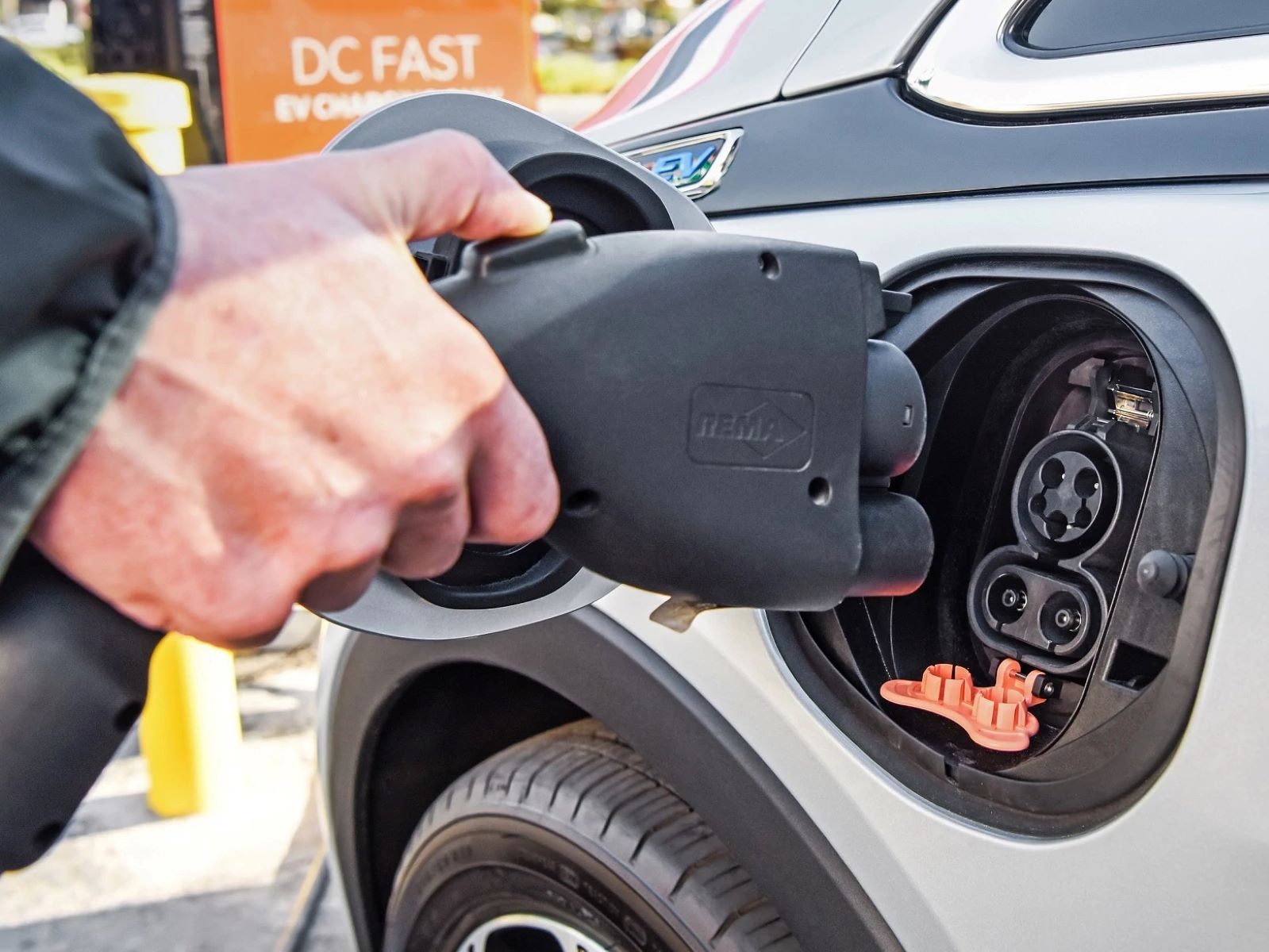
- Connector: The connector is the interface that allows the charging cable to connect to the vehicle’s charging port. Different types of connectors exist, such as the widely used SAE J1772 connector in North America and the Type 2 connector in Europe, each designed to accommodate specific charging standards.
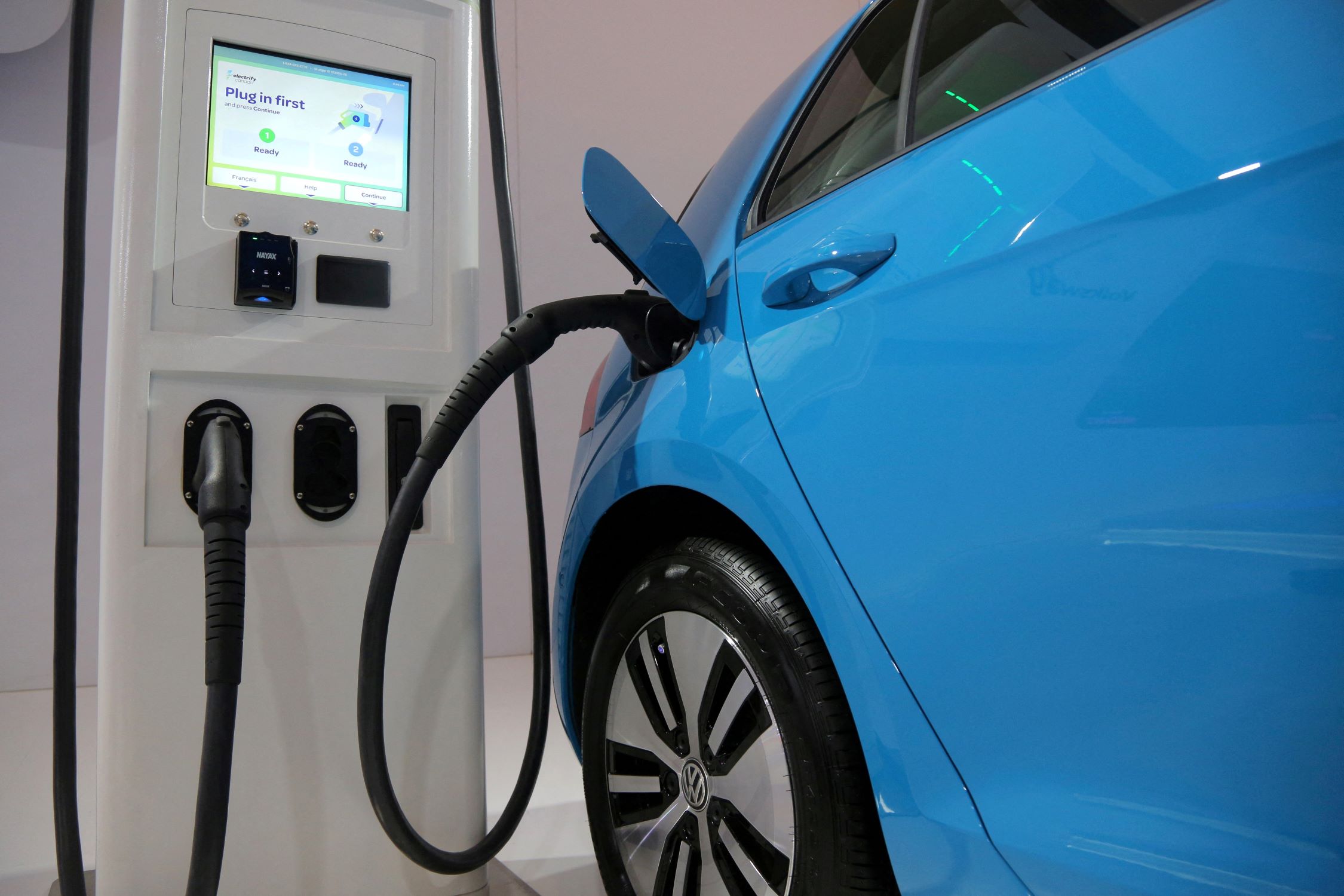
- Control Unit: The control unit, housed within the charging station, manages the flow of electricity and monitors the charging process. It regulates the voltage and current, ensuring that the vehicle’s battery is charged safely and efficiently. Advanced control units may incorporate smart features for enhanced functionality.
- Display and User Interface: Many modern charging stations are equipped with user-friendly displays and interfaces that provide essential information to users. This may include the charging status, energy consumption, and payment options, offering a seamless and informative experience for EV owners.
- Authentication and Payment System: To enable access control and payment processing, car charging stations often feature authentication and payment systems. These may include RFID card readers, mobile apps, or credit card terminals, allowing users to initiate and pay for charging sessions conveniently.
- Networking Capabilities: Some charging stations are equipped with networking capabilities, enabling them to connect to centralized management systems. This connectivity facilitates remote monitoring, software updates, and data collection, contributing to the efficient operation and maintenance of the charging infrastructure.
By integrating these components, car charging stations provide a reliable and user-friendly platform for EV owners to recharge their vehicles, supporting the widespread adoption of electric mobility.
Working Principle of a Car Charging Station
Understanding the working principle of a car charging station is essential for grasping the intricacies of electric vehicle charging. At its core, the charging process involves the transfer of electrical energy from the grid to the vehicle’s battery, and the charging station serves as the intermediary that facilitates this transfer.
Here’s a breakdown of the fundamental working principle of a car charging station:
1. Initiating the Charging Process: The charging process begins when an EV owner plugs the charging cable into the vehicle’s charging port and selects the desired charging parameters, if applicable. This action signals the charging station to commence the flow of electricity to the vehicle.
2. Authentication and Authorization: In scenarios where access control and payment are required, the user may need to authenticate their identity and authorize the charging session. This can be achieved through RFID cards, mobile apps, or other authentication methods supported by the charging station.
3. Power Conversion and Regulation: Once the charging process is initiated, the charging station’s control unit manages the conversion and regulation of electrical power. It adjusts the voltage and current to match the requirements of the vehicle’s onboard charger and battery, ensuring safe and efficient charging.
4. Charging Progress Monitoring: Throughout the charging session, the charging station monitors the progress of the process, tracking parameters such as energy consumption, charging duration, and battery status. This data is often displayed to the user via the station’s interface, providing real-time insights into the charging status.
5. Completion and Termination: Upon reaching the predefined charging level or when the user manually terminates the session, the charging station ceases the flow of electricity and completes the charging process. It may also provide a summary of the charging session, including energy consumed and associated costs, if applicable.
By adhering to these fundamental principles, car charging stations enable seamless and efficient charging experiences for electric vehicle owners, contributing to the widespread adoption of sustainable transportation solutions.
When using a car charging station, make sure to fully insert the charging cable into the port on your car to ensure a secure connection and efficient charging.
Types of Car Charging Stations
Car charging stations come in various types, each offering distinct charging capabilities and catering to different user requirements. Understanding the different types of charging stations is crucial for both EV owners and infrastructure planners, as it influences charging speed, compatibility, and the overall charging experience.
Here are the primary types of car charging stations:
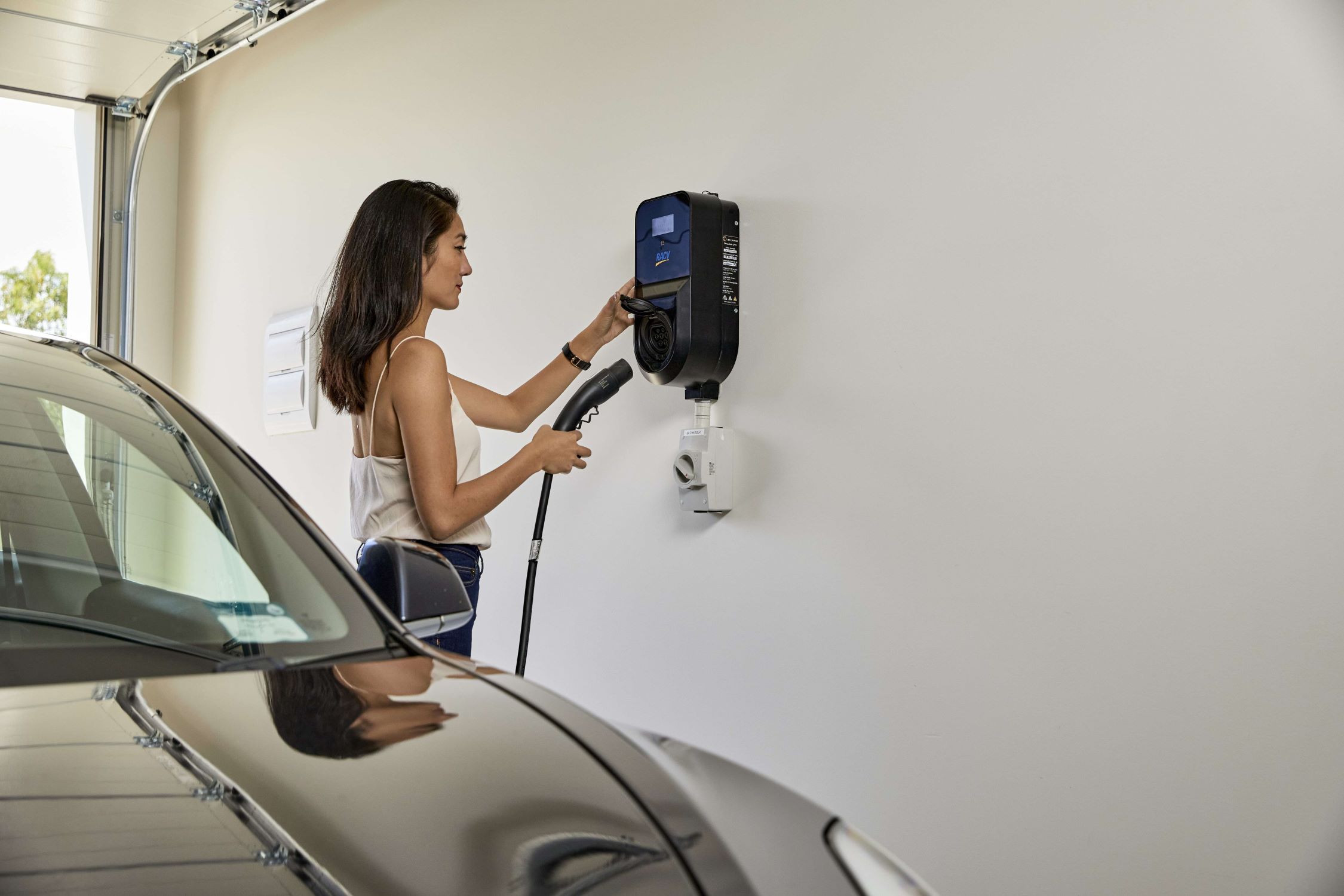
- Level 1 Charging Stations: Level 1 charging stations, also known as trickle chargers, utilize a standard 120-volt AC household outlet to deliver power to the vehicle. While convenient for basic charging needs, they provide the slowest charging rates, typically adding around 2-5 miles of range per hour of charging. Level 1 stations are well-suited for overnight charging at home or in locations where faster charging options are unavailable.
- Level 2 Charging Stations: Level 2 stations operate on 240-volt power and offer significantly faster charging compared to Level 1. They are commonly found in residential settings, workplaces, and public charging infrastructure. Level 2 charging can add approximately 10-60 miles of range per hour, making it a practical choice for daily charging needs and longer stops at public charging points.
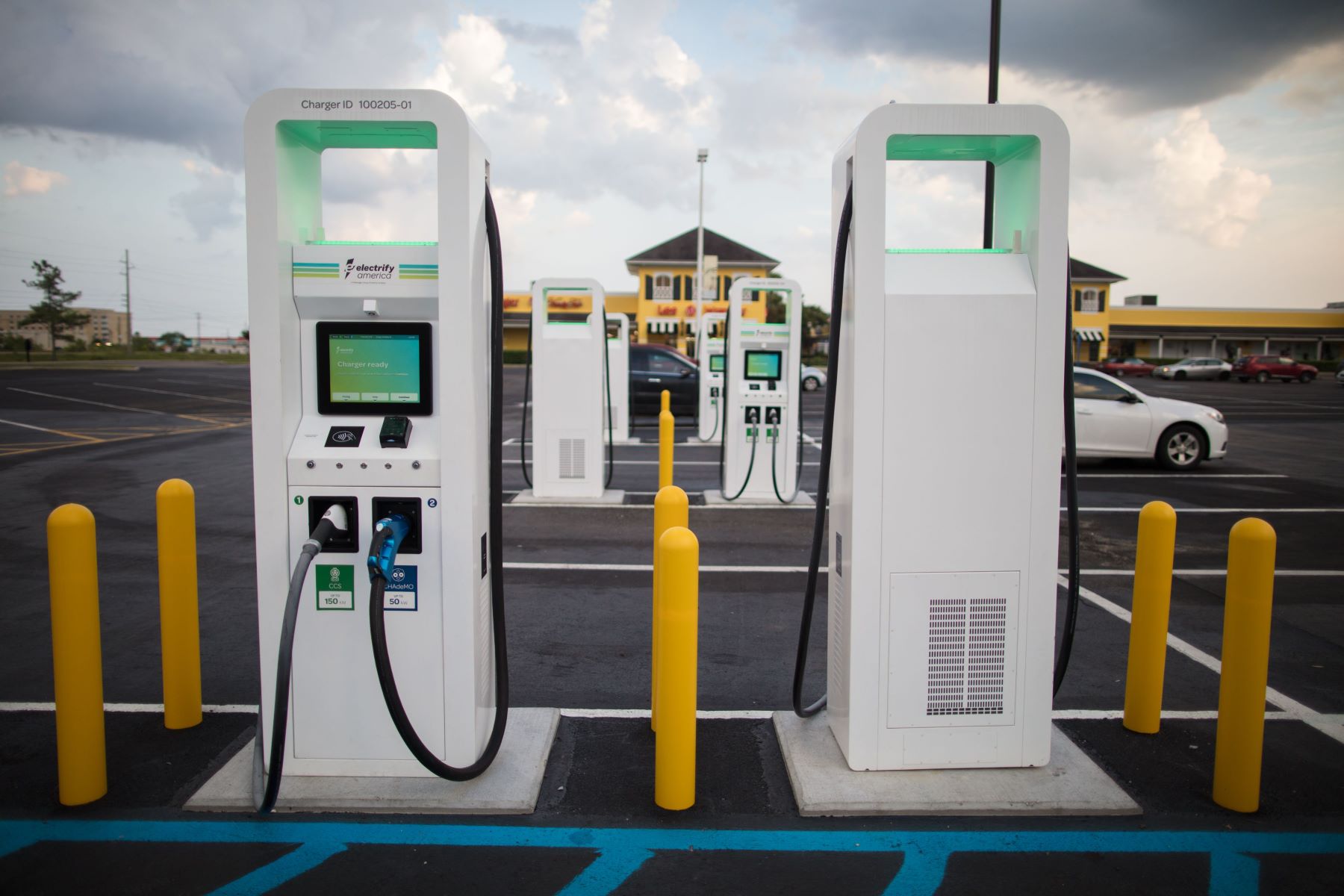
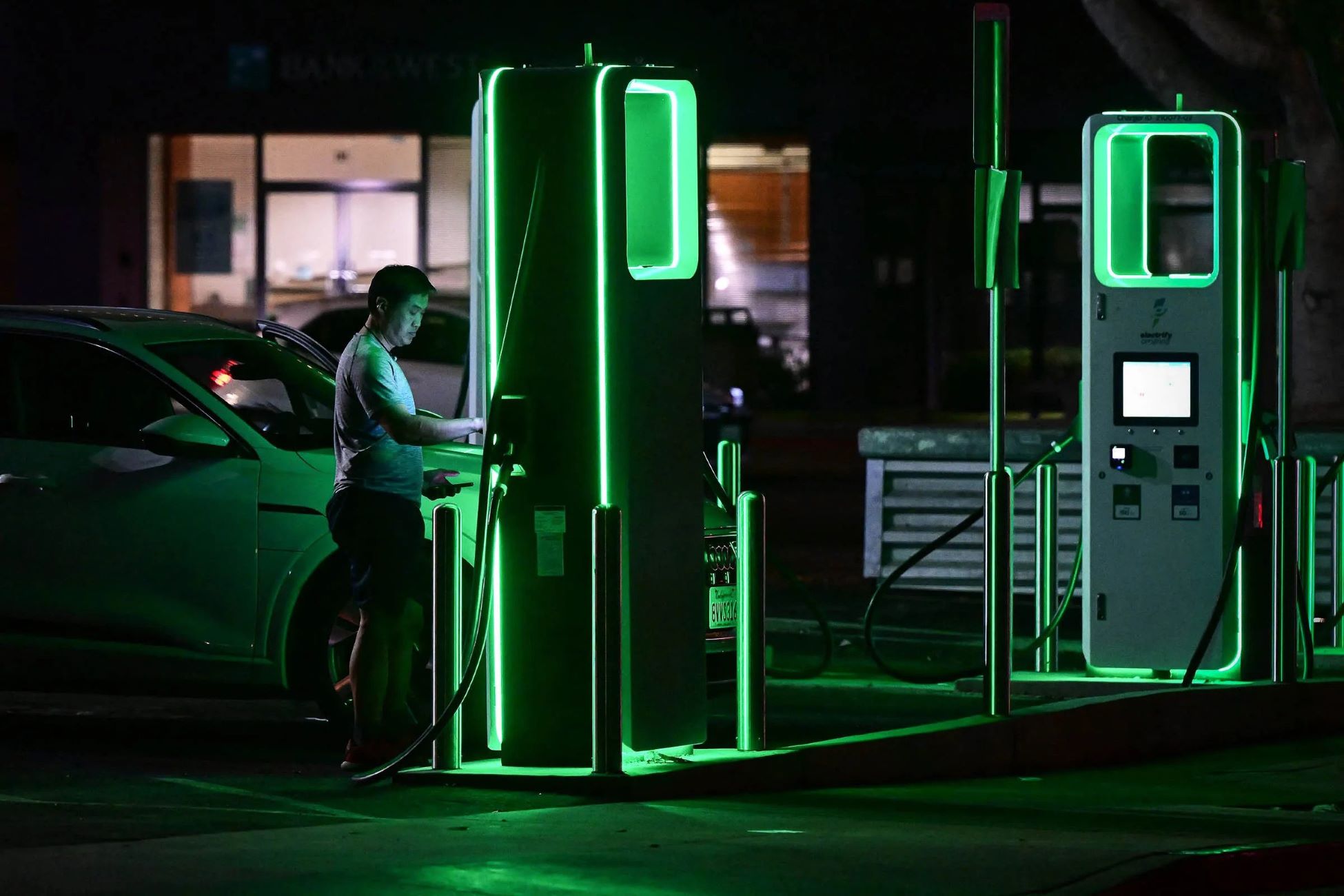
- DC Fast Charging Stations: DC fast charging stations, also known as Level 3 chargers, are designed for rapid charging, delivering high-voltage DC power directly to the vehicle’s battery. These stations are typically located along highways, major travel routes, and commercial areas, catering to drivers who require quick charging sessions. DC fast chargers can add around 60-80 miles of range in just 20 minutes, offering unparalleled convenience for long-distance travel and time-sensitive charging needs.
- Wireless Charging Stations: Wireless charging technology eliminates the need for physical cables, allowing EVs to charge by simply parking over a wireless charging pad installed in the ground. While still emerging, wireless charging stations offer the convenience of hassle-free charging and seamless integration into parking infrastructure. They are particularly suitable for urban environments and locations where traditional charging infrastructure may be impractical or visually intrusive.
By offering a diverse range of charging options, these stations cater to the varying needs of electric vehicle owners, promoting accessibility and convenience while accelerating the transition towards sustainable mobility.
Benefits of Using a Car Charging Station
Embracing the use of car charging stations yields a multitude of benefits, ranging from environmental sustainability to enhanced convenience for electric vehicle (EV) owners. By leveraging these charging facilities, individuals, businesses, and communities can contribute to a cleaner, more efficient transportation ecosystem while enjoying several practical advantages.
Here are the key benefits associated with using car charging stations:
- Environmental Impact: By opting for electric vehicles and utilizing car charging stations, individuals significantly reduce their carbon footprint. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, leading to improved air quality and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, thereby contributing to global efforts to combat climate change and environmental degradation.
- Cost Savings: Charging an electric vehicle is often more cost-effective than fueling a conventional gasoline-powered car. With lower electricity prices compared to gasoline and the potential for off-peak charging rates, EV owners can achieve substantial savings on their transportation expenses, making electric mobility an economically attractive option.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Car charging stations, especially Level 2 and DC fast chargers, offer convenient and accessible charging solutions for EV owners. Whether at home, work, or on the go, the availability of charging infrastructure provides peace of mind and flexibility, eliminating the need for frequent visits to traditional gas stations.
- Energy Independence: Electric vehicles and their associated charging infrastructure contribute to reducing reliance on fossil fuels, promoting energy independence and diversification. This shift towards electrified transportation aligns with sustainable energy goals and supports the development of renewable energy sources, further enhancing energy security and resilience.
- Technological Advancements: The proliferation of car charging stations fosters innovation and technological advancements in the electric mobility sector. This includes the development of faster charging technologies, smart grid integration, and enhanced energy management solutions, driving progress towards more efficient and sustainable transportation systems.
- Community Development: Deploying car charging stations within communities and urban areas fosters a culture of sustainability and forward-thinking urban planning. It encourages local economic development, promotes tourism, and enhances the overall attractiveness of regions that prioritize eco-friendly transportation infrastructure.
By reaping these benefits, individuals and communities can embrace a cleaner, more sustainable approach to transportation while enjoying practical advantages that contribute to a more efficient and resilient mobility ecosystem.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of car charging stations, it becomes evident that these innovative facilities are instrumental in shaping the future of transportation. By providing a reliable and efficient platform for charging electric vehicles, car charging stations play a pivotal role in promoting sustainable mobility and reducing the environmental impact of transportation.
From the intricate components that form the backbone of these stations to the diverse types of charging options available, it is clear that car charging infrastructure is evolving to meet the dynamic needs of electric vehicle owners and support the widespread adoption of electric mobility.
Furthermore, the numerous benefits associated with utilizing car charging stations underscore the transformative potential of electric transportation. From cost savings and energy independence to environmental stewardship and technological advancements, the advantages extend beyond individual vehicle owners, influencing communities, businesses, and the global effort to combat climate change.
As the electrification of transportation continues to gain momentum, the expansion and enhancement of car charging stations will be crucial in facilitating this transition. By embracing the latest technological innovations and sustainable energy solutions, these stations are poised to revolutionize the way we power our vehicles, shaping a cleaner, more efficient, and more accessible transportation landscape for generations to come.
So, whether you’re an electric vehicle enthusiast, a sustainability advocate, or simply curious about the future of transportation, car charging stations stand as beacons of progress, illuminating the path towards a greener, more sustainable future on the road.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does A Car Charging Station Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.






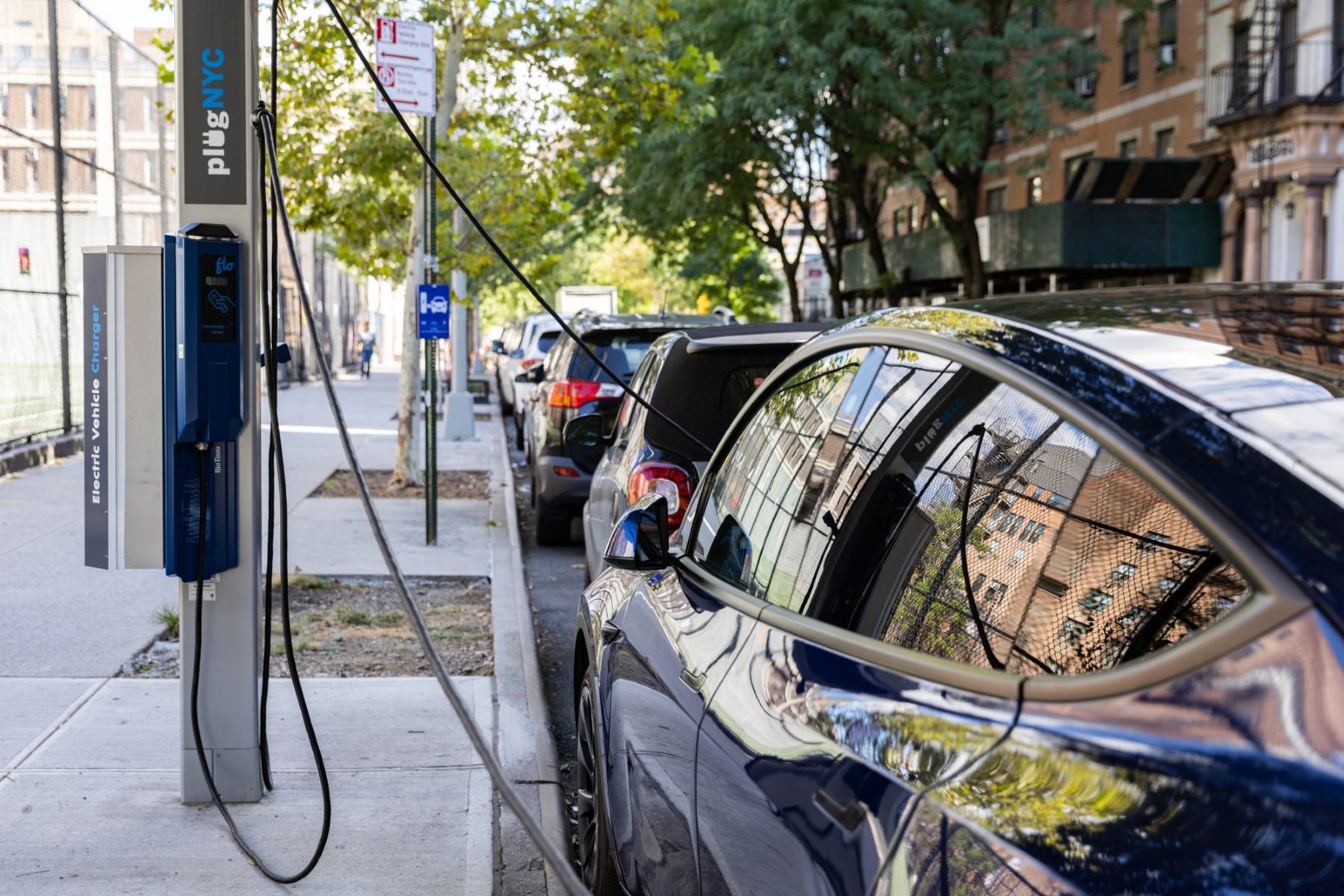








0 thoughts on “How Does A Car Charging Station Work”