

Articles
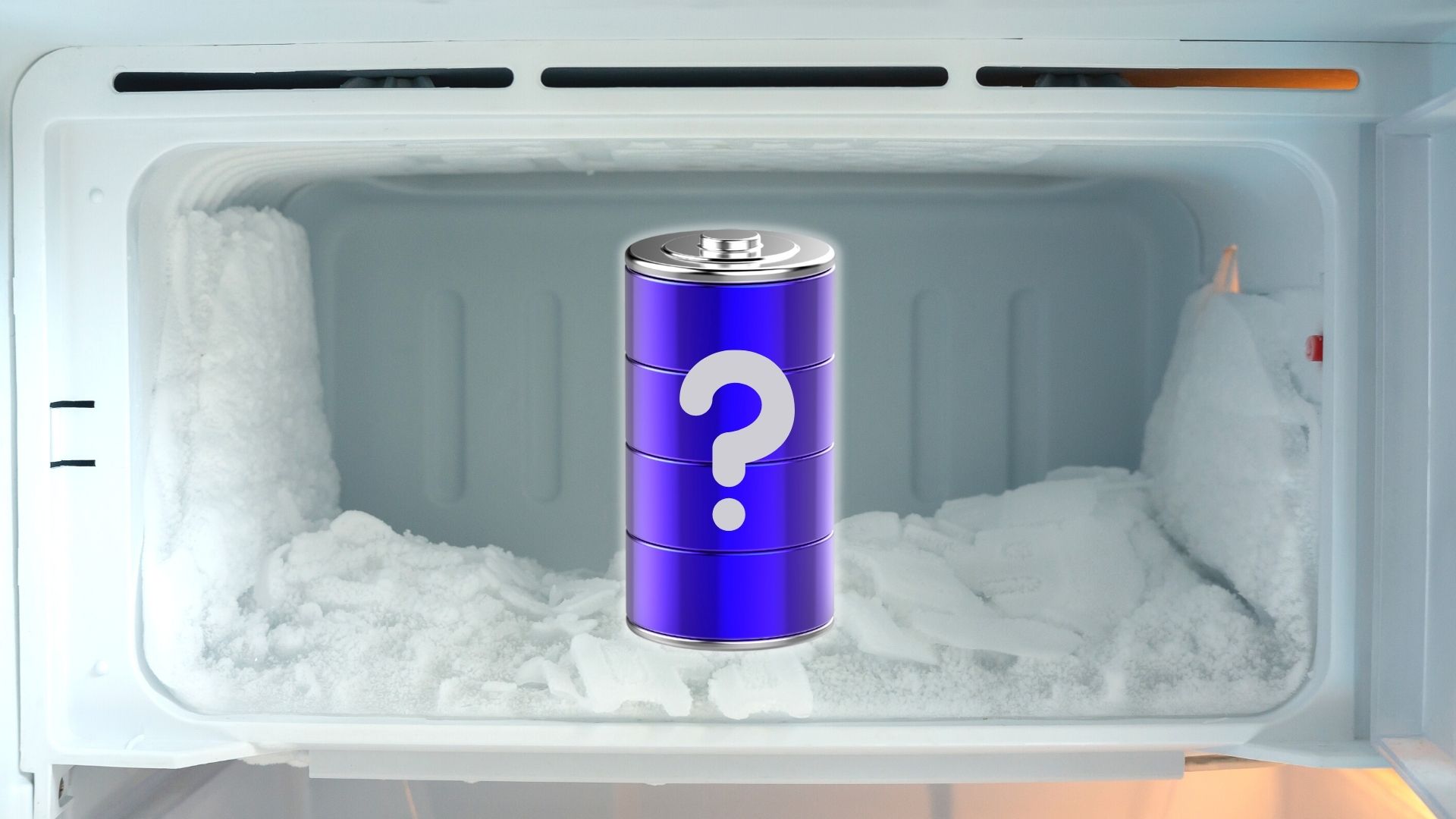
How To Recharge AA Batteries In Freezer
Modified: January 19, 2024
Learn how to recharge AA batteries in the freezer with these informative articles. Discover tips and tricks for maximizing battery life and saving money.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
AA batteries are a staple power source for a wide range of devices, from remote controls to flashlights. However, these batteries can lose their charge over time, resulting in the need for frequent replacements. Recharging AA batteries is not only an environmentally friendly option but also a cost-effective one. While there are various methods to recharge AA batteries, one unusual technique that has drawn attention is freezing them.
In this article, we will explore the concept of recharging AA batteries using a freezer. We will discuss the reasons why you may want to recharge your batteries, delve into the effectiveness of freezing as a recharging method, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to properly execute this process.
Key Takeaways:
- Recharging AA batteries in the freezer can be a cost-effective and eco-friendly option, but it should be approached with caution and used as a temporary measure. Regular battery maintenance, including proper charging and testing, is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
- Freezing AA batteries is not a guaranteed method for recharging, and results may vary. It is always advisable to use a dedicated battery charger for regular and reliable recharging. Experiment with freezing and recharging at your own discretion, considering the risks and potential outcomes.
Read more: How To Store Aa Batteries
Why Recharge AA Batteries?
Using rechargeable AA batteries offers several advantages over disposable batteries. Rechargeable batteries are more cost-effective in the long run, as they can be reused multiple times before needing replacement. This not only saves you money but also reduces the amount of waste going into landfills. Furthermore, recharging batteries is an environmentally friendly choice, as it reduces the need for constantly producing and disposing of single-use batteries.
Rechargeable AA batteries are also more convenient, as you can always have a set of fully charged batteries on hand whenever you need them. Whether you require batteries for a portable gaming device, a camera, a wireless mouse, or any other electronic device, having rechargeable batteries ensures that you won’t be caught without power at a crucial moment. Additionally, rechargeable batteries tend to have a higher capacity and longer lifespan than disposable batteries, providing reliable performance over an extended period.
Freezing Batteries: Will It Work?
The idea of using a freezer to recharge AA batteries might seem unconventional, but it is rooted in scientific principles. The concept is based on the theory that exposing batteries to cold temperatures can slow down the rate of self-discharge, which is one of the main reasons batteries lose their charge over time. By temporarily halting this self-discharge process, it is believed that the batteries can retain their charge for a longer period.
While freezing AA batteries may not work in all cases, it has been reported to be effective for some individuals. However, it is important to note that freezing batteries is not a guaranteed method for recharging them and should be approached with caution. Proper execution of the process is crucial to increase the chances of success. In the following sections, we will outline the steps to properly recharge AA batteries in the freezer.
Key Takeaways:
- Recharging AA batteries in the freezer can be a cost-effective and eco-friendly option, but it should be approached with caution and used as a temporary measure. Regular battery maintenance, including proper charging and testing, is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
- Freezing AA batteries is not a guaranteed method for recharging, and results may vary. It is always advisable to use a dedicated battery charger for regular and reliable recharging. Experiment with freezing and recharging at your own discretion, considering the risks and potential outcomes.
Read more: How To Store Aa Batteries
Why Recharge AA Batteries?
Using rechargeable AA batteries offers several advantages over disposable batteries. Rechargeable batteries are more cost-effective in the long run, as they can be reused multiple times before needing replacement. This not only saves you money but also reduces the amount of waste going into landfills.
Disposable AA batteries contribute to environmental pollution as they contain harmful chemicals that can seep into the earth when improperly disposed of. By opting for rechargeable batteries, you can help minimize the environmental impact and be more eco-conscious.
Rechargeable AA batteries are also more convenient, as you can always have a set of fully charged batteries on hand whenever you need them. Whether you require batteries for a portable gaming device, a camera, a wireless mouse, or any other electronic device, having rechargeable batteries ensures that you won’t be caught without power at a crucial moment.
Additionally, rechargeable batteries tend to have a higher capacity and longer lifespan than disposable batteries. This means that they provide reliable performance over an extended period. You won’t have to worry about your batteries dying in the middle of an important task.
Recharging AA batteries is a simple process that can be done with the help of a battery charger. You just need to connect the batteries to the charger and leave them to recharge. Once they are fully charged, you can use them again. This eliminates the need to continuously purchase disposable batteries, saving you both time and money in the long run.
Furthermore, some rechargeable batteries come with advanced features like rapid charging and low self-discharge rates. This means that they can be charged quickly and retain their charge for longer periods when not in use. This is especially useful in scenarios where you need to have backup batteries ready at all times.
Rechargeable AA batteries also offer a more stable power output compared to disposable batteries. This means that devices that require a consistent and reliable power source, such as cameras or audio recording equipment, will perform better with rechargeable batteries.
Overall, recharging AA batteries is a practical and cost-effective solution. By opting for rechargeable batteries, you can save money, reduce waste, and ensure that you always have reliable power for your electronic devices. So why not make the switch to rechargeable AA batteries today?
Freezing Batteries: Will It Work?
The idea of using a freezer to recharge AA batteries might seem unconventional, but it is rooted in scientific principles. The concept is based on the theory that exposing batteries to cold temperatures can slow down the rate of self-discharge, which is one of the main reasons batteries lose their charge over time. By temporarily halting this self-discharge process, it is believed that the batteries can retain their charge for a longer period.
While freezing AA batteries may not work in all cases, it has been reported to be effective for some individuals. However, it is important to note that freezing batteries is not a guaranteed method for recharging them and should be approached with caution.
The effectiveness of freezing batteries for recharging purposes depends on various factors, such as the battery chemistry and the level of discharge. Some types of batteries, like alkaline batteries, may not respond well to freezing and can even be damaged by the process. It is generally recommended to use rechargeable nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries for freezing experiments, as they tend to be more suitable for this method.
It is also worth noting that freezing batteries should not be considered a long-term solution for recharging. While it may provide a temporary boost in battery performance, it is not a substitute for proper charging methods using a battery charger. Regular charging using the appropriate equipment is still the most reliable and effective way to recharge batteries.
Proper execution of the freezing method is crucial to increase the chances of success. Here are a few steps to follow:
- Check Battery Condition: Before attempting to recharge batteries in the freezer, make sure they are in good condition. Inspect for any signs of leakage, corrosion, or damage. If the batteries are damaged, it is advisable not to freeze them.
- Prepare for Freezing: Remove the batteries from the device they are currently in and clean the contacts if necessary. Place the batteries in a sealed plastic bag to protect them from moisture during the freezing process. Label the bag with the date to keep track of the duration the batteries spend in the freezer.
- Properly Store Batteries in Freezer: Place the bag of batteries in the coldest part of the freezer, avoiding direct contact with frozen items. It is recommended to store them in a dedicated section or container to prevent them from getting lost or damaged.
- Monitor Freezing Duration: Ideally, freeze the batteries for 24 to 48 hours. Excessive freezing time can cause damage, so it is important not to extend the duration beyond the recommended period.
- Thaw Batteries: Once the freezing duration is complete, remove the batteries from the freezer and let them thaw naturally at room temperature. Avoid using any external heat source to speed up the process, as this can potentially damage the batteries.
- Recharge Batteries: After thawing, connect the batteries to a compatible battery charger and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for recharging. It is important to use a charger specifically designed for the type of batteries you are using.
- Test Recharged Batteries: Once the batteries are fully recharged, test their performance in the device they are intended for. Monitor their power output and overall functionality to assess the success of the recharging process.
Remember, freezing batteries should not be the go-to method for recharging. It is best reserved for specific situations where traditional charging methods are unavailable, and you are seeking a temporary boost in battery performance. Always prioritize proper battery management and charging practices to ensure the longevity and reliability of your batteries.
Read more: How To Store Aa And Aaa Batteries
Step 1: Check Battery Condition
Before attempting to recharge AA batteries in the freezer, it is important to check their condition. This step ensures that the batteries are suitable for the recharging process and minimizes the risk of potential damage.
Here are some key factors to consider when checking the battery condition:
- Physical Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the batteries for any signs of leakage, corrosion, or physical damage. If you notice any abnormalities, such as a swollen battery or a leaking battery, it is best not to proceed with the freezing and recharging process. Damaged batteries can pose a safety hazard and may not yield reliable results.
- Clean the Contacts: Battery contacts can accumulate dirt, dust, and residue over time, which can interfere with proper electrical connections. Use a clean cloth or an alcohol wipe to gently clean the battery contacts and the contacts in the device where the batteries will be inserted. Ensuring clean and well-maintained contacts will help maximize the efficiency of the rechargeable batteries.
- Battery Age: Consider the age of the batteries. Rechargeable batteries have a limited lifespan, and their performance may deteriorate over time. If the batteries are old and have been used extensively, they may not hold a charge effectively even after freezing and recharging. It is recommended to rotate and replace batteries periodically to maintain optimal performance.
- Compatibility: Verify that you are using the correct type of battery for the device you intend to power. Different devices have specific requirements, and using the wrong type of battery can result in poor performance or potential damage. Make sure the batteries you are planning to freeze and recharge are compatible with the device in question.
- Charge Remaining: Finally, check the remaining charge level of the batteries, if possible. Some battery chargers have indicators that display the current charge status. If the batteries are already partially charged, freezing may not provide significant benefits, and it may be more effective to use a regular charging method.
By thoroughly examining the condition of the batteries and ensuring they meet the necessary criteria, you can minimize the risk of unsuccessful freezing and recharging attempts. It is essential to prioritize safety and effectiveness when handling rechargeable batteries, as improper care can lead to performance issues or even damage to the batteries or the devices they power.
Once you have determined that the batteries are in good condition, you can proceed to the next step of preparing them for the freezing process.
Step 2: Prepare for Freezing
After checking the condition of the AA batteries, the next step is to properly prepare them for the freezing process. Taking the necessary precautions will help ensure the effectiveness of the recharging method and protect the batteries from potential damage.
Follow these steps to prepare the batteries for freezing:
- Remove Batteries: Start by removing the batteries from the device they are currently powering. It is important to disconnect the batteries from any electronics to prevent any potential electrical discharge or damage.
- Clean the Contacts: Inspect the battery contacts for any dirt, dust, or corrosion. If necessary, use a clean cloth or an alcohol wipe to gently clean the battery contacts. This step helps maintain optimal electrical connections during the freezing process.
- Protect from Moisture: Place the AA batteries in a sealed plastic bag to protect them from any moisture in the freezer. Moisture can affect the battery’s performance and potentially cause damage. Ensure the bag is tightly sealed to prevent any water or ice from coming into contact with the batteries.
- Label the Bag: Label the bag with the date of freezing. This allows you to keep track of how long the batteries have been in the freezer. It is important not to exceed the recommended freezing duration, as excessive freezing time can potentially harm the batteries.
By following these steps, you can ensure that the batteries are properly prepared for the freezing process. Properly cleaning the contacts and protecting the batteries from moisture increases the likelihood of a successful recharge. Additionally, labeling the bag with the freezing date helps you keep track of the freezing duration, ensuring that you don’t exceed the recommended time.
With the batteries prepared for freezing, you can proceed to the next step of storing them in the freezer. This controlled environment will temporarily halt the self-discharge process and potentially extend the battery life.
Storing AA batteries in the freezer can help extend their lifespan, but it’s not recommended to recharge them in the freezer. Instead, use a dedicated battery charger to safely recharge AA batteries.
Step 3: Properly Store Batteries in Freezer
Once you have prepared AA batteries for freezing, it is important to store them in the freezer properly. Proper storage ensures that the batteries are protected from damage and allows them to benefit from the controlled temperature environment.
Here are the steps to properly store batteries in the freezer:
- Choose the Right Spot: Select the coldest part of your freezer to store the batteries. This area typically maintains the most consistent and uniform temperature. Avoid placing the batteries near the freezer door or any areas where they may be exposed to frequent temperature fluctuations.
- Protect from Direct Contact: To prevent damage or potential leakage, do not place the batteries directly on frozen surfaces or in direct contact with other frozen items. It is advisable to use a small container or a dedicated section of the freezer to store the batteries. This helps protect them from being accidentally dislodged or damaged.
- Seal the Bag: Ensure that the plastic bag containing the batteries is tightly sealed. This prevents any moisture or liquid from entering the bag and potentially damaging the batteries. A properly sealed bag helps maintain the integrity of the batteries during the freezing process.
It is important to note that storing batteries in the freezer is a temporary measure and should not be a long-term solution. The freezing process is meant to slow down self-discharge and extend battery life temporarily. It is not a substitute for regular charging methods.
Remember to keep track of the freezing duration by labeling the bag with the date you placed the batteries in the freezer. This will help you monitor the time and make sure you do not exceed the recommended freezing period. Excessive freezing time can potentially harm the batteries and reduce their overall performance.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that the AA batteries are safely stored in the freezer, maximizing the chances of successful recharging. With the batteries securely stored, it’s important to monitor the freezing period and prepare for the next step: thawing the batteries.
Step 4: Monitor Freezing Duration
After properly storing AA batteries in the freezer, it is crucial to monitor the freezing duration to ensure optimal results. Monitoring the duration helps prevent over-freezing, which can potentially damage the batteries and diminish their performance.
Here’s how to effectively monitor the freezing duration:
- Set a Timer: Use a timer or an alarm to track the time the batteries spend in the freezer. Set the timer according to the recommended freezing duration, which is typically between 24 to 48 hours. Excessive freezing time can have negative effects on the batteries, so it is important not to go beyond the recommended timeframe.
- Don’t Disturb: Avoid frequently opening the freezer door during the freezing period. Opening the door too often can introduce warm air and cause temperature fluctuations, which may affect the freezing process. By minimizing disturbance, you can maintain a consistent temperature environment for the batteries.
- Refer to Label: If you labeled the plastic bag with the date of freezing, refer back to it to accurately track the duration. This ensures that you have an exact record of when the batteries were placed in the freezer and helps you avoid any potential miscalculations.
Monitoring the freezing duration is crucial to prevent excessive freezing, which can lead to potential damage to the batteries. If the batteries are frozen for too long, it may affect their performance and reduce their overall capacity.
Remember that the freezing process is intended as a temporary measure to slow down self-discharge and potentially extend battery life. It is not a substitute for regular charging methods using a battery charger.
Once the freezing duration has been completed, it’s time to move on to the next step: thawing the batteries in preparation for recharging.
Read more: How To Store Rechargeable Batteries
Step 5: Thaw Batteries
After the AA batteries have been frozen for the recommended duration, it’s time to thaw them before proceeding with the recharging process. Thawing the batteries helps bring them back to their normal temperature and prepares them for recharging.
Follow these steps to effectively thaw the batteries:
- Remove from Freezer: Carefully remove the bag containing the frozen batteries from the freezer. It’s important to handle them gently to avoid any potential damage or dislodging of the batteries.
- Allow Natural Thawing: Place the bag of frozen batteries in a cool and dry area at room temperature. Avoid using any external heat sources, such as a microwave or direct sunlight, as rapid thawing can cause thermal shock and damage the batteries. Let them thaw naturally.
- Wait for Thorough Thawing: Give the batteries sufficient time to thaw completely. The duration will depend on various factors, such as the ambient room temperature and the size of the batteries. It usually takes a few hours for the batteries to return to their normal temperature.
Thawing the batteries gradually helps prevent any potential damage that may occur due to sudden temperature changes. Allowing them to thaw naturally ensures a safe and controlled process.
It’s important to note that frozen batteries might accumulate condensation during the thawing process. To avoid any potential moisture damage, make sure to wipe down the batteries with a dry cloth before proceeding to the next step of recharging.
Once the batteries have thawed completely, they are ready to be recharged. Proper thawing ensures that the batteries are at the appropriate temperature for the recharging process, maximizing the chances of a successful recharge.
Step 6: Recharge Batteries
Now that the AA batteries have been thawed, it’s time to recharge them. Recharging is the essential step that replenishes the batteries’ energy and prepares them for future use. Follow these steps to effectively recharge the batteries:
- Choose the Right Charger: Select a battery charger that is compatible with the type of batteries you are using. Different battery types may require specific chargers to ensure safe and efficient charging. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or labels on the batteries to determine the appropriate charger.
- Insert Batteries into the Charger: Insert the thawed AA batteries into the charger, following the polarity markings (positive and negative) indicated on the charger and batteries. Ensure a secure and proper connection to facilitate effective charging.
- Connect to Power Source: Plug in the charger to a power source, such as an electrical outlet. Ensure that the power source is stable and reliable to support the charging process. Avoid using extension cords or power strips that may cause fluctuations in electricity supply.
- Follow Charging Instructions: Refer to the charger’s user manual or instructions for the recommended charging time and settings. Different chargers may have varying modes, such as fast charging or trickle charging. Select the appropriate mode based on the instructions to ensure safe and efficient charging.
- Monitor the Charging Process: Keep an eye on the charging progress, either through the charger’s indicator lights or the display panel. This allows you to track how much charge the batteries have accumulated and ensure they are being charged properly.
- Do Not Overcharge: Avoid overcharging the batteries, as this can lead to overheating and potential damage. Once the batteries have reached their full charge, disconnect them from the charger promptly. Overcharging may negatively impact the overall lifespan and performance of the batteries.
It is important to note that the charging time will vary depending on the charger and the battery capacity. Follow the recommended charging time provided by the manufacturer for optimal results.
By following these steps, you can effectively recharge the AA batteries and restore their energy for future use. Proper charging techniques ensure safe and efficient operation, prolonging the lifespan of the batteries.
Once the batteries are fully charged, it’s time to move on to the final step: testing the recharged batteries to ensure their functionality.
Step 7: Test Recharged Batteries
After recharging the AA batteries, it is essential to test them to ensure their functionality and determine if the recharging process was successful. Testing the batteries allows you to verify their performance and assess whether they can effectively power your devices. Follow these steps to test the recharged batteries:
- Prepare Test Devices: Gather the devices you intend to power with the recharged batteries. This can include flashlights, remote controls, portable game consoles, or any other device that uses AA batteries.
- Insert Recharged Batteries: Insert the recharged batteries into the respective battery compartments of the test devices. Ensure proper polarity alignment, following the symbols indicated inside the compartments.
- Power on the Devices: Turn on the test devices to verify if they are receiving power from the recharged batteries. Make sure the devices are functioning as expected and that the batteries are providing enough energy for their operation.
- Observe Performance: Pay attention to any signs of reduced performance or diminished battery life. Monitor the devices’ operation to detect any issues or inconsistencies. If the batteries discharge quickly or the devices exhibit abnormal behavior, it may indicate that the recharged batteries are not functioning optimally.
- Replace or Recharge: If the test devices do not function properly or the batteries quickly lose their charge, it may be necessary to replace the batteries or try recharging them again using a different method. In some cases, recharging in the freezer may not provide the desired results, and using a dedicated battery charger could yield better outcomes.
Testing the recharged batteries allows you to gauge their performance and determine if they are suitable for your devices. It helps identify any issues that may arise during operation and allows you to take appropriate measures, whether that be recharging again or selecting alternative batteries.
It’s worth noting that not all batteries can be successfully revived through recharging. Batteries that have reached the end of their lifespan or have suffered significant degradation may not hold a charge effectively, even after recharging. In such cases, it may be necessary to replace the batteries with new ones.
By following these steps and assessing the performance of the recharged batteries, you can determine their suitability for powering your devices. Regular testing and maintenance of batteries ensure reliable and efficient operation, extending their overall lifespan.
Congratulations! You have successfully completed the process of recharging AA batteries and testing their functionality. Remember to properly dispose of any used batteries and prioritize environmentally friendly practices when it comes to battery usage.
Precautions and Considerations
While recharging AA batteries in the freezer can be a potential method to extend their lifespan, it is important to take certain precautions and considerations to ensure the safety of the batteries and the effectiveness of the recharging process. Here are some important points to keep in mind:
- Battery Compatibility: Not all batteries are suitable for freezing and recharging. It is recommended to use rechargeable nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries for this method, as they tend to be more suitable for the process. Alkaline batteries, for example, may not respond well to freezing and can even be damaged by it. Always check the battery type and manufacturer’s recommendations before attempting to freeze and recharge.
- Check Battery Condition: Before freezing or recharging, carefully inspect the batteries for leakage, corrosion, or physical damage. Damaged batteries should not be frozen or used for recharging, as they can pose safety risks and may not hold a charge effectively.
- Freezing Duration: It is important to adhere to the recommended freezing duration, typically between 24 to 48 hours. Excessive freezing time can potentially harm the batteries and reduce their overall performance. Keep track of the freezing duration by labeling the bag containing the batteries with the date they were placed in the freezer.
- Thaw Naturally: Allow the batteries to thaw naturally at room temperature after removing them from the freezer. Avoid using external heat sources to speed up the thawing process, as rapid temperature changes can damage the batteries.
- Proper Charging: Use a charger that is designed for the specific type of batteries you are using. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging time and settings. Avoid overcharging the batteries, as it can cause overheating and reduce their overall lifespan.
- Test Recharged Batteries: Always test the recharged batteries before relying on them to power your devices. Ensure that they can provide the necessary energy and operate the devices effectively. Monitor the performance and consider replacing the batteries if they do not meet your expectations.
- Dispose of Batteries Properly: When batteries have reached the end of their lifespan and can no longer hold a charge effectively, it is important to dispose of them properly. Recycling centers and designated battery collection points can safely handle the disposal of used batteries and prevent environmental pollution.
Remember, freezing AA batteries is not a guaranteed method for recharging, and results may vary. It is always advisable to use a dedicated battery charger for regular and reliable recharging. Experiment with freezing and recharging at your own discretion, considering the risks and potential outcomes.
Lastly, if you are uncertain about the process or have concerns regarding battery safety, it is recommended to consult the battery manufacturer’s guidelines or seek professional advice.
By taking these precautions and considerations into account, you can maximize the potential benefits of freezing and recharging AA batteries while ensuring their safe and effective operation.
Conclusion
Recharging AA batteries in the freezer can be a unique and potentially effective method to extend their lifespan and reduce waste. While it is not a guaranteed solution, many individuals have reported success in reviving rechargeable nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries using this method.
By following the step-by-step process outlined in this article, you can properly prepare, freeze, thaw, and recharge AA batteries in a controlled manner. However, it is important to remember that freezing batteries is not a substitute for regular charging methods using a dedicated battery charger.
Before attempting to freeze and recharge batteries, always check their condition and compatibility. Damaged batteries should not be frozen or recharged, as they can pose safety risks and may not hold a charge effectively. It is recommended to use NiMH batteries for freezing and recharging experiments.
Monitor the freezing duration, thaw the batteries naturally, and recharge them using a compatible battery charger. Be mindful of the recommended charging time and avoid overcharging the batteries to prevent potential damage.
After recharging, test the batteries’ performance by using them in devices to assess their functionality and power output. Replace or recharge them again if necessary to ensure reliable operation.
Always adhere to proper disposal practices for used batteries. Recycling centers and designated collection points can safely handle the disposal of batteries and help minimize environmental impact.
In conclusion, freezing AA batteries to recharge them can be a cost-effective and eco-friendly option, but it should be approached with caution and used as a temporary measure. Regular battery maintenance, including proper charging and testing, is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
Remember to prioritize safety, manufacturer guidelines, and the suitability of the batteries for freezing and recharging. With the proper precautions and considerations, you can make informed decisions about recharging AA batteries and potentially extend their lifespan, saving money and reducing waste in the process.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Recharge AA Batteries In Freezer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “How To Recharge AA Batteries In Freezer”