Home>Articles>How Do Fuses And Circuit Breakers Protect Your Home Against Electrical Fires?


Articles
How Do Fuses And Circuit Breakers Protect Your Home Against Electrical Fires?
Modified: May 6, 2024
Learn how fuses and circuit breakers safeguard your home from electrical fires with informative articles. Protect your family and property today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
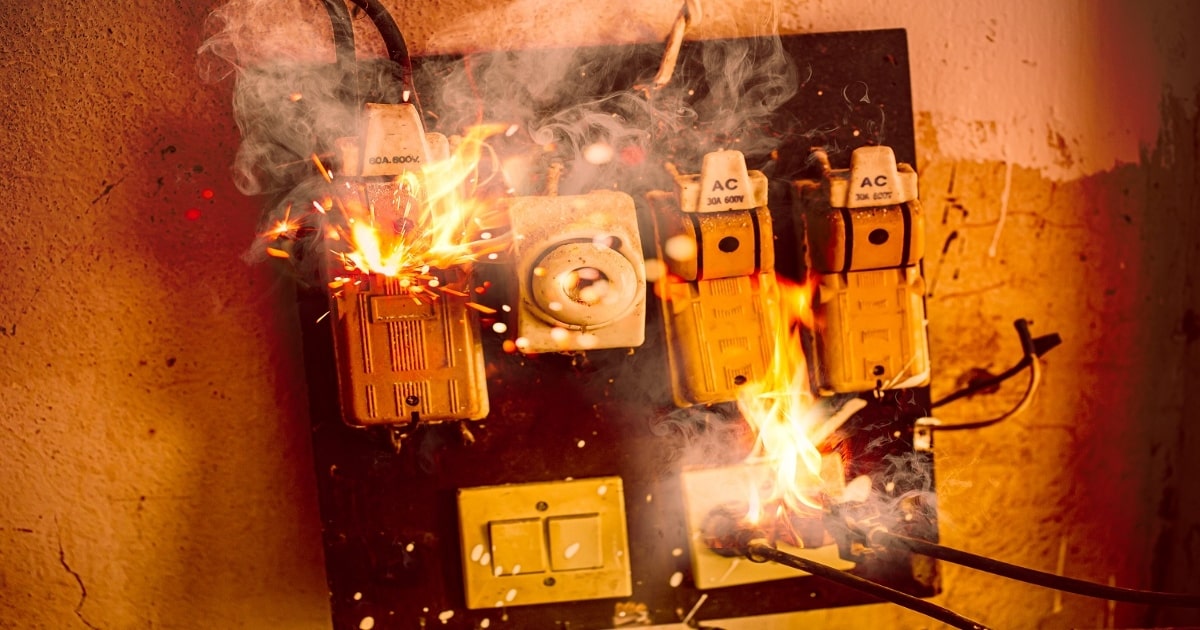
Electrical fires pose a significant threat to homes, causing damage, injuries, and even fatalities. It is crucial for homeowners to understand the importance of fire prevention measures and the role that fuses and circuit breakers play in safeguarding their homes against electrical fires.
Electrical fires can be caused by a variety of factors, including faulty wiring, overloaded circuits, damaged appliances, and electrical system malfunctions. These fires can quickly escalate, engulfing an entire home in flames within minutes. In addition to the destruction of property, electrical fires also put lives at risk, making it imperative for homeowners to take proactive measures to prevent them.
Fuses and circuit breakers are key components of a home’s electrical system that are designed to protect against electrical fires. They serve as safeguards by interrupting the flow of electricity when an overload or fault occurs, preventing electrical fires from starting or spreading.
In this article, we will explore the role of fuses and circuit breakers in protecting your home against electrical fires. We will discuss how they work, the different types available, and their respective advantages. Additionally, we will highlight the differences between fuses and circuit breakers, and the importance of following electrical safety practices.
By understanding the function and importance of these protective devices, homeowners can take appropriate steps to ensure the safety of their homes and loved ones.
Key Takeaways:
- Fuses and circuit breakers are essential in preventing electrical fires by interrupting the flow of electricity during overloads or faults, offering quick response times, affordability, resetability, and enhanced safety features.
- Prioritizing proper electrical system installation, regular maintenance, safe usage habits, and seeking professional help when needed are crucial in reducing the risks of electrical fires and safeguarding our homes.
Understanding Electrical Fires
Electrical fires can have devastating consequences, causing significant damage to property and posing a serious threat to lives. To effectively protect our homes, it is important to have a clear understanding of the causes of electrical fires, the dangers they present, and the importance of fire prevention measures.
Causes of Electrical Fires
Electrical fires can be triggered by various factors, many of which are preventable. Some common causes include:
- Faulty wiring: Outdated or damaged wiring can increase the risk of electrical fires. Over time, worn-out insulation or exposed wires can lead to short circuits, sparking, and heat buildup.
- Overloaded circuits: Plugging too many devices into a single outlet or circuit can overload the system and cause overheating, potentially leading to a fire.
- Malfunctioning appliances: Appliances with faulty electrical components, such as frayed cords or damaged plugs, are prone to causing electrical fires.
- Improper installation: Incorrectly installed electrical systems can pose a fire hazard. This includes incorrect wiring connections, insufficient grounding, and inadequate protection devices.
Dangers of Electrical Fires
Electrical fires can have devastating consequences. Not only do they result in the loss of property, but they also put lives at risk. Some of the dangers associated with electrical fires include:
- Loss of life: Electrical fires can quickly escalate and engulf a property, trapping occupants and making escape difficult.
- Smoke inhalation: The smoke produced by electrical fires is toxic and can cause respiratory problems, leading to serious injuries or even death.
- Structural damage: Electrical fires can cause extensive damage to the structure of a building, making it unsafe to inhabit and resulting in costly repairs.
- Emotional trauma: Experiencing a fire can be a traumatic event, causing long-term emotional distress for those affected.
Importance of Fire Prevention in Homes
Preventing electrical fires is paramount to ensuring the safety of our homes and loved ones. By taking proactive measures, homeowners can significantly reduce the risk of electrical fires. Some important fire prevention practices include:
- Regular electrical inspections: A professional electrician should conduct routine inspections to identify any potential hazards or issues with the electrical system.
- Proper wiring and installation: Electrical systems should be installed correctly, with appropriate wiring techniques and adherence to safety codes and regulations.
- Avoiding overloading circuits: Distribute electrical load evenly across multiple circuits and avoid plugging too many devices into a single outlet.
- Regular maintenance of appliances: Ensure that all electrical appliances are well-maintained, with cords and plugs in good condition.
- Using surge protectors: Install surge protectors to safeguard sensitive electronics from power surges which can cause electrical fires.
- Educating household members: Teach everyone in the household about the dangers of electrical fires and how to prevent them.
By implementing these fire prevention measures and understanding the risks associated with electrical fires, we can create a safer environment for ourselves and our families.
The Role of Fuses in Fire Protection
In the realm of fire protection, fuses play a crucial role in preventing electrical fires. By interrupting the flow of electrical current when an overload or fault occurs, fuses act as a protective barrier, safeguarding our homes and preventing potentially dangerous situations.
What are Fuses?
A fuse is a small, electrical safety device that is designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. It consists of a metal strip or wire inside a protective casing. When a current exceeding the fuse’s rating passes through it, the metal strip or wire heats up and ultimately melts, breaking the circuit and preventing further flow of electricity.
How do Fuses Work?
When an excessive current flows through an electrical circuit, the metal strip or wire inside the fuse heats up due to its resistance. As the temperature rises, the metal strip or wire reaches its melting point, causing it to break and open the circuit. This interruption stops the flow of electricity and prevents damage to the electrical system and potential fire hazards.
Types of Fuses
There are several types of fuses available, each with its own specific characteristics and applications:
- Cartridge Fuses: These fuses consist of a cylindrical body with metal end caps. They are commonly used in industrial and commercial applications.
- Plug Fuses: These fuses are commonly found in residential electrical systems. They have a body that resembles a plug and are installed in fuse boxes or electrical panels.
- Time-Delay Fuses: Also known as slow-blow fuses or time-lag fuses, these fuses provide temporary overcurrent protection, allowing for a brief surge in current without immediately blowing.
- Resettable Fuses (PTCs): Unlike traditional fuses, resettable fuses do not require replacement once they have blown. Instead, they automatically reset themselves after the fault has been rectified.
Benefits of Fuses in Preventing Electrical Fires
Fuses offer several benefits when it comes to preventing electrical fires:
- Overcurrent Protection: Fuses protect against current overloads, which can occur when there are too many devices drawing power from a single circuit. By interrupting the flow of excessive current, fuses prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Short-Circuit Protection: In the event of a short circuit, where a hot wire comes into contact with a neutral wire, fuses quickly interrupt the current flow, isolating the fault and preventing the wires from overheating and causing a fire.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Fuses are generally more affordable compared to circuit breakers, making them a cost-effective option for providing electrical safety.
- Reliability: Fuses have a simple design and operate based on the fundamental principle of electrical resistance. They do not rely on complex mechanisms and are less prone to failure.
Overall, fuses are an essential component of electrical systems, providing effective protection against overcurrents and short circuits, and serving as effective measures in preventing electrical fires.
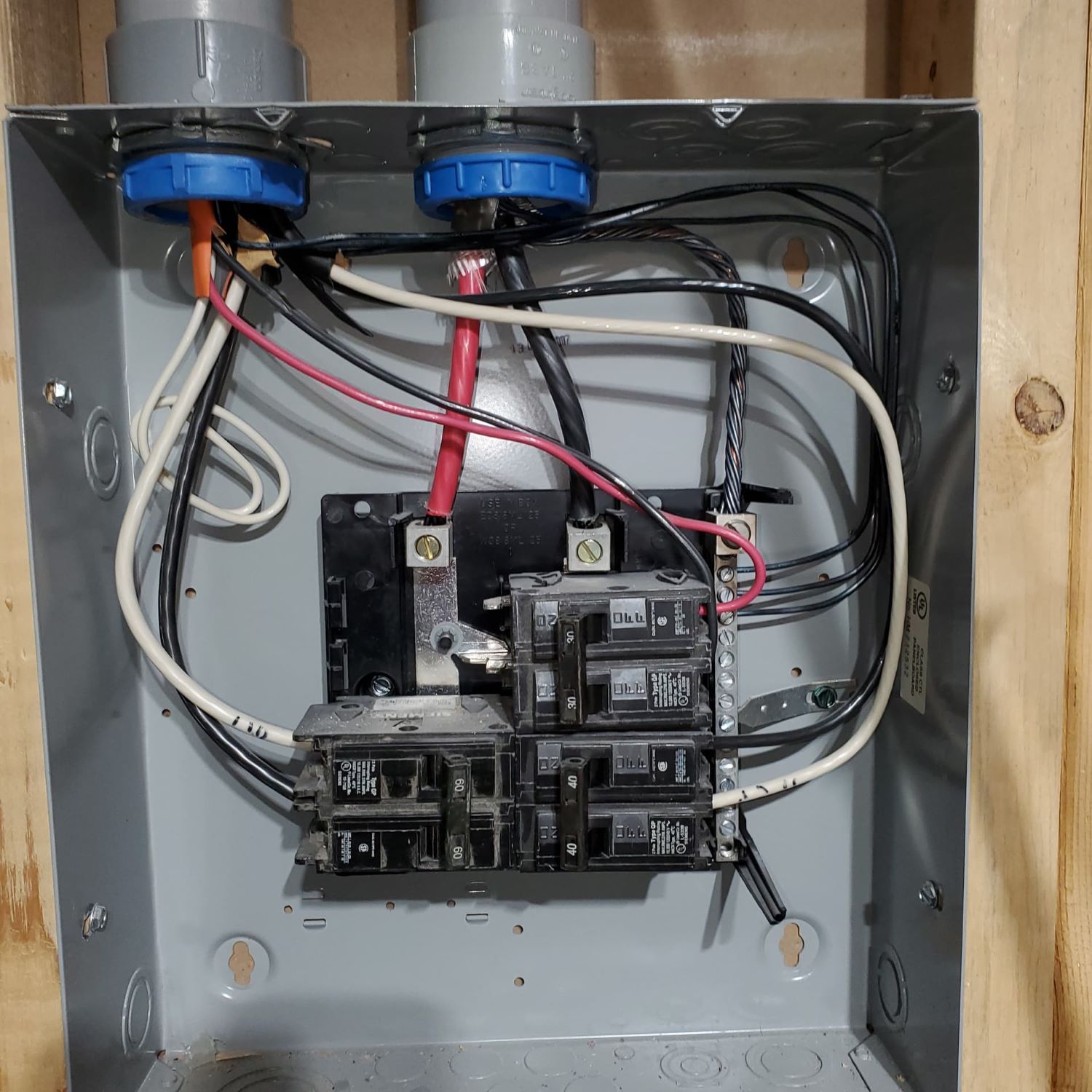
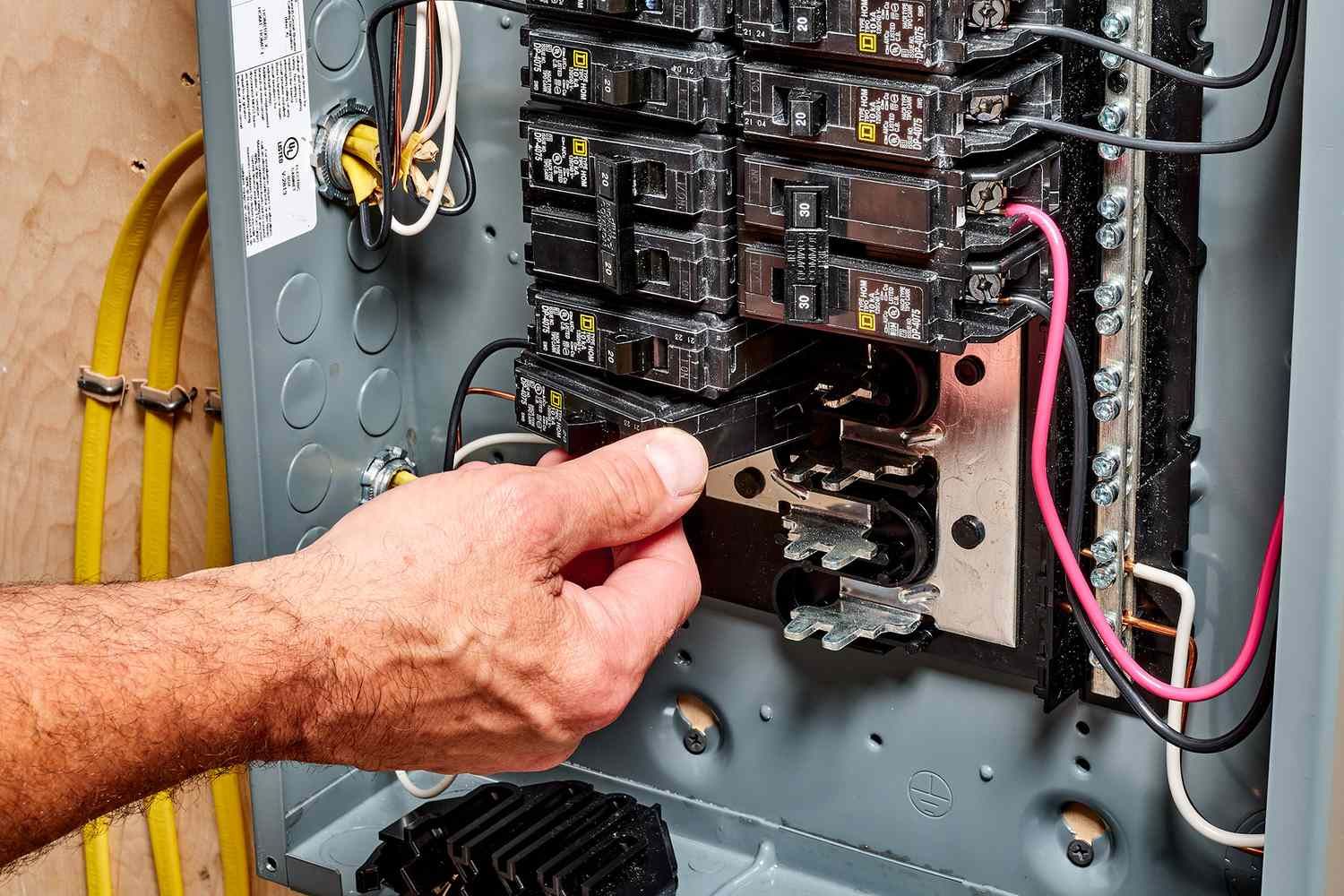
The Role of Circuit Breakers in Fire Protection
In addition to fuses, circuit breakers play a vital role in fire protection by safeguarding electrical systems against overloads and short circuits. These devices are designed to automatically detect and interrupt excessive currents, preventing potential fire hazards and ensuring the safety of our homes.
What are Circuit Breakers?
A circuit breaker is an electrical switch that automatically interrupts the flow of electrical current when it detects an overload or fault in the circuit. It consists of a switch mechanism and a tripping mechanism housed within a protective casing. When the circuit breaker senses an abnormal current, it trips and interrupts the electrical flow.
How do Circuit Breakers Work?
Circuit breakers operate on a thermal-magnetic trip mechanism or an electronic trip unit, depending on the type. In the case of a thermal-magnetic trip mechanism, the breaker contains a bimetallic strip that bends when exposed to heat generated by an overload. This bending of the strip causes the contacts to separate, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity.
For electronic trip unit circuit breakers, sensors monitor the electrical current. If an abnormal current is detected, the trip unit sends a signal to the mechanical components, resulting in the opening of the circuit breaker and disconnecting the electrical flow.
Read more: How Do Tandem Breakers Work
Types of Circuit Breakers
There are different types of circuit breakers available to accommodate various electrical needs and applications:
- Standard Circuit Breakers: These are the most common type and are used in residential and commercial electrical systems. They provide protection against overloads and short circuits.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): GFCIs are specifically designed to protect against electrical shock. They quickly interrupt the circuit when a ground fault occurs, preventing potential electrocution hazards.
- Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs): AFCIs detect and interrupt dangerous arc faults, which can cause electrical fires. They provide enhanced fire protection by responding to abnormal arcing in electrical circuits.
- Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs): MCBs are compact circuit breakers used in low-voltage electrical systems. They are commonly found in residential and commercial applications.
Advantages of Circuit Breakers in Preventing Electrical Fires
Circuit breakers offer several advantages in terms of fire protection:
- Rapid Response: Circuit breakers can detect overloads and faults almost instantaneously, providing a quick response to potentially hazardous situations.
- Easy Resetting: Unlike fuses that require replacement once they have blown, circuit breakers can be simply reset by flipping the switch, restoring the electrical supply after the issue has been resolved.
- Flexibility: Circuit breakers offer the advantage of adjustable trip levels, allowing customization based on the specific electrical load and requirements of different circuits.
- Enhanced Safety Features: GFCIs and AFCIs provide additional safety by specifically addressing ground faults and arc faults, minimizing the risk of electrical shock and fires.
With their automatic detection and interruption capabilities, circuit breakers effectively prevent electrical fires by rapidly disconnecting the power supply in the event of an abnormal current or fault. Their versatility and advanced safety features make them essential components in fire protection systems.
Differences between Fuses and Circuit Breakers
While both fuses and circuit breakers serve the purpose of protecting electrical systems from overloads and short circuits, there are notable differences in their performance, cost, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these distinctions can help homeowners choose the most suitable option for their specific needs.
Performance Differences
One of the main performance differences between fuses and circuit breakers lies in their response time and resetability:
– Fuses: Fuses have a quick response time, reacting almost instantaneously to overloads or faults in the electrical circuit. Once a fuse blows, it must be replaced with a new one to restore power. This process can be time-consuming during an electrical issue, especially if spare fuses are not readily available.
– Circuit Breakers: Circuit breakers also respond quickly to overloads and faults. However, unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be easily reset by flipping the switch after addressing the underlying problem. This resetability provides convenience and saves time when troubleshooting electrical issues.
Cost Differences
Another significant difference between fuses and circuit breakers lies in their cost:
– Fuses: Fuses are generally more affordable compared to circuit breakers. They are readily available and come in a variety of sizes and ratings to accommodate different applications and electrical systems. Fuses are a cost-effective choice, particularly in situations where multiple fuses are required.
– Circuit Breakers: Circuit breakers tend to be more expensive upfront compared to fuses. The cost varies depending on factors such as brand, type, and amperage rating. However, circuit breakers offer long-term cost savings as they can be reset and reused multiple times without the need for replacements.
Maintenance Differences
The maintenance requirements for fuses and circuit breakers also differ:
– Fuses: Fuses are relatively low-maintenance components. However, whenever a fuse blows, it needs to be replaced to restore electrical function. It is crucial to ensure that the correct type and rating of fuse are used to maintain the integrity of the electrical system.
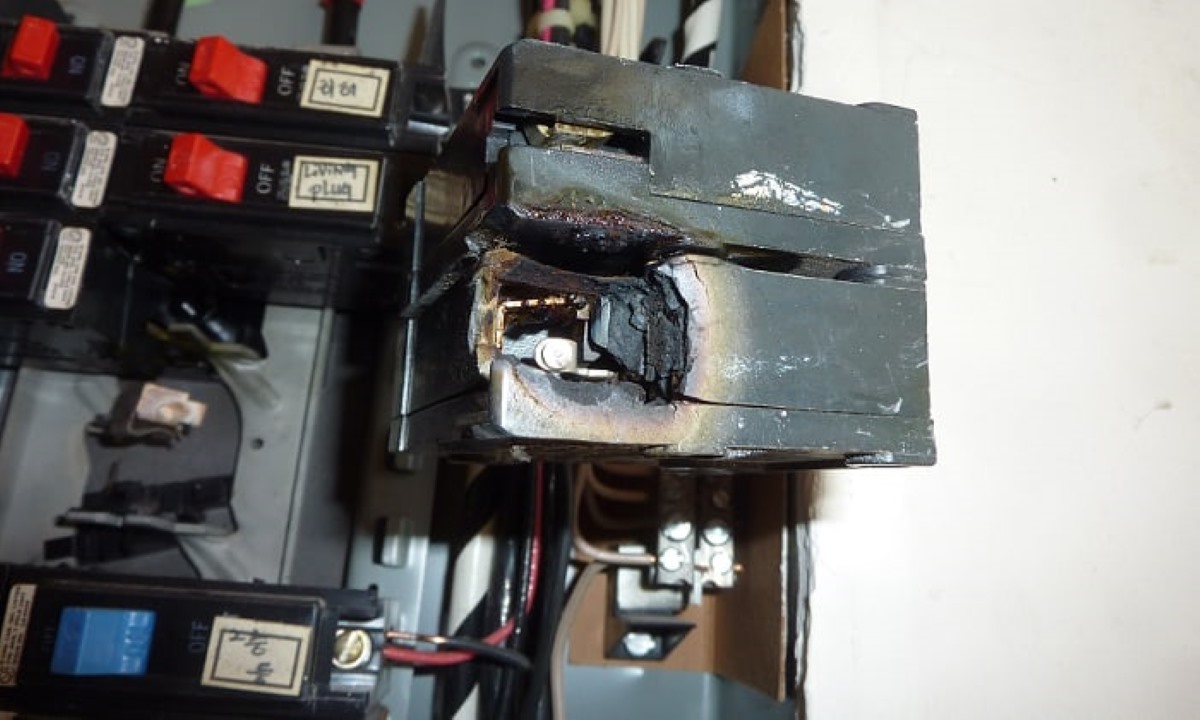
– Circuit Breakers: Circuit breakers require minimal maintenance. In most cases, periodic visual inspections to ensure they are in good condition are sufficient. However, if a circuit breaker trips frequently, it may indicate an underlying issue that requires professional attention.
Additionally, circuit breakers may require occasional testing to ensure proper functionality. This can be done by manually activating the test button or using specialized testing equipment.
Ultimately, the choice between fuses and circuit breakers depends on factors such as budget, system requirements, and personal preference. While fuses are cost-effective and offer quick response times, circuit breakers provide convenience with their resetability and long-term cost savings. It is essential to assess the specific needs of the electrical system and consult with a professional electrician to determine the best option for reliable fire protection.
Importance of Electrical Safety Practices
Ensuring electrical safety is paramount in protecting our homes from fires and potential hazards. By implementing proper electrical system installation, regular maintenance, safe usage habits, and seeking professional help when needed, we can mitigate the risks associated with electricity and safeguard the well-being of our families.
Proper Electrical System Installation
Proper installation of the electrical system is a fundamental aspect of electrical safety. It involves hiring a licensed electrician to handle the installation process, ensuring that it complies with all local building codes and safety regulations. Improper installation can lead to faulty wiring, inadequate grounding, and increased fire risks. By entrusting the task to professionals, we can ensure that our electrical systems are safely and properly set up.
Read more: What Do Arc Fault Breakers Do
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to identify and address potential electrical hazards. It is recommended to schedule routine inspections by a qualified electrician who can assess the condition of the electrical system, identify any signs of wear or damage, and address them promptly. Timely maintenance and repairs can prevent issues from escalating into fire hazards, minimizing the risk of electrical fires.
Safe Electrical Usage Habits
Developing safe electrical usage habits is crucial in reducing the likelihood of accidents and fires:
- Avoid overloading electrical outlets and circuits by using power strips and extension cords responsibly. Distribute electrical loads properly and refrain from plugging multiple high-wattage appliances into a single outlet or circuit.
- Inspect electrical cords regularly for damage or fraying and replace them when necessary. Damaged cords can lead to short circuits, electrical shocks, and fires.
- Unplug appliances and devices when not in use to minimize the risk of electrical faults or accidental activation.
- Keep flammable materials away from electrical sources to prevent potential fires. This includes ensuring that curtains, furniture, and other combustible items are kept clear of baseboard heaters, electrical panels, and outlets.
Importance of Professional Help When Needed
It is crucial to recognize the importance of seeking professional help when dealing with any electrical issues or concerns:
- If you notice any signs of electrical problems such as flickering lights, frequently tripping circuit breakers, or burning smells, do not attempt to fix the issue yourself. Instead, contact a licensed electrician to diagnose and repair the problem.
- When planning home renovations or additions that involve electrical work, consult with an electrician to ensure that the electrical system can support the changes and meet safety requirements.
- Do not attempt to modify or tamper with the electrical system unless you have the necessary expertise. DIY electrical work can pose significant risks and may result in electrical shocks, fires, or even fatalities.
Professional assistance ensures that electrical issues are addressed correctly and safely, minimizing the potential for accidents or further damage.
By adhering to these electrical safety practices, we can create a safer living environment for ourselves and our families. Electrical safety is a collective responsibility that requires vigilance, awareness, and the willingness to prioritize safety above all else.
Conclusion
Electrical fires pose a significant threat to our homes and overall safety. As responsible homeowners, it is crucial to prioritize fire prevention and take proactive measures to protect our properties and loved ones. Fuses and circuit breakers play vital roles in preventing electrical fires by interrupting the flow of electricity during overloads or faults, effectively mitigating potential hazards.
Understanding the differences between fuses and circuit breakers allows us to make informed decisions based on our needs and budget. Fuses offer quick response times and affordability, while circuit breakers provide the convenience of resetability and long-term cost savings. Both options effectively protect against electrical fires, with circuit breakers offering enhanced safety features like ground fault and arc fault protection.
However, the effectiveness of these protective devices relies on proper electrical safety practices. Installing electrical systems correctly, conducting regular maintenance and inspections, and following safe usage habits are crucial in reducing the risks of electrical fires. By seeking professional help when needed and being proactive in addressing electrical issues, we can ensure the integrity and safety of our electrical systems.
In conclusion, electrical safety is a shared responsibility that requires our attention and diligence. By equipping ourselves with knowledge and implementing proper fire prevention measures, we can create a secure environment for our homes and loved ones. Let us prioritize electrical safety and work toward preventing electrical fires, reducing the risks, and safeguarding our homes for years to come.
Curious about other dangers lurking behind your electrical gadgets? Dive into our next discussion, where we unravel various types of fires ignited by electrical cords. This informative piece will shed light on common hazards and provide valuable safety tips to protect your residence and loved ones.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Do Fuses And Circuit Breakers Protect Your Home Against Electrical Fires?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “How Do Fuses And Circuit Breakers Protect Your Home Against Electrical Fires?”