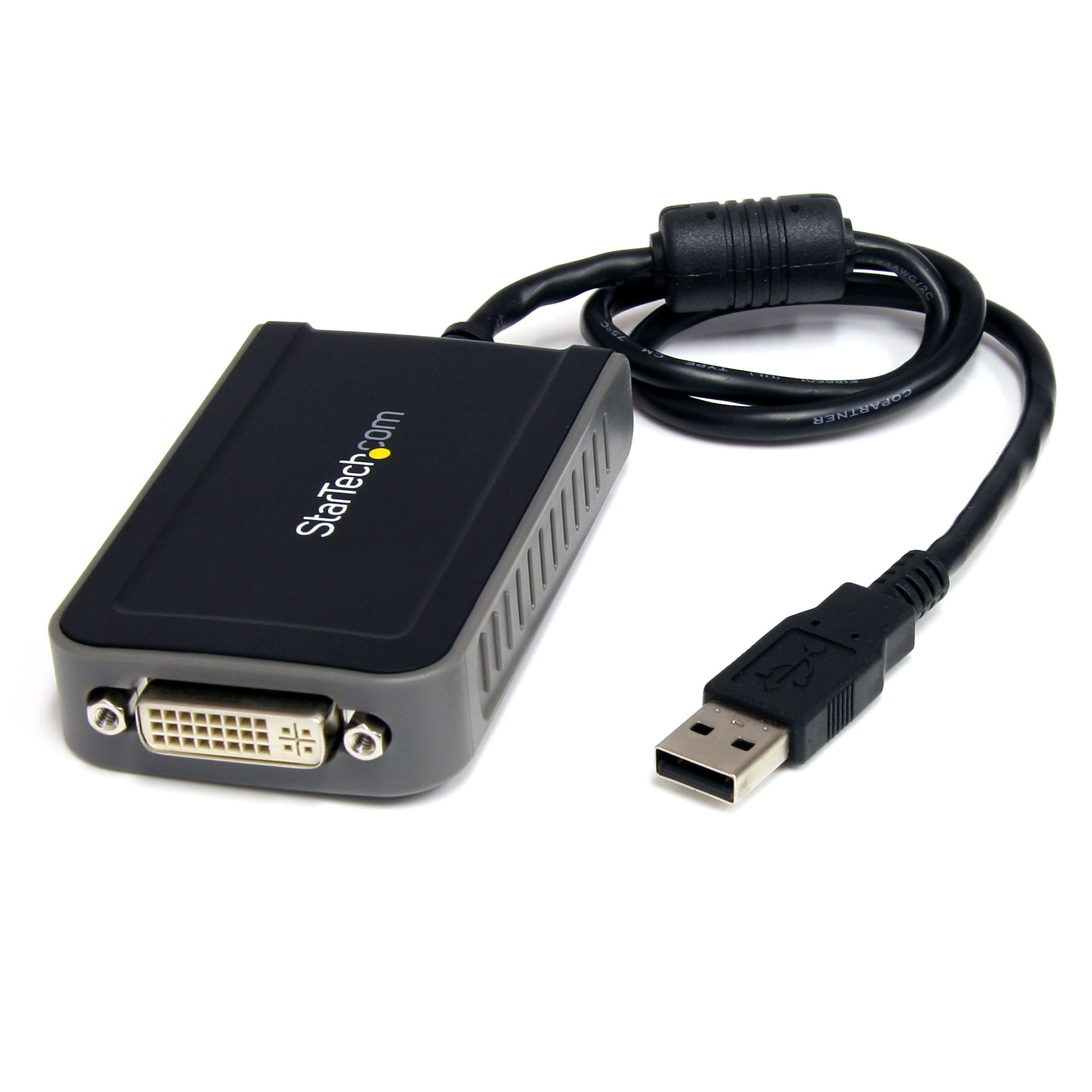


Articles
What Is A Video Adapter
Modified: January 6, 2024
Looking for articles on video adapters? Learn everything you need to know about video adapters and their functions in our informative articles.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
A video adapter, also known as a graphics card, is an essential component of a computer system that connects the computer to the display device, such as a monitor or a projector. It is responsible for rendering and transmitting visual data from the computer’s processor to the display, allowing users to see images, videos, games, and other graphical content.
The video adapter acts as an intermediary between the computer’s processor and the display device, translating the digital information from the processor into a format that the display can understand and render. This conversion process involves transforming binary code into pixels, colors, and various visual effects that create the images displayed on the screen.
Over the years, video adapter technology has advanced significantly, resulting in improved graphics capabilities and enhanced visual experiences for computer users. Modern video adapters are equipped with powerful processors, high-speed memory, and advanced rendering techniques that can handle complex graphics operations, high resolutions, and smooth frame rates.
Not only are video adapters essential for displaying visual content, but they also play a crucial role in facilitating tasks such as video editing, 3D modeling, gaming, and other graphic-intensive applications. They offload the graphics processing from the computer’s CPU, allowing for better performance and smoother operation.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of video adapters, including their functions, types, compatibility options, factors to consider when choosing one, installation and setup procedures, common troubleshooting issues, and more. Whether you are a computer enthusiast, a gamer, or simply someone in need of a new video adapter, this article will provide you with the necessary knowledge to make an informed decision and optimize your visual experience.
Key Takeaways:
- Video adapters, also known as graphics cards, are essential for rendering high-quality visual content on computer systems. They enhance graphics performance, support multiple monitors, and cater to various user needs, from casual browsing to professional applications.
- When choosing a video adapter, consider factors such as intended usage, compatibility, graphics performance, connectivity options, and power requirements. Proper installation, driver updates, and troubleshooting can ensure a seamless visual experience and optimal performance.
Read more: What Is An Adapter
Definition of Video Adapter
A video adapter, also known as a graphics card or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), is a hardware component that is responsible for processing and rendering visual data on a computer system. It is designed to enhance the graphics capabilities of a computer and deliver high-quality images and videos to the connected display device.
The video adapter serves as a bridge between the computer’s central processing unit (CPU) and the monitor or other display devices such as projectors or HDTVs. It takes the digital information generated by the CPU and converts it into a video signal that the display device can understand and present on the screen.
The video adapter consists of several key components that work together to provide optimal graphics performance. The GPU, which is the heart of the video adapter, is responsible for executing complex mathematical calculations required for rendering graphics. It contains thousands of processing cores that allow for parallel processing, enabling faster rendering and smoother animations.
In addition to the GPU, video adapters also include dedicated video memory (VRAM) to store and access the graphical data quickly. The VRAM acts as a buffer, providing fast access to textures, shaders, and other graphics-related information. The amount of VRAM available on a video adapter determines its ability to handle high-resolution content and multiple displays.
Furthermore, video adapters feature various connectors and ports to establish a connection between the computer and the display device. Common connectors include HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, and VGA, each supporting different resolutions and refresh rates. These connectors allow for seamless transmission of video signals, enabling the display device to present a clear and vibrant image.
Video adapters also support various graphics APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) such as DirectX and OpenGL, which provide a set of functions and libraries for developers to create and optimize graphics-intensive applications. These APIs enable enhanced graphics effects, realistic lighting, and smooth animations in games, multimedia applications, and other visual content.
In summary, a video adapter is a crucial hardware component that enables computers to generate and display high-quality visual content. With its powerful GPU, dedicated video memory, and connection options, the video adapter plays a vital role in delivering a visually immersive experience for gaming, multimedia, and other graphics-intensive tasks.
Functions of Video Adapter
A video adapter, or graphics card, performs several important functions that contribute to the overall graphics performance and visual experience of a computer system. Let’s delve into the key functions of a video adapter:
- Graphics Processing: The primary function of a video adapter is to handle the processing and rendering of visual data. It takes the digital information generated by the computer’s CPU and performs complex calculations to transform it into pixels, colors, and graphical effects. This includes tasks such as geometry processing, texture mapping, shading, and rasterization.
- Display Output: Video adapters are responsible for transmitting the processed graphics data to the monitor or display device. They convert the digital information into a compatible video signal that can be understood by the display. The video adapter determines the resolution, refresh rate, and color depth of the output, impacting the clarity and smoothness of the displayed images.
- Multiple Monitor Support: Many video adapters support multiple monitor configurations, allowing users to connect and display content on multiple monitors simultaneously. This feature is particularly useful for professionals who require an extended workspace for tasks such as video editing, graphic design, and multitasking.
- Graphics Memory Management: Video adapters have dedicated video memory (VRAM) used to store graphical data, including textures, shaders, and frame buffers. The VRAM provides fast access to the graphical resources, improving performance and reducing the need to access the computer’s main memory. It also allows for higher-resolution texture mappings and supports anti-aliasing, which smooths the jagged edges of rendered objects.
- Hardware Acceleration: Video adapters often come with specialized hardware features that can accelerate specific graphics tasks. For example, they may include dedicated hardware for video decoding and encoding, enhancing performance and efficiency when playing back high-definition videos or streaming content.
- 3D Rendering: Video adapters excel in rendering three-dimensional graphics for gaming, simulations, and 3D modeling applications. They utilize advanced algorithms and shading techniques to create realistic lighting, shadows, reflections, and other visual effects, resulting in immersive and visually stunning experiences.
- Compatibility: Video adapters are designed to be compatible with various operating systems, software applications, and graphics APIs. They provide the necessary drivers and software interfaces to ensure seamless integration with the computer system and enable efficient communication between the CPU and GPU.
Overall, video adapters serve as the powerhouse behind a computer’s graphical capabilities. By handling graphics processing, display output, memory management, and specialized hardware acceleration, video adapters enable users to enjoy smooth, high-quality visuals and unlock the full potential of their computer system for gaming, graphics-intensive applications, and multimedia experiences.
Types of Video Adapters
Video adapters come in various types, each designed for specific purposes and catering to different needs. Let’s explore some of the common types of video adapters available in the market:
- Integrated Graphics: Integrated graphics, also known as onboard graphics, are built-in video adapters that are integrated into the motherboard of a computer. They are typically found in entry-level or budget computers and laptops. Integrated graphics share system memory with the CPU and offer basic graphics performance suitable for everyday computing tasks, such as web browsing, document editing, and media playback.
- Discrete Graphics: Discrete graphics cards, also referred to as dedicated graphics cards, are separate video adapters that are installed into expansion slots on the motherboard. They have their own dedicated GPU, VRAM, and cooling system. Discrete graphics cards offer significantly better performance and features compared to integrated graphics, making them ideal for gaming, multimedia editing, and other graphics-intensive applications.
- Professional Graphics: Professional graphics cards, often referred to as workstation graphics cards, are targeted at professionals working in fields such as computer-aided design (CAD), 3D modeling, animation, and video editing. These cards are optimized for demanding workloads, offering higher computational power, more VRAM, and specialized drivers for professional software applications.
- Gaming Graphics: Gaming graphics cards are specifically designed for gaming enthusiasts and offer superior performance, advanced features, and support for high-resolution gaming. These cards often come with additional features such as RGB lighting, overclocking capabilities, and software for game optimization. They are suitable for gamers who want to experience the latest games at high settings and smooth frame rates.
- External Graphics: External graphics solutions allow users to enhance the graphics performance of laptops or systems with limited or integrated graphics by connecting an external graphics enclosure. These enclosures enable the use of desktop-grade graphics cards and provide a significant boost in graphics performance, making them popular among gamers and professionals who require portable yet powerful graphics capabilities.
- Low-Profile Graphics: Low-profile graphics cards are compact and slim-designed cards that are suitable for small-form-factor computers such as mini-ITX and slim desktops. They are ideal for systems where space is limited and offer a balance between performance and size.
Each type of video adapter comes with its own set of features, performance levels, and price ranges. When selecting a video adapter, consider the specific requirements of your computer setup and the intended usage, whether it’s casual web browsing, graphic design, gaming, or professional applications. Understanding the different types of video adapters will help you make an informed decision and choose the right one that meets your needs and budget.
Compatibility and Connection Options
When it comes to video adapters, compatibility is an important aspect to consider to ensure that the adapter works seamlessly with your computer system and the display device. Additionally, understanding the different connection options will help you select the right video adapter and ensure proper connectivity. Let’s explore compatibility and connection options in more detail:
Compatibility:
Video adapters are designed to be compatible with specific hardware and software configurations. Key compatibility factors to consider include:
- Motherboard Compatibility: Ensure that the video adapter is compatible with your computer’s motherboard and has the appropriate expansion slot for installation. Common interface standards include PCI Express (PCIe) and Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP).
- Power Supply: Some video adapters require additional power connectors from the power supply unit (PSU) to operate properly. Ensure that your power supply can provide sufficient power to the video adapter, or upgrade your PSU if necessary.
- Operating System Compatibility: Check if the video adapter has drivers available for your operating system. Most modern operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, and Linux, have compatible drivers for a wide range of video adapters.
Connection Options:
Video adapters offer various connection options to establish a link between the computer and the display device. Some common connection options include:
- HDMI: High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a popular digital connection standard that supports both video and audio transmission. HDMI cables provide high image quality and are widely used in modern displays, including TVs, monitors, and projectors.
- DisplayPort: DisplayPort is another digital connection standard that offers high bandwidth and supports high resolutions and refresh rates. It is commonly found on monitors and is increasingly being incorporated into various devices, including laptops, graphics cards, and displays.
- DVI: Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a versatile connection option that supports both analog and digital signals. It is commonly used for connecting monitors and displays that do not have HDMI or DisplayPort ports. DVI can transmit high-quality video signals but does not carry audio.
- VGA: Video Graphics Array (VGA) is an older analog connection that supports lower resolutions. It is commonly found on older monitors, projectors, and some older computers. VGA connections do not provide as high image quality as digital connections like HDMI or DisplayPort.
- USB-C: USB-C is a versatile and increasingly popular connection option that can carry both video and power. It allows for the transmission of high-resolution video signals and can also charge compatible devices. Many modern laptops and displays feature USB-C ports.
When selecting a video adapter, ensure that it supports the appropriate connection options for your display device. If needed, adapters or converters are also available to convert signals between different connection types, allowing for compatibility between devices with differing ports.
By considering compatibility and connection options, you can ensure that the video adapter is a seamless fit with your computer system and the display device, providing you with high-quality visuals and a hassle-free experience.
When choosing a video adapter, consider the type of ports it has (HDMI, DisplayPort, etc.), its compatibility with your computer’s operating system, and the resolution and refresh rate it supports.
Read more: What Is A Vga Adapter
Factors to Consider when Choosing a Video Adapter
Choosing the right video adapter is crucial to ensure optimal graphics performance and compatibility with your computer system and display device. Here are several factors to consider when selecting a video adapter:
- Intended Usage: Determine the primary purpose of the video adapter. Are you a gamer in need of high-performance graphics for the latest games? Are you a professional working with graphic-intensive applications? Or are you a casual user looking for basic graphics capabilities? Knowing your intended usage will help you identify the level of performance and features required.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the video adapter is compatible with your computer system. Check if the adapter supports your computer’s motherboard interface, such as PCIe or AGP, and if there are compatible drivers available for your operating system.
- Graphics Performance: Consider the graphics performance you need for your specific use cases. This includes factors such as the GPU’s clock speed, the number of cores, and memory bandwidth. Check benchmarks and reviews to assess the performance of different video adapters.
- Memory: Video adapters come with dedicated video memory (VRAM). The amount of VRAM impacts the performance and ability to handle high-resolution graphics and multiple displays. Choose a video adapter with sufficient VRAM to meet your requirements.
- Connectivity: Ensure that the video adapter has the necessary connectivity options to connect to your display device. Consider the type of connections your display supports, such as HDMI, DisplayPort, or DVI, and choose a video adapter with compatible ports.
- Power Requirements: Check the power requirements of the video adapter. Some high-performance adapters may require additional power connectors from the power supply unit (PSU). Make sure your PSU can provide sufficient power to support the video adapter.
- Budget: Consider your budget when selecting a video adapter. It is important to strike a balance between performance and price. Higher-end video adapters with more advanced features and better performance tend to be more expensive.
- Brand and Support: Research reputable brands known for their quality and reliable customer support. Look for warranties, driver support, and customer reviews to ensure long-term satisfaction and assistance if any issues arise.
It’s important to note that the choice of video adapter also depends on individual preferences and priorities. Evaluate your specific needs and assess which factors are most important to you.
By considering these factors, you can select a video adapter that aligns with your needs, offers optimal performance, and provides a seamless graphics experience for your computer system.
Installation and Setup of Video Adapter
Installing and setting up a video adapter is a straightforward process that can greatly enhance your computer’s graphics performance. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you install and set up your video adapter:
- Prepare Your System: Before proceeding, ensure that your computer is powered off and unplugged from the power source. Take necessary precautions to prevent static electricity discharge by grounding yourself.
- Identify Expansion Slot: Locate an available expansion slot on your computer’s motherboard. Commonly used slots are PCI Express (PCIe) or Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP). Refer to your motherboard’s manual to identify the appropriate slot for your video adapter.
- Remove Existing Adapter: If you already have a video adapter installed, carefully remove it by unscrewing any retaining screws and gently unplugging it from the slot. Place the adapter in an anti-static bag for safekeeping.
- Insert the New Adapter: Take your new video adapter and align it with the expansion slot. Firmly and evenly insert the adapter into the slot until it is seated properly. Use screws to secure the adapter (if required), but be careful not to overtighten.
- Connect Power Supply (if required): Some video adapters require additional power from the power supply unit (PSU). If your video adapter needs extra power, locate the appropriate power connectors from your PSU and connect them to the adapter securely.
- Connect the Display: Depending on the video adapter and the display device, connect the appropriate cable, such as HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, or VGA, from the video adapter to the display. Ensure a secure and proper connection on both ends.
- Boot Up and Install Drivers: Once the hardware installation is complete, power on your computer. It should detect the new video adapter. If necessary, insert the driver installation disc provided with the video adapter, or download the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the drivers.
- Configure Display Settings: After the drivers are installed, you may need to adjust the display settings. Access the display settings from your operating system’s control panel or settings menu to set the resolution, refresh rate, and other relevant graphics options based on your preferences and display capabilities.
- Test and Troubleshoot: With the video adapter installed and drivers configured, make sure to restart your computer and test the graphics performance. Use benchmarking software, play games, or run visually demanding applications to ensure the video adapter is functioning correctly. If any issues arise, consult the troubleshooting guide provided with the video adapter or reach out to the manufacturer’s customer support.
It’s essential to always refer to the specific instructions provided by the video adapter manufacturer for installation and setup, as these steps may vary slightly depending on the model and make of the video adapter.
By following these steps carefully, you should be able to install and set up your new video adapter, unlocking improved graphics performance and a better visual experience on your computer.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
While video adapters are generally reliable, occasional issues may arise during installation or usage. Here are some common troubleshooting tips for video adapters:
- No Display: If you are not getting any display after installing a new video adapter, ensure that the cable connecting the adapter to the display device is securely plugged in. Try reconnecting the cable or using a different cable to rule out any connectivity problems.
- Driver Issues: If you experience graphical glitches, low performance, or other issues, it could be due to outdated or incompatible drivers. Verify that you have the latest drivers for your video adapter installed. Download them from the manufacturer’s website if necessary.
- Black Screen: If your display is completely black, it could indicate a problem with the resolution or refresh rate settings. Restart your computer in Safe Mode and adjust the display settings to a lower resolution and refresh rate. Then, restart normally and choose suitable settings for your display.
- Artifacting or Flickering: If you notice unusual artifacts or flickering on the screen, it could be a sign of a faulty video adapter or incompatible drivers. Try reinstalling the drivers or updating to the latest version. If the issue persists, consider contacting the manufacturer for further assistance.
- Overheating: Video adapters can generate a significant amount of heat, especially during intensive use. Ensure that your computer has proper airflow and ventilation to prevent overheating. Clean the fans and heatsinks regularly to remove any dust buildup that can impede heat dissipation.
- Compatibility Issues: Ensure that the video adapter is compatible with your computer’s hardware and operating system. Check for any conflicts with other installed hardware or driver incompatibilities that may cause issues. Verify compatibility specifications before purchasing a video adapter.
- Insufficient Power: If your computer experiences sudden shutdowns or instability after installing a video adapter, it may be drawing more power than your power supply can handle. Consider upgrading to a higher wattage power supply to provide sufficient power to the video adapter.
- Memory Issues: If your system experiences frequent crashes or freezing during graphics-intensive tasks, it could be due to insufficient video memory. Upgrade your video adapter to one with more VRAM to handle the demanding workload.
- Hardware Faults: If you have tried troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing issues, it’s possible that the video adapter or another hardware component is faulty. Contact the manufacturer’s customer support or seek assistance from a professional technician for further diagnosis and possible repairs.
If you encounter any issues with your video adapter, it’s important to refer to the manufacturer’s documentation, user manuals, and troubleshooting guides for specific instructions. Additionally, online forums and communities can provide valuable insights and solutions for common video adapter issues.
By following these troubleshooting steps and seeking assistance when needed, you can address common video adapter problems, optimize performance, and enjoy a smooth visual experience on your computer.
Conclusion
Video adapters play a vital role in enhancing the visual experience of a computer system, from delivering crisp images and vibrant colors to enabling smooth gaming and graphics-intensive applications. Understanding the functions, types, compatibility options, and other factors related to video adapters is crucial in selecting the right adapter for your needs.
Whether you are a casual user, a professional, or a gamer, choosing a video adapter that aligns with your requirements and budget is essential. Consider factors such as intended usage, compatibility, graphics performance, connectivity options, and power requirements when making your decision.
The installation and setup of a video adapter is a straightforward process, involving identifying the appropriate expansion slot, connecting the adapter to the display, installing drivers, and configuring display settings. By following the manufacturer’s instructions and troubleshooting common issues, you can ensure a smooth installation and optimal performance.
However, in the event of any problems, such as no display, driver issues, overheating, or compatibility conflicts, refer to the manufacturer’s documentation, seek assistance online, or contact customer support for troubleshooting steps and resolution.
In conclusion, video adapters are integral components that enhance the visual capabilities of a computer system. By understanding their functions, considering the compatibility and connection options, and following proper installation and troubleshooting procedures, you can make the most of your video adapter’s capabilities and enjoy high-quality graphics, immersive gaming experiences, and efficient graphics-intensive workflows.
Remember to stay updated with the latest drivers and ensure proper maintenance to ensure longevity and optimal performance of your video adapter. With a well-chosen and properly set up video adapter, you can unlock the full potential of your computer’s graphical capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Video Adapter
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is A Video Adapter”