

Articles
How To Recharge AC In Car R134A
Modified: February 26, 2024
Learn how to recharge your car's AC system with R134A refrigerant. Read our comprehensive articles on AC recharging techniques and troubleshooting tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In the scorching summer heat, a properly functioning air conditioning (AC) system in your car becomes a lifeline for a comfortable and enjoyable journey. However, over time, your car’s AC may start to lose its cooling power, leaving you sweating and uncomfortable on your travels. Luckily, recharging the AC in your car with R134A refrigerant is a straightforward process that can restore its cooling efficiency.
R134A is the most widely used refrigerant today due to its environmentally friendly properties and compatibility with modern AC systems. Recharging your car’s AC with R134A is a cost-effective solution that can save you from expensive trips to the mechanic.
In this article, we will guide you through the step-by-step process of recharging your car’s AC using R134A. We will also discuss the signs that indicate your AC needs recharging, safety precautions to follow, and troubleshooting common issues.
So, if you’re ready to take control of your car’s AC and beat the heat, let’s dive into the world of recharging your AC with R134A!
Key Takeaways:
- Recharging your car’s AC with R134A is a straightforward DIY process that can restore cooling efficiency, but it’s crucial to recognize signs like weak airflow and warm air to know when it’s time for a recharge.
- Prioritize safety by wearing protective gear, working in a well-ventilated area, and following safety precautions when recharging your car’s AC with R134A. Address common issues like leaking refrigerant and insufficient cooling promptly or seek professional assistance.
Read more: How To Read AC Gauges R134A
Understanding R134A
R134A, also known as Tetrafluoroethane, is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerant commonly used in car air conditioning systems. It replaced the previously used R12 refrigerant, which was found to have detrimental effects on the ozone layer. R134A is non-toxic, non-flammable, and environmentally friendly, making it the preferred choice for automotive AC systems.
One of the main properties of R134A is its ability to absorb heat from the surrounding air and transfer it outside the car. It operates under high pressure and temperature conditions, enabling efficient cooling of the air passing through the AC system. R134A has a low boiling point, which allows it to easily evaporate and absorb heat from the car’s interior, providing a cool and comfortable atmosphere.
It’s important to note that R134A is not compatible with AC systems designed for R12 refrigerant. If your car’s AC system still uses R12, it will need to be converted to R134A before recharging can occur. This conversion involves replacing various components, such as the compressor and condenser, to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
You can identify whether your car’s AC system uses R134A or R12 by checking the label under the hood. The label will indicate the type of refrigerant specified for your vehicle. If it mentions R134A, you’re good to go.
Now that we have a basic understanding of R134A and its role in car air conditioning, let’s move on to identifying the signs that indicate your car’s AC needs recharging.
Signs that Your Car’s AC Needs Recharging
As the summer heat intensifies, your car’s AC system works overtime to keep you cool and comfortable on the road. However, over time, the refrigerant levels in the system can deplete, affecting its cooling efficiency. It’s important to recognize the signs that indicate your car’s AC needs recharging. Here are some telltale signs:
- Weak Airflow: If you notice a significant decrease in the amount of cool air coming out of your car’s vents, it could be a sign that the refrigerant levels are low. Insufficient refrigerant can hinder the system’s ability to cool the air properly.
- Warm Air: When your car’s AC is running, but the air coming out of the vents is warm or not as cold as it used to be, it’s a clear indication that the refrigerant needs to be recharged. The lack of cold air can be caused by low refrigerant levels or a leak in the system.
- Strange Noises: Unusual noises, such as hissing or banging sounds, coming from your car’s AC system can signal a refrigerant leak. Leaks not only lead to a decrease in cooling performance but can also damage the compressor if left unaddressed.
- Foul Odors: If your car’s AC emits unpleasant odors, it could indicate the growth of mold or bacteria in the system. Low refrigerant levels can lead to moisture buildup, creating an environment conducive to the growth of these microorganisms.
- Condensation: Excessive condensation or water pooling on the dashboard or floor of your car could be an indication of AC problems. Low refrigerant levels can cause the evaporator coil to freeze and then thaw, leading to water leakage.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to take action and recharge your car’s AC system with R134A. Ignoring these signs can not only result in discomfort during your rides but may also cause further damage to the AC components.
Now that we know the signs that indicate your car’s AC needs recharging, let’s move on to the preparation process for recharging.
Preparing for Recharging
Before diving into the process of recharging your car’s AC with R134A, it’s essential to properly prepare for the task. Taking the time to gather the necessary tools and ensuring a safe working environment will contribute to a smooth and successful recharge. Here’s what you need to do to prepare:
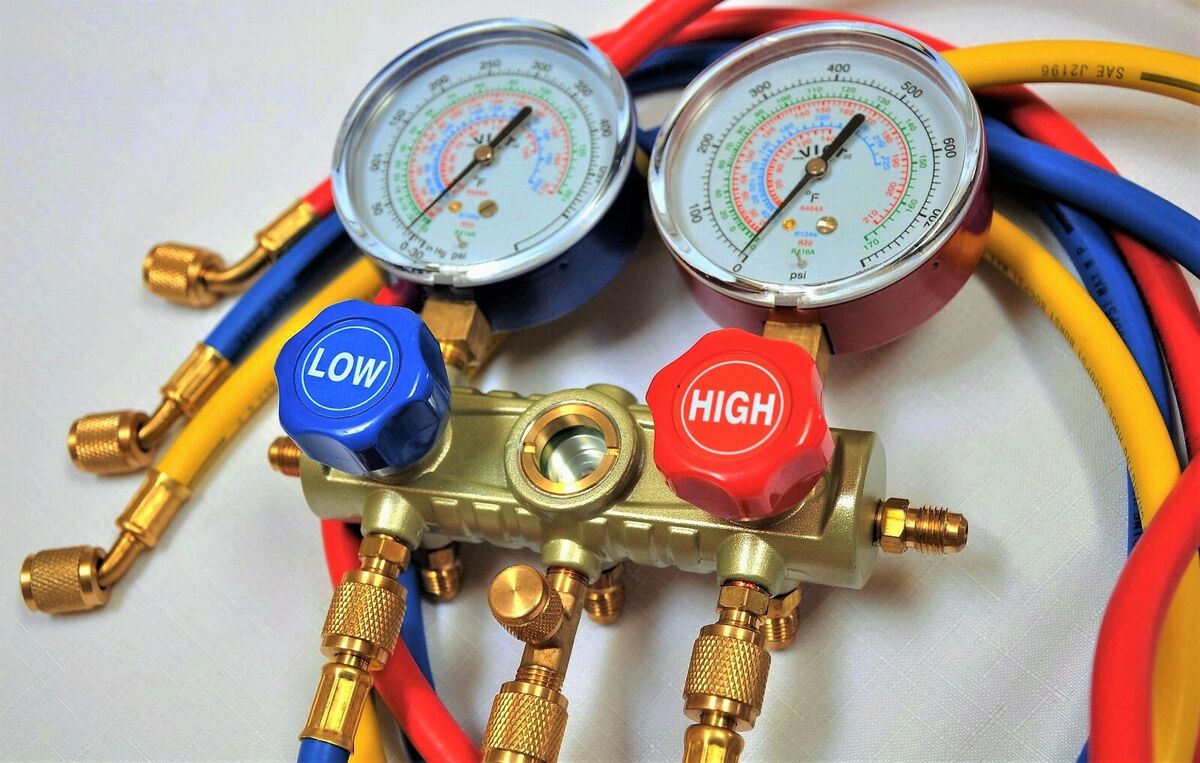
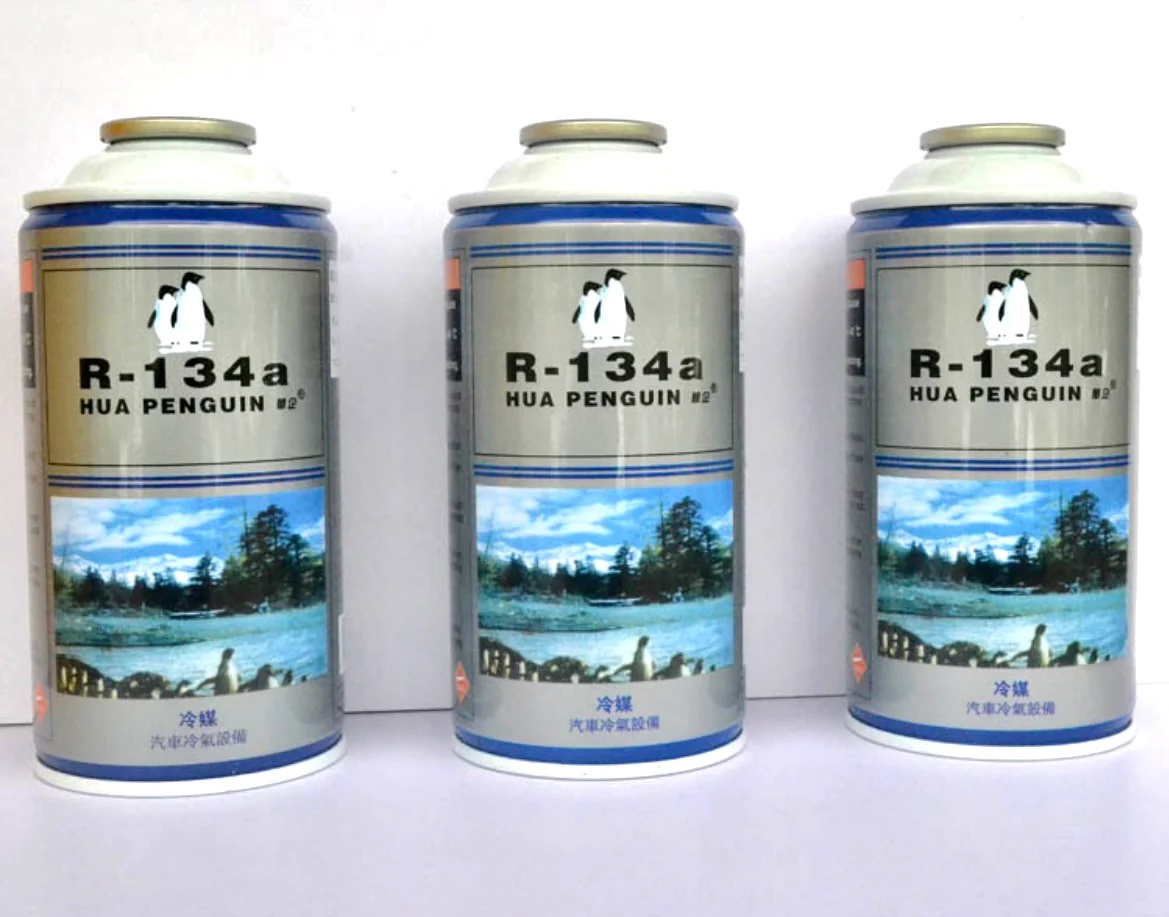
- Gather the Tools: You will need a few tools and equipment to recharge your car’s AC. This includes an R134A refrigerant can with a gauge, AC manifold gauge set, safety goggles, gloves, and a thermometer.
- Choose the Right Refrigerant: It is crucial to use the correct refrigerant for your car’s AC system. Check the owner’s manual or consult a professional to ensure you are using R134A, the appropriate refrigerant for most modern cars.
- Locate the Low-Pressure Port: Familiarize yourself with the location of the low-pressure port in your car’s AC system. This port is usually located near the AC compressor and is marked with an “L” or labeled as the low-pressure side.
- Inspect for Leaks: Before recharging, inspect the AC system for any visible signs of leaks. Look for oil stains, wet spots, or damaged AC components. If you detect a leak, it’s best to have it repaired before proceeding with the recharge.
- Ensure Safety: Recharging your car’s AC involves handling refrigerants and working with high-pressure systems. Wear gloves and safety goggles to protect your hands and eyes. Additionally, ensure that you are working in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling the refrigerant.
- Check the Ambient Temperature: It’s important to recharge your AC on a moderately warm day. Extreme temperatures can affect the accuracy of the pressure readings and potentially hinder the recharge process.
By following these preparation steps, you can ensure a safe and efficient recharging process. Now that you’re ready, let’s move on to the step-by-step procedure for recharging your car’s AC with R134A.
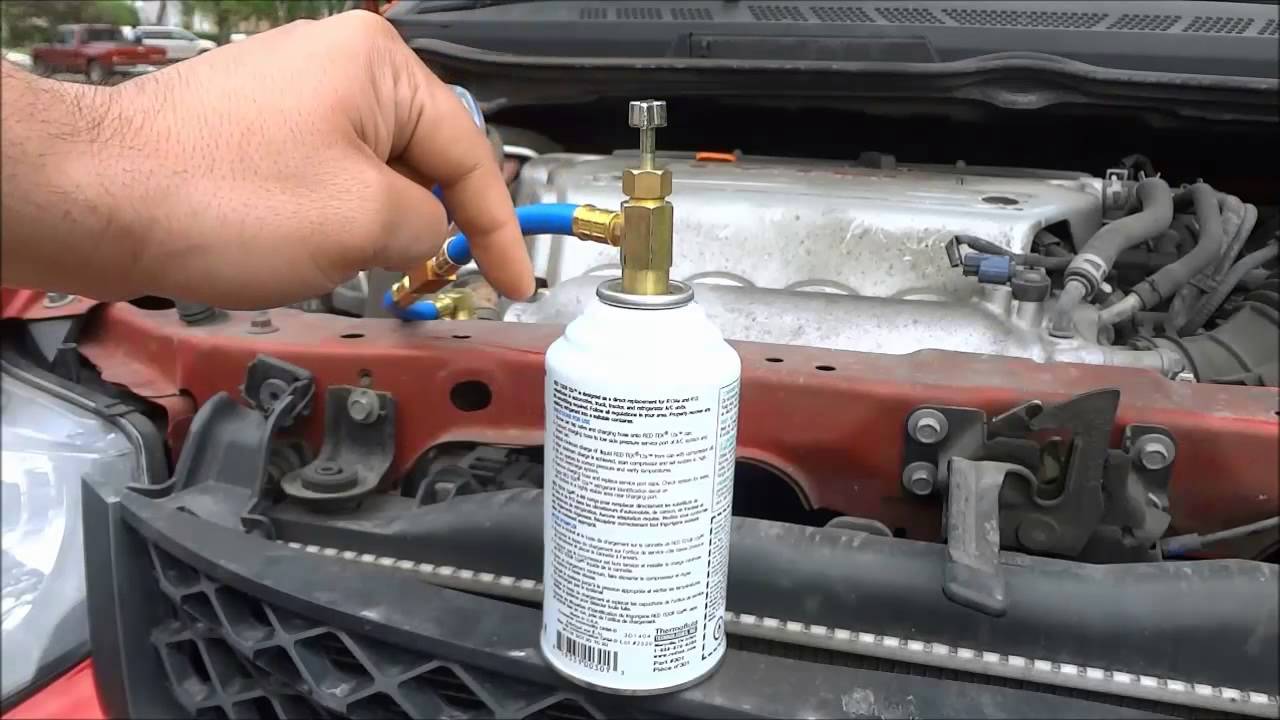
When recharging the AC in your car with R134A, make sure to wear gloves and safety goggles to protect yourself from the refrigerant. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use a pressure gauge to ensure you don’t overfill the system.
Steps to Recharge AC in Car with R134A
Recharging your car’s AC system with R134A refrigerant is a straightforward process that can be done at home with the right tools and precautions. Follow these step-by-step instructions to successfully recharge your car’s AC:
- Prepare the Environment: Park your car in a well-ventilated area and engage the parking brake. Make sure the engine is turned off before starting the process.
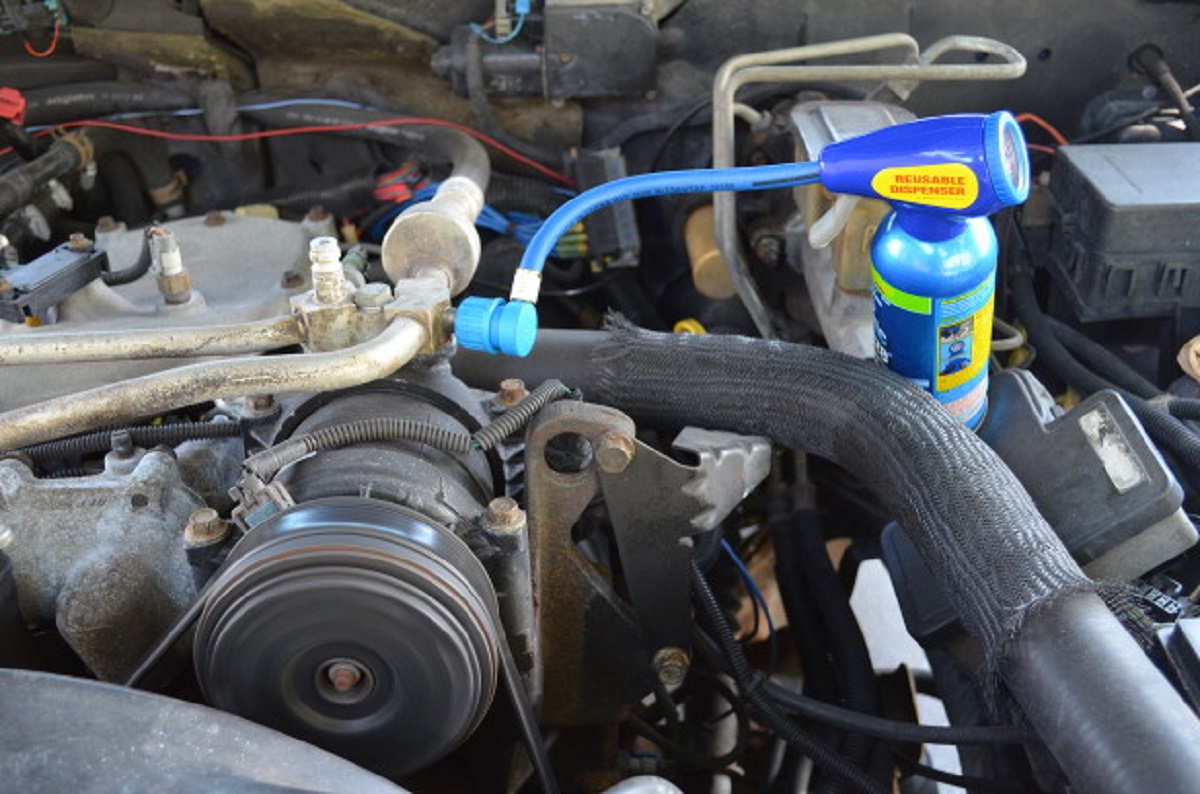
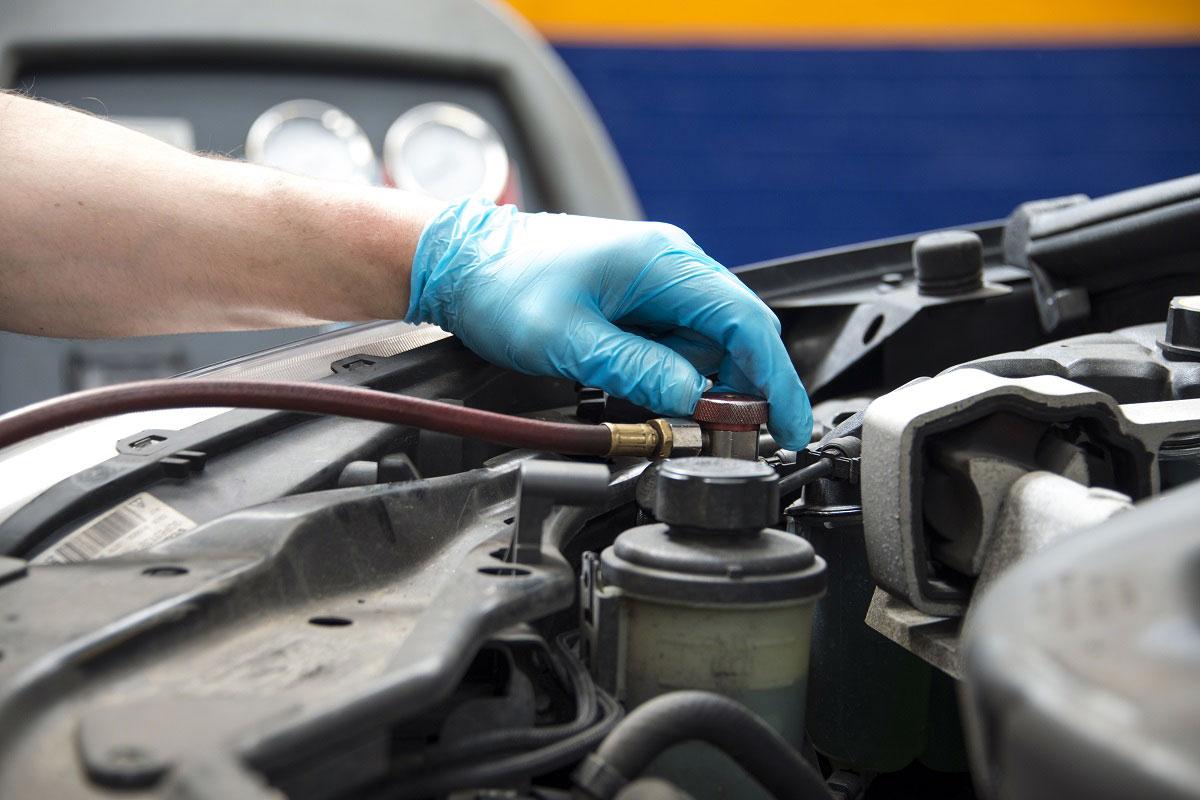
- Locate the Low-Pressure Port: Open the hood of your car and locate the low-pressure port. The port is usually situated near the AC compressor and is marked with an “L” or labeled as the low-pressure side.
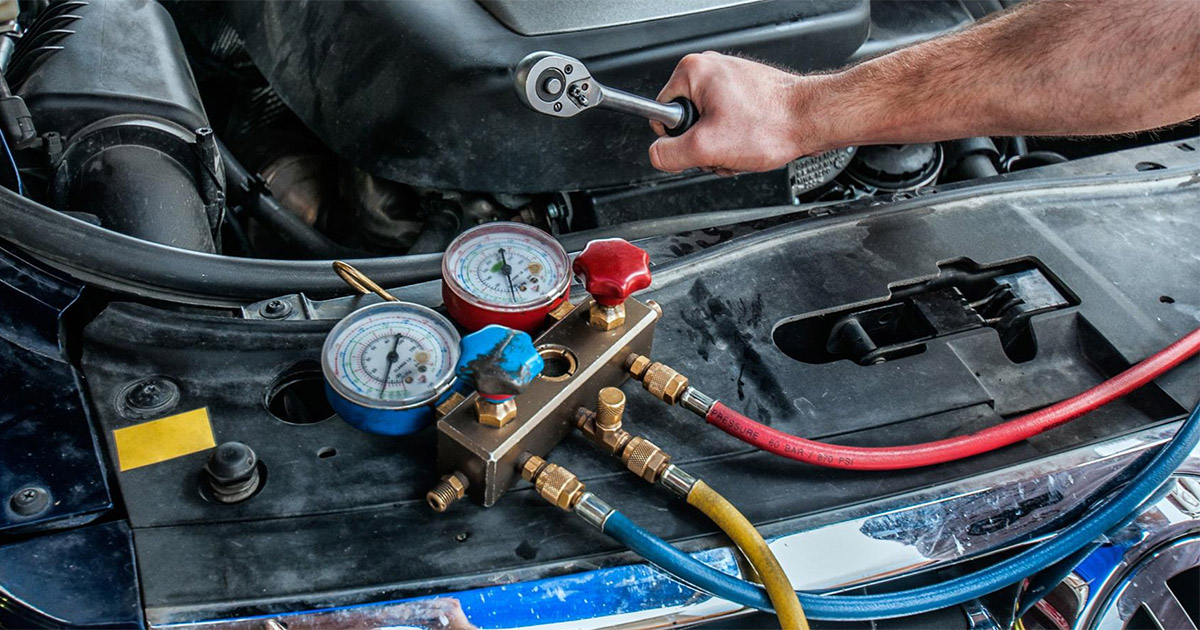
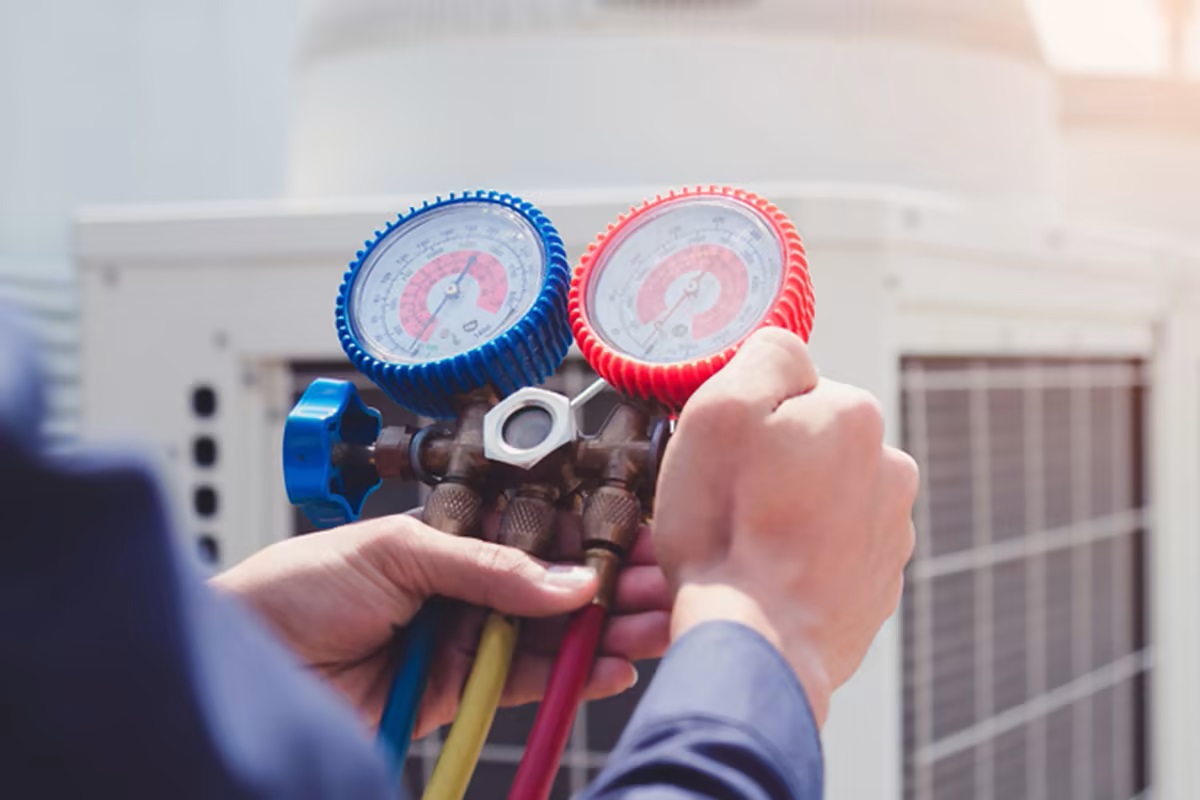
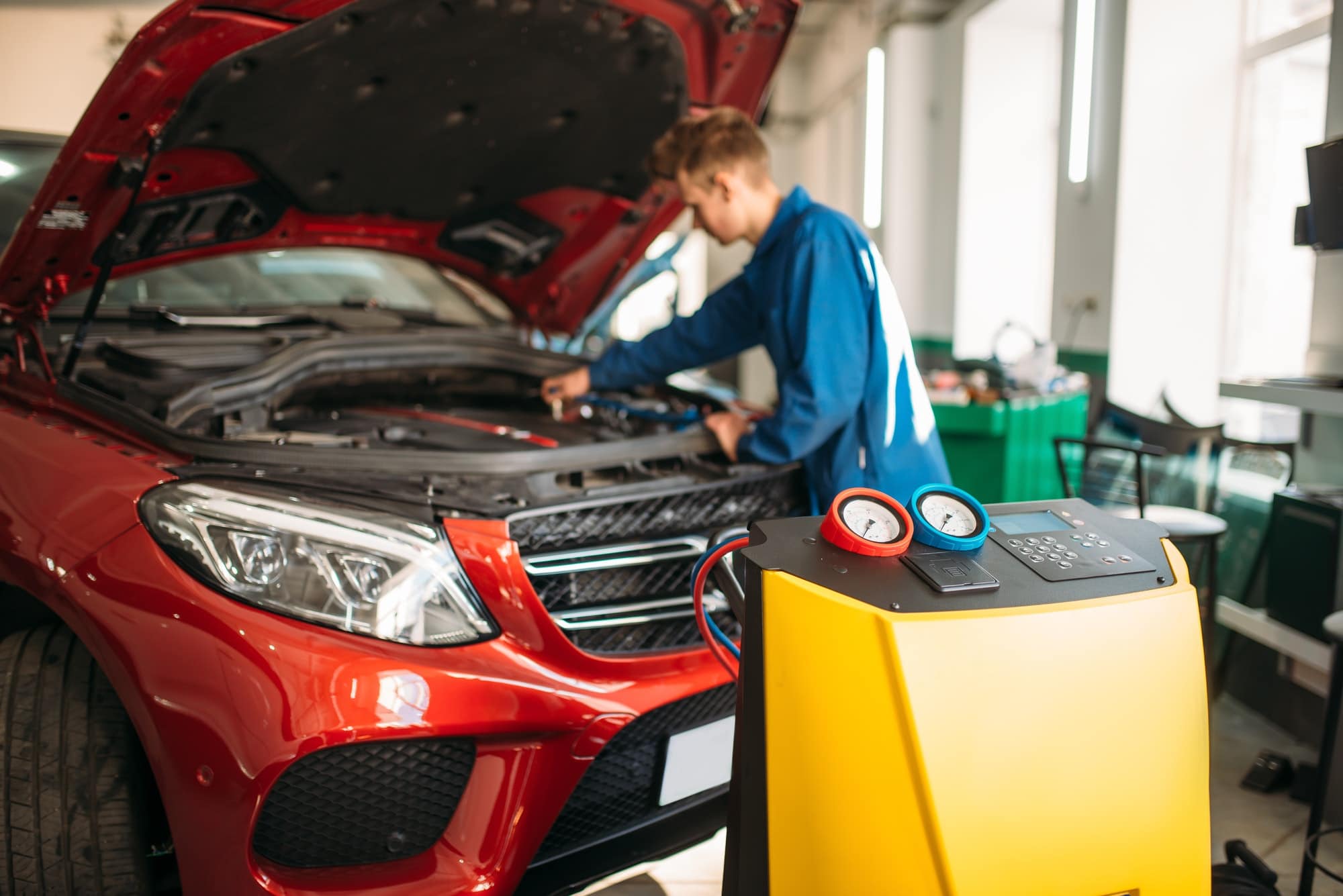
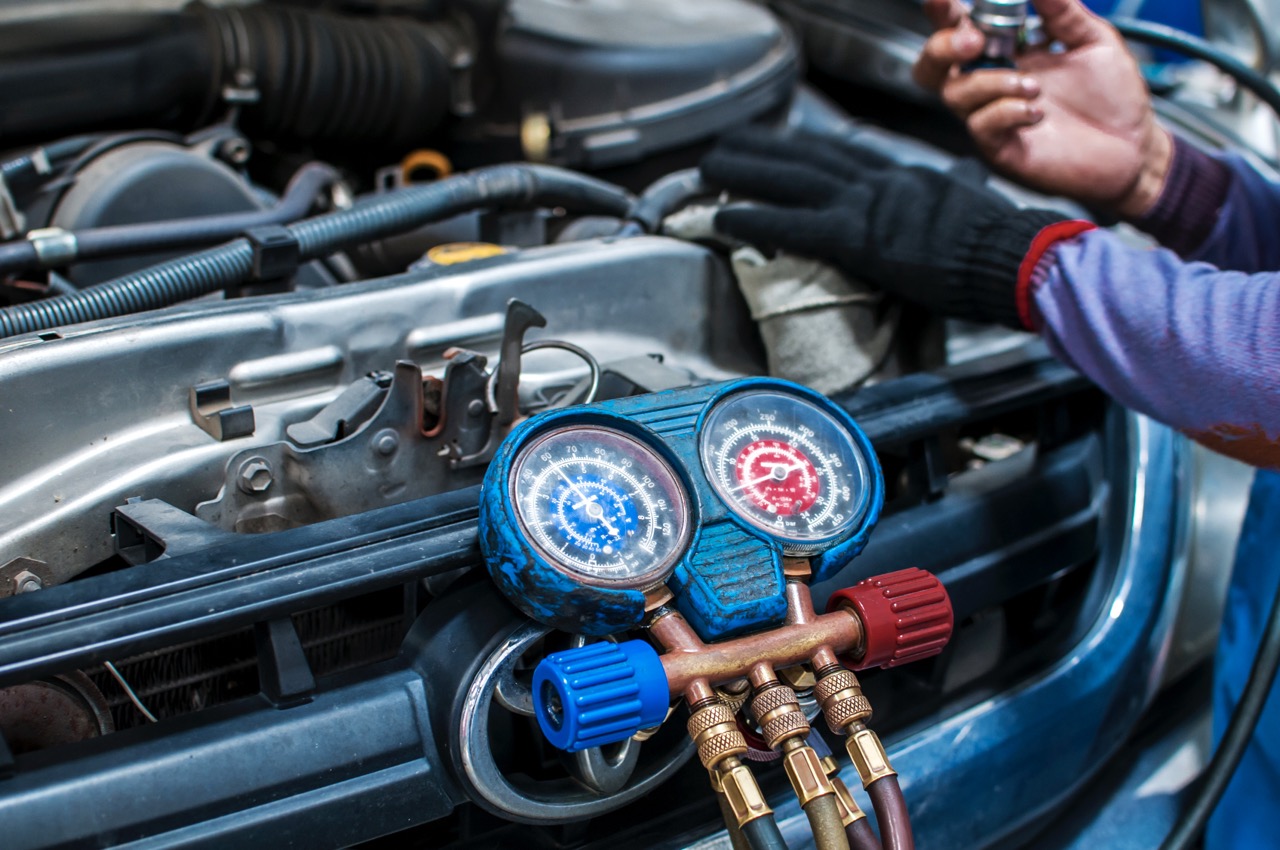
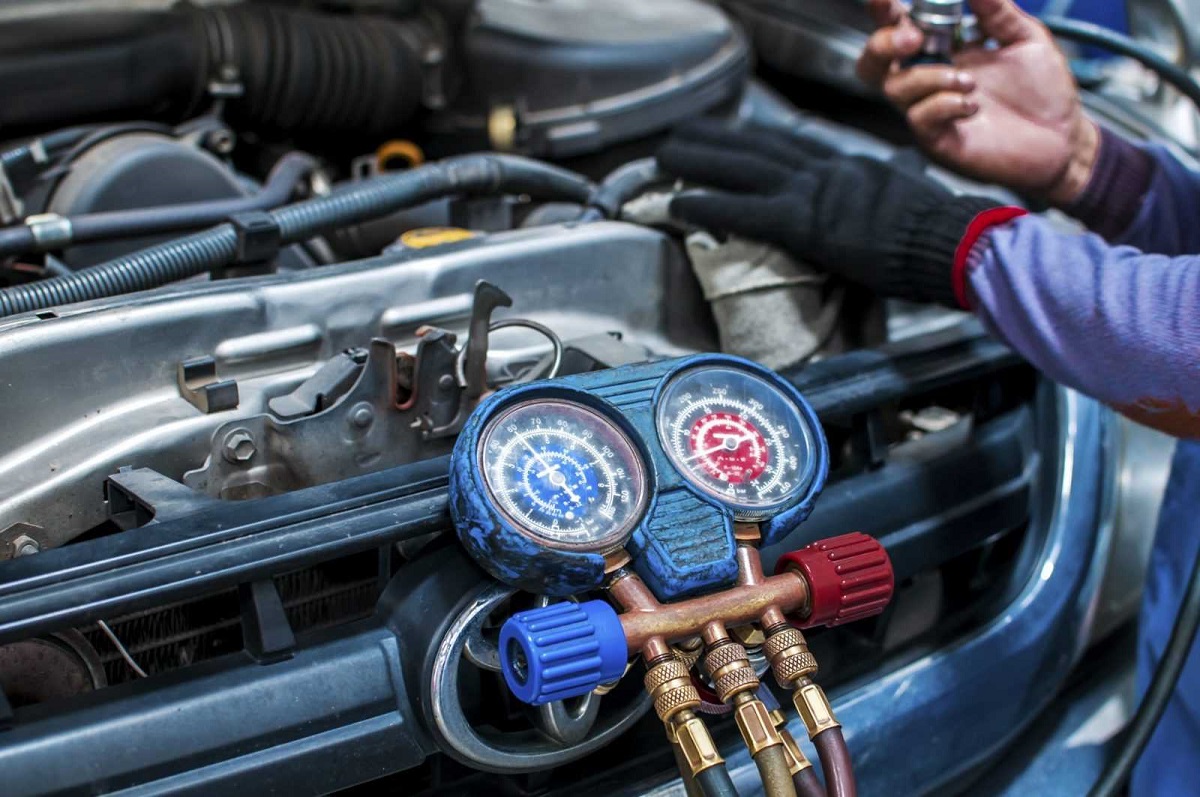
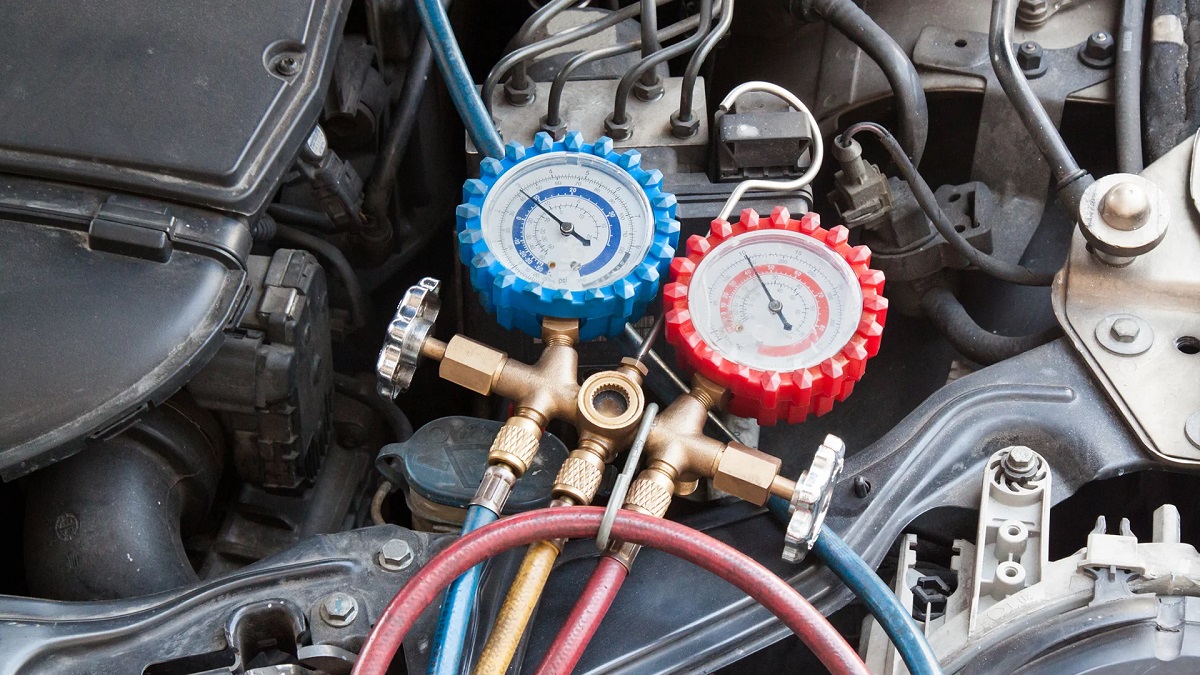
- Screw on the AC Manifold Gauge Set: Attach the AC manifold gauge set to the low-pressure port. Ensure a secure connection by twisting it clockwise until it is firmly in place.
- Check the Gauge Readings: With the gauge set connected, check the readings on the manifold gauge. The low-pressure side gauge will display the pressure in the AC system.
- Prepare the Refrigerant Can: Shake the R134A refrigerant can vigorously to ensure its proper mixing. Attach the refrigerant can to the gauge set and screw it in clockwise until it is tightly connected.
- Begin Recharging: Start the engine and turn on the AC at its highest setting. Open the valve on the refrigerant can by turning it counterclockwise. This will allow the refrigerant to flow into the AC system.
- Monitor the Gauge Readings: As the refrigerant flows into the system, keep an eye on the gauge readings. The pressure should rise steadily, indicating that the refrigerant is being transferred effectively.
- Stop Recharging: Once the desired pressure is reached or the refrigerant can is empty, close the valve on the can by turning it clockwise. This will stop the flow of refrigerant into the system.
- Disconnect the Gauge Set: With the recharge process complete, disconnect the AC manifold gauge set from the low-pressure port. Close the hood of your car.
- Check the AC Performance: Start the car’s engine and test the AC system’s performance. Feel the air coming out of the vents to ensure that it is cold and refreshing.
It is important to note that each car’s AC system may have slight variations in the specific steps and instructions. Therefore, always refer to your car’s owner’s manual or seek guidance from a professional if you encounter any difficulties during the recharge process.
Congratulations! You have successfully recharged your car’s AC with R134A. However, it’s crucial to prioritize safety and remain cautious throughout the process. Let’s take a look at some safety precautions to keep in mind while recharging the AC in your car.
Safety Precautions
When recharging the AC in your car with R134A refrigerant, it is important to prioritize safety to avoid any potential risks or accidents. Here are some key safety precautions to follow:
- Protective Gear: Wear safety goggles and gloves to protect your eyes and hands from exposure to refrigerant and potential leaks.
- Well-Ventilated Area: Work in a well-ventilated area as R134A, although less harmful than previous refrigerants, can still be harmful if inhaled in large quantities.
- Engine Off: Always ensure that the engine is turned off before starting the recharge process. This prevents any accidents that could occur from moving parts.
- Pressure Gauge Safety: Monitor the pressure gauge readings closely. If the pressure becomes too high, it could indicate an issue with the AC system, and you should stop the recharge process.
- No Smoking: Do not smoke or use open flames during the recharge process, as R134A is flammable, and it can be dangerous to have open flames near the refrigerant.
- Refrigerant Storage: Store any unused refrigerant in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Follow local regulations and dispose of any empty refrigerant cans properly.
- Professional Assistance: If you’re unsure about the recharge process or encounter any difficulties, it’s always recommended to seek assistance from a professional mechanic or AC technician.
By following these safety precautions, you can ensure a safe and hassle-free recharge process. It’s important to prioritize your well-being and the well-being of those around you during any DIY maintenance tasks.
Now that we have covered the safety precautions, let’s discuss some common issues that you may encounter during the AC recharge process and how to troubleshoot them.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While recharging the AC in your car with R134A is generally a straightforward process, you may encounter some common issues along the way. Here are a few troubleshooting tips to help you address these issues:
- No Change in Cooling: If you have completed the recharge process but there is no noticeable change in cooling, it’s possible that the issue lies beyond low refrigerant levels. Check for other potential problems such as a faulty compressor, clogged condenser, or damaged AC components. It’s recommended to consult a professional if you cannot identify the exact cause.
- Leaking Refrigerant: If you notice refrigerant leaking from the AC system, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly. Check for visible signs of leaks such as oil stains, wet spots, or damaged components. Have the leaks repaired before attempting to recharge the AC to avoid wasting refrigerant and potential damage to the environment.
- Inaccurate Pressure Readings: If you suspect that the pressure gauge readings are inaccurate, double-check that the gauge set is securely connected to the low-pressure port. Also, ensure that the engine is off and the AC system is not running during the pressure readings for accurate results.
- Insufficient Cooling: If you notice that the AC is still not cooling sufficiently after recharging, it could indicate an issue with the AC system itself. Check for signs of reduced airflow, a malfunctioning compressor, or a clogged air filter. It may be necessary to seek professional assistance to diagnose and address the problem.
- Unusual Noises: If you hear strange noises from the AC system after recharging, it could indicate an issue such as a loose component or a damaged compressor. It’s best to consult a professional to identify and resolve the problem before it causes further damage to the AC system.
Remember, if you encounter any difficulties or are unsure about troubleshooting the issues yourself, it’s always recommended to seek assistance from a professional mechanic or AC technician. They have the expertise and knowledge to diagnose and resolve complex AC problems.
Now that we have discussed the common issues and troubleshooting tips, let’s wrap up this article.
Conclusion
Recharging the AC in your car with R134A refrigerant is a simple and cost-effective way to restore your AC system’s cooling efficiency. By following the step-by-step process and taking the necessary precautions, you can enjoy a cool and comfortable driving experience even in the hottest summer months.
Understanding the signs that indicate your car’s AC needs recharging is essential to address any issues promptly. Weak airflow, warm air, strange noises, foul odors, and condensation are all signs that it’s time to recharge your AC system with R134A.
Before starting the recharge process, make sure you gather the required tools, choose the correct refrigerant (R134A), and locate the low-pressure port in your car’s AC system. Additionally, prioritize safety by wearing protective gear, working in a well-ventilated area, and ensuring the engine is off.
The step-by-step process of recharging involves connecting the AC manifold gauge set, checking gauge readings, preparing the refrigerant can, and recharging the system while monitoring the pressure. Once complete, disconnect the gauge set, start the car’s engine, and test the AC system’s performance.
Remember to always prioritize safety, follow safety precautions, and seek professional assistance when necessary. Keep an eye out for common issues such as no change in cooling, leaking refrigerant, inaccurate pressure readings, insufficient cooling, or unusual noises. Address these issues promptly or consult a professional to ensure proper functionality of your car’s AC system.
Recharging your car’s AC with R134A can save you from discomfort and expensive trips to the mechanic. However, if you’re not confident in your abilities, it’s always recommended to consult a professional to perform the recharge and address any underlying issues.
Enjoy a refreshing journey on the road with a fully functioning AC system in your car. Stay cool, stay safe, and beat the heat with a properly recharged AC system using R134A!
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Recharge AC In Car R134A
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How To Recharge AC In Car R134A”