Home>Articles>Essential Wall Types And Measurements To Know Before Renovating


Articles
Essential Wall Types And Measurements To Know Before Renovating
Modified: January 23, 2024
Discover essential wall types and measurements to know before renovating. Our articles provide valuable information to help you plan your project effectively.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to renovating your home or building a new structure, understanding the different types of walls and their measurements is crucial. Walls not only provide structure and support, they also define the layout and functionality of a space. Whether you are a homeowner, a contractor, or a DIY enthusiast, having a solid understanding of wall types and measurements will help you plan your project effectively and ensure its success.
In this article, we will explore some of the essential wall types and measurements that you need to know before starting any renovation. From load-bearing walls to exterior walls and partition walls, each type serves a specific purpose. So, let’s dive into the world of walls and discover the key information you need to make informed decisions for your project.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the measurements and construction of different wall types, from load-bearing to non-load-bearing, is crucial for successful renovation and construction projects. Each type serves a specific purpose and requires careful consideration to ensure safety and stability.
- Whether you’re a homeowner, contractor, or DIY enthusiast, having a comprehensive understanding of wall types and measurements will help you make informed decisions and achieve successful results in your building projects. Paying attention to these details is essential for creating functional, beautiful, and structurally sound spaces.
Stud Wall
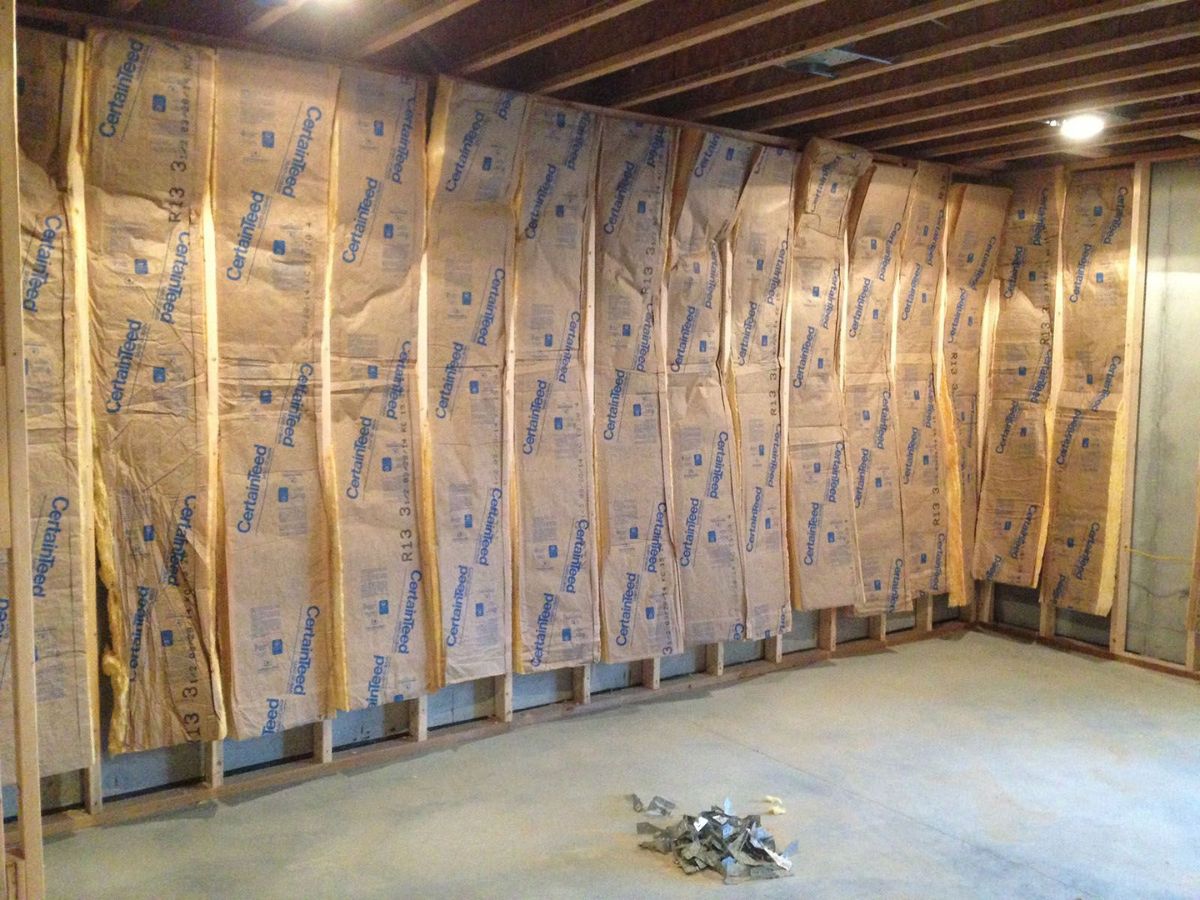
A stud wall is one of the most common types of walls found in residential and commercial buildings. It consists of vertical columns called studs, which are typically made of wood or metal, and horizontal boards known as plates. Stud walls are designed to provide structure and support for the building.
The spacing between the studs is crucial for the strength and stability of the wall. In most cases, the standard spacing is 16 inches on center (OC) or 24 inches OC. This means that the center of each stud is placed 16 or 24 inches apart from the center of the adjacent stud. The choice between 16 inches OC and 24 inches OC depends on the load-bearing capacity required for the wall and the building code regulations in your area.
In addition to the studs and plates, stud walls also have headers and sills. Headers are horizontal beams placed above openings, such as doors and windows, to support the weight of the wall above. Sills, on the other hand, are horizontal beams located at the base of the wall, providing a stable foundation for the structure.
Stud walls offer flexibility in terms of insulation, electrical wiring, and plumbing. The space between the studs can be filled with insulation material to improve energy efficiency and soundproofing. Moreover, electrical wiring and plumbing pipes can be easily routed through the stud wall, making it convenient for installing electrical outlets, switches, and fixtures.
Overall, the stud wall is a versatile and widely used type of wall that provides strength, stability, and flexibility in building design. Understanding its measurements and components is essential for proper construction and renovation projects.
Load-Bearing Wall
A load-bearing wall, also known as a structural wall, is a wall that carries the weight of the building’s structure from the roof or upper floors down to the foundation. These walls play a crucial role in supporting the overall stability and integrity of the structure.
Identifying load-bearing walls is important when planning any interior renovations or modifications, as removing or altering a load-bearing wall without proper support can lead to structural problems and compromise the safety of the building. Load-bearing walls are typically positioned in a way that distributes the weight of the structure evenly to the foundation.
Unlike non-load-bearing walls, load-bearing walls require specific measurements to ensure their strength and stability. The dimensions of a load-bearing wall are determined based on factors such as the height of the building, the materials used, and the load it needs to support. In general, load-bearing walls are wider and thicker compared to non-load-bearing walls. The width can vary depending on the design and weight distribution, but it is typically around 8 to 12 inches. The thickness, known as the gauge of the wall, is determined by the load it needs to support. It is common to find load-bearing walls with a gauge of 2×4 or 2×6 inches.
If you are planning to remove or modify a load-bearing wall, it is essential to consult with a structural engineer or a qualified professional to assess the feasibility of the project and determine the proper measures to ensure the stability of the structure. This may involve installing additional supports, such as beams or columns, to transfer the load to other areas of the building.
Understanding load-bearing walls and their measurements is crucial for any renovation or construction project. Always consult with experts to ensure the safety and integrity of the structure when dealing with load-bearing walls.
Non-Load-Bearing Wall
A non-load-bearing wall, also called a partition wall, is a wall that does not carry any structural weight of the building. Unlike load-bearing walls, these walls are primarily used to define spaces, provide privacy, and separate rooms or areas within a structure.
Non-load-bearing walls are typically thinner and lighter compared to load-bearing walls. The dimensions of a non-load-bearing wall can vary depending on the design and purpose of the wall. They are often constructed using lightweight materials such as drywall, wood, or metal studs.
One of the key advantages of non-load-bearing walls is their flexibility. Since they do not bear any weight, they can be easily modified, moved, or removed without affecting the structural integrity of the building. This makes them ideal for interior renovations and remodeling projects where the layout of the space needs to be altered.
The measurements of non-load-bearing walls depend on various factors, including the desired thickness, the material used, and the specific requirements of the project. In general, the thickness of a non-load-bearing wall is around 4 to 6 inches. The standard height of most walls is 8 feet, although it can be adjusted to suit the needs of the space.
Non-load-bearing walls can also provide additional functionalities, such as insulation, soundproofing, and the installation of electrical and plumbing systems. Insulation material can be added between the studs to improve energy efficiency and regulate temperature. Additionally, soundproofing materials can be incorporated into the wall to minimize noise transmission between rooms. Electrical wiring and plumbing pipes can run through the hollow cavity of the wall, allowing for easy installation of outlets, switches, and fixtures.
Whether you are remodeling your home or designing a commercial space, understanding non-load-bearing walls and their measurements is crucial for optimizing the functionality and aesthetics of the space.
Partition Wall
A partition wall, also known as a non-structural wall or a dividing wall, is a type of wall that is used to create separate spaces within a larger area. Unlike load-bearing walls, partition walls do not bear any structural weight of the building and are primarily designed for dividing purposes.
Partition walls are widely used in both residential and commercial settings to maximize the functionality of a space and create separate rooms or areas. These walls can be constructed using various materials, including drywall, glass, wood, or even movable panels, depending on the desired aesthetic and functionality.
When it comes to measuring partition walls, there are a few key factors to consider. The thickness of the wall largely depends on the material used and the specific requirements of the project. Generally, partition walls range from 3 to 6 inches in thickness. The height of the partition wall is typically determined by the ceiling height or the desired level of privacy and sound insulation. In most cases, partition walls are designed to reach the full height of the ceiling, but they can also be installed at a lower height for a more open or visually connected space.
Partition walls offer flexibility and versatility in terms of their construction and functionality. They can be easily modified, moved, or removed without affecting the structural integrity of the building. This flexibility allows for changes in room layouts and adaptations to accommodate evolving needs.
Furthermore, partition walls can incorporate various features to enhance their functionality. Electrical outlets, switches, and wiring can be easily integrated into the wall, facilitating the installation of lighting fixtures and electrical devices. Additionally, partition walls can be soundproofed with the use of insulation materials or acoustic panels to improve privacy and reduce noise transfer between rooms.
Overall, understanding the measurements and characteristics of partition walls is crucial for creating functional and aesthetically pleasing spaces. Whether you are dividing a room into multiple offices, creating separate living areas in an open-plan home, or designing a retail space, partition walls play a vital role in defining the layout and functionality of the space.
Read more: How To Frame A Curved Wall
Exterior Wall
An exterior wall is an essential component of any building, providing protection and insulation from the outdoor elements. It serves as the outermost layer of a structure, separating the interior living or working spaces from the external environment.
When it comes to measuring and constructing exterior walls, several factors come into play. The thickness of an exterior wall is determined by various considerations, including the construction materials used and the desired level of insulation and structural support. Exterior walls can range from a few inches thick in the case of lightweight materials like wood or metal siding, to several feet thick for more substantial materials like reinforced concrete or stone.
In addition to thickness, the construction of an exterior wall involves multiple layers. The main components typically include the outer cladding, insulation, vapor barrier, and inner sheathing or drywall. The outer cladding acts as the protective layer against weather elements and can be made of materials such as brick, stucco, siding, or panels. Insulation is crucial for energy efficiency and thermal regulation, helping to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and reduce heat loss or gain. A vapor barrier is installed to prevent moisture buildup within the wall assembly, and inner sheathing or drywall provides the finished interior appearance.
Exterior walls are designed to withstand various climatic conditions, such as rain, wind, snow, and temperature changes. Building codes and regulations play a significant role in determining the specifications and requirements for exterior walls, ensuring structural integrity and safety. These codes also take into account factors like wind resistance, moisture management, and thermal performance.
When it comes to renovating or modifying exterior walls, it’s important to consider the compatibility of materials, insulation values, weatherproofing, and aesthetics. Consulting with professionals and following local building regulations is crucial to ensure the proper installation and maintenance of exterior walls.
Overall, exterior walls are integral to a building’s structure and provide essential protection and insulation. Understanding their measurements and construction is key to creating a durable, energy-efficient, and aesthetically pleasing building envelope.
When renovating, be sure to measure the height, width, and depth of your walls. This will help you accurately plan for materials and furniture placement.
Interior Wall
An interior wall is a partition wall that separates interior spaces within a building. Unlike load-bearing walls, interior walls do not carry any structural weight and are primarily used for division, privacy, and functionality purposes.
Measuring and constructing interior walls varies depending on the specific needs and design of the space. The thickness of an interior wall is typically determined by the desired level of sound insulation, functionality, and room layout. Standard interior walls are usually around 4 to 6 inches thick and can be constructed using materials such as drywall, wood, or metal studs.
The height of an interior wall is generally determined by the ceiling height of the space. Most interior walls are constructed to reach the full height of the ceiling, ensuring privacy and defining separate areas. However, in certain cases, such as open floor plans or areas with unique architectural features, interior walls can be installed at a lower height to create visual connections or unique design elements.
Interior walls provide flexibility in terms of modifications and customization. They can be easily altered, moved, or removed without impacting the structure of the building. This allows for changes in room layouts, expansions, or reconfigurations to accommodate evolving needs or design preferences.
In terms of functionality, interior walls can incorporate various features to enhance the usability and aesthetics of the space. Electrical outlets, switches, and wiring can be easily integrated into the walls, allowing for the installation of lighting fixtures and electrical devices. Additionally, interior walls can be used for the installation of built-in shelves, cabinets, or entertainment units, maximizing storage space and improving organization.
When planning interior renovations or modifications, it’s important to consider the purpose of the space and the specific requirements of each room. Consulting with professionals, such as interior designers or contractors, can help ensure that the measurements and construction of interior walls align with the overall design objectives and functionality goals.
Overall, understanding the measurements and characteristics of interior walls is essential for creating functional and visually appealing spaces. Whether you are dividing rooms, creating separate functional areas, or incorporating unique design elements, interior walls play a vital role in defining the layout and functionality of the interior space.
Shear Wall
A shear wall is a type of wall that provides structural stability and resistance against lateral forces, such as wind and seismic loads. It is designed to transfer these forces from the roof or upper floors to the foundation, ensuring the stability and integrity of the building.
The measurements and construction of shear walls are of utmost importance to ensure their effectiveness in resisting lateral forces. Shear walls are typically made of reinforced concrete or masonry and are strategically placed in a building to resist the horizontal forces that act on the structure.
The thickness of a shear wall depends on several factors, including the height of the building, the location, and the expected magnitude of the lateral forces. Walls thicker than standard load-bearing walls are often used to provide the necessary strength and stiffness to withstand these forces. These walls can range in thickness from 8 to 14 inches or more, depending on the specific structural requirements.
The height of a shear wall is typically determined based on the vertical loads it needs to support and the overall height of the building. In taller structures, shear walls are designed to extend over multiple floors to provide continuous support and resistance against lateral forces throughout the height of the building.
Shear walls work by distributing the applied lateral loads to the foundation, which resists the forces and prevents excessive horizontal movement. The strength and effectiveness of shear walls are further enhanced by reinforcing steel bars, also known as rebar, which are embedded within the wall during construction. The use of rebar provides additional tensile strength and ensures the integrity of the wall under significant lateral forces.
Proper design and construction of shear walls are crucial for the overall stability and safety of a building. It is essential to consult with a structural engineer or a qualified professional to determine the appropriate measurements, materials, and reinforcement needed for shear walls in your specific building project. Adhering to local building codes and regulations is also essential to ensure compliance and structural integrity.
Overall, shear walls play a critical role in providing lateral stability to buildings and are essential in areas prone to high winds or seismic activities. Understanding their measurements and construction is crucial for architects, engineers, and construction professionals involved in structural design and the construction of buildings.
Retaining Wall
A retaining wall is a type of wall that is designed to provide structural support and retain soil or other materials at different elevations. These walls are commonly used in landscapes, gardens, and construction projects to prevent erosion, control slopes, and create level areas in uneven terrain.
The measurements and construction of retaining walls are crucial for their effectiveness in retaining the soil and providing stability. The dimensions of a retaining wall depend on factors such as the height of the wall, the type of soil being retained, and the anticipated pressure from the soil or materials behind it.
The height of a retaining wall is an essential consideration in determining its measurements. Retaining walls can range in height from a few feet to several meters, depending on the specific needs and requirements of the project. Walls that are higher in height generally require additional structural reinforcement and a wider base for stability.
The thickness of a retaining wall is determined by the type of material used and the design requirements. Concrete and masonry are commonly used for retaining walls due to their strength and durability. Depending on the height and soil conditions, the thickness of a retaining wall can vary from 8 inches to several feet.
Retaining walls also require proper drainage systems to prevent the buildup of hydrostatic pressure and ensure the long-term stability of the wall. Drainage stones, perforated pipes, and geotextile fabrics are often used to facilitate the proper drainage of water behind the wall and prevent soil erosion.
In addition to measurements, the design and aesthetics of the retaining wall are important considerations. Retaining walls can be constructed using various materials, including concrete blocks, natural stone, or timber, to achieve the desired visual appeal that complements the surrounding landscape.
It is crucial to consult with a structural engineer or a qualified professional when designing and constructing a retaining wall. They can assess the specific site conditions, soil properties, and the desired function of the wall to determine the appropriate measurements and construction techniques.
In summary, retaining walls are essential elements in landscaping and construction projects that provide stability and prevent soil erosion. Understanding their measurements and proper construction techniques is crucial for creating durable and effective retaining walls that enhance the functionality and aesthetics of outdoor spaces.
Read more: How Do I Know What Size Blinds I Need
Foundation Wall
A foundation wall is a critical component of a building’s structure, serving as the base or support for the entire edifice. It is typically constructed below ground level and is responsible for distributing the weight of the building to the underlying soil or foundation system.
The measurements and construction of foundation walls are crucial to ensure the stability and integrity of the building. The dimensions of a foundation wall depend on various factors, including the load-bearing capacity of the soil, the height and weight of the structure, and the local building regulations. The proper thickness and width of the foundation wall are determined to withstand the structural loads exerted upon it.
The thickness of a foundation wall is typically greater than that of other walls in the building due to the critical role it plays in supporting the entire structure. It commonly ranges from 8 to 12 inches or more, depending on the specific design requirements, soil conditions, and structural considerations. A wider foundation wall can provide additional stability and bearing capacity, particularly in areas with expansive or weak soils.
Foundation walls can be constructed using different materials, including reinforced concrete, stone, or concrete block. The choice of material depends on factors such as site conditions, loading requirements, and construction techniques. Reinforced concrete is a popular choice due to its durability, strength, and resistance to moisture penetration.
In addition to measurements, foundation walls also require proper reinforcement to ensure their structural integrity. Steel reinforcement, in the form of rebar, is often embedded within the foundation walls during construction. This reinforcement adds tensile strength and helps to minimize cracks and structural failures caused by shifting or settling of the soil.
Foundation walls may also incorporate waterproofing and drainage systems to prevent water infiltration and protect against potential moisture-related issues. These systems can include waterproof coatings, damp-proofing membranes, drainage boards, and weep holes to divert water away from the foundation.
Proper construction and measurement of foundation walls are essential to ensure a solid and stable building structure. It is imperative to consult with a structural engineer or a qualified professional to determine the appropriate measurements, materials, and reinforcement needed for the specific building project. Adhering to local building codes and regulations is also crucial to ensure compliance and structural integrity.
In summary, foundation walls are critical components of a building’s structure that provide support and stability. Understanding their measurements and proper construction techniques is vital for ensuring the long-term durability and integrity of the building’s foundation.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of walls and their measurements is crucial for any renovation or construction project. Walls play a vital role in providing structure, support, and functionality to buildings, while also defining the layout and aesthetics of the space.
From load-bearing walls to non-load-bearing walls, partition walls to shear walls, each type serves a specific purpose and requires careful consideration in terms of measurements and construction techniques.
Load-bearing walls carry the weight of the building’s structure and require specific measurements to ensure their strength and stability. On the other hand, non-load-bearing walls provide privacy and division within a space and allow for flexibility in terms of modifications and customization.
Partition walls are used to create separate areas within a larger space, offering functionality and design possibilities. Shear walls provide crucial stability against lateral forces, such as wind and seismic loads, while retaining walls help prevent soil erosion and maintain the integrity of landscapes.
Exterior walls protect against the outdoor elements, while interior walls define and separate interior spaces. Foundation walls form the base and support of a building, distributing weight to the underlying soil.
Understanding the measurements and construction of each type of wall is essential for proper planning, design, and execution of any renovation or construction project. Consultation with professionals, adherence to local building codes, and following best practices are crucial for ensuring the safety, stability, and longevity of the structure.
Whether you are a homeowner, contractor, or a DIY enthusiast, having a comprehensive understanding of wall types and measurements will help you make informed decisions and achieve successful results in your building projects.
So, the next time you embark on a renovation or construction journey, pay close attention to the various wall types and their measurements. By doing so, you’ll be well-equipped to create functional, beautiful, and structurally sound spaces that stand the test of time.
Frequently Asked Questions about Essential Wall Types And Measurements To Know Before Renovating
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “Essential Wall Types And Measurements To Know Before Renovating”