

Articles
How To Store Stem Cells
Modified: March 1, 2024
Discover the latest articles on how to store stem cells. Explore best practices, techniques, and preservation methods for optimal cell viability and future medical applications.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of stem cells, where the possibilities for medical advancements seem endless. Stem cells have the remarkable ability to transform into various types of cells in the body, making them a valuable resource for regenerative medicine. As our understanding of stem cells and their potential grows, so does the interest in storing and preserving these precious cells for future use.
In this article, we will explore the concept of stem cell storage, why it is important, and the different types of stem cell storage available. We will also discuss the process of storing stem cells and offer tips on how to choose a reputable stem cell storage facility. So, let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of storing stem cells!
Note: It’s important to consult with medical professionals or specialized companies for personalized advice on stem cell storage.
Key Takeaways:
- Storing stem cells opens the door to personalized medicine, potential future therapies, and family health support. It’s a proactive investment in health, offering peace of mind and hope for the future.
- Choosing a reputable stem cell storage facility is crucial. Accreditation, expertise, and transparency are key factors to consider when securing the long-term preservation of valuable stem cells.
What are Stem Cells
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the remarkable ability to develop into specialized cells with specific functions in the body. They can divide and reproduce themselves, replenishing the body’s supply of cells throughout life. This unique characteristic allows stem cells to play a crucial role in the growth, repair, and regeneration of tissues and organs.
There are two primary types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of a developing embryo and have the potential to differentiate into any type of cell in the body. Adult stem cells, on the other hand, are found in various tissues and organs in the body, such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, and dental pulp. They have a more limited differentiation capacity, typically giving rise to cells specific to the tissue they reside in.
Stem cells can be further classified based on their potency or developmental potential. Totipotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell, including both embryonic and extra-embryonic tissues. Pluripotent stem cells can differentiate into almost any cell type, but not into the extra-embryonic tissues. Multipotent stem cells can differentiate into a limited range of cell types within a specific tissue or organ.
Understanding the unique characteristics and classification of stem cells is crucial for their successful storage and potential future use in regenerative medicine. Harnessing the power of stem cells holds great promise for the treatment and cure of numerous diseases and injuries, making stem cell storage a valuable investment for individuals and families.
Importance of Storing Stem Cells
The importance of storing stem cells cannot be overstated. Stem cells have the potential to revolutionize medicine by providing new treatments and therapies for a wide range of diseases and conditions. Here are some key reasons why storing stem cells is crucial:
1. Future Therapeutic Potential: Stem cells have the unique ability to develop into different types of cells in the body. This versatility opens up countless possibilities for their use in regenerative medicine. Stored stem cells can be utilized in the future to treat conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, and even certain types of cancer. Storing stem cells now ensures that you have a valuable resource readily available for potential future treatments.
2. Personalized Medicine: Storing your own stem cells allows for personalized medicine. These cells are a perfect genetic match for you, minimizing the risk of rejection or complications associated with using cells from an unrelated donor. It provides a unique opportunity for personalized therapies tailored specifically to your individual needs and genetic makeup.
3. Family Health Support: Stem cell storage also benefits your immediate family members. Siblings and parents may have a higher chance of being a compatible match for a stem cell transplant, should the need arise. By storing stem cells, you are not only protecting your own health but also potentially saving the lives of your family members in the future.
4. Insurance Against Age-Related Diseases: As we age, the risk of developing age-related diseases increases. Storing stem cells from a younger age can provide a valuable resource if you are diagnosed with a condition later in life. Having access to your younger and healthier stem cells may improve the success of future treatments and therapies.
5. Research Advancements: By storing stem cells, you contribute to the progress of scientific research and medical advancements. Stem cell research is an ever-evolving field, and the availability of stored stem cells enables researchers to study and explore new treatment options and potential breakthroughs that can benefit society as a whole.
Storing stem cells is an investment in your future health and the health of your loved ones, providing a safety net against unforeseen medical challenges. It is a proactive approach that offers peace of mind, knowing that you have taken a step towards accessing potentially life-saving treatments and groundbreaking therapies.
Types of Stem Cell Storage
There are various types of stem cell storage available, each designed to cater to different sources of stem cells and specific storage needs. Let’s explore the different options:
1. Umbilical Cord Blood Banking: One of the most well-known and widely available types of stem cell storage is umbilical cord blood banking. After a baby is born, blood is collected from the umbilical cord and the placenta, which contains a rich source of stem cells. This blood is then processed, tested, and cryogenically frozen for long-term storage. Umbilical cord blood banking provides a valuable source of stem cells that can be used for various medical treatments in the future.
2. Dental Stem Cell Banking: Dental stem cell banking involves storing stem cells extracted from dental pulp found in the teeth. Teeth, particularly baby teeth or wisdom teeth, contain a specific type of stem cell called dental pulp stem cells. These cells have the potential to differentiate into various types of cells, such as bone cells and nerve cells. Dental stem cell banking offers an opportunity to bank on the regenerative potential of stem cells derived from dental sources.
3. Adipose Tissue Stem Cell Banking: Adipose tissue (fat) is another source of adult stem cells. These stem cells can be obtained through a minimally invasive procedure known as liposuction. Adipose tissue stem cell banking involves isolating and storing these cells for future use. The advantage of adipose tissue stem cell banking is the abundance of stem cells in fat tissue, making it a rich and easily accessible source for potential applications in regenerative medicine.
4. Bone Marrow Stem Cell Banking: Bone marrow is a key source of adult stem cells and has been used in medical treatments for many years. The procedure involves extracting stem cells from the bone marrow, usually from the hip or sternum, under anesthesia. These stem cells are then stored for potential future use. Bone marrow stem cell banking is often chosen by individuals who are already undergoing bone marrow procedures, such as transplantation or therapy, as it allows for the preservation of additional stem cells for potential further treatments.
These are just a few examples of the types of stem cell storage available. It’s important to research and consult with a specialized stem cell storage facility to understand the options that best suit your specific needs. Whether it’s cord blood banking, dental stem cell banking, adipose tissue stem cell banking, or bone marrow stem cell banking, each type offers unique advantages and potential applications in the field of regenerative medicine.
Umbilical Cord Blood Banking
Umbilical cord blood banking is a type of stem cell storage that involves the collection and preservation of the blood from the umbilical cord and placenta immediately after childbirth. This blood is a rich source of valuable stem cells, known as hematopoietic stem cells, which have the ability to develop into various types of blood cells.
The process of umbilical cord blood banking begins with the expectant parents making the decision to store their baby’s cord blood. Prior to delivery, they must choose a reputable cord blood bank that offers storage services. On the day of birth, the umbilical cord is clamped and cut, and a trained healthcare professional collects the blood from the cord using a sterile collection kit.
Once the blood is collected, it is transported to the cord blood bank where it undergoes a series of rigorous testing procedures to ensure its viability and safety for long-term storage. The blood is processed to separate and isolate the stem cells from other components, such as red blood cells and plasma. The isolated stem cells are then cryogenically frozen and stored at extremely low temperatures to preserve their viability.
Umbilical cord blood banking offers several advantages:
1. Unique Source of Stem Cells: Cord blood contains a rich supply of hematopoietic stem cells, which are capable of developing into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These stem cells can be used to treat a variety of blood disorders, immune system disorders, and certain cancers.
2. Easy and Non-Invasive Collection: The collection of umbilical cord blood is a safe and non-invasive procedure that poses no harm to the mother or the baby. It is collected after the baby is born and the umbilical cord is clamped and cut, and the procedure does not interfere with the normal birthing process.
3. Compatibility with Siblings and Family Members: The stored cord blood may be a suitable match for siblings or other family members in need of a stem cell transplant. It reduces the risk of rejection and increases the chances of a successful transplant.
4. Potential for Future Therapies: Researchers are continually exploring new ways to utilize stem cells from umbilical cord blood in various medical treatments and therapies. By banking cord blood, individuals are investing in the potential future therapeutic applications of these valuable stem cells.
It’s important to note that the decision to store umbilical cord blood should be made well in advance of delivery. Expectant parents should thoroughly research and choose a reputable and accredited cord blood bank that meets stringent quality standards and has a solid track record in storing and providing quality samples for transplantation or medical research.
Umbilical cord blood banking opens the door to a world of medical possibilities for the future health and well-being of your child and potentially your entire family. It offers the potential to harness the regenerative power of stem cells for a wide range of diseases and conditions, providing peace of mind and hope for the future.
Read more: How To Store Button Cell Batteries
Dental Stem Cell Banking
Dental stem cell banking is a type of stem cell storage that involves the collection and preservation of stem cells found in dental pulp, which is present in teeth. Teeth, specifically baby teeth that are naturally shed or wisdom teeth that are extracted, can serve as a valuable source of dental stem cells.
The process of dental stem cell banking begins with the extraction of the tooth containing dental pulp. The extracted tooth is transported to a specialized laboratory for processing. In the laboratory, the dental pulp is carefully isolated and processed to extract the dental stem cells. These stem cells are then cryogenically frozen and stored at ultra-low temperatures for long-term preservation.
Dental stem cells, also known as dental pulp stem cells, possess unique characteristics and regenerative properties. They have the potential to differentiate into various types of cells, including bone cells, nerve cells, and dental tissues. This versatility makes them an attractive resource for potential future medical applications.
Here are a few key benefits of dental stem cell banking:
1. Non-Invasive and Safe Procedure: Dental stem cell extraction is a non-invasive procedure that does not require invasive surgery or other major interventions. Baby teeth naturally shed on their own, while wisdom teeth extractions are commonly performed for various reasons. The collection process is generally well-tolerated and poses minimal risk to the donor.
2. Potential for Regenerative Treatments: Dental stem cells have the potential to be used in regenerative therapies and treatments. They can be used to regenerate dental tissues, such as dentin and pulp, in cases of dental trauma or disease. Additionally, they hold promise in the regeneration of other tissues, such as bone and nerve, for potential treatments of various medical conditions.
3. Genetic Match for the Donor: Storing dental stem cells ensures a perfect genetic match for the donor. This eliminates the need to search for a compatible donor in case a stem cell transplant is required in the future. Having your own dental stem cells readily available can increase the chances of a successful transplantation and reduce the risk of rejection.
4. Potential for Personalized Medicine: Dental stem cell banking offers the potential for personalized medicine. By preserving your own dental stem cells, you have access to cells that are a genetic match, potentially allowing for customized treatments and therapies tailored to your specific needs.
It’s important to note that the decision to store dental stem cells should be made before the teeth are naturally shed or before the extraction procedure. Choosing a reliable and accredited dental stem cell bank, which uses proper protocols for collection, processing, storage, and delivery, is crucial to ensuring the viability and quality of the stored stem cells.
Dental stem cell banking provides an opportunity to secure a valuable resource for potential future medical treatments. It offers peace of mind, knowing that you have taken a proactive step to preserve your own stem cells and potentially benefit from the advancements in regenerative medicine that may arise in the future.
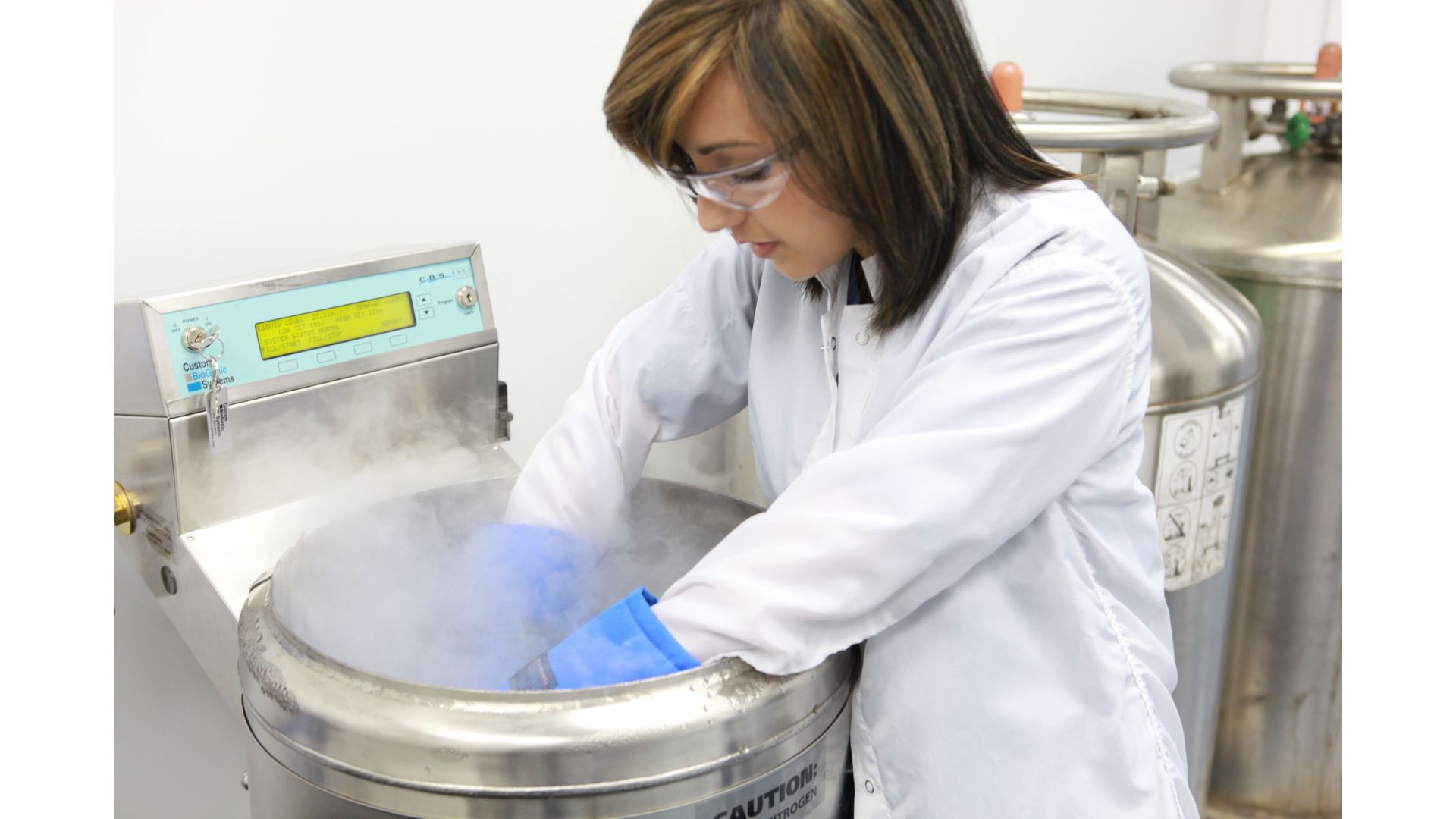
Store stem cells in a cryogenic freezer at temperatures below -150°C to maintain their viability and potency for future use. Regularly monitor and maintain the freezer to ensure consistent temperature.
Adipose Tissue Stem Cell Banking
Adipose tissue stem cell banking involves the collection and preservation of stem cells found in adipose tissue, which is commonly known as fat tissue. Adipose tissue is a rich source of adult stem cells, known as adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), which have the potential to differentiate into various cell types, including adipocytes, osteocytes, and chondrocytes.
The process of adipose tissue stem cell banking typically begins with a minimally invasive procedure called liposuction. During liposuction, a small incision is made to access an area of adipose tissue, such as the abdomen or thigh. A cannula is inserted into the incision to suction out a small amount of fat tissue. The extracted fat tissue is then processed in a specialized laboratory to isolate and collect the ADSCs.
Once isolated, the ADSCs are cryogenically frozen and stored at ultra-low temperatures to preserve their viability and properties. The stem cells can be stored for long periods, ensuring their availability for potential future use in regenerative medicine.
Here are a few key benefits of adipose tissue stem cell banking:
1. Abundant Source of Stem Cells: Adipose tissue is a plentiful source of stem cells, containing higher concentrations of stem cells compared to other sources, such as bone marrow. The abundance of ADSCs in adipose tissue makes it an attractive option for stem cell banking.
2. Minimally Invasive Procedure: Liposuction, the procedure used to collect adipose tissue, is a relatively safe and minimally invasive procedure that is commonly performed. The small incisions and low risk of complications make it a viable option for individuals seeking stem cell storage.
3. Potential for Diverse Regenerative Applications: Adipose tissue-derived stem cells have the potential to differentiate into various cell types, including adipocytes, osteocytes, and chondrocytes. This opens up possibilities for their use in regenerative medicine, such as in the repair and regeneration of fat, bone, and cartilage tissues.
4. Compatibility within an Individual: Preserving your own adipose tissue stem cells ensures that they are a genetic match for you. This compatibility reduces the risk of rejection or complications that may arise when using stem cells from unrelated donors. Having your own stored stem cells increases the chances of successful therapies and treatments if the need arises.
When considering adipose tissue stem cell banking, it is essential to choose a reputable stem cell bank that follows proper protocols for collection, processing, storage, and delivery. The bank should have a track record of maintaining high-quality standards and adhering to regulatory guidelines.
Adipose tissue stem cell banking offers a unique opportunity to preserve a valuable resource for potential future applications in regenerative medicine. By banking your own stem cells, you have access to a readily available source of ADSCs, potentially offering personalized treatments and therapies that harness the regenerative potential of your own cells.
Bone Marrow Stem Cell Banking
Bone marrow stem cell banking involves the collection and preservation of stem cells found in the bone marrow, the spongy tissue located inside certain bones. Bone marrow contains a variety of stem cells, including hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which have the ability to differentiate into different cell types and play a crucial role in the formation of blood cells and the regeneration of tissues.
The process of bone marrow stem cell banking typically begins with a procedure known as bone marrow aspiration. During this procedure, a healthcare professional uses a special needle to extract a small amount of bone marrow from the hip or sternum under local or general anesthesia. The collected bone marrow is then processed in a laboratory to isolate and collect the stem cells for storage.
Once the stem cells are collected, they are cryogenically frozen and stored at extremely low temperatures to maintain their viability and functionality. The stored stem cells can be preserved for long periods, ensuring their availability for potential future use in regenerative medicine or stem cell transplantation.
Here are some key benefits of bone marrow stem cell banking:
1. Proven Source of Stem Cells: Bone marrow is a well-established and reliable source of stem cells. It has been used in medical treatments, such as bone marrow transplants, for many years. The stem cells found in bone marrow have the capacity to differentiate into various cell types, making them valuable for regenerative medicine applications.
2. Compatibility within the Individual: Storing your own bone marrow stem cells ensures that they are a perfect genetic match for you. This eliminates the need to search for a compatible donor in case a stem cell transplant is required in the future. Having your own stored stem cells increases the chances of a successful transplantation and reduces the risk of rejection.
3. Supplementary Stem Cell Source: If you are already undergoing bone marrow procedures, such as transplantation or therapy, preserving additional stem cells through banking ensures the availability of a supplementary source of stem cells. This can be particularly beneficial in potential future treatments or if additional rounds of transplantation are needed.
Choosing a reputable stem cell bank that specializes in bone marrow stem cell storage is crucial. The bank should adhere to strict protocols for collection, processing, storage, and delivery, ensuring the viability and quality of the stored stem cells.
Bone marrow stem cell banking offers the potential for future medical applications and treatments. By preserving your own stem cells, you gain access to a valuable resource that can be used for regenerative medicine purposes or potentially benefit others in need of a compatible stem cell donation.
How to Choose a Stem Cell Storage Facility
Choosing the right stem cell storage facility is a crucial decision to ensure the long-term preservation and viability of your stored stem cells. With numerous options available, it’s important to consider several factors when selecting a stem cell storage facility. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision:
1. Accreditation and Compliance: Look for a facility that is accredited by reputable organizations, such as AABB (formerly known as the American Association of Blood Banks) or FACT (Foundation for the Accreditation of Cellular Therapy). Accreditation ensures that the facility meets stringent quality standards and follows best practices in stem cell collection, processing, and storage. Additionally, ensure that the facility complies with regulatory guidelines set by the appropriate governing bodies.
2. Expertise and Experience: Consider the facility’s expertise and experience in stem cell storage. Look for a facility with a solid track record and a team of experienced professionals who specialize in stem cell banking. They should have in-depth knowledge of the latest scientific advancements and storage techniques, ensuring the highest quality and safety standards for your stored stem cells.
3. Storage Technology and Facilities: Evaluate the technology and facilities used by the storage facility. Modern cryogenic storage systems, such as liquid nitrogen-based storage tanks, are essential for maintaining the vitality and viability of stem cells over the long term. Additionally, assess the facility’s backup power systems and security measures to ensure the continuous and secure preservation of your stem cells.
4. Quality Assurance and Testing: Inquire about the facility’s quality assurance protocols and testing procedures. They should have strict quality control measures in place to assess the viability, potency, and purity of the stored stem cell samples. Ask about their testing capabilities and how often they perform quality checks to ensure the integrity of your stem cells.
5. Transparency and Communication: Choose a facility that prioritizes transparency and open communication. They should provide clear information about their processes, fees, and terms. The facility should be readily available to address any queries or concerns you have regarding the storage or potential future use of your stem cells. Seek a facility that fosters a strong client-provider relationship and provides regular updates on the status of your stored stem cells.
6. Client Testimonials and Reviews: Research client testimonials and reviews to gauge the satisfaction and experiences of previous customers. Look for feedback regarding the facility’s customer service, professionalism, and the overall storage experience. Positive reviews and testimonials can provide valuable insights into the facility’s credibility and reliability.
7. Cost and Financial Stability: Evaluate the cost of storage and any associated fees. Compare the pricing structures of different facilities to ensure they align with your budget. Additionally, consider the financial stability and long-term sustainability of the storage facility to ensure the uninterrupted maintenance of your stored stem cells.
By considering these factors, you can make an educated decision when choosing a stem cell storage facility. Remember, the facility you choose will be responsible for the long-term preservation and potential use of your precious stem cells, so it’s essential to select a reputable and reliable facility that aligns with your specific needs and concerns.
Read more: How To Store Floral Stems
Process of Storing Stem Cells
The process of storing stem cells involves several crucial steps to ensure the preservation and viability of these valuable cells. Let’s explore the key processes involved in storing stem cells:
1. Consultation and Enrollment: The process typically begins with a consultation with a stem cell storage facility. During this consultation, the facility will provide information about stem cell storage options, costs, and the necessary paperwork. Once you decide to proceed, you will enroll in their storage program by completing the required enrollment forms and agreements.
2. Collection: The next step involves the collection of the stem cells. Depending on the type of stem cells being stored, the collection method may vary. For example, if you are storing umbilical cord blood, the blood is collected immediately after childbirth, while dental stem cells are collected during tooth extraction or when a baby tooth naturally falls out. Bone marrow stem cells are collected through a bone marrow aspiration procedure, and adipose tissue stem cells are collected through liposuction.
3. Transportation and Processing: After collection, the stem cells are transported to the storage facility for processing. During this stage, the stem cells undergo a series of rigorous laboratory processes to isolate and purify them from other components. These processes may include centrifugation, filtration, and cell counting to ensure the quality and purity of the stem cell sample.
4. Cryopreservation: Once processed, the stem cells are cryogenically frozen using state-of-the-art cryopreservation technology. The cells are slowly cooled to extremely low temperatures, typically around -196 degrees Celsius (-320 degrees Fahrenheit), to halt all biological activity without damaging the cells. The use of cryoprotectants helps prevent ice crystal formation and cell damage during freezing and storage.
5. Storage and Monitoring: The frozen stem cells are then transferred to specialized storage tanks designed for long-term preservation. These storage tanks are typically filled with liquid nitrogen, which helps maintain the ultra-low temperatures required for optimal preservation. During storage, the stem cells undergo regular monitoring and quality checks to ensure their viability and integrity over time.
6. Maintenance and Security: The stem cell storage facility is responsible for the ongoing maintenance and security of the stored cells. They ensure that the storage tanks are properly maintained, with backup power systems in place to prevent any disruptions in temperature control. Security measures, such as access control and surveillance systems, are implemented to safeguard the stem cell samples.
7. Retrieval and Delivery: In the event that the stored stem cells are needed for medical use, the facility will retrieve and prepare the samples for delivery. The stem cells are carefully thawed and undergo quality checks to ensure their viability and potency. The facility coordinates with the healthcare provider or transplant center to arrange for the safe and timely delivery of the stem cell sample.
It’s important to note that stem cell storage facilities follow strict protocols and regulatory guidelines to ensure the highest standards of quality and safety throughout the storage process. By following these processes diligently, stem cell storage facilities can provide individuals and families with the assurance of having a valuable resource for potential future medical treatments and therapies.
Future Potential of Stored Stem Cells
The stored stem cells hold immense future potential in the field of regenerative medicine and medical advancements. As scientific research and understanding of stem cells continue to progress, there are numerous exciting possibilities for the utilization of stored stem cells. Here are some of their potential future applications:
1. Regenerative Treatments: Stored stem cells can be utilized in regenerative treatments to repair, replace, or regenerate damaged or diseased tissues and organs. Stem cells have the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types, making them ideal for regenerating tissues such as heart muscle, nerve cells, cartilage, and bone. This potential opens up possibilities for treating conditions such as heart disease, spinal cord injuries, Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, and osteoarthritis.
2. Personalized Therapies: Stored stem cells offer the possibility of personalized therapies. Because the stem cells are a genetic match for the individual, they can potentially be used in creating personalized treatments tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup. Personalized stem cell therapies can enhance treatment outcomes, reduce the need for immunosuppressive drugs, and minimize the risk of rejection or adverse reactions.
3. Drug Development and Disease Modeling: Stem cells stored from a specific individual can serve as a valuable resource for drug development and disease modeling. These stem cells can be used to study diseases in a laboratory setting, allowing researchers to better understand disease mechanisms, test new drugs, and develop targeted therapies. The ability to generate disease-specific stem cells provides a unique opportunity to advance the field of precision medicine.
4. Immunotherapy and Cancer Treatments: Stored stem cells can be utilized in immunotherapy and cancer treatments. Stem cells can be genetically modified or engineered to improve their anti-tumor properties, making them a potential tool for targeted cancer therapies. They can be used to develop novel immunotherapies, such as CAR-T cell therapy, that harness the power of the immune system to fight cancer.
5. Tissue Engineering and Organ Transplantation: Stored stem cells can contribute to advancements in tissue engineering and organ transplantation. They can be used to create artificial organs, regenerate damaged tissues, or provide a continuous supply of cells for organ transplantation. This has the potential to revolutionize the field of transplantation, addressing the shortage of donor organs and eliminating the need for immunosuppression in transplant recipients.
It’s important to note that while the future potential of stored stem cells is incredibly promising, it is still an evolving field and the exact applications and therapies may not yet be fully realized. Continued research and clinical trials are necessary to fully explore and harness the potential of stored stem cells.
By preserving and storing stem cells today, individuals and families are positioning themselves to take advantage of future breakthroughs in regenerative medicine and personalized therapies. The stored stem cells represent a valuable resource that may hold the key to transforming the treatment of numerous diseases and conditions, offering renewed hope for improved health and well-being.
Conclusion
Storing stem cells is a forward-thinking decision that holds immense potential for the future of medicine. Stem cells possess unique regenerative properties, making them a valuable resource for developing innovative treatments and therapies. Through various types of stem cell storage, including umbilical cord blood banking, dental stem cell banking, adipose tissue stem cell banking, and bone marrow stem cell banking, individuals and families can secure a valuable resource that may play a pivotal role in their health journey.
By storing stem cells, individuals can potentially benefit from personalized therapies, improved treatment outcomes, and the potential advancements in regenerative medicine. Stem cells offer the potential to regenerate damaged tissues, develop targeted therapies, and revolutionize organ transplantation. The stored stem cells can serve as a genetic match for the individual or their family members, reducing the risk of rejection and increasing the chances of successful treatments and transplants.
Choosing a reputable stem cell storage facility is crucial for ensuring the highest standards of quality, safety, and long-term preservation of the stem cells. Facilities that are accredited, experienced, and transparent in their processes will provide individuals with the peace of mind that their stem cells are in capable hands.
While the full extent of the future potential of stored stem cells is yet to be realized, ongoing research and advancements in the field continue to unveil exciting possibilities. Stem cell research holds great promise for developing treatments for a wide range of diseases and conditions, offering hope to individuals and families facing various health challenges.
In conclusion, storing stem cells is a proactive investment in the future of healthcare. It offers the potential for personalized therapies, regenerative treatments, and advancements in medical science. By taking this step today, individuals and families can secure a valuable resource that may pave the way for improved health, well-being, and medical breakthroughs in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Stem Cells
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Store Stem Cells”