Home>Articles>What Is The Difference Between A Veranda And A Balcony


Articles
What Is The Difference Between A Veranda And A Balcony
Modified: February 28, 2024
Discover the key distinctions between a veranda and a balcony in this informative article. Gain insights on their designs, uses, and benefits.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the difference between a veranda and a balcony. These two architectural features are often confused due to their similarities in function and design. However, there are distinct differences that set them apart.
A veranda and a balcony are both outdoor spaces attached to a building, providing a unique area for relaxation and enjoyment. They are commonly found in residential properties, hotels, and commercial establishments. Understanding the features and purposes of each can help you make informed decisions when designing or choosing a property.
In this article, we will explore the definitions, architectural features, similarities, and differences between a veranda and a balcony. We will also discuss the benefits and various uses of these outdoor spaces. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of verandas and balconies!
Key Takeaways:
- Verandas offer a shaded, open-air retreat at ground level, seamlessly integrating indoor and outdoor spaces, enhancing property value, and providing flexible entertainment and relaxation options.
- Balconies provide private, elevated retreats with panoramic views, extended living space, personalized aesthetics, and opportunities for al fresco dining and gardening, adding value and charm to any building.
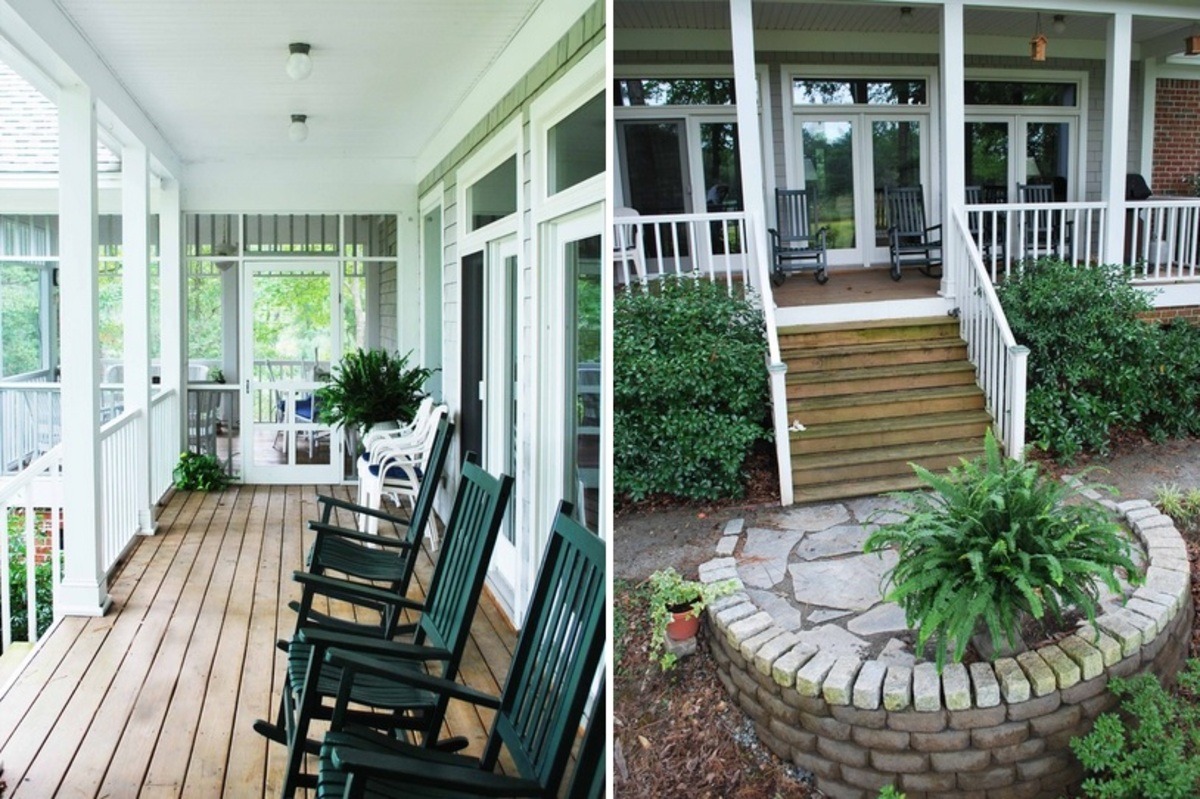
Definition of a Veranda
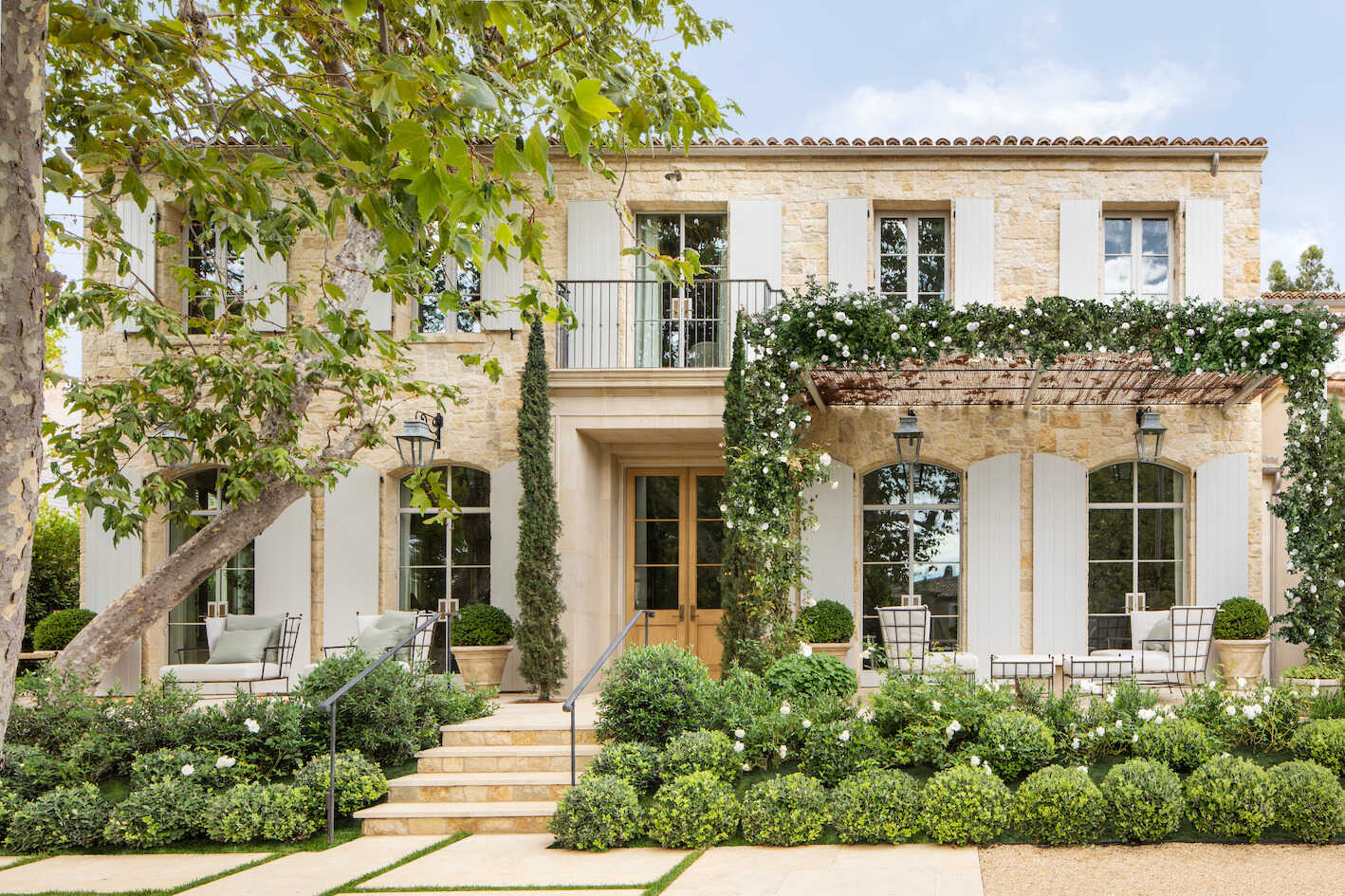
A veranda is an architectural feature that is typically a covered, open-air space attached to the front or side of a building. It is characterized by a roof and has one or more sides that are partially or completely open. Verandas are often supported by pillars, columns, or posts, adding to their aesthetic appeal.
Verandas originated in colonial and Victorian-era architecture and were popular in countries with warm climates. They were initially designed as a shaded area where residents could relax, socialize, and enjoy the outdoors without being exposed to direct sunlight or adverse weather conditions.
One of the distinguishing features of a veranda is its extended roof, which provides additional protection from the elements. This allows individuals to enjoy the outdoor space even during rain showers or intense sunshine.
Verandas are commonly found in single-family homes, country estates, and historic buildings. They are often positioned at the front of the house, serving as an inviting entrance and providing a space for guests to wait or be greeted. Verandas can also wrap around the side or rear of a building, offering panoramic views of the surrounding landscape.
These outdoor spaces are often adorned with comfortable seating, dining areas, and decorative elements such as potted plants, hanging baskets, and lighting fixtures. They create a seamless transition between the indoors and outdoors, providing a tranquil retreat for homeowners and visitors alike.
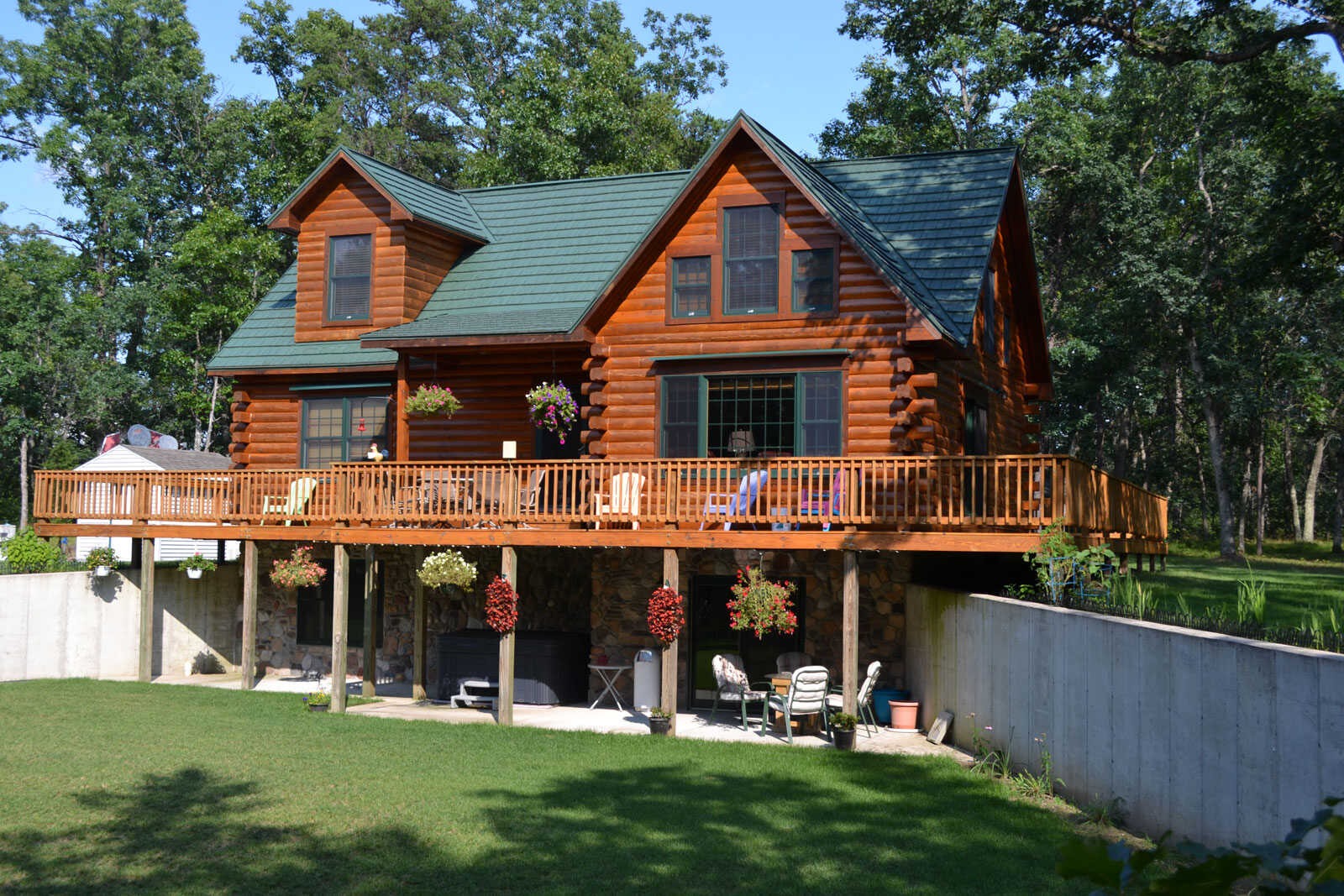
Definition of a Balcony
A balcony is an elevated platform or structure that extends from the upper levels of a building. Unlike a veranda, a balcony is typically attached to the side or rear of a building rather than the front. It is commonly constructed with a solid floor and has a railing or balustrade for safety.
Balconies serve as private outdoor spaces that provide residents with an intimate area to enjoy fresh air and panoramic views. They are commonly found in apartments, condominiums, and multi-story buildings where outdoor space may be limited.
One of the distinguishing features of a balcony is its elevated position, offering an elevated perspective of the surroundings. This can range from views of the cityscape to scenic landscapes or even a bustling street below.
Balconies are often designed with aesthetic and functional considerations in mind. They can be enhanced with decorative elements such as flower boxes, seating arrangements, or outdoor furniture. Some balconies may also have additional features like awnings or retractable screens to provide shade and privacy.
In addition to their recreational uses, balconies can serve practical purposes as well. They can provide additional access points to the building, emergency exits, or even a place to hang laundry or store items, depending on the building’s design and regulations.
Due to their elevated position, balconies offer a sense of privacy and seclusion compared to other outdoor spaces. They are often used as a personal retreat, a spot to enjoy a morning cup of coffee, or a cozy nook for reading or relaxation.
It’s important to note that while balconies are predominantly featured in residential buildings, they can also be found in commercial establishments such as hotels, restaurants, and bars, where they serve as outdoor seating areas or observation decks.
Architecture and Design Features of a Veranda
The architecture and design of a veranda are key factors that contribute to its unique charm and functionality. Here are some notable features:
Roof and Covering: A veranda is distinguished by its roof, which provides shelter and protection from the elements. The roof can take various forms, from a simple flat design to a gabled roof with sloping sides. It is often constructed with materials such as wood, metal, or tiles.
Open Sides: Unlike a fully enclosed room, a veranda has one or more sides that are partially or completely open. This allows for a seamless integration of the indoor and outdoor spaces. Open sides can be created through the use of columns, pillars, or posts that support the roof structure.
Pillars and Columns: Verandas are often supported by pillars or columns, adding a touch of architectural elegance. These structural elements not only provide stability but also contribute to the overall aesthetics of the veranda. Pillars can be made from various materials such as wood, stone, or metal.
Flooring: Verandas typically have a solid, durable flooring material that is suitable for outdoor use. Common options include tiles, stone, concrete, or even treated wood. The choice of flooring material can greatly impact the overall look and feel of the veranda.
Decorative Elements: To enhance the visual appeal of the veranda, decorative elements are often incorporated. These can include ornate railings, intricate carvings, hanging plants, and lighting fixtures. These elements not only add beauty but also create a welcoming ambiance.
Seating and Furniture: Verandas are commonly furnished with comfortable seating, such as lounge chairs, sofas, or dining tables. The choice of furniture depends on the intended use of the space, whether it be a cozy reading nook or an alfresco dining area.
Integration with Surroundings: Verandas are designed to seamlessly blend with the surrounding environment. The layout and position of the veranda may take advantage of scenic views or create a private oasis within a garden. Consideration is given to the orientation of the veranda to maximize sunlight and airflow.
These architectural and design features all contribute to creating a veranda that is aesthetically pleasing, functional, and enhances the overall appearance and value of a building.
Architecture and Design Features of a Balcony
The architecture and design of a balcony play a crucial role in creating an appealing and functional outdoor space. Here are some key features to consider:
Location and Attachment: Balconies are typically attached to the upper levels of a building, whether it’s a residential apartment, condominium, or commercial establishment. They are often positioned on the side or rear of the building, providing residents with privacy and panoramic views. Balconies can be accessed directly from interior rooms, such as bedrooms or living areas.
Structure and Safety: Balconies are structurally built to withstand weight and ensure the safety of occupants. They are constructed with a solid floor and enclosed by a railing or balustrade. The railing serves as a protective barrier and can be made of various materials such as metal, glass, or wood. Safety regulations and building codes dictate the minimum height requirements for balcony railings to prevent accidents.
Size and Layout: The size of a balcony can vary depending on the building’s design and available space. Balconies can range from small, intimate spaces for a single person to larger ones that can accommodate seating arrangements or potted plants. The layout of a balcony can be rectangular, square, or have unique contours, adding visual interest to the overall architecture of the building.
Flooring: Balcony floors are often made of durable materials that can withstand outdoor conditions. Common options include concrete, tiles, decking, or composite materials. The choice of flooring material depends on factors such as maintenance requirements, aesthetics, and budget.
Privacy and Views: Depending on the location of the building and the surrounding environment, privacy can be an important consideration in balcony design. Privacy screens, partitions, or landscaping elements can be incorporated to create a sense of seclusion. Balconies also offer the advantage of providing residents with breathtaking views of the surrounding cityscape, nature, or other scenic vistas.
Accessories and Decor: Balconies can be customized with accessories and decor to enhance their appeal and functionality. This can include adding outdoor furniture such as chairs, tables, or loungers for relaxation or dining. Plants, flowers, and hanging baskets can bring a touch of nature and color to the balcony. Lighting fixtures can also be installed to create ambiance and extend the usability of the outdoor space into the evenings.
Integration with Architecture: Balconies should be designed in harmony with the overall architecture of the building. They can feature architectural details that match the style of the structure, such as ornamental railings, decorative pillars, or unique finishes. Proper integration ensures that the balcony becomes an attractive and cohesive element of the building’s façade.
By carefully considering these architectural and design features, balconies can provide a functional, visually appealing, and enjoyable outdoor space for residents to relax, socialize, and take in the surrounding views.
A veranda is a roofed platform along the outside of a house, while a balcony is a platform that projects from the wall of a building. Verandas are typically at ground level, while balconies are elevated.
Similarities between a Veranda and a Balcony
While verandas and balconies have distinct characteristics, there are several similarities that they share. These similarities include:
Outdoor Spaces: Both verandas and balconies are outdoor spaces attached to a building. They provide an extension of the indoor living area, allowing residents to enjoy the outdoors without leaving the comfort of their homes.
Relaxation and Recreation: Verandas and balconies serve as areas for relaxation and recreation. They offer a place to unwind, soak up the sun, enjoy the fresh air, or simply take in the views. Both spaces can be furnished with seating arrangements, outdoor furniture, and other amenities to enhance comfort and enjoyment.
Architectural Enhancements: Verandas and balconies contribute to the architectural aesthetics of a building. They add visual interest, depth, and dimension to the exterior façade. Both features can be designed to complement the architectural style of the building, whether it’s a traditional, contemporary, or modern design.
Integration with Indoor Space: Verandas and balconies create a seamless transition between the indoor and outdoor areas. They allow residents to easily access the outdoor space and enjoy the benefits of nature while still being connected to the interior of the building. This integration provides a sense of continuity and expands the living area.
Purpose and Function: Verandas and balconies are intended to provide a space for homeowners and residents to enjoy the outdoors. They offer a private sanctuary to relax, entertain guests, or engage in various activities. Both spaces can be personalized and adapted to suit individual preferences and needs.
Enhanced Property Value: The presence of a veranda or a balcony can greatly enhance the value of a property. These outdoor spaces are desirable features that potential buyers or tenants look for, as they add charm, character, and practicality to a building.
While verandas and balconies may have different architectural designs and purposes, their shared similarities make them both valuable additions to any building, providing homeowners and residents with enjoyable and functional outdoor spaces.
Differences between a Veranda and a Balcony
Although verandas and balconies may seem similar at first glance, there are significant differences that set them apart. Here are the key distinctions:
Position and Location: Verandas are typically located at the front or side of a building, serving as a welcoming entrance or an outdoor extension of the main living area. Balconies, on the other hand, are usually attached to the upper levels of a building, providing private outdoor spaces accessed directly from interior rooms.
Structure and Design: Verandas are characterized by a covered roof and open sides, supported by pillars or columns. They provide a shaded outdoor area with protection from the elements. Balconies, on the other hand, have a solid floor and are enclosed by railings for safety. They offer elevated views and a more private outdoor experience.
Size and Usage: Verandas are generally larger in size compared to balconies. They provide more space for seating arrangements, dining, and socializing. Verandas can serve various purposes, such as outdoor living rooms or entertainment areas. Balconies, due to their smaller footprint, are often used as intimate retreats for relaxation or as a lookout point to enjoy views.
Access: Verandas are accessible from the ground floor level and can be accessed directly from the interior living spaces. Balconies, on the other hand, are typically accessible from upper levels of a building, such as bedrooms or living areas.
Building Type: Verandas are commonly found in residential properties, country estates, and historic buildings. They are often associated with traditional or colonial architectural styles. Balconies, on the other hand, are prevalent in urban environments, particularly in apartment complexes, condominiums, and high-rise buildings.
Privacy and Views: Verandas are more open and exposed, allowing for interaction with the surrounding environment. They can provide views of the garden, street, or front yard. Balconies, due to their elevated position and enclosed design, offer a higher level of privacy and often provide elevated views of the cityscape, mountains, or other scenic vistas.
Aesthetic Appeal: Verandas are often seen as traditional and elegant, offering a classic charm to the building’s façade. Balconies, on the other hand, are sleek and modern in their design, adding a contemporary touch to the building’s appearance.
These differences in position, structure, size, and usage make verandas and balconies distinct architectural features, each with their own unique characteristics and benefits. Understanding these differences can help when planning and designing outdoor spaces for residential or commercial properties.
Benefits and Uses of a Veranda
A veranda offers numerous benefits and can be a versatile addition to any building. Here are some of the key benefits and popular uses of a veranda:
Outdoor Living Space: A veranda provides an outdoor extension of the living area, allowing residents to enjoy the benefits of being outside while staying protected from the elements. It serves as a comfortable and shaded space for relaxation, entertainment, and spending quality time with family and friends.
Protection from Weather: One of the primary advantages of a veranda is its roof, which provides protection from rain, sun exposure, and other weather conditions. This allows individuals to use the veranda even during light showers or intense sunlight, making it a functional space throughout the year.
Enhanced Aesthetics: Verandas can enhance the architectural appeal of a building. They add depth, dimension, and visual interest to the façade. Verandas are often beautifully designed with decorative elements, such as ornate columns, intricate railings, hanging plants, and lighting fixtures, further enhancing the overall aesthetics of the property.
Increased Property Value: The addition of a well-designed veranda can significantly increase the value of a property. It adds both functional space and aesthetic appeal, making the property more attractive to potential buyers or tenants. A well-maintained veranda is often considered a desirable feature in real estate listings.
Flexible Usage: Verandas offer flexibility in their usage. They can be used for a variety of purposes, depending on the homeowner’s preferences and needs. Verandas can serve as outdoor dining areas, lounging spaces, reading nooks, or even home offices. The versatility of a veranda allows homeowners to adapt the space to their lifestyle.
Entertainment and Socializing: Verandas are ideal spaces for hosting gatherings and entertaining guests. They provide a comfortable and inviting area where individuals can gather for intimate parties, barbecues, or simply enjoy casual conversations in a relaxed outdoor setting.
Connection with Nature: Verandas create a seamless connection with the natural surroundings. They offer a space to appreciate the beauty of the outdoors, whether it’s a lush garden, a scenic view, or a carefully landscaped yard. Verandas provide a peaceful retreat where individuals can unwind and rejuvenate amidst nature.
Overall, the benefits of a veranda, including the additional outdoor living space, protection from the elements, enhanced aesthetics, increased property value, flexibility in usage, and opportunities for entertainment and connection with nature, make it a valuable feature for any property.
Benefits and Uses of a Balcony
A balcony offers a range of benefits and can greatly enhance the functionality and appeal of a building. Here are some of the key benefits and popular uses of a balcony:
Outdoor Retreat: A balcony provides a private outdoor retreat within a building. It offers a space for residents to relax, unwind, and enjoy fresh air and open sky without leaving the comfort of their home. It serves as a tranquil sanctuary where individuals can find solitude and solitude.
Panoramic Views: Balconies, being elevated platforms, offer breathtaking panoramic views of the surrounding environment. Whether it’s a bustling cityscape, scenic landscapes, or a serene garden, balconies provide residents with the opportunity to enjoy and appreciate their surroundings from a unique vantage point.
Extended Living Space: Balconies offer an extension of the indoor living area, providing additional space for various activities. They can be used as an outdoor dining area, a cozy reading corner, or even a mini herb or flower garden. Balconies provide homeowners with the opportunity to maximize their living space and enjoy the benefits of both indoor and outdoor living.
Al Fresco Dining: Many people enjoy dining outdoors, especially during pleasant weather. Balconies serve as ideal spaces for al fresco dining, allowing residents to enjoy meals while taking in the views and enjoying the fresh air. Balconies can be furnished with a dining table and chairs, creating an intimate and inviting dining setting.
Personalization and Aesthetics: Balconies provide individuals with an opportunity to express their personal style and creativity. They can be adorned with plants, flowers, and decorative elements, making them visually appealing and creating a relaxing ambiance. Balconies can also be customized with outdoor furniture, cushions, and accent pieces to reflect individual tastes and preferences.
Privacy: Balconies offer a sense of privacy, especially in comparison to other outdoor spaces like verandas or patios. Residents can enjoy their balcony, whether for sunbathing, reading, or simply enjoying a cup of coffee, without feeling exposed to the prying eyes of neighbors or pedestrians.
Alternative Gardening Space: Balconies provide a space for individuals to pursue their green thumb and indulge in gardening. Even with limited ground space, balcony gardening allows for growing potted plants, herbs, flowers, or even small vegetables. It offers the joy of nurturing plants while adding beauty and vibrancy to the balcony’s environment.
Overall, the benefits of a balcony, including providing an outdoor retreat, panoramic views, extended living space, al fresco dining, personalization and aesthetics, privacy, and alternative gardening space, make it a valuable and cherished feature in any building.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between a veranda and a balcony is key when designing or choosing a property. While both verandas and balconies provide outdoor spaces attached to a building, they have distinct characteristics that set them apart.
A veranda is a covered, open-air space typically located at the front or side of a building. It features a roof, open sides, and often supported by pillars. Verandas offer a shaded area for relaxation, entertainment, and seamless integration with the indoor living space.
On the other hand, a balcony is an elevated platform attached to the upper levels of a building. It has a solid floor, enclosed by railings, and offers elevated views. Balconies provide private retreats, panoramic views, and additional living space.
Despite their differences, both verandas and balconies offer unique benefits and multiple uses. They provide opportunities to enjoy the outdoors, connect with nature, and enhance the aesthetics of the building.
A well-designed veranda adds value to a property, offers protection from the elements, and creates a flexible space for relaxation and entertainment. On the other hand, a balcony provides a private retreat, panoramic views, and an extension of the indoor living area.
Ultimately, whether you prefer the open and shaded charm of a veranda or the elevated seclusion of a balcony, both architectural features contribute to the overall attractiveness, functionality, and value of a building.
When considering your design or selection, weigh the architectural and design features, consider your preferred uses, and envision how each option will best suit your lifestyle and preferences.
Regardless of your choice, a veranda or a balcony can transform a property into a more inviting, aesthetically pleasing, and enjoyable living space.
So, when it comes to creating your outdoor oasis, be it a veranda or a balcony, embrace the beauty of the outdoors while adding value and charm to your property.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Difference Between A Veranda And A Balcony
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is The Difference Between A Veranda And A Balcony”